react源码解析12.状态更新流程
视频课程(高效学习):进入课程
课程目录:
setState&forceUpdate
在react中触发状态更新的几种方式:
- ReactDOM.render
- this.setState
- this.forceUpdate
- useState
- useReducer
我们重点看下重点看下this.setState和this.forceUpdate,hook在第13章讲
-
this.setState内调用this.updater.enqueueSetState,主要是将update加入updateQueue中
//ReactBaseClasses.js Component.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) { if (!(typeof partialState === 'object' || typeof partialState === 'function' || partialState == null)) { { throw Error( "setState(...): takes an object of state variables to update or a function which returns an object of state variables." ); } } this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, 'setState'); };//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js enqueueSetState(inst, payload, callback) { const fiber = getInstance(inst);//fiber实例 const eventTime = requestEventTime(); const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig(); const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber, suspenseConfig);//优先级 const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane, suspenseConfig);//创建update update.payload = payload; if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) { //赋值回调 update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);//update加入updateQueue scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);//调度update }enqueueUpdate用来将update加入updateQueue队列
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js export function enqueueUpdate<State>(fiber: Fiber, update: Update<State>) { const updateQueue = fiber.updateQueue; if (updateQueue === null) { return; } const sharedQueue: SharedQueue<State> = (updateQueue: any).shared; const pending = sharedQueue.pending; if (pending === null) { update.next = update;//与自己形成环状链表 } else { update.next = pending.next;//加入链表的结尾 pending.next = update; } sharedQueue.pending = update; }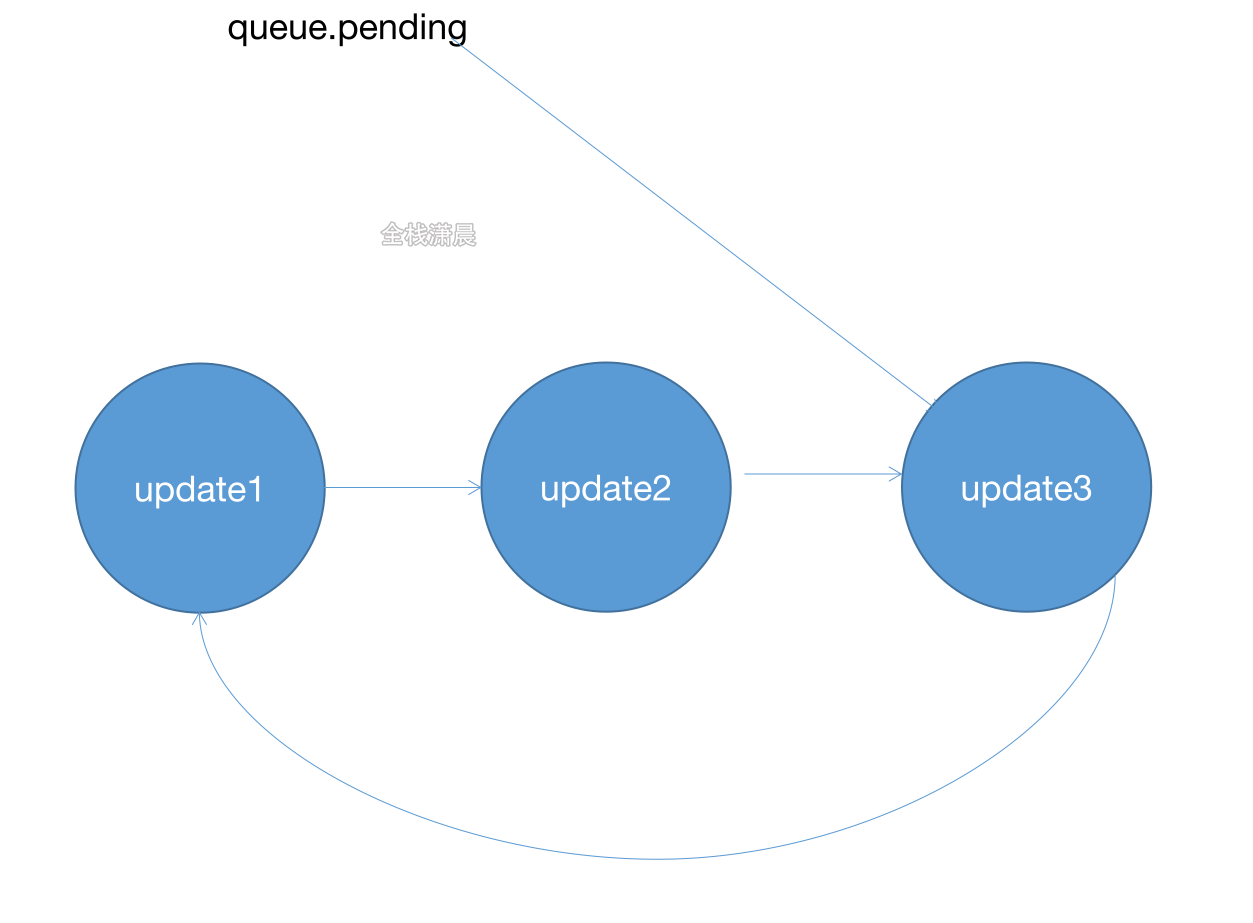
