大厂算法面试之leetcode精讲17.栈
视频讲解(高效学习):点击学习
目录:
-
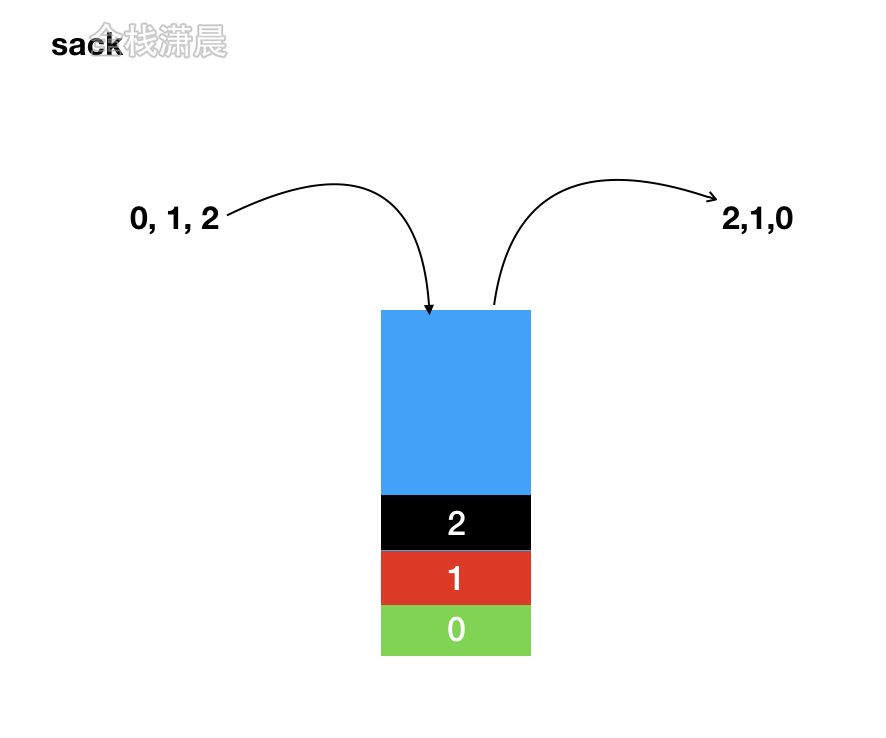
Stack的特点:先进后出(FILO)
-
使用场景:十进制转2进制 函数调用堆栈
-
js里没有栈,但是可以用数组模拟
42/2 42%2=0 21/2 21%2=1 10/2 10%2=0 5/2 5%2=1 2/2 2%2=0 1/2 1%2=1 stack: [0,1,0,1,0,1] res: 1 0 1 0 1 0 fn1(){ fn2() } fn2(){ fn3() } fn3(){} fn1() stack:[fn1,fn2,fn3] -
栈的时间复杂度:入栈和出栈
O(1),查找O(n)
20. 有效的括号 (easy)
方法1.栈
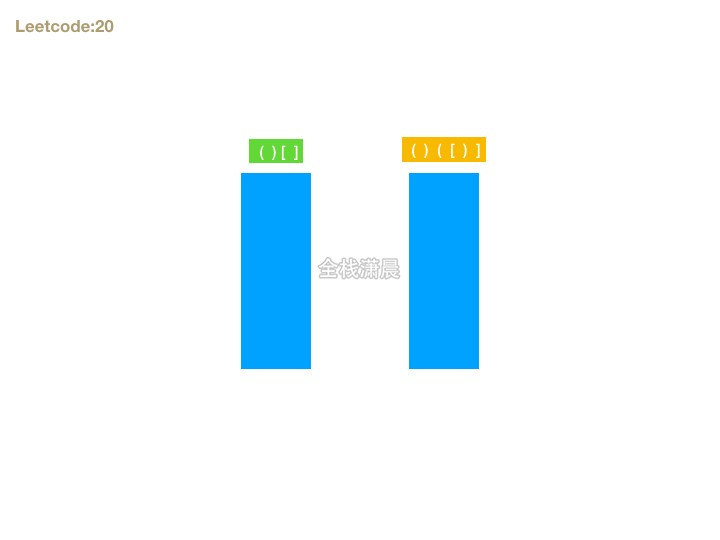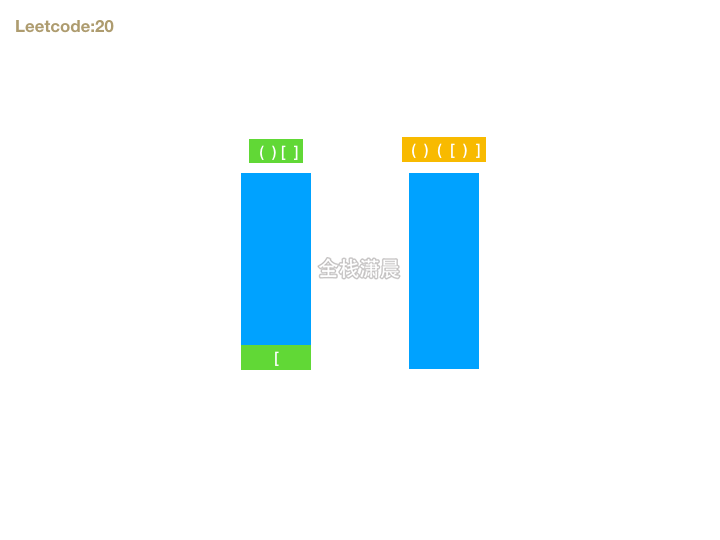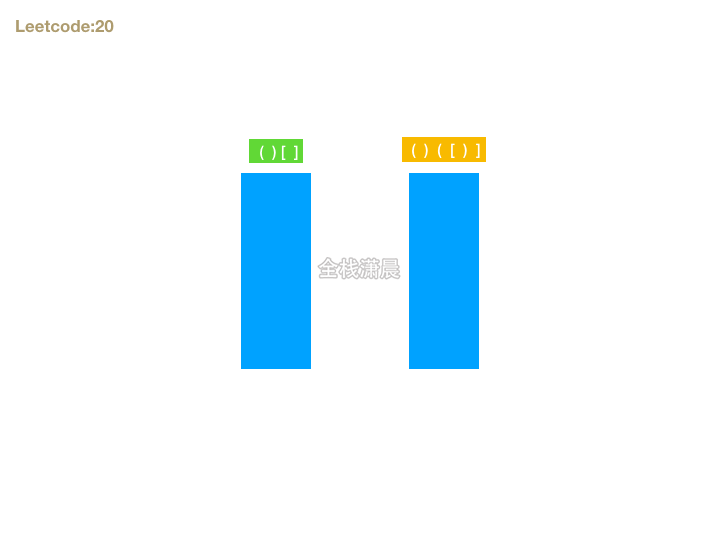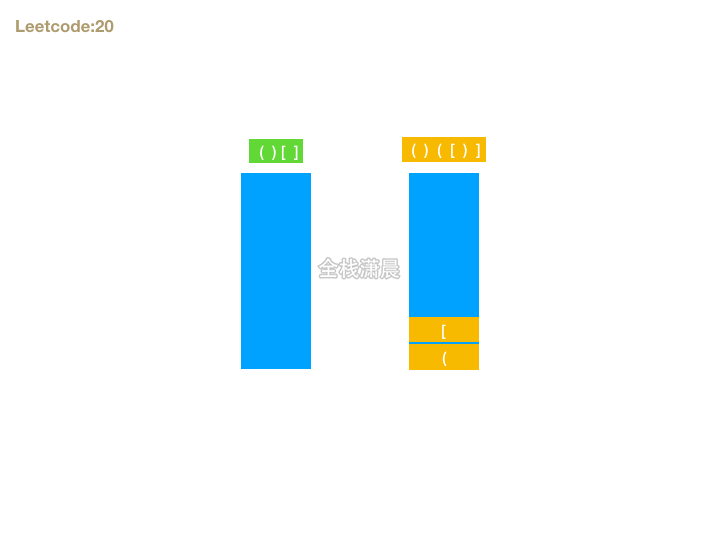
- 思路:首先如果字符串能组成有效的括号,则长度一定是偶数,我们可以遍历字符串,遇到左括号则暂存,期待后面有右括号可以和它匹配,如果遇到右括号则检查是否能和最晚暂存的做括号匹配。这就和栈这种数据结构先进后出的特性相吻合了。所以我们可以准备一个栈存放括号对,遍历字符串的时候,如果遇到左括号入栈,遇到右括号则判断右括号是否能和栈顶元素匹配,在循环结束的时候还要判断栈是否为空,如果不为空,则不是有效括号匹配的字符串
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(n),n为字符串的长度
js:
var isValid = function(s) {
const n = s.length;
if (n % 2 === 1) {//如果字符串能组成有效的括号,则长度一定是偶数
return false;
}
const pairs = new Map([//用栈存储括号对
[')', '('],
[']', '['],
['}', '{']
]);
const stk = [];
for (let ch of s){//循环字符串
if (pairs.has(ch)) {
//遇到右括号则判断右括号是否能和栈顶元素匹配
if (!stk.length || stk[stk.length - 1] !== pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stk.pop();
} else {
stk.push(ch);//如果遇到左括号入栈
}
};
return !stk.length;//循环结束的时候还要判断栈是否为空
};
Java:
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
232. 用栈实现队列 (easy)
方法1.栈
- 思路:这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。最后如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
- 复杂度分析:push时间复杂度
O(1),pop时间复杂度为O(n),因为pop的时候,输出栈为空,则把输入栈所有的元素加入输出栈。空间复杂度O(n),两个栈空间
js:
var MyQueue = function() {
//准备两个栈
this.stack1 = [];
this.stack2 = [];
};
MyQueue.prototype.push = function(x) {//push的时候加入输入栈
this.stack1.push(x);
};
