小结
1--springboot:搭建spring应用的脚手架,内置tomcat。打成jar包就可以运行
自动配置(根据引入的依赖):解决混乱的依赖管理,简化配置
2--springboot的基本使用
搭建springboot基本应用
1-引入统一父工程,以及需要的启动器
2-覆盖默认配置,可在application.properties配置覆盖
3-添加引导类:@SpringBootApplication(该注解包含@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ConponentScan @SpringBootConfiguratin)
3--java配置
原生java配置:
1--@Configura java类作为一个配置类
2--@Bean 把方法的返回值注入到spring容器
3--@Value 属性注入
3--@PropertySource 读取属性配置文件
springboot提供的java配置
1--@ConfigurationProperties(profix="jdbc")
声明一个类是一个属性读取类 通过set方法注入数据给类属性,默认读取application.properties/yml
jdbc==前缀,即其在application通过前缀为jdbc的配置读取属性并通过set方法注入到类属性中
2--@EnbleConfigurationProperties(属性读取类.class) 引入属性读取类然后可以注入属性读取类到其他类
--@Autowired注入
--构造方法注入
--通过@Bean方法参数注入
--直接在@Bean方法上使用@ConfigurationProperties(profix="jdbc")注入,此注入连属性读取类都可以省了
--默认配置是怎么配置的,在哪里配置的呢?
引入了一个依赖,其中定义了大量自动配置类,
--为何依赖引入就会触发配置呢?
SpringBoot为我们提供了默认配置,而默认配置生效的条件一般有两个:
--你引入了相关依赖
--你自己没有配置
配置是否生效,取决于我们是否引入了对应库所需的依赖,如果有那么默认配置就会生效。
--这些默认配置的属性来自哪里呢?
通过@EnableAutoConfiguration注解引入了其他属性类,通过定义的其他属性类获取对应的默认属性。
我们要覆盖这些默认属性,只需要在application.properties中定义与其前缀和字段名一致的属性即可。
spring/springboot一些注解
@RestController 表示java类为controller类
@EnableAutoConfiguration 开启springboot的自动配置
@ComponentScan 扫描属性配置文件
@SpringBootApplication java类作为引导类
@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration 声明一个类为java配置类
@propertySource 加载指定配置文件 和ComponentScan
@Bean 方法返回值注入到spring容器
@Value 获取配置文件值注入到属性
@ConfigurationProperties 属性读取类,通过前缀读取属性配置文件中的属性
@EnableConfigurationProperties 载入属性类
1)启动器
我们如果不想配置,只需要引入依赖即可,而依赖版本我们也不用操心,
因为只要引入了SpringBoot提供的stater (启动器),就会自动管理依赖及版本了。
因此,玩SpringBoot的第一件事情, 就是找启动器,SpringBoot提供了大量的默认启动器,
1. Spring Boot application starters
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
使用Thymeleaf视图构建MVC Web应用程序
spring-boot-starter-ws
使用Spring Web服务。1.4不推荐使用,推荐使用spring-boot-starter-web-services
spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase
Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase
spring-boot-starter-artemis
使用Apache Artemis启动JMS消息传递
spring-boot-starter-web-services
使用Spring Web服务
spring-boot-starter-mail
支持使用Java Mail和Spring Framework发送电子邮件
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
使用Redis键值数据存储与Spring Data Redis和Jedis客户端
spring-boot-starter-web
启动器构建web,包括RESTful,使用Spring MVC的应用程序。使用Tomcat作为默认嵌入式容器
spring-boot-starter-data-gemfire
Starter for using GemFire distributed data store and Spring Data GemFire
spring-boot-starter-activemq
使用Apache ActiveMQ启动JMS消息传递
spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch
使用Elasticsearch搜索和分析引擎和Spring Data Elasticsearch
spring-boot-starter-integration
Starter for using Spring Integration
spring-boot-starter-test
Spring Boot应用程序用于测试包括JUnit,Hamcrest和Mockito
spring-boot-starter-hornetq
使用HornetQ启动JMS消息传递。1.4已弃用,推荐使用spring-boot-starter-artemis
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
使用HikariCP连接池
spring-boot-starter-mobile
使用Spring Mobile构建Web应用程序的入门
spring-boot-starter-validation
使用Java Bean校验与Hibernate校验器
spring-boot-starter-hateoas
使用Spring MVC和Spring HATEOAS构建基于超媒体的RESTful Web应用程序的入门
spring-boot-starter-jersey
使用JAX-RS和Jersey构建RESTful Web应用程序的入门。 spring-boot-starter-web的替代品
spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j
使用Neo4j图数据库和Spring Data Neo4j
spring-boot-starter-websocket
使用Spring Framework的WebSocket支持构建WebSocket应用程序
spring-boot-starter-aop
使用Spring AOP和AspectJ进行面向方面编程
spring-boot-starter-amqp
使用Spring AMQP和Rabbit MQ的入门
spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra
使用Cassandra分布式数据库和Spring Data Cassandra
spring-boot-starter-social-facebook
使用Spring Social Facebook
spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos
使用Atomikos进行JTA事务
spring-boot-starter-security
使用Spring Security
spring-boot-starter-mustache
使用Mustache视图构建MVC Web应用程序
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
使用Spring Data JPA与Hibernate
spring-boot-starter
核心启动器,包括自动配置支持,日志记录和YAML
spring-boot-starter-velocity
使用Velocity视图构建MVC Web应用程序。1.4已弃用
spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates
使用Groovy模板视图构建MVC Web应用程序
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
使用FreeMarker视图构建MVC Web应用程序