-
this.forceUpdate和this.setState一样,只是会让tag赋值ForceUpdate
//ReactBaseClasses.js Component.prototype.forceUpdate = function(callback) { this.updater.enqueueForceUpdate(this, callback, 'forceUpdate'); };//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js enqueueForceUpdate(inst, callback) { const fiber = getInstance(inst); const eventTime = requestEventTime(); const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig(); const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber, suspenseConfig); const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane, suspenseConfig); //tag赋值ForceUpdate update.tag = ForceUpdate; if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) { update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(fiber, update); scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime); }, }; 如果标记ForceUpdate,render阶段组件更新会根据checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing,和checkShouldComponentUpdate来判断,如果Update的tag是ForceUpdate,则checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing为true,当组件是PureComponent时,checkShouldComponentUpdate会浅比较state和props,所以当使用this.forceUpdate一定会更新
//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js const shouldUpdate = checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing() || checkShouldComponentUpdate( workInProgress, ctor, oldProps, newProps, oldState, newState, nextContext, );状态更新整体流程
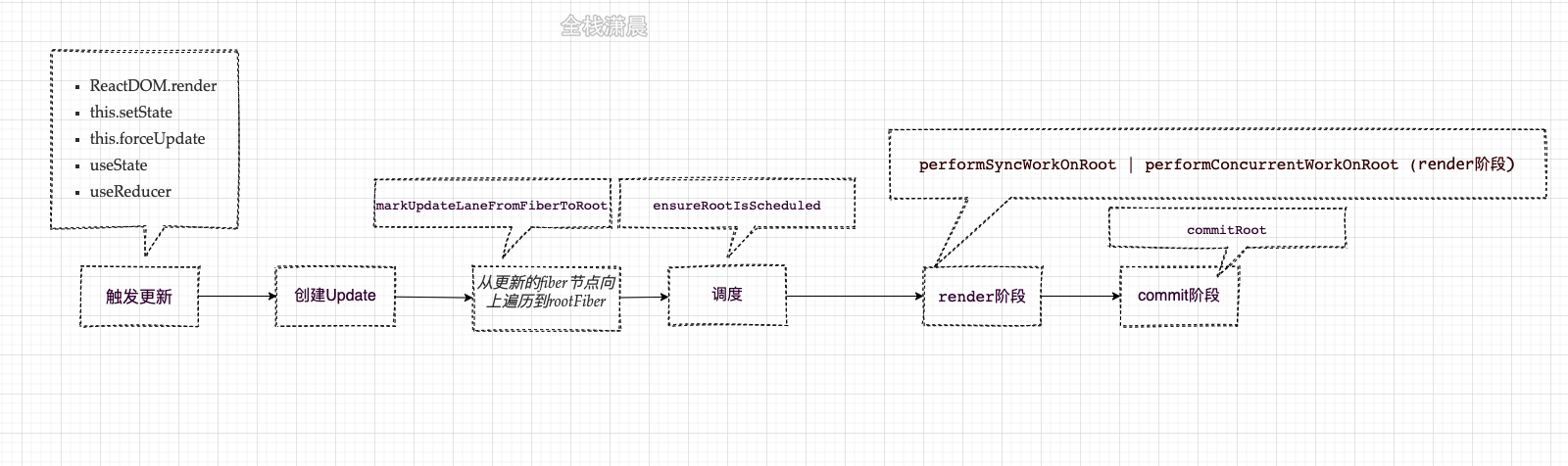
Update&updateQueue
HostRoot或者ClassComponent触发更新后,会在函数createUpdate中创建update,并在后面的render阶段的beginWork中计算Update。FunctionComponent对应的Update在第11章讲,它和HostRoot或者ClassComponent的Update结构有些不一样
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function createUpdate(eventTime: number, lane: Lane): Update<*> {//创建update