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function() {
const size = this.stack2.length;
if(size) {//push的时候判断输出栈是否为空
return this.stack2.pop();//不为空则输出栈出栈
}
while(this.stack1.length) {//输出栈为空,则把输入栈所有的元素加入输出栈
this.stack2.push(this.stack1.pop());
}
return this.stack2.pop();
};
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function() {
const x = this.pop();//查看队头的元素 复用pop方法,然后在让元素push进输出栈
this.stack2.push(x);
return x;
};
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.stack1.length && !this.stack2.length
};
Java:
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
dumpStack1();
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
dumpStack1();
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
private void dumpStack1(){
if (stack2.isEmpty()){
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
}
}
155. 最小栈 (easy)
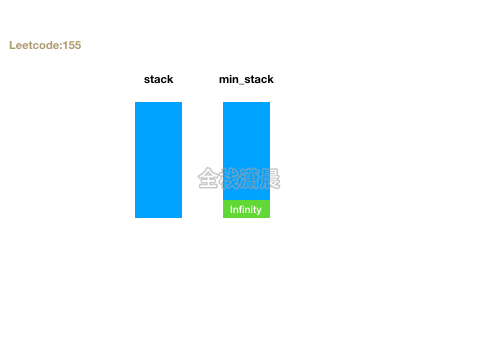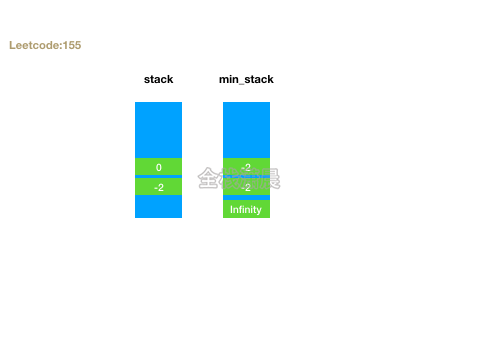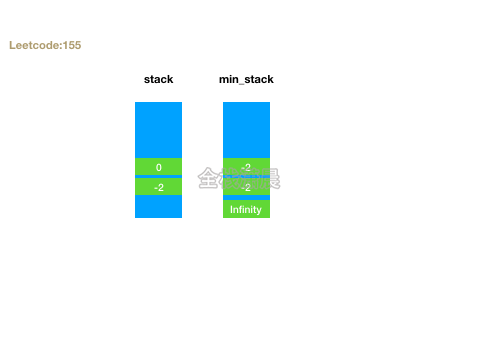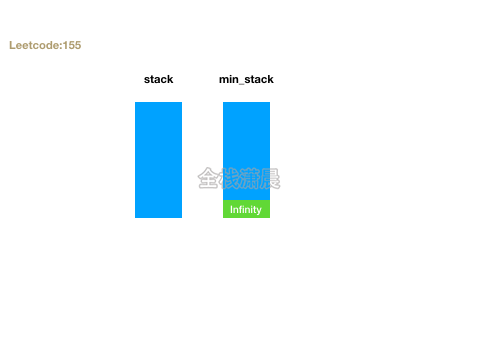
- 思路:定义两个栈stack和min_stack,stack正常push,min_stack只会push需要入栈和栈顶中较小的元素。getMin返回min_stack栈顶元素,top返回stack栈顶元素。
- 复杂度:所有操作的时间复杂度是
O(1)
js:
var MinStack = function () {
this.stack = [];
this.min_stack = [Infinity];
};
//stack正常push,min_stack只会push需要入栈和栈顶中较小的元素
MinStack.prototype.push = function (x) {
this.stack.push(x);
this.min_stack.push(Math.min(this.min_stack[this.min_stack.length - 1], x));
};
//stack正常pop,min_stack正常pop
MinStack.prototype.pop = function () {
this.stack.pop();
this.min_stack.pop();
};
//返回stack栈顶元素
MinStack.prototype.top = function () {
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1];
};
//返回min_stack栈顶元素
MinStack.prototype.getMin = function () {
