https://oracle-base.com/articles/misc/utl_http-and-ssl
http://blog.whitehorses.nl/2010/05/27/access-to-https-via-utl_http-using-the-orapki-wallet-command/
UTL_HTTP and SSL (HTTPS) using Oracle Wallets
Since Oracle 9i Release 2, the UTL_HTTP package has had the ability to access resources over HTTPS as well as HTTP. This article describes the method for enabling HTTPS access from the UTL_HTTPpackage.
- Access Control List (ACL)
- Test Unsecured Connection
- Get Site Certificates
- Create an Oracle Wallet Containing the Certificates
- Test Secured Connection
- Authentication
- SSLv3, TLSv1 and POODLE
Access Control List (ACL)
If you are using Oracle 11g, you will need to provide an ACL to allow the UTL_HTTP package to interact with an external host. This is described here.
Test Unsecured Connection
Before we start trying to configure SSL, lets see what happens if we attempt to access a HTTPS resource using the UTL_HTTP package. To do this, create the following procedure.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE show_html_from_url (p_url IN VARCHAR2,
p_username IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL,
p_password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) AS
l_http_request UTL_HTTP.req;
l_http_response UTL_HTTP.resp;
l_text VARCHAR2(32767);
BEGIN
-- Make a HTTP request and get the response.
l_http_request := UTL_HTTP.begin_request(p_url);
-- Use basic authentication if required.
IF p_username IS NOT NULL and p_password IS NOT NULL THEN
UTL_HTTP.set_authentication(l_http_request, p_username, p_password);
END IF;
l_http_response := UTL_HTTP.get_response(l_http_request);
-- Loop through the response.
BEGIN
LOOP
UTL_HTTP.read_text(l_http_response, l_text, 32766);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (l_text);
END LOOP;
EXCEPTION
WHEN UTL_HTTP.end_of_body THEN
UTL_HTTP.end_response(l_http_response);
END;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
UTL_HTTP.end_response(l_http_response);
RAISE;
END show_html_from_url;
/
This procedure works for a regular HTTP resource, but what happens if we call it using a HTTPS resource? The following example uses "https://gb.redhat.com/".
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
EXEC show_html_from_url('https://gb.redhat.com/');
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-29273: HTTP request failed
ORA-06512: at "SYS.UTL_HTTP", line 1527
ORA-29261: bad argument
ORA-06512: at "TEST.SHOW_HTML_FROM_URL", line 22
ORA-29273: HTTP request failed
ORA-06512: at "SYS.UTL_HTTP", line 1130
ORA-29024: Certificate validation failure
ORA-06512: at line 1
SQL>
The error stack shows the "ORA-29024: Certificate validation failure" error.
Get Site Certificates
In order to make connections to a secured resource, we need to get the necessary certificate. The easiest way to do this is using a browser. The example below uses the Chrome browser.
Using the browser, go to the URL you are attempting to access from PL/SQL. In this case "https://gb.redhat.com/". Click the lock icon in the URL bar to display the certificate menu and click on the "Connection" tab.
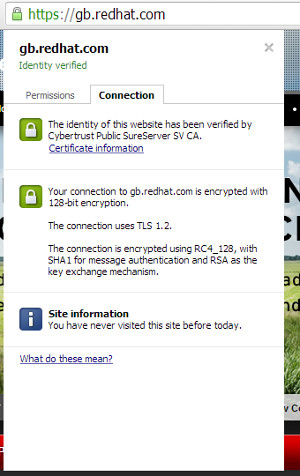
Click the "Certificate information" link and click the "Certification Path" tab on the resulting dialog.
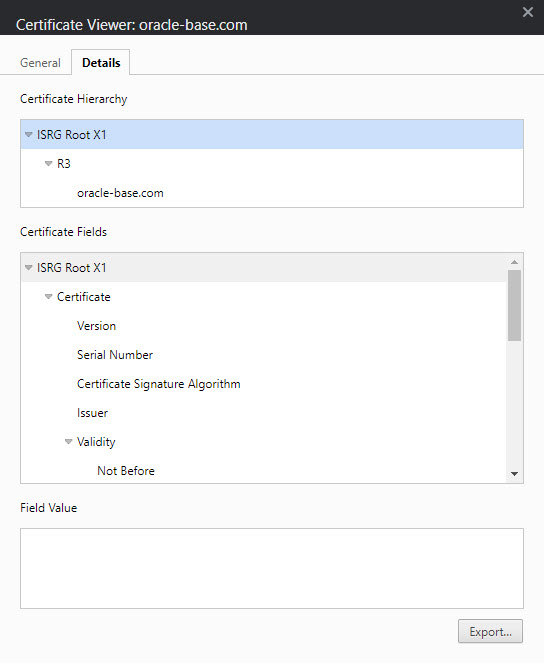
For the root node in the "Certification path", highlight the node and click the "View Certificate" button. On the resulting dialog, click the "Details" tab and click the "Copy to File..." button to save the certificate information.