const update: Update<*> = {
eventTime,
lane,
tag: UpdateState,
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null,
};
return update;
}
我们主要关注这些参数:
-
lane:优先级(第12章讲)
-
tag:更新的类型,例如UpdateState、ReplaceState
-
payload:ClassComponent的payload是setState第一个参数,HostRoot的payload是ReactDOM.render的第一个参数
-
callback:setState的第二个参数
-
next:连接下一个Update形成一个链表,例如同时触发多个setState时会形成多个Update,然后用next 连接
对于HostRoot或者ClassComponent会在mount的时候使用initializeUpdateQueue创建updateQueue,然后将updateQueue挂载到fiber节点上
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function initializeUpdateQueue<State>(fiber: Fiber): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState: fiber.memoizedState,
firstBaseUpdate: null,
lastBaseUpdate: null,
shared: {
pending: null,
},
effects: null,
};
fiber.updateQueue = queue;
}
- baseState:初始state,后面会基于这个state,根据Update计算新的state
- firstBaseUpdate、lastBaseUpdate:Update形成的链表的头和尾
- shared.pending:新产生的update会以单向环状链表保存在shared.pending上,计算state的时候会剪开这个环状链表,并且链接在lastBaseUpdate后
- effects:calback不为null的update
从触发更新的fiber节点向上遍历到rootFiber
在markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot函数中会从触发更新的节点开始向上遍历到rootFiber,遍历的过程会处理节点的优先级(第15章讲)
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
function markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(
sourceFiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
): FiberRoot | null {
sourceFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(sourceFiber.lanes, lane);
let alternate = sourceFiber.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, lane);
}
let node = sourceFiber;
let parent = sourceFiber.return;
while (parent !== null) {//从触发更新的节点开始向上遍历到rootFiber
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);//合并childLanes优先级
alternate = parent.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.childLanes = mergeLanes(alternate.childLanes, lane);
