设置视图的宽高:
视图宽度通过属性android:layout_width表达,视图高度通过属性android:layout_height表达,宽高的取值主要有下列三种:
(1)match_parent:表示与上级视图保持一致。
(2)wrap_content:表示与内容自适应。
(3)以dp为单位的具体尺寸。
手机屏幕是长方形区域:短的叫宽,长的叫高:
(1)、控件宽度通过--------android:layout_width-----------设置
(2)、控件高度通过--------android:layout_height-----------设置
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
宽和高的取值,主要有3种:
(1)、match_parent:表示与上级视图保持一致。上级视图的尺寸有多大,当前视图的尺寸就有多大。
(2)、wrap_content:表示与内容自适应。对于文本视图来说,内部文字需要多大的显示空间,当前视图就要占据多大的尺寸。
但最宽不能超过上级视图的宽度,一旦超过,就会换行;最高不能超过上级视图的高度,一旦超过就会隐藏。
(3)、以dp为单位的具体尺寸,比如300dp,表示宽度和高度就这么大。
布局文件:
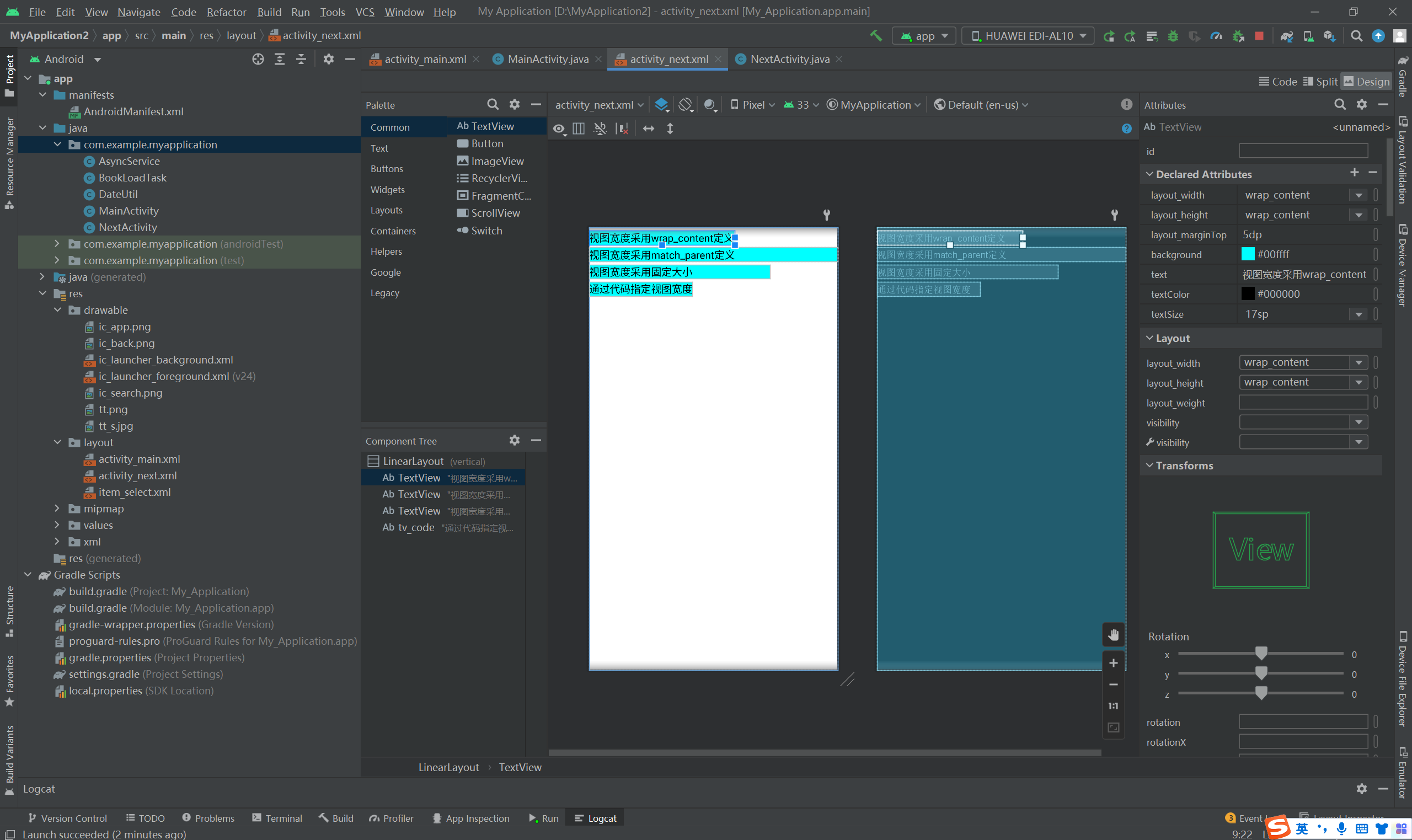