return this.min_stack[this.min_stack.length - 1];
};
java:
class MinStack {
Deque<Integer> stack;
Deque<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
946. 验证栈序列 (medium)
- 思路:用栈模拟出栈入栈的过程,当popped中index指向的位置的元素和stack栈顶的元素一致时,出栈 并且
index++,最后判断stack是否为空 - 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),pushed中的元素入栈出栈一次,空间复杂度O(n),栈的大小
js:
const validateStackSequences = (pushed, popped) => {
const stack = [];//用栈模拟出栈入栈的过程
let index = 0;
const len = pushed.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
stack.push(pushed[i]);
//当popped中index指向的位置的元素和stack栈顶的元素一致时,出栈 并且 index++
while (popped[index] !== undefined && popped[index] === stack[stack.length - 1]) {
stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
return !stack.length;//最后判断stack是否为空
};
java:
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
if(pushed == null){
return true;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;
for(int i=0;i<pushed.length;i++){
stack.push(pushed[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && index < popped.length && popped[index] == stack.peek()){
int pop = stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
445. 两数相加 II (medium)
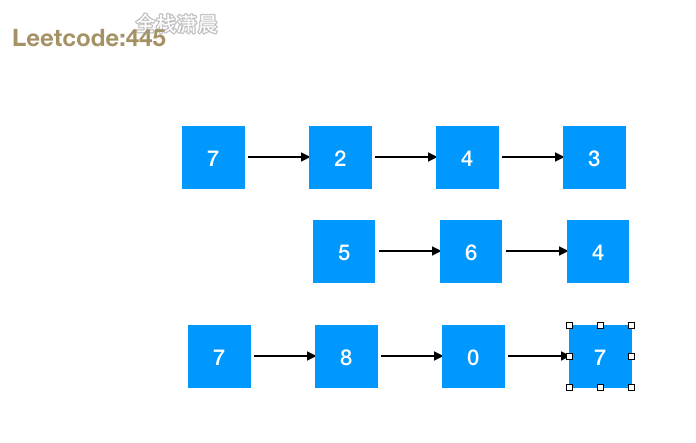
- 思路:将两个链表的节点都推入栈中,然后不断出栈,计算每个位置的值和进位,串连成一个新的链表
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(max(m,n)),m,n是两个链表的长度,空间复杂度O(m+n)
js:
var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) {
const stack1 = [];
const stack2 = [];
while (l1 || l2) {//两链表入栈
if (l1) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
let carry = 0;
let ansList = null;
while (stack1.length || stack2.length || carry !== 0) {//不断出栈
const s1 = stack1.length ? stack1.pop() : 0;
const s2 = stack2.length ? stack2.pop() : 0;