spring-boot-starter-batch
使用Spring Batch
spring-boot-starter-redis
使用Redis键值数据存储与Spring Data Redis和Jedis客户端的入门。1.4已弃用,建议使用spring-boot-starter-data-redis
spring-boot-starter-social-linkedin
Stater for using Spring Social LinkedIn
spring-boot-starter-cache
支持使用Spring Framework的缓存
spring-boot-starter-data-solr
使用带有Spring Data Solr的Apache Solr搜索平台
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb
使用MongoDB和Spring Data MongoDB
spring-boot-starter-jooq
使用jOOQ访问SQL数据库。 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa或spring-boot-starter-jdbc的替代方法
spring-boot-starter-jta-narayana
Spring Boot启动Narayana JTA
spring-boot-starter-cloud-connectors
启动者使用Spring Cloud连接器,简化了连接到云平台中的服务,如Cloud Foundry和Heroku
spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix
使用Bitronix进行JTA事务
spring-boot-starter-social-twitter
使用Spring Social Twitter
spring-boot-starter-data-rest
使用Spring Data REST通过REST暴露Spring数据存储库
2. Spring Boot production starters
spring-boot-starter-actuator
使用Spring Boot的Actuator,提供生产就绪的功能,以帮助您监视和管理您的应用程序
spring-boot-starter-remote-shell
使用CRaSH远程shell通过SSH监视和管理您的应用程序
3. Spring Boot technical starters
spring-boot-starter-undertow
使用Undertow作为嵌入式servlet容器。 spring-boot-starter-tomcat的替代方法
spring-boot-starter-jetty
使用Jetty作为嵌入式servlet容器的。 spring-boot-starter-tomcat的替代方法
spring-boot-starter-logging
使用Logback进行日志记录。 默认日志启动器
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
使用Tomcat作为嵌入式servlet容器。 spring-boot-starter-web使用的默认servlet容器
spring-boot-starter-log4j2
使用Log4j2进行日志记录。 spring-boot-starter-logging的替代方法
2)全局配置
另外,SpringBoot的默认配置都会读取默认属性,SpringBoot的默认属性key,非常多,而这些属性可以通过自定义application.properties文件来进行覆盖。
这样虽然使用的还是默认配置,但是配置中的值改成了我们自定义的。因此,玩SpringBoot的第二件事情,就是通过application.properties来覆盖默认属性值,形成自定义配置。
启动器就是一堆关联的依赖(jar包)
springboot默认配置文件:application.properties、application.yml 可以一起使用,不过有优先级
查看默认属性:spring-boot-autoconfigure -》spring-boot-autoconfigure-xxx.release.jar -》org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure -》web -》ResourceProperties类中
springboot属性注入
一、属性定义到application.properties配置文件中,
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysq1.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url= jdbc:mysq1://127.0.0.1:3306/1eyou
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
二、创建属性读取类 其会根据配置文件中对应前缀名称赋值类对应属性
package com.xiaoai.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties (prefix = "jdbc") //通过前缀获取配置文件中对应的属性然后通过set方法赋值给类属性
public class JdbcProperties {
private String driverClassName;
private String url;
private String username ;
private String password;
......属性对应get和set方法
}
三、在配置类中有四种方式注入属性
package com.xiaoai.springboot.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@Configuration //声明一个类是一个java配置类,相当于一个xml配置文件
//@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") // 读取资源
@EnableConfigurationProperties(JdbcProperties.class) //springboot属性注入需要先引入属性读取类
public class JdbcConfiguration {
//-----------------------------spring配置的方式
// @Value("${driverClassName}")
// private String driverClassName;
// @Value("${url}")
// private String url;
// @Value("${username}")
// private String username ;
// @Value("${password}")
// private String password;
// @Bean//把方法的返回值注入到spring容器
// public DataSource dataSource(){
// DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
// dataSource.setDriverClassName(this.driverClassName);
// dataSource.setUrl(this.url);
// dataSource.setUsername(this.username);
// dataSource.setPassword(this.password);
// }
//-----------------------------spring配置的方式
//springboot第一种注入方式:注解
// @Autowired
// private JdbcProperties jdbcProperties;
//springboot第二种注入方式:通过构造方法注入
// private JdbcProperties jdbcProperties;
// public JdbcConfiguration(JdbcProperties jdbcProperties){
// this.jdbcProperties = jdbcProperties;
// }
// @Bean//把方法的返回值注入到spring容器
// public DataSource dataSource(){//第一、二种注入方式所需要的方法
// DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
// dataSource.setDriverClassName(this.jdbcProperties.getDriverClassName());
// dataSource.setUrl(this.jdbcProperties.getUrl());
// dataSource.setUsername(this.jdbcProperties.getUsername());