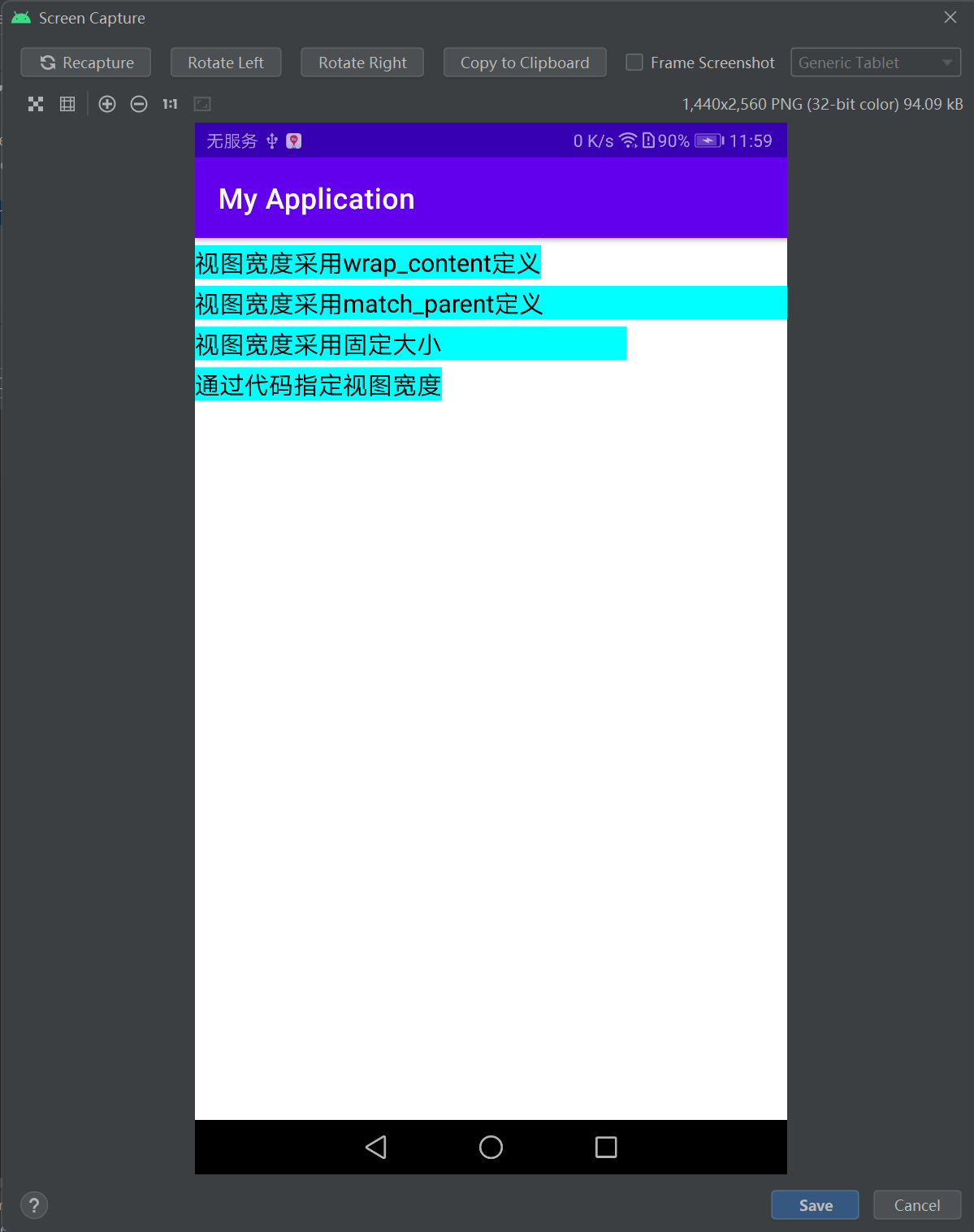
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="5dp" android:background="#00ffff" android:text="视图宽度采用wrap_content定义" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="17sp" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="5dp" android:background="#00ffff" android:text="视图宽度采用match_parent定义" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="17sp" /> <TextView android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="5dp" android:background="#00ffff" android:text="视图宽度采用固定大小" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="17sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_code" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="5dp" android:background="#00ffff" android:text="通过代码指定视图宽度" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="17sp" /> </LinearLayout>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
设置视图之间的间距:
设置视图的间距有两种方式:
(1)采用layout_margin属性,它指定了当前视图与周围平级视图之间的距离(包括上级视图和平级视图)。
包括:layout_margin、layout_marginLeft、layout_marginTop、layout_marginRight、layout_marginBottom;
(2)采用padding属性,它指定了当前视图与内部下级视图之间的距离(包括下级视图和内部文本)。
包括:padding、paddingLeft、paddingTop、paddingRight、paddingBottom;
android:layout_margin="30dp" ———— 一次性设置四周的间距
android:layout_marginTop="30dp" -----该属性的作用是让当前视图与上方间隔一段距离
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"-----该属性的作用是让当前视图与下方间隔一段距离
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"-----该属性的作用是让当前视图与左边间隔一段距离
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"-----该属性的作用是让当前视图与右边间隔一段距离
注意:layout_margin不单单用于文本视图,还可以用于所有视图,包括各类布局和各类控件。
因为不管是布局还是控件,它们统统由视图基类View派生而来,而layout_margin正式View的一个通用属性。
除了layout_margin外,padding也是View的一个通用属性,它用来设置视图的内部间距。
布局:
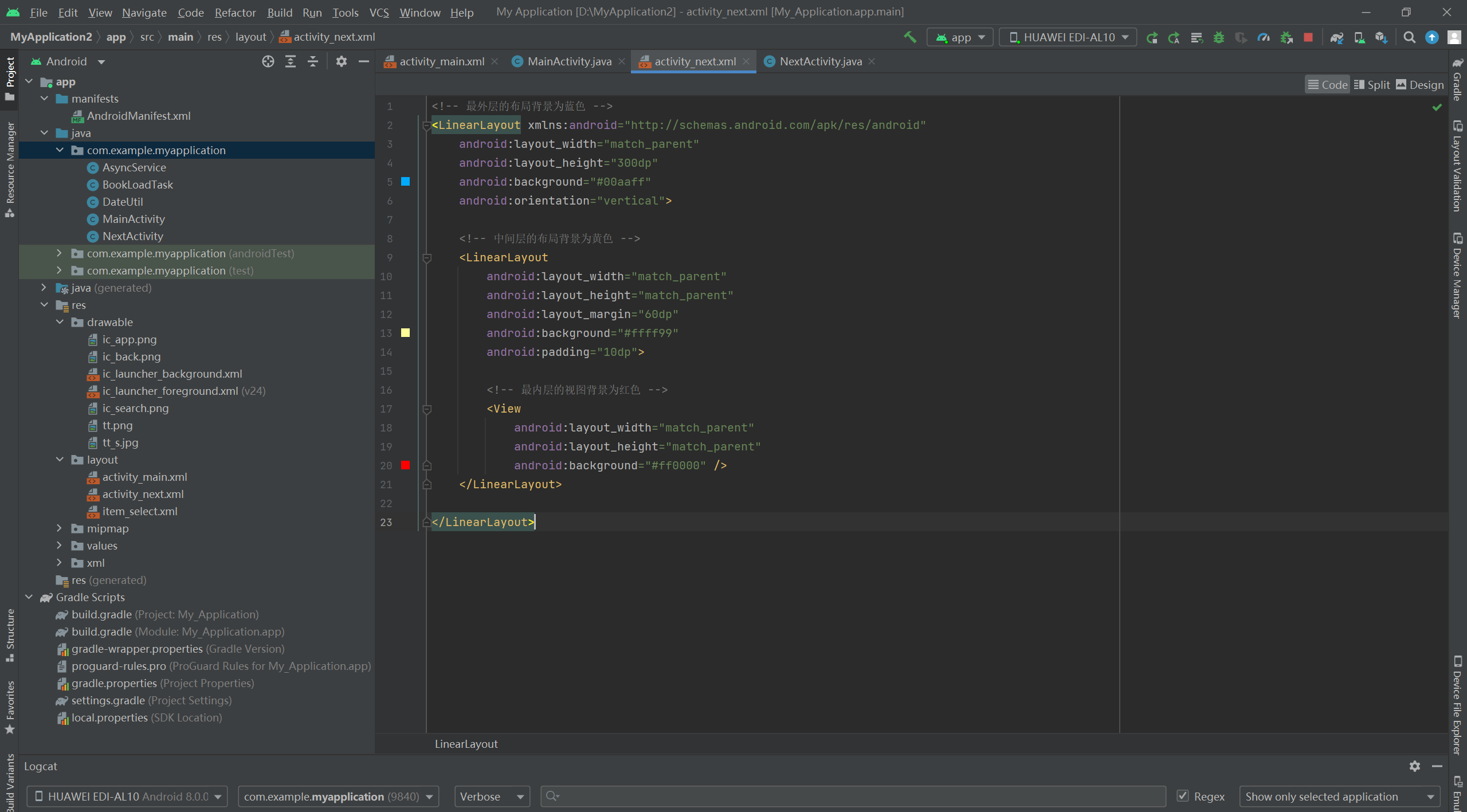
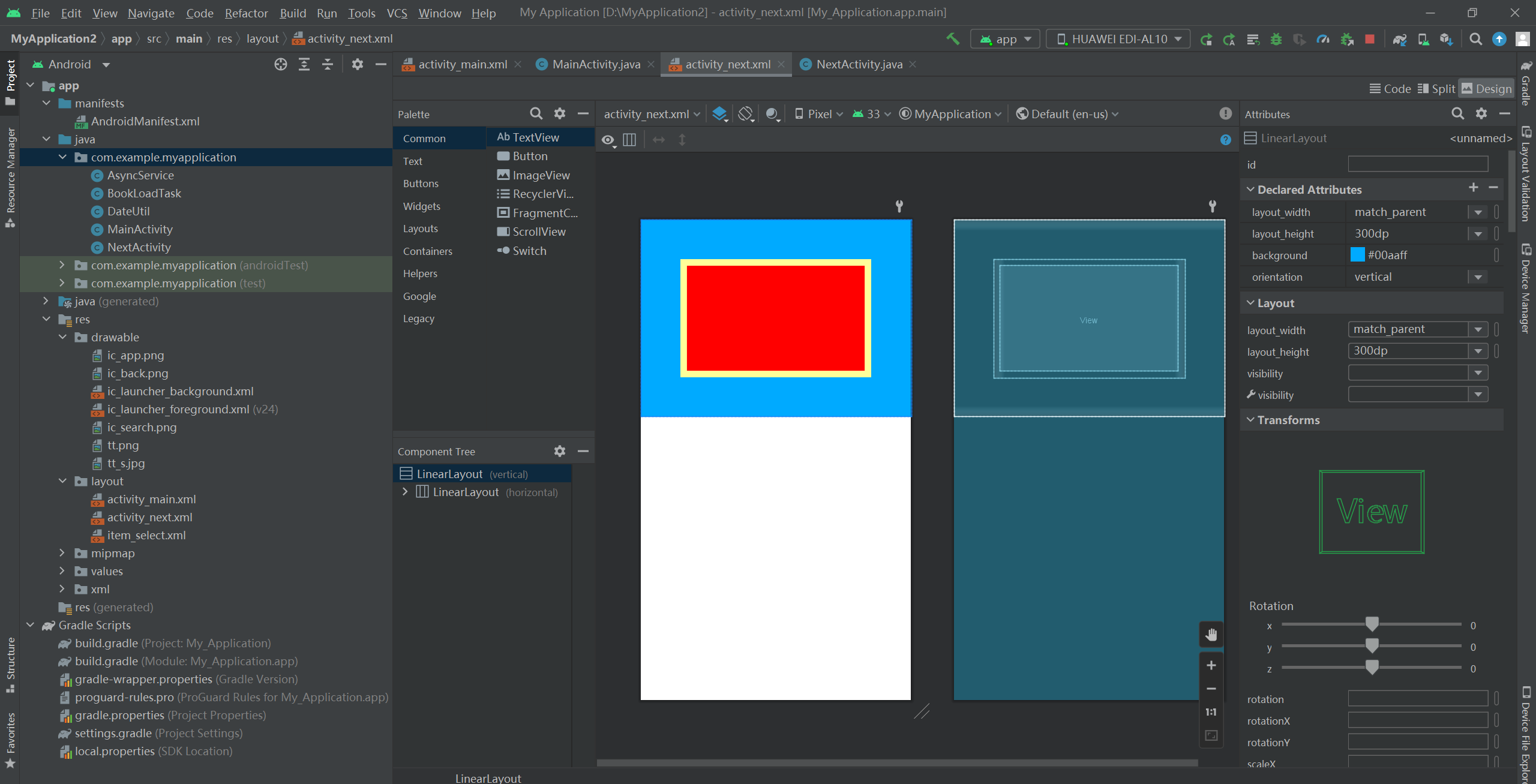