} else {
}
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
const root: FiberRoot = node.stateNode;
return root;
} else {
return null;
}
}
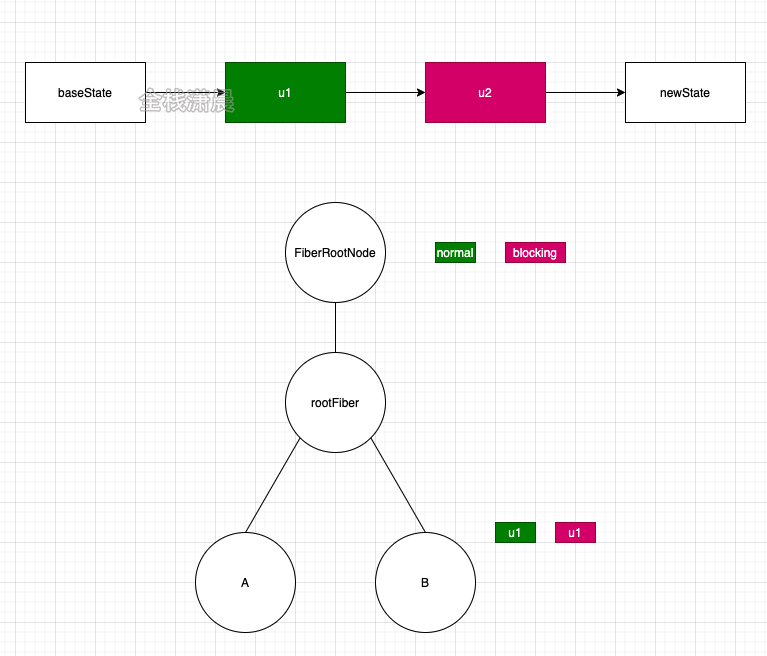
例如B节点触发更新,B节点被被标记为normal的update,也就是图中的u1,然后向上遍历到根节点,在根节点上打上一个normal的update,如果此时B节点又触发了一个userBlocking的Update,同样会向上遍历到根节点,在根节点上打上一个userBlocking的update。
如果当前根节点更新的优先级是normal,u1、u2都参与状态的计算,如果当前根节点更新的优先级是userBlocking,则只有u2参与计算
调度
在ensureRootIsScheduled中,scheduleCallback会以一个优先级调度render阶段的开始函数performSyncWorkOnRoot或者performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLanePriority) {
// 任务已经过期,需要同步执行render阶段
newCallbackNode = scheduleSyncCallback(
performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root)
);
} else {
// 根据任务优先级异步执行render阶段
var schedulerPriorityLevel = lanePriorityToSchedulerPriority(
newCallbackPriority
);
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root)
);
}
状态更新
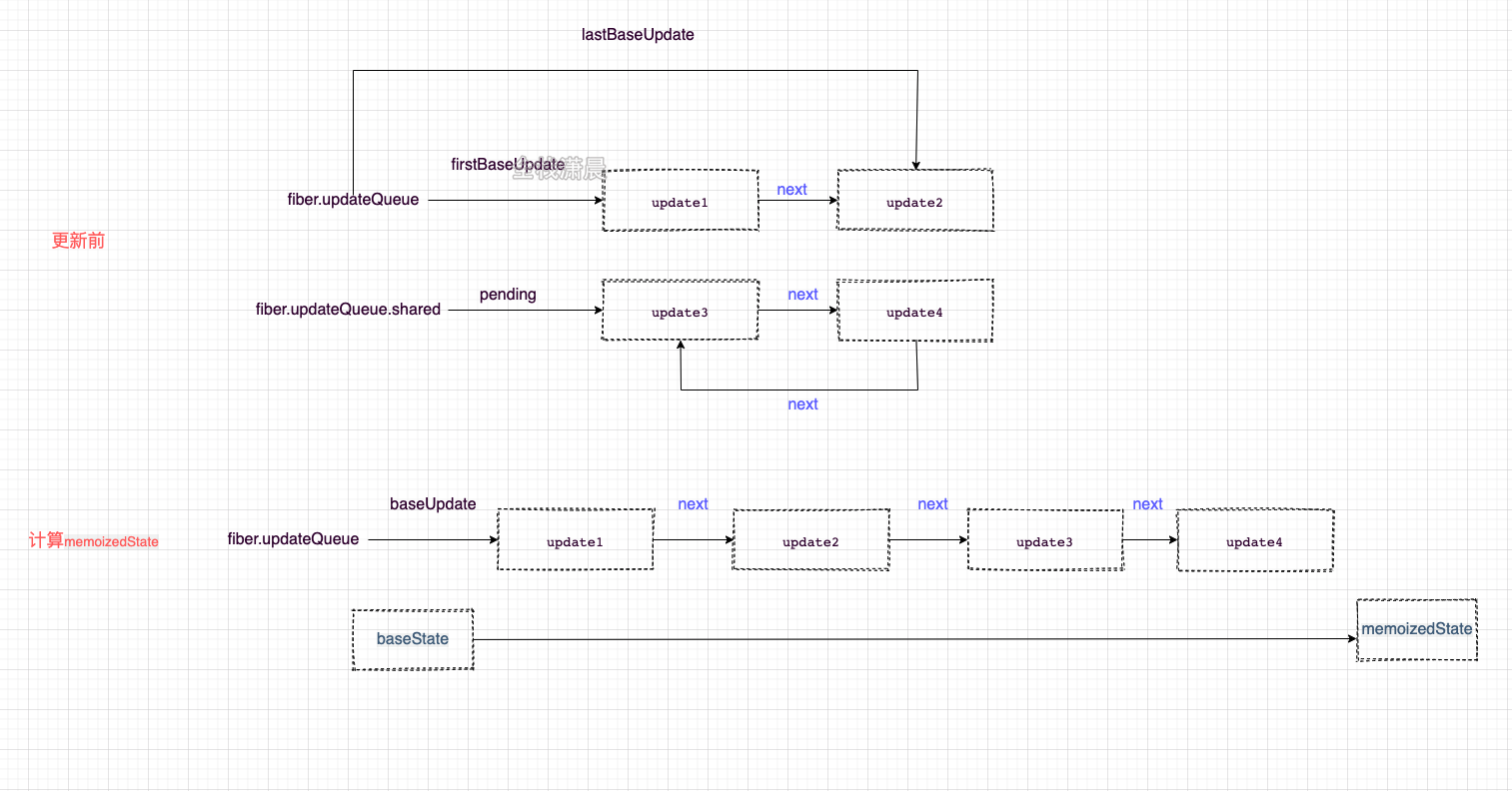
classComponent状态计算发生在processUpdateQueue函数中,涉及很多链表操作,看图更加直白
-
初始时fiber.updateQueue单链表上有firstBaseUpdate(update1)和lastBaseUpdate(update2),以next连接
-
fiber.updateQueue.shared环状链表上有update3和update4,以next连接互相连接
-
计算state时,先将fiber.updateQueue.shared环状链表‘剪开’,形成单链表,连接在fiber.updateQueue后面形成baseUpdate
-
然后遍历按这条链表,根据baseState计算出memoizedState
带优先级的状态更新
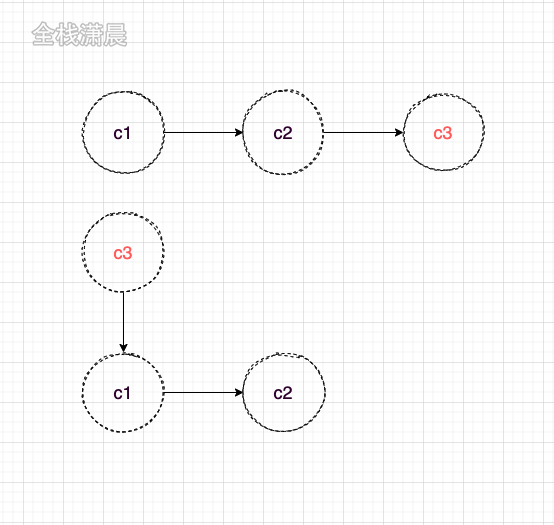
类似git提交,这里的c3意味着高优先级的任务,比如用户出发的事件,数据请求,同步执行的代码等。
-
通过ReactDOM.render创建的应用没有优先级的概念,类比git提交,相当于先commit,然后提交c3
-
在concurrent模式下,类似git rebase,先暂存之前的代码,在master上开发,然后rebase到之前的分支上
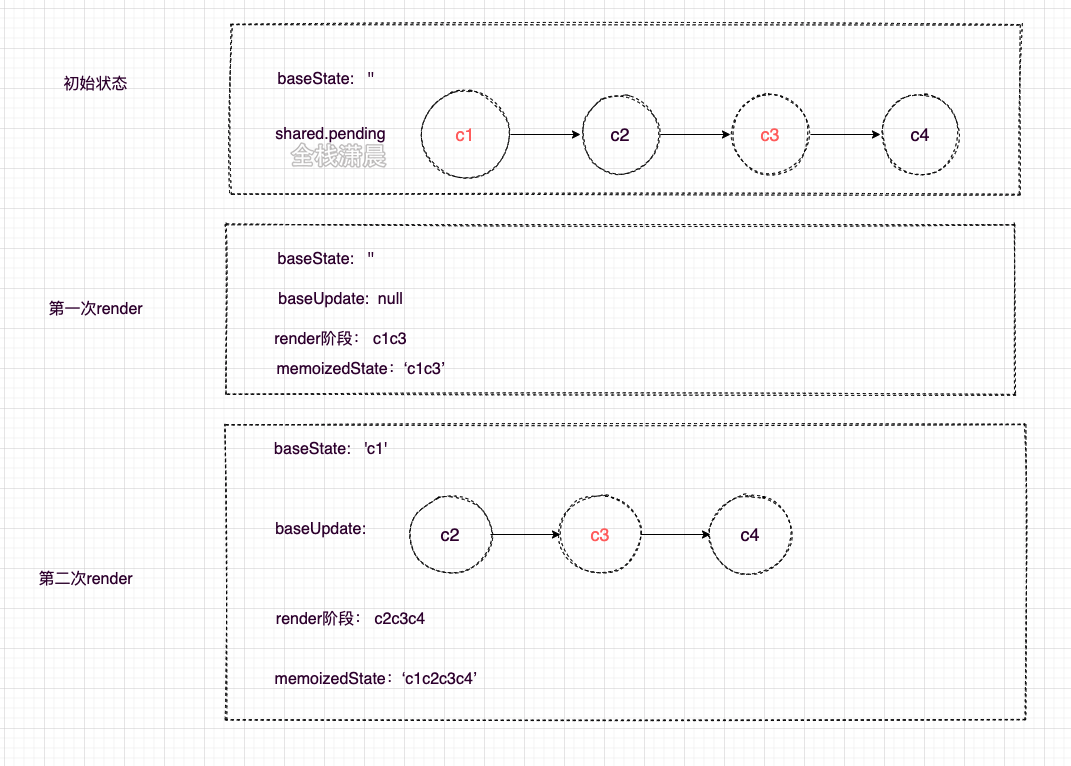
优先级是由Scheduler来调度的,这里我们只关心状态计算时的优先级排序,也就是在函数processUpdateQueue中发生的计算,例如初始时有c1-c4四个update,其中c1和c3为高优先级
- 在第一次render的时候,低优先级的update会跳过,所以只有c1和c3加入状态的计算
- 在第二次render的时候,会以第一次中跳过的update(c2)之前的update(c1)作为baseState,跳过的update和之后的update(c2,c3,c4)作为baseUpdate重新计算