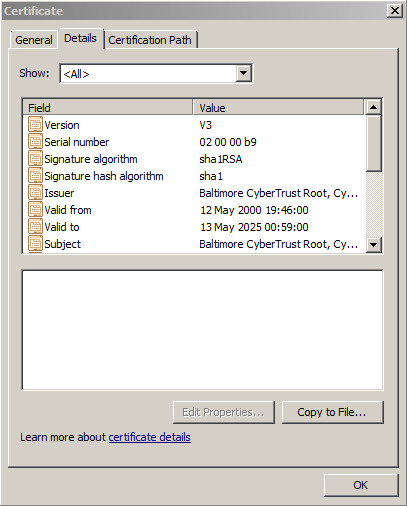
On the resulting wizard, do the following.
- Click the "Next" button on the welcome screen.
- Select the "Base-64 encoded X.509 (.CER)" option and click the "Next" button. Other formats work, but I've found this to be the most consistent.
- Enter suitable file name and click the "Next" button.
- Click the "Finish" button.
A similar dialog is displayed in Firefox by clicking "URL Icon > More Information > View Certificate > Details Tab".
Create an Oracle Wallet Containing the Certificates
Create a new location to hold the wallet.
$ mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet
Create a new wallet.
$ orapki wallet create -wallet /u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet -pwd WalletPasswd123 -auto_login
If the wallet password is too weak, you will get a message telling you so.
Invalid password.... PASSWORD_POLICY : Passwords must have a minimum length of eight characters and contain alphabetic characters combined with numbers or special characters.
In Oracle 11.2 the same issue causes a failure to create the wallet with the following message.
Unable to save wallet at /u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet
With the wallet created, we can add the certificate we saved earlier.
$ orapki wallet add -wallet /u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet -trusted_cert -cert "/host/BaltimoreCyberTrustRoot.crt" -pwd WalletPasswd123
The root certificate may fail to load with the following message, which can be ignored. It just means it was already present by default.
Could not install trusted cert at/host/Builtin Object Token:GTE CyberTrust Global Root PKI-04003: The trusted certificate is already present in the wallet.
Test Secured Connection
We are now ready to access the secured resource, but we must provide the UTL_HTTP package with the wallet details so it can make the secured connections. This is done using the UTL_HTTP.SET_WALLET procedure. Repeating the previous test now works successfully.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
EXEC UTL_HTTP.set_wallet('file:/u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet', 'WalletPasswd123');
EXEC show_html_from_url('https://gb.redhat.com/');
... HTML output removed ...
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL>
Authentication
If you are accessing a site that requires authentication, you will need to do one of two things depending on the type of authentication used.
If the site uses basic authentication, simply specify the credentials in the call to SHOW_HTOM_FROM_URL, which will use them in the UTL_HTTP.SET_AUTHENTICATION call.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
EXEC UTL_HTTP.set_wallet('file:/u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet', 'WalletPasswd123');
EXEC show_html_from_url('https://gb.redhat.com/', 'username', 'password');
... HTML output removed ...
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL>
If the page uses digest authentication, then you will need to will need to install the digest_auth_api package, then make the following modification to the test code.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE show_html_from_url (p_url IN VARCHAR2,
p_username IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL,
p_password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) AS
l_http_request UTL_HTTP.req;
l_http_response UTL_HTTP.resp;
l_text VARCHAR2(32767);
BEGIN
-- Make a HTTP request and get the response.
l_http_request := digest_auth_api.begin_request(p_url => p_url,
p_username => p_username,
p_password => p_password,
p_method => 'GET');
l_http_response := UTL_HTTP.get_response(l_http_request);
-- Loop through the response.
BEGIN
LOOP
UTL_HTTP.read_text(l_http_response, l_text, 32766);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (l_text);
END LOOP;
EXCEPTION
WHEN UTL_HTTP.end_of_body THEN
UTL_HTTP.end_response(l_http_response);
END;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
UTL_HTTP.end_response(l_http_response);
RAISE;
END show_html_from_url;
/
You can then call the test code in the same way you did for basic authentication.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
EXEC UTL_HTTP.set_wallet('file:/u01/app/oracle/admin/DB11G/wallet', 'WalletPasswd123');
EXEC show_html_from_url('https://gb.redhat.com/', 'username', 'password');
... HTML output removed ...
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL>
SSLv3, TLSv1 and POODLE
With the publicity about the POODLE bug, many web masters are turning off SSLv3 support. Depending on your Oracle database version/patch, that can present a bit of a problem for people using UTL_HTTP to access HTTPS resources, as described here.
UTL_HTTPPackage Fails With ORA-29273 ORA-28860 When Using TLSv1 (Doc ID 727118.1) : Basically, older database releases only allow HTTPS using the SSLv3 protocol fromUTL_HTTP. If you want to use the TLSv1 protocol you need to make sure you are on a patched up version of 11.2.
Interestingly, if you upgrade to