<!-- 最外层的布局背景为蓝色 -->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00aaff"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 中间层的布局背景为黄色 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="60dp" 指定当前视图与周围平级视图之间的间距
android:background="#ffff99"
android:padding="10dp"> 指定当前视图与内部下级视图之间的距离
<!-- 最内层的视图背景为红色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ff0000" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 最外层的布局背景为蓝色 --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="300dp" android:background="#00aaff" android:orientation="vertical"> <!-- 中间层的布局背景为黄色 --> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="60dp" android:background="#ffff99" android:padding="10dp"> <!-- 最内层的视图背景为红色 --> <View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#ff0000" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
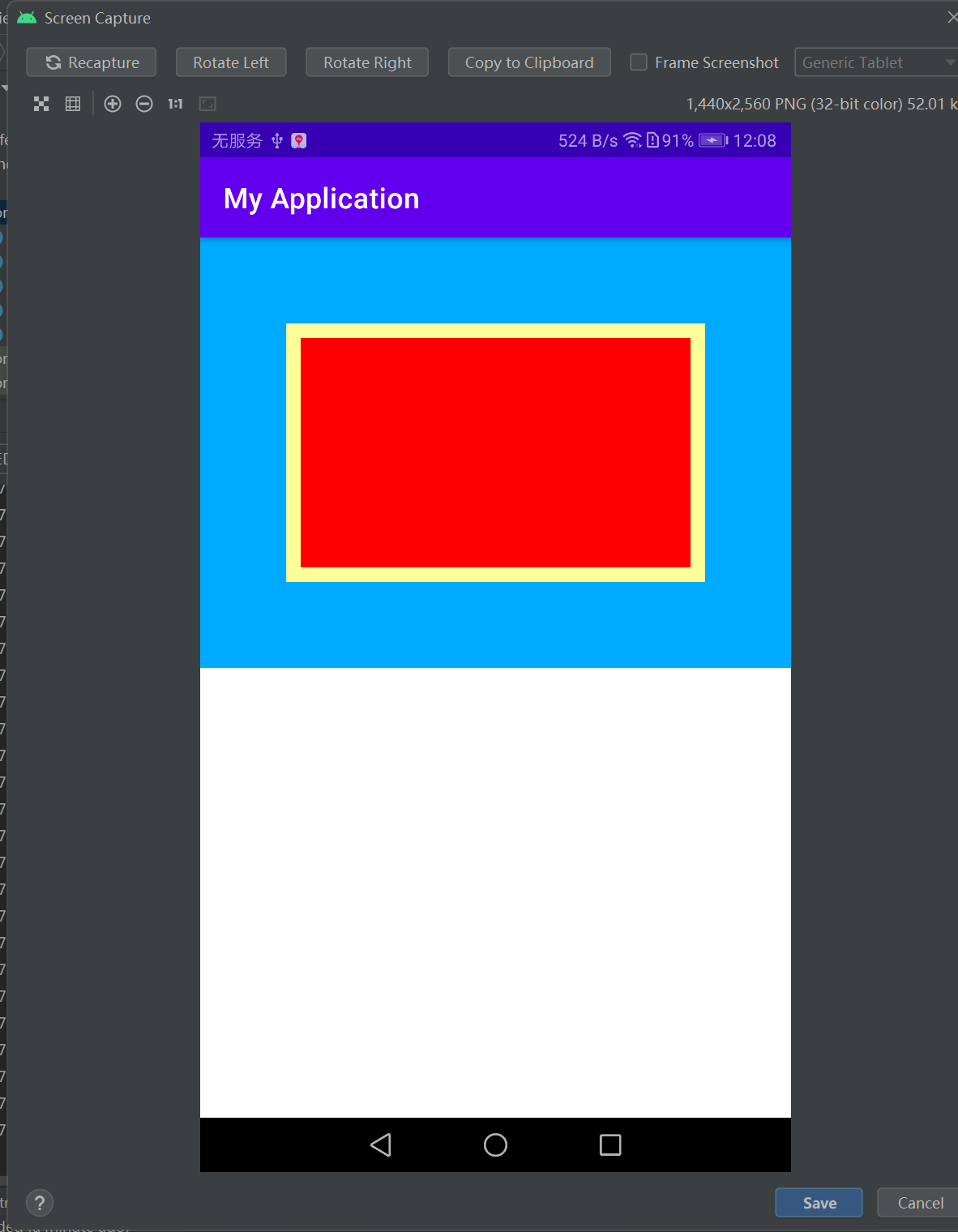
===================================================================================================
设置视图的对齐方式:
设置视图的对齐方式有两种途径:
(1)采用layout_gravity属性,它指定了当前视图相对于上级视图的对齐方式。
(2)采用gravity属性,它指定了下级视图相对于当前视图的对齐方式。
layout_gravity与gravity的取值包括:left、top、right、bottom,还可以用竖线连接各取值,例如“left|top”表示即靠左又靠上,也就是朝左上角对齐。
布局:
<!-- 最外层的布局背景为橙色,它的下级视图在水平方向排列 --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="300dp" android:background="#ffff99" android:padding="10dp"> <!