在在concurrent模式下,componentWillMount可能会执行多次,变现和之前的版本不一致
注意,fiber.updateQueue.shared会同时存在于workInprogress Fiber和current Fiber,目的是为了防止高优先级打断正在进行的计算而导致状态丢失,这段代码也是发生在processUpdateQueue中
看demo_8的优先级
现在来看下计算状态的函数
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function processUpdateQueue<State>(
workInProgress: Fiber,
props: any,
instance: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = (workInProgress.updateQueue: any);
hasForceUpdate = false;
let firstBaseUpdate = queue.firstBaseUpdate;//updateQueue的第一个Update
let lastBaseUpdate = queue.lastBaseUpdate;//updateQueue的最后一个Update
let pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;//未计算的pendingQueue
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
queue.shared.pending = null;
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue;//未计算的ppendingQueue的最后一个update
const firstPendingUpdate = lastPendingUpdate.next;//未计算的pendingQueue的第一个update
lastPendingUpdate.next = null;//剪开环状链表
if (lastBaseUpdate === null) {//将pendingQueue加入到updateQueue
firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
lastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
const current = workInProgress.alternate;//current上做同样的操作
if (current !== null) {
const currentQueue: UpdateQueue<State> = (current.updateQueue: any);
const currentLastBaseUpdate = currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate;
if (currentLastBaseUpdate !== lastBaseUpdate) {
if (currentLastBaseUpdate === null) {
currentQueue.firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
currentLastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
}
}
}
if (firstBaseUpdate !== null) {
let newState = queue.baseState;
let newLanes = NoLanes;
let newBaseState = null;
let newFirstBaseUpdate = null;
let newLastBaseUpdate = null;
let update = firstBaseUpdate;
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
