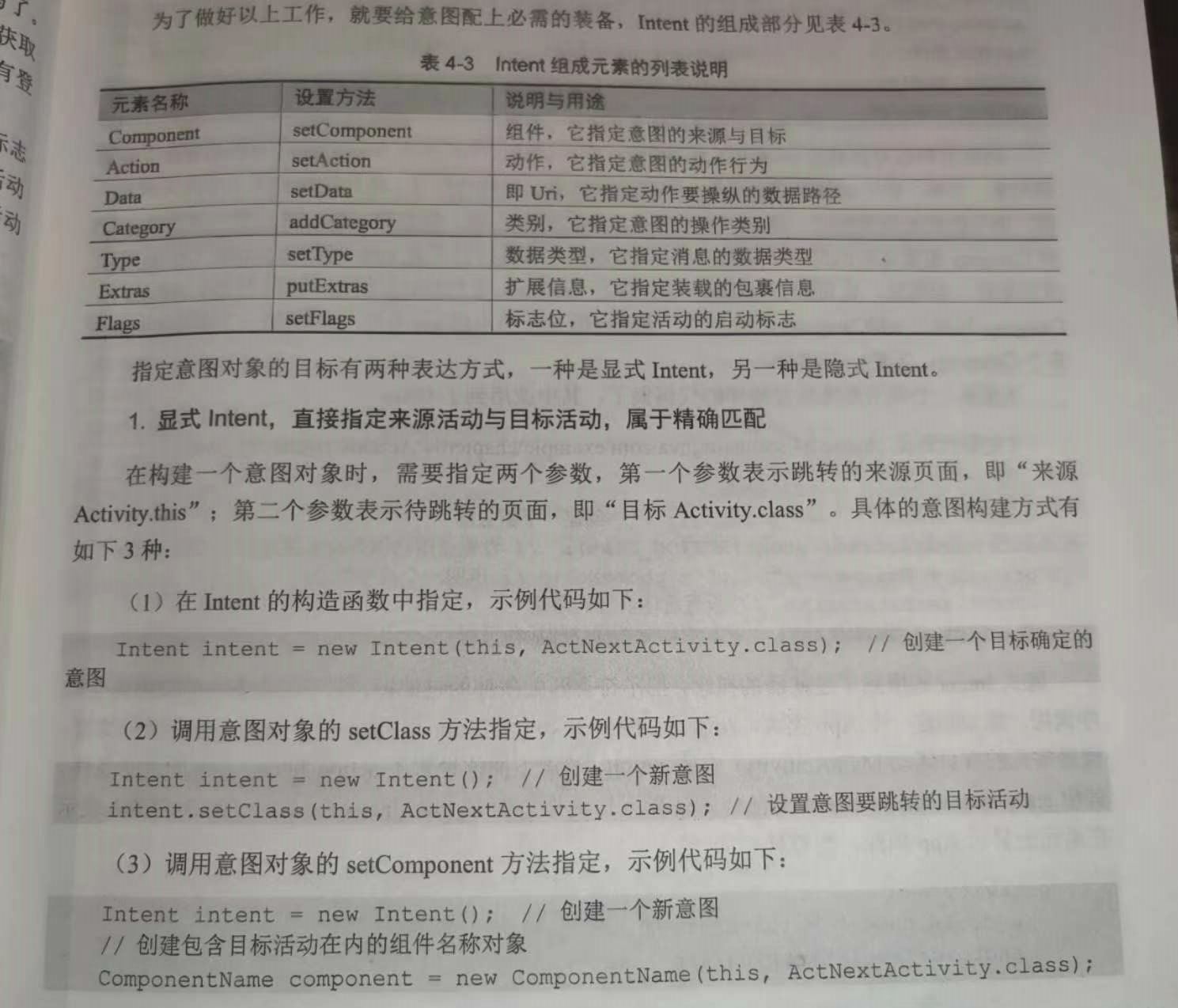
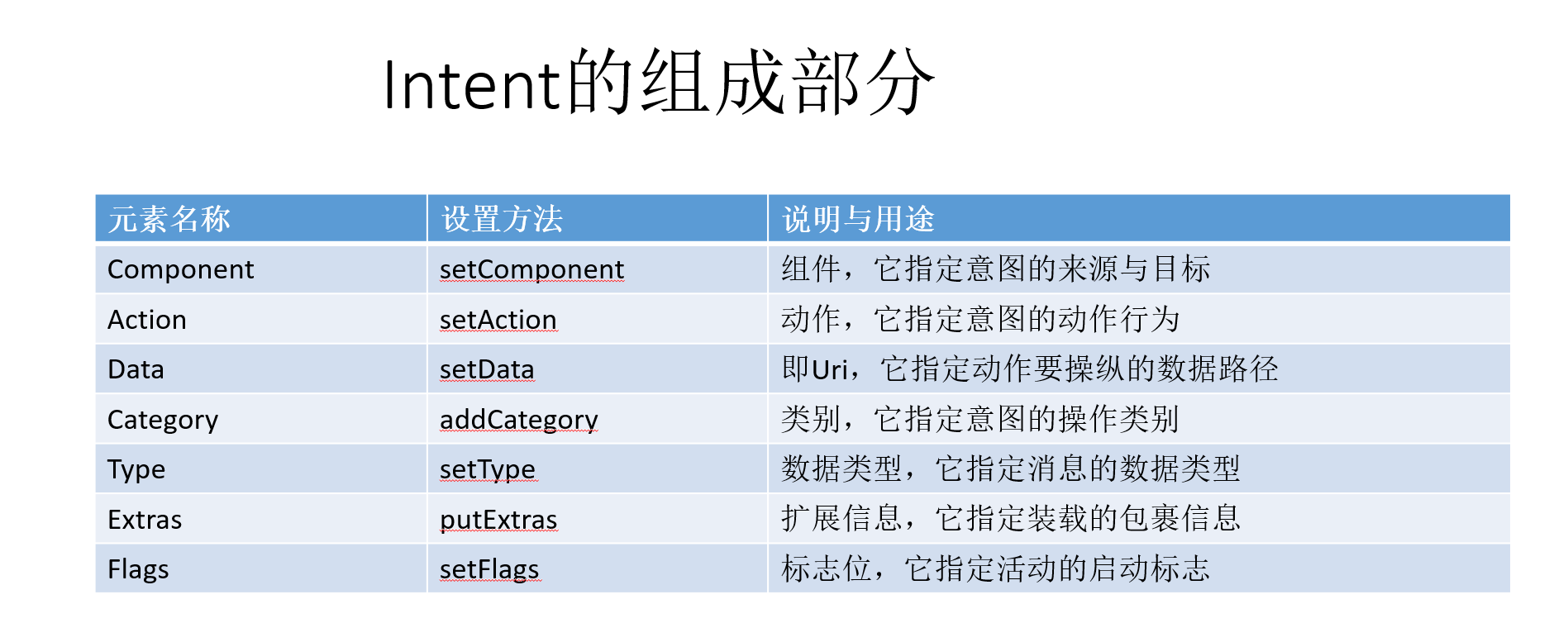
Intent是各个组件之间信息沟通的桥梁,它用于Android各组件之间的通信,主要完成下列工作:
(1)标明本次通信请求从哪里来、到哪里去、要怎么走。
(2)发起方携带本次通信需要的数据内容,接收方从收到的意图中解析数据。
(3)发起方若想判断接收方的处理结果,意图就要负责让接收方传回应答的数据内容。

显式Intent,直接指定来源活动与目标活动,属于精确匹配。它有三种构建方式:
(1)在Intent的构造函数中指定,示例代码如下:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ActNextActivity.class); // 创建一个目标确定的意图
(2)调用意图对象的setClass方法指定,示例代码如下:
Intent intent = new Intent(); // 创建一个新意图
intent.setClass(this, ActNextActivity.class); // 设置意图要跳转的目标活动
(3)调用意图对象的setComponent方法指定,示例代码如下:
Intent intent = new Intent(); // 创建一个新意图
// 创建包含目标活动在内的组件名称对象
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(this, ActNextActivity.class);
intent.setComponent(component); // 设置意图携带的组件信息

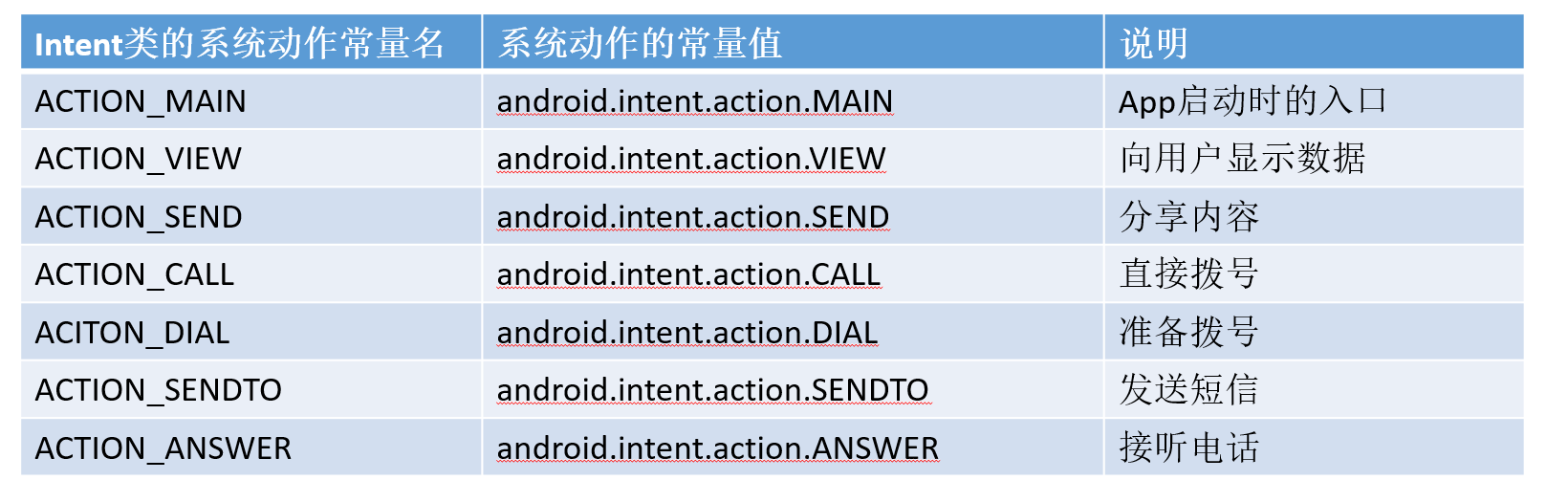
隐式Intent,没有明确指定要跳转的目标活动,只给出一个动作字符串让系统自动匹配,属于模糊匹配。