-- 第一个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝下对齐,它的下级视图则靠左对齐 --> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_gravity="bottom" android:gravity="left" android:background="#ff0000" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:padding="10dp"> <!-- 内部视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 --> <View android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#00ffff" /> </LinearLayout> <!-- 第二个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝上对齐,它的下级视图则靠右对齐 --> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_gravity="top" android:gravity="right" android:background="#ff0000" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:padding="10dp"> <!-- 内部视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 --> <View android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#00ffff" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
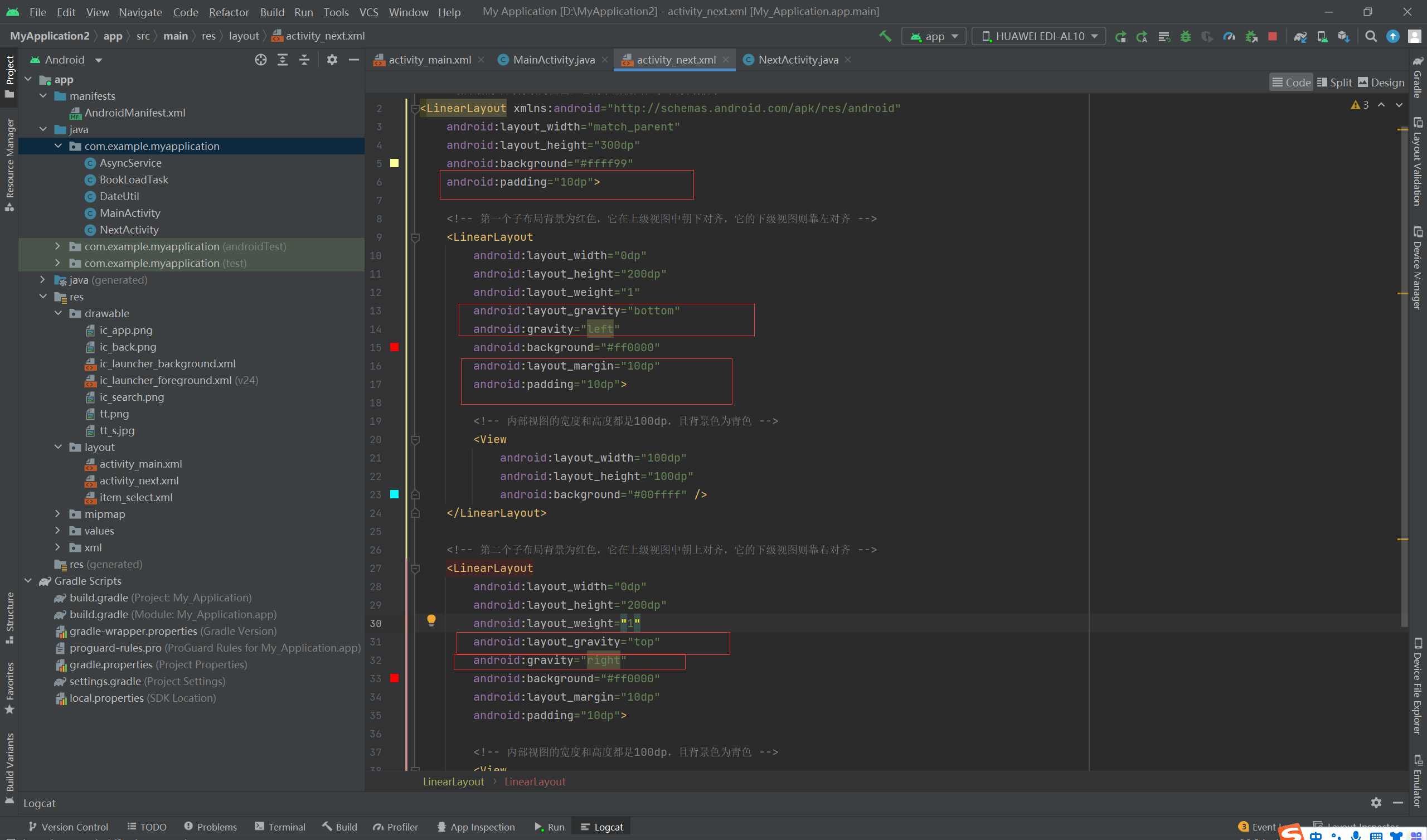
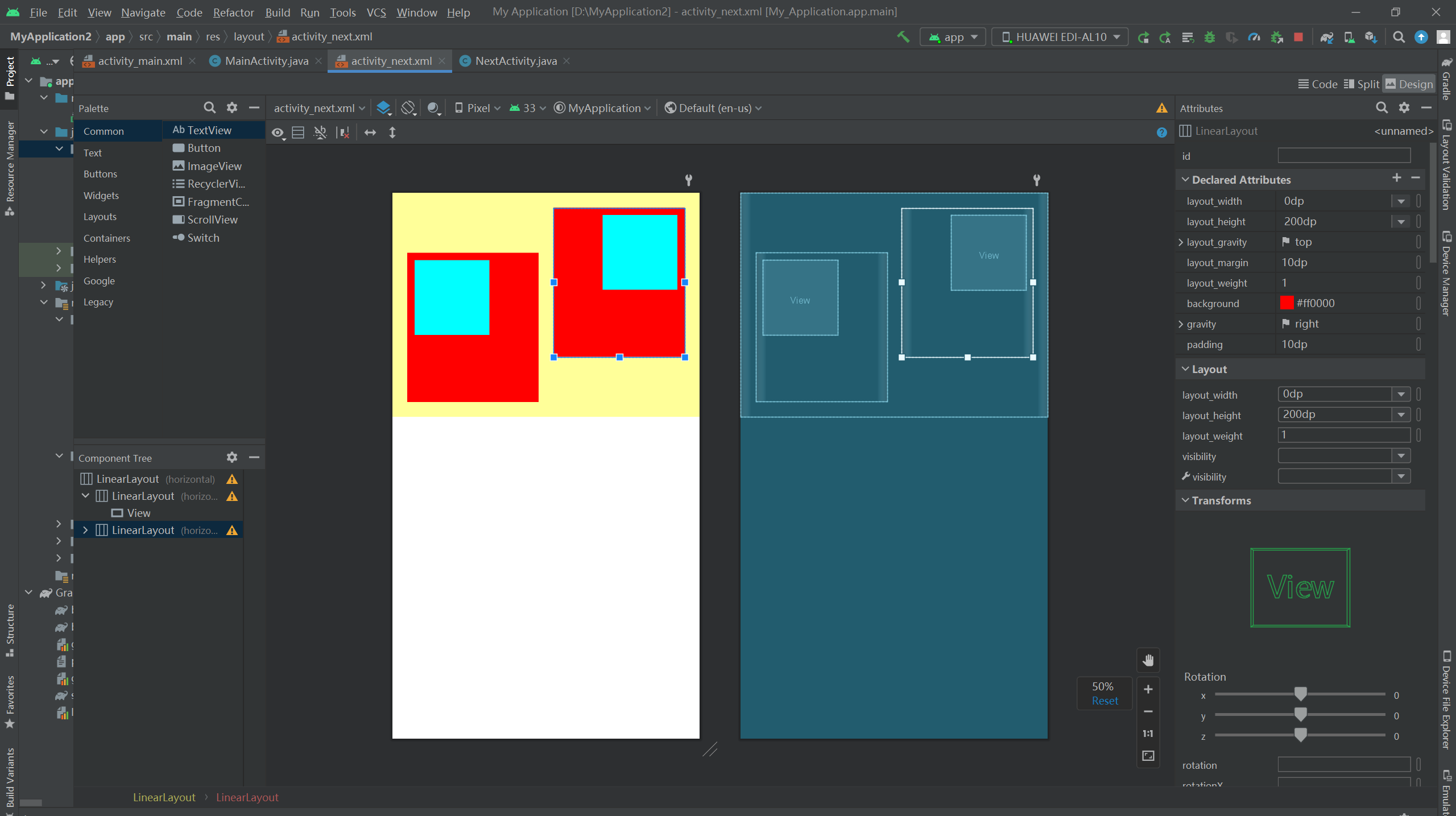
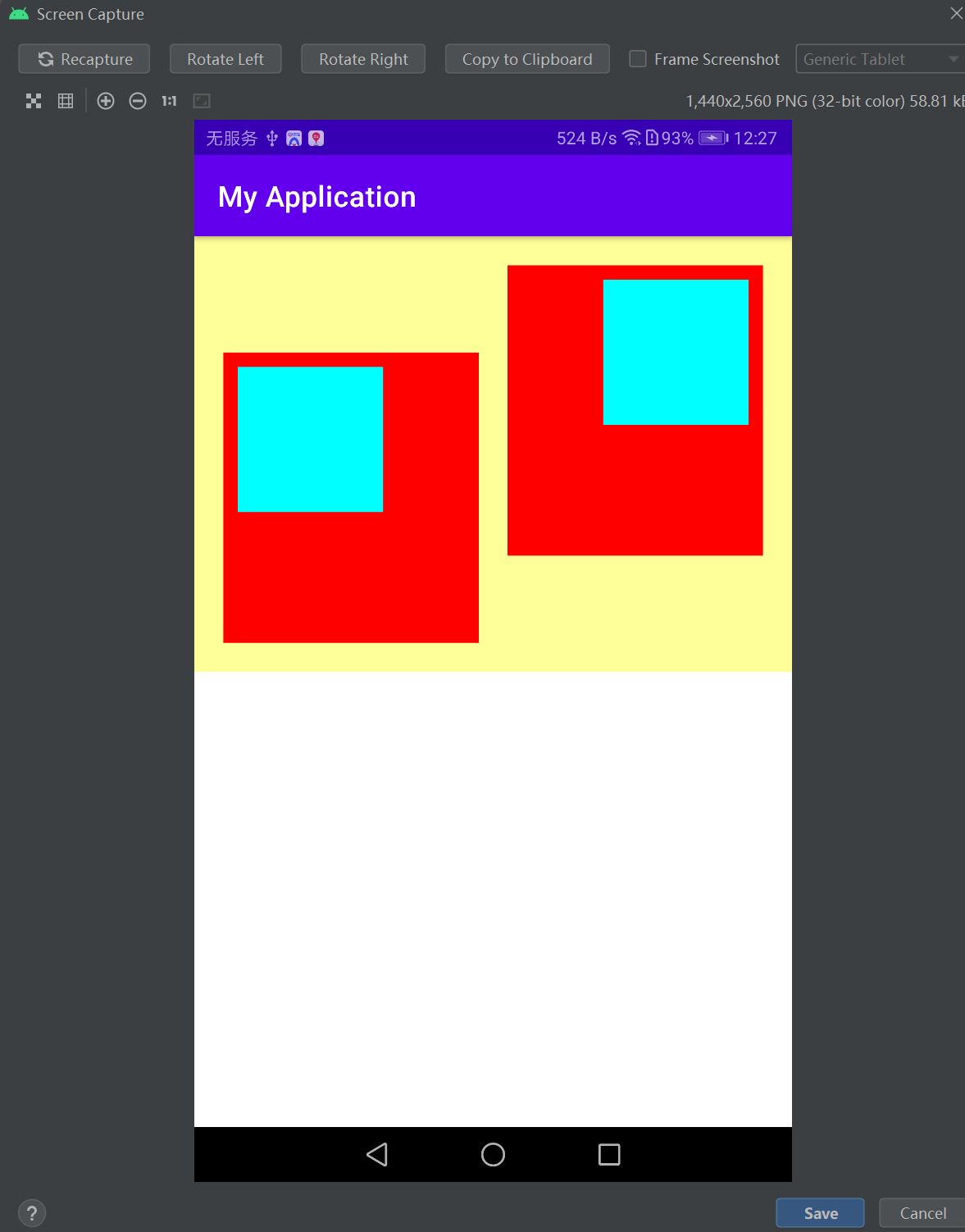
由效果图可见,第一个子布局朝下,并且它的内部视图靠左;而第二个子布局朝上,并且它的内部视图靠右。
对比 XML 文件中的 layout_gravity 和 gravity 取值,证明了二者的对齐情况正如之前所言:layout_ gravity 决定当前视图位于上级视图的哪个方位,而 gravity 决定了下级视图位于当前视图的哪个方位。