const updateEventTime = update.eventTime;
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {//判断优先级是够足够
const clone: Update<State> = {//优先级不够 跳过当前update
eventTime: updateEventTime,
lane: updateLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {//保存跳过的update
newFirstBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
newLanes = mergeLanes(newLanes, updateLane);
} else {
//直到newLastBaseUpdate为null才不会计算,防止updateQueue没计算完
if (newLastBaseUpdate !== null) {
const clone: Update<State> = {
eventTime: updateEventTime,
lane: NoLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
newState = getStateFromUpdate(//根据updateQueue计算state
workInProgress,
queue,
update,
newState,
props,
instance,
);
const callback = update.callback;
if (callback !== null) {
workInProgress.flags |= Callback;//Callback flag
const effects = queue.effects;
if (effects === null) {
queue.effects = [update];
} else {
effects.push(update);
}
}
}
update = update.next;//下一个update
if (update === null) {//重置updateQueue
pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;
if (pendingQueue === null) {
break;
} else {
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue;
const firstPendingUpdate = ((lastPendingUpdate.next: any): Update<State>);
lastPendingUpdate.next = null;
update = firstPendingUpdate;
queue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
queue.shared.pending = null;
}
}
} while (true);
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {
newBaseState = newState;
}
queue.baseState = ((newBaseState: any): State);//新的state
queue.firstBaseUpdate = newFirstBaseUpdate;//新的第一个update
queue.lastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate;//新的最后一个update
markSkippedUpdateLanes(newLanes);
workInProgress.lanes = newLanes;
workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;
}
//...
}