动作名称既可以通过setAction方法指定,也可以通过构造函数Intent(String action)直接生成意图对象。
常见的系统动作如下表:
=================================================================================
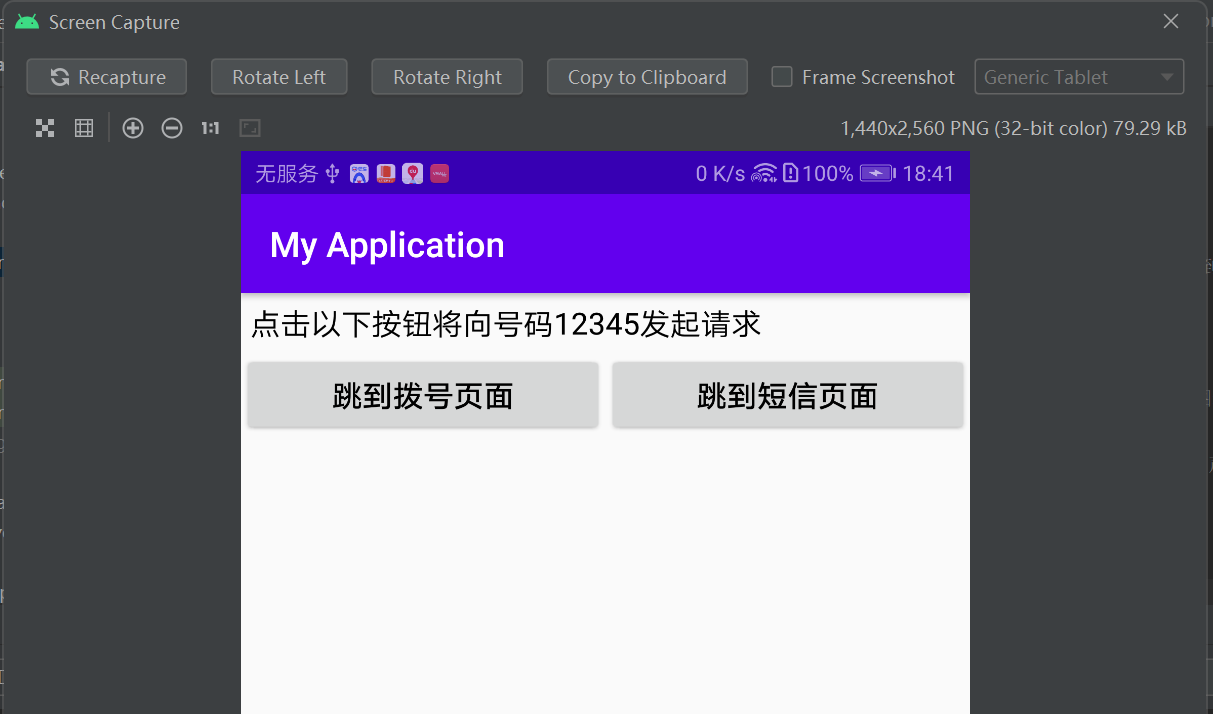
PS:页面跳转示例:
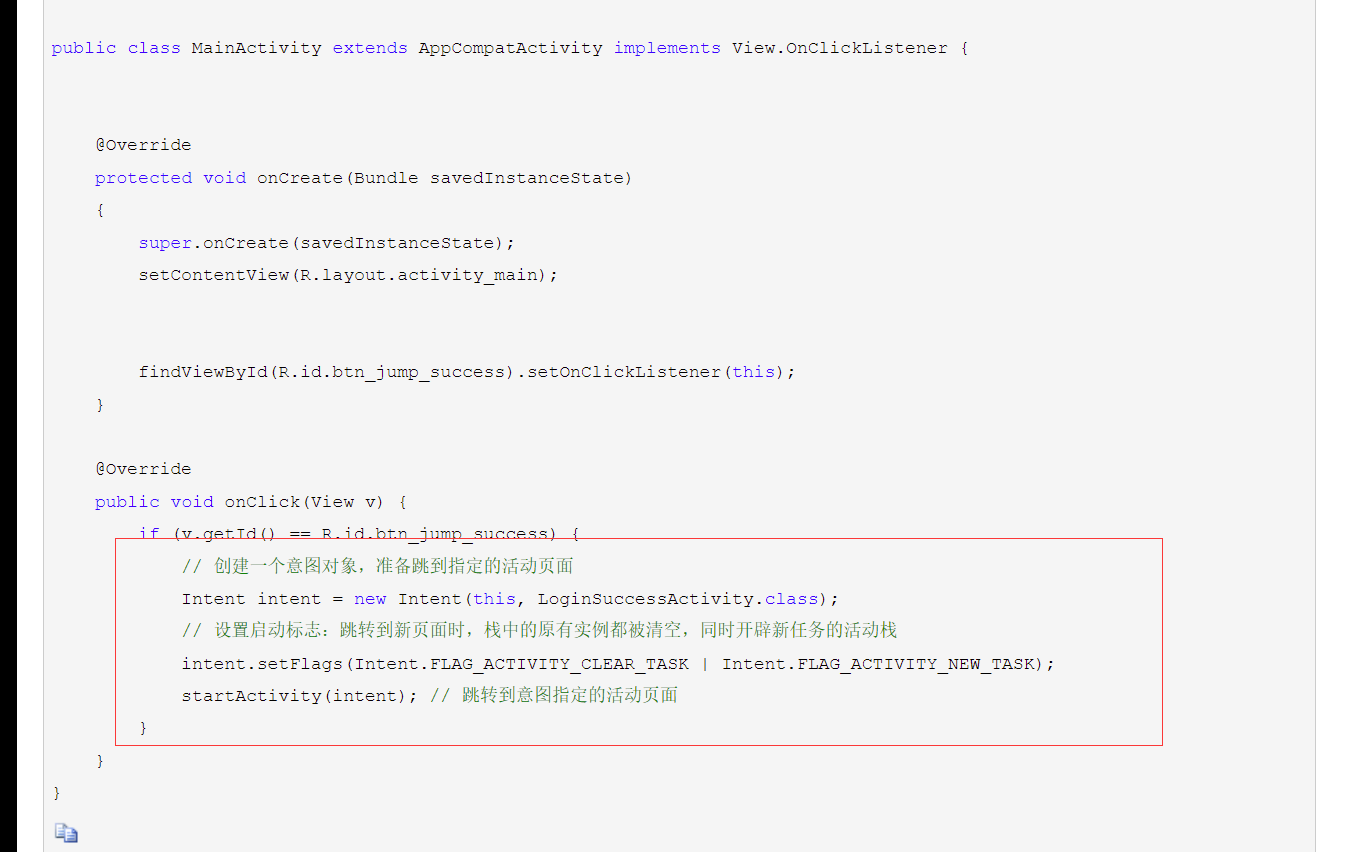
隐式示例:
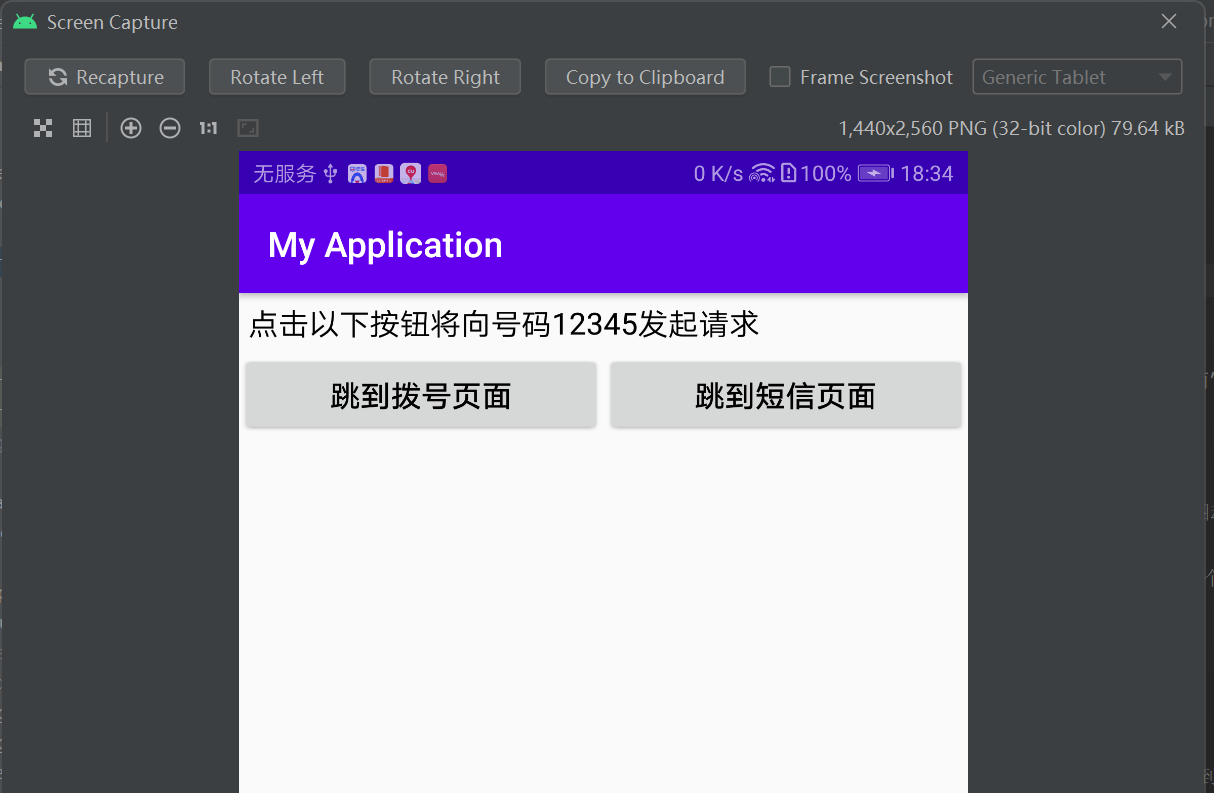
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:padding="5dp" android:text="点击以下按钮将向号码12345发起请求" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_dial" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="跳到拨号页面" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_sms" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="跳到短信页面" android:textColor="@color/black" android:textSize="17sp" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
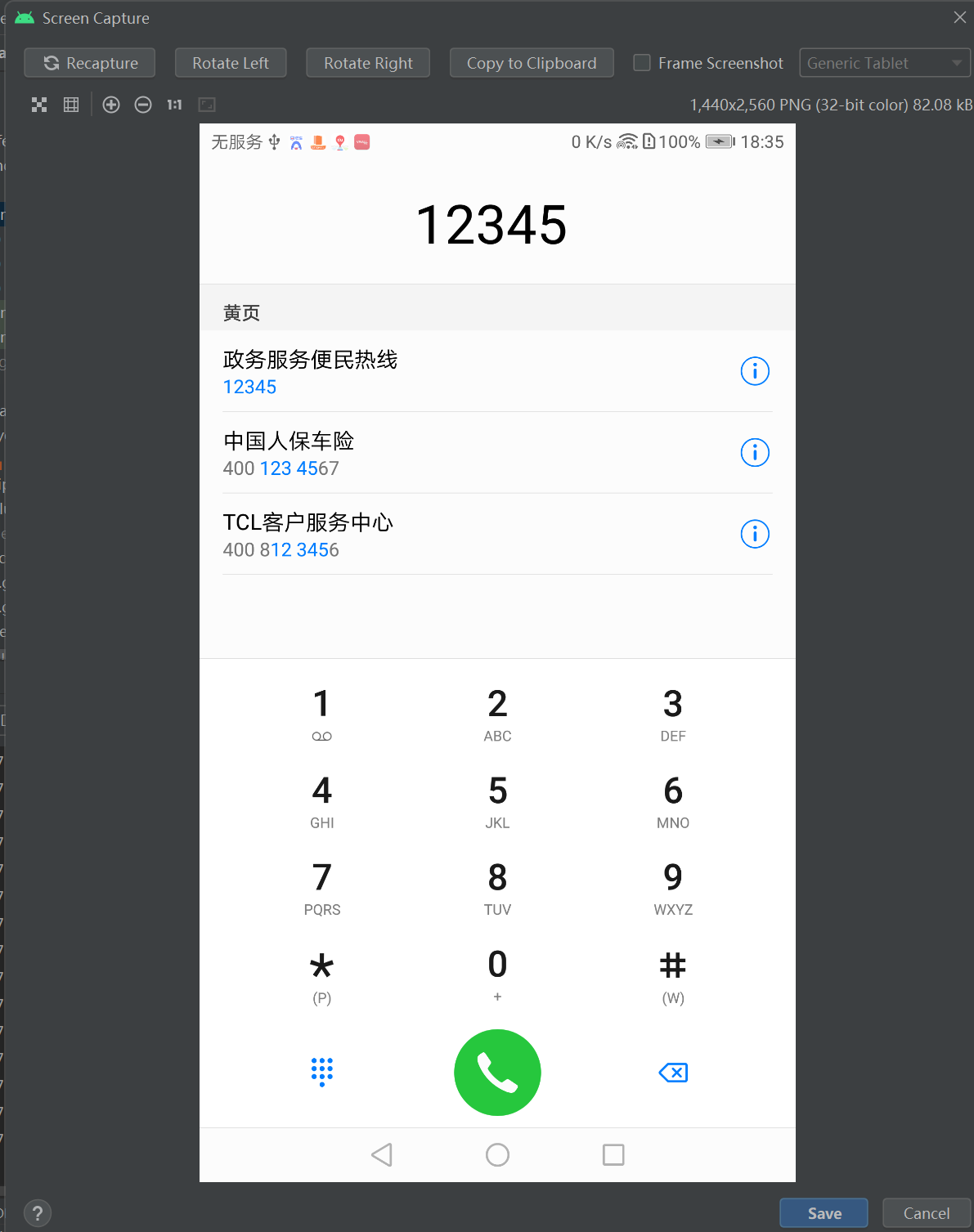