let val = s1 + s2 + carry;
carry = parseInt(val / 10);//计算进位
val = val % 10;//计算当前节点的值
const curNode = new ListNode(val);
curNode.next = ansList;//向链表前插入新节点
ansList = curNode;//重新赋值ansList
}
return ansList;
};
java:
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Deque<Integer> stack1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Deque<Integer> stack2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode ansList = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int s1 = stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
int s2 = stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
int val = s1 + s2 + carry;
carry = val / 10;
val %= 10;
ListNode curNode = new ListNode(val);
curNode.next = ansList;
ansList = curNode;
}
return ansList;
}
}
682. 棒球比赛 (easy)
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
js:
let calPoints = function(ops) {
let res = [];
for(let i = 0; i < ops.length; i++){
switch(ops[i]){
case "C":
res.pop();
break;
case "D":
res.push(+res[res.length - 1] * 2);
break;
case "+":
res.push(+res[res.length - 1] + +res[res.length - 2]);
break;
default:
res.push(+ops[i]);
}
}
return res.reduce((i, j) => i + j);
};
java:
class Solution {
public int calPoints(String[] ops) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
for(String op : ops) {
if (op.equals("+")) {
int top = stack.pop();
int newtop = top + stack.peek();
stack.push(top);
stack.push(newtop);
} else if (op.equals("C")) {
stack.pop();
} else if (op.equals("D")) {
stack.push(2 * stack.peek());
} else {
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(op));
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int score : stack) ans += score;
return ans;
}
}