// dataSource.setPassword(this.jdbcProperties.getPassword());
// return dataSource;
// }
//springboot第三种注入方式:直接把属性类定义到方法形参上
// @Bean //把方法的返回值注入到spring容器
// public DataSource dataSource(JdbcProperties jdbcProperties){
// DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
// dataSource.setDriverClassName(jdbcProperties.getDriverClassName());
// dataSource.setUrl(jdbcProperties.getUrl());
// dataSource.setUsername(jdbcProperties.getUsername());
// dataSource.setPassword(jdbcProperties.getPassword());
// return dataSource;
// }
//springboot第四种注入方式:直接把属性前缀注解定义到方法上,连属性类都可以省了
@Bean //把方法的返回值注入到spring容器
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc")
public DataSource dataSource(){ //因为其会直接调用DruidDataSource类中各参数的set方法直接把属性设置进去
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
return dataSource;
}
}
// 注:使用最多的是第一种方法,因为更符合平时spring的使用,第四种有一定的局限性,因为通过set方法设置,所以要求set方法名称去掉set后和属性名称要一致
springboot整合springMVC:
1--引入web启动器
<!-- 整合springmvc 引入web启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2--可以修改端口
通过application.properties配置文件重新覆盖
#修改默认端口8080为8888
server.port=8888
#修改日记记录级别
logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG
3--访问静态资源:默认静态资源路径在springboot配置类可以找到,如下:
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
4--配置拦截器:
---springMVC:可以在springMVC配置文件配置
1--编写拦截器
2--配置文件配置拦截器
例如:
<!--配置拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/user/*"/><!--要拦截的具体的方法 /**==所有方法都拦截 /user/*==user路径下所有方法拦截-->
<!--<mvc:exclude-mapping path=""></mvc:exclude-mapping><!–不要拦截的方法–>-->
<!--配置拦截器对象-->
<bean id="myInterceptor1" class="cn.xiaoai.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"></bean><!--注册拦截器-->
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
---springboot:通过配置类
1----编写拦截器
package com.xiaoai.user.interceptor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Component
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 前置方法
* 在handler方法执行之前执行
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("user--interceptor1--------前置方法正在执行。。。。");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("user--interceptor1--------后置方法正在执行。。。。");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("user--interceptor1--------完成方法正在执行。。。。");
}
}
2----通过java配置类配置拦截器
package com.xiaoai.user.config;
import com.xiaoai.user.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 配置拦截器
* 1-声明该类是一个java配置类
* 2-实现WebMvcConfigurer接口
* 3-重写方法注册并设置拦截器
*
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Autowired
private MyInterceptor myInterceptor;
//注册拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**"); //注册拦截器并设置拦截路径 这里拦截所有
}
}
springboot整合mybatis:
1-springboot整合连接池:
1--pom.xml引入启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
2--pom.xml引入mysql驱动
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
3--application.properties配置连接池四大参数
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
默认使用hikariCP内置数据源
2-springboot整合mybatis:springboot没有mybatis的启动器,mybatis官方提供了一个启动器
1--引入mybatis启动器
<!--mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
2--application.properties配置文件可配置,覆盖默认配置
#mybatis相关
#---实体类重命名
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.xiaoai.user.pojo
#---接口映射文件
#mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mappers/**/*.xml
3--加入mapper启动器 通用Mapper的作者也为自己的插件编写了启动器,我们直接引入即可:
<!--通用mapper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
4--代码使用,定义接口添加@Mapper注解继承mapper接口
package com.xiaoai.user.mapper;
import com.xiaoai.user.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper<User> {
}
3--springboot整合事务:spring已经依赖tx包,所以不用启动器 方法添加@transactional注解即可
package com.xiaoai.user.service;
import com.xiaoai.user.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.xiaoai.user.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//通过id查找用户
public User queryUserById(Long id){
return this.userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
//通过id删除用户
@Transactional
public void deleteUserById(Long id){
this.userMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
}
}
springboot不推荐使用jsp,但是支持一些模板引擎技术
如:freeMarker(老牌模板技术)、thymeleaf(springboot推荐使用)、mustache
5.1.为什么是Thymeleaf?