package com.example.myapplication; import android.content.Intent; import android.net.Uri; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); findViewById(R.id.btn_dial).setOnClickListener(this); findViewById(R.id.btn_sms).setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { String phoneNo = "12345"; if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_dial) // 点击了“跳到拨号页面”按钮 { Intent intent = new Intent(); // 创建一个新意图 intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_DIAL); // 设置意图动作为准备拨号 Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:" + phoneNo); // 声明一个拨号的Uri intent.setData(uri); // 设置意图前往的路径 startActivity(intent); // 启动意图通往的活动页面 } else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_sms) // 点击了“跳到短信页面”按钮 { Intent intent = new Intent(); // 创建一个新意图 intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO); // 设置意图动作为发短信 Uri uri = Uri.parse("smsto:" + phoneNo); // 声明一个发送短信的Uri intent.setData(uri); // 设置意图前往的路径 startActivity(intent); // 启动意图通往的活动页面 } } }

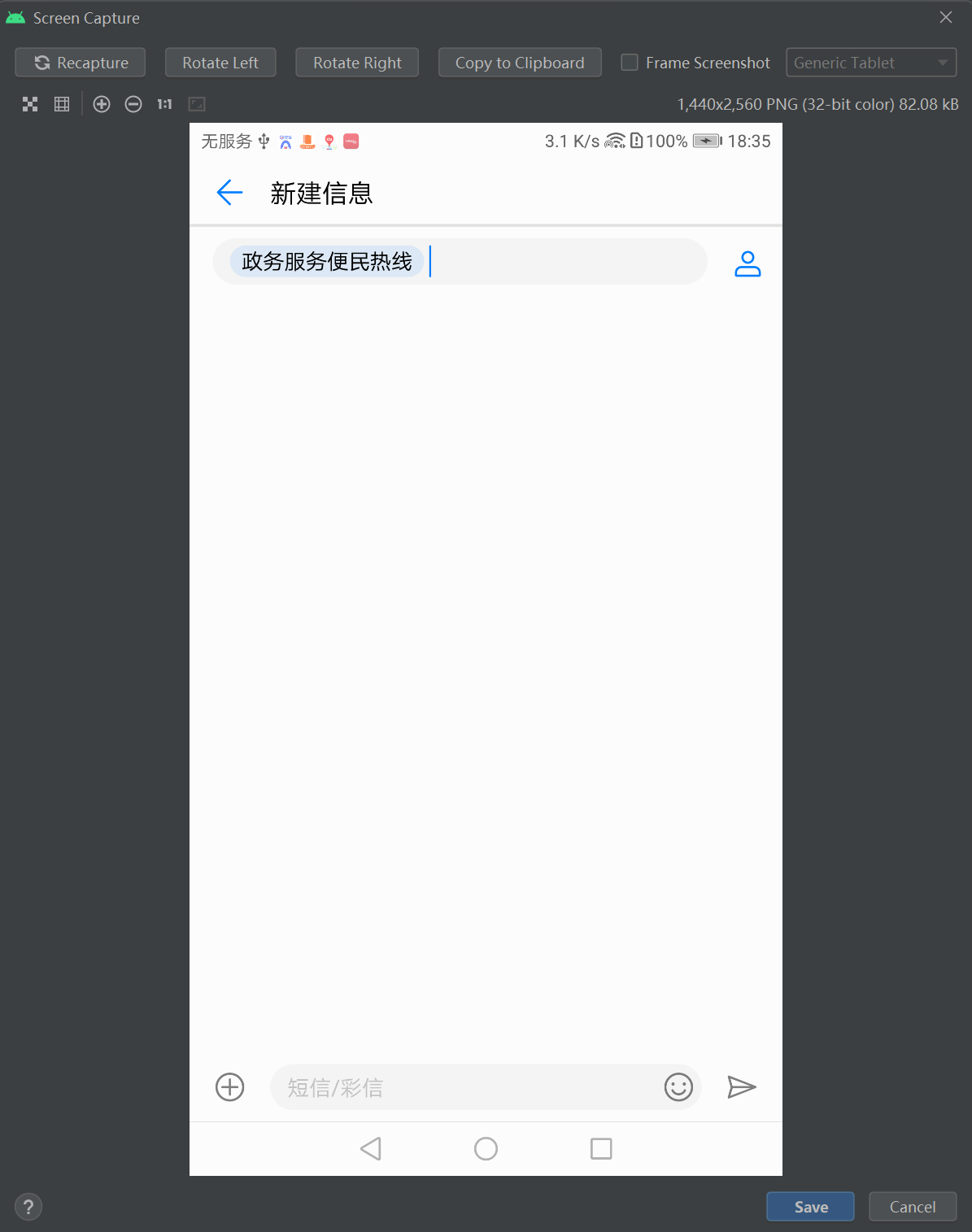
====================================================================================
PS:其他隐式:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_35181040/article/details/52710638
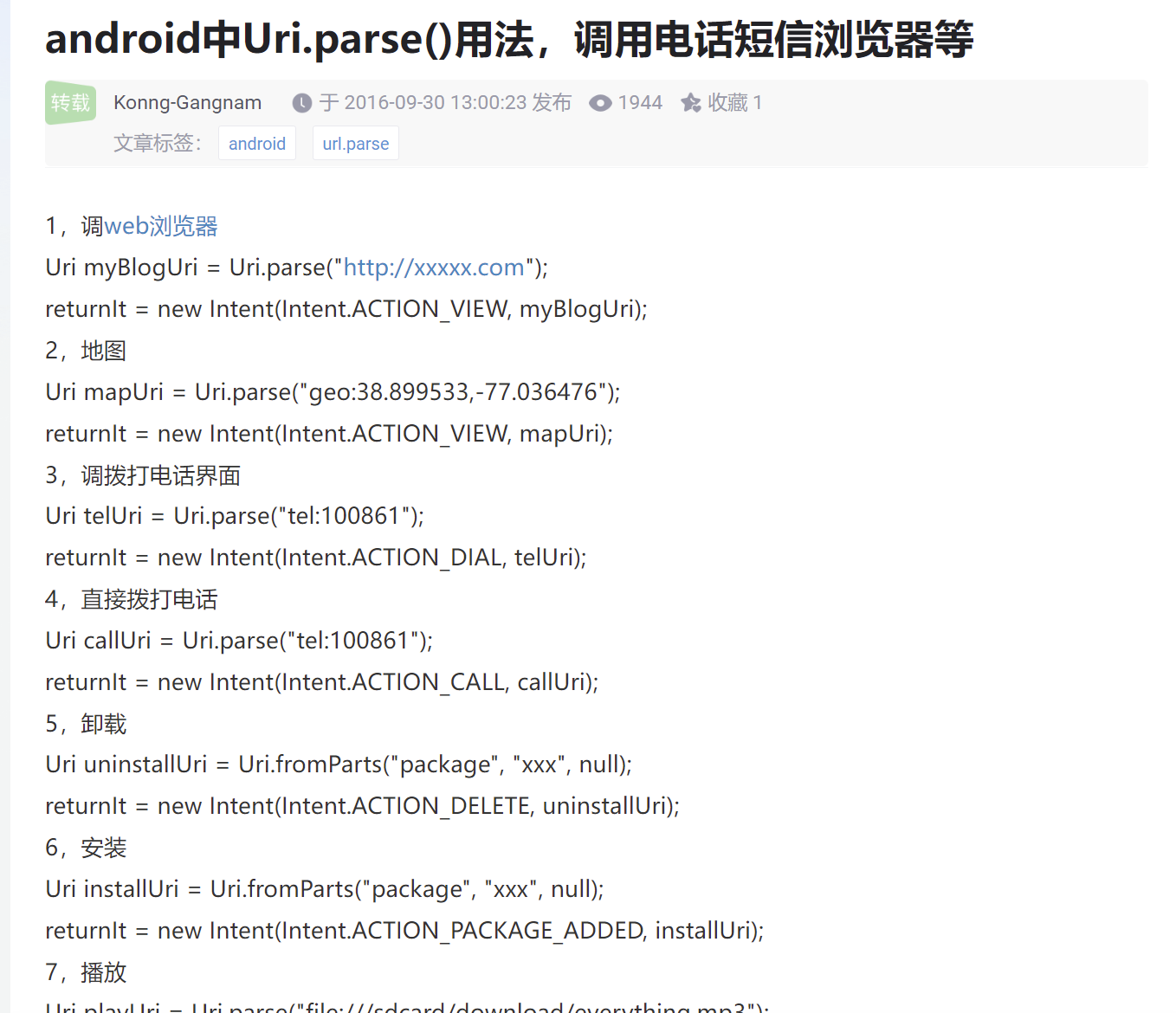