简单说,Thymeleaf 是一个跟Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代JSP。相较于其他的模板
引擎,它有如下四个极吸引人的特点:
动静结合:Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效
果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持html原型,然后在html标签里
增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释html时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以
thymeleaf的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
开箱即用:它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套
模板、改jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
多方言支持:Thymeleaf提供spring标准方言和一个与SpringMVC完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现
表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
与SpringBoot完美整合:SpringBoot提供了Thymeleaf的默认配置,并且为Thymeleaf设置了视图解析器,
我们可以像以前操作jsp-样来操作Thymeleaf。代码几乎没有任何区别,就是在模板语法上有区别。
thymeleaf体验
1--springboot内置thymeleaf,所以直接用就可以
2--ThymeleafAutoConfiguration自动配置类已经有默认模板解析器
3--引入Thymeleaf启动器,使默认配置生效
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
4--编写controller类方法
//Thymeleaf体验
@GetMapping("all")
public String toUsers(Model model){
List<User> users = this.userService.queryUserAll();
model.addAttribute("users",users);
return "users";
}
5--可以在配置类找到默认(路径)已经后缀,如下:
@Confi gurat ionProperties(prefix =" spring- thymeleaf )
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT ENCODING = StandardCharsets. UTF 8;
public static final String DEFAULT_ PREFIX ="classpath:/templates/" ;
public static final String DEFAULT_ SUFFAX=".html" ;
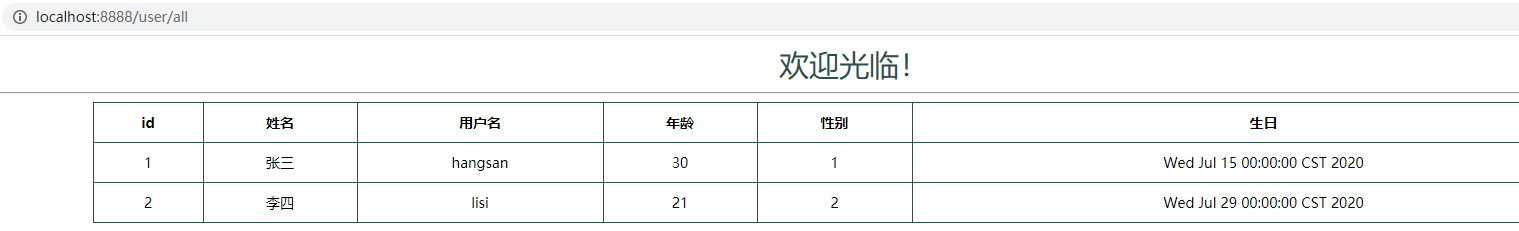
6--创建对应路径并在路径下编写页面及内容,如以下Thymeleaf语法编写的html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
<style type="text/css">
table {border-collapse: collapse; font-size: 14px; 80%; margin: auto}
table, th, td {border: 1px solid darkslategray;padding: 10px}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="text-align: center">
<span style="color: darkslategray; font-size: 30px">欢迎光临!</span>
<hr/>
<table class="list">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>用户名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>生日</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.id}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.name}">张三</td>
<td th:text="${user.userName}">zhangsan</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">20</td>
<td th:text="${user.sex}">男</td>
<td th:text="${user.birthday}">1980-02-30</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7--启动应用并访问相应路径即可