-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
修改,跳到短信页面的事件:
Intent intent = new Intent(); // 创建一个新意图 intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); // 设置意图动作为发短信 Uri uri = Uri.parse("https:www.baidu.com"); // 声明一个发送短信的Uri intent.setData(uri); // 设置意图前往的路径 startActivity(intent); // 启动意图通往的活动页面
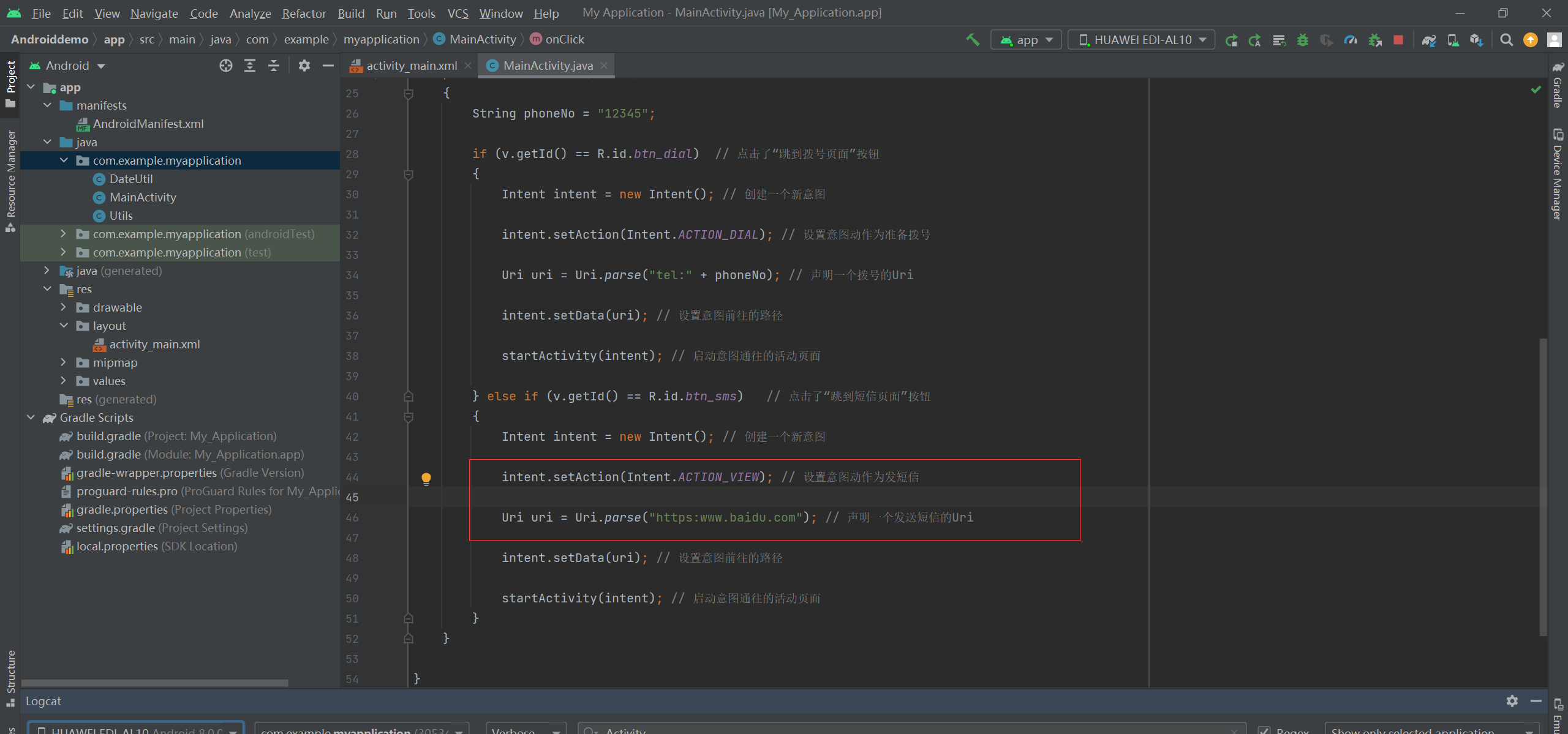
=============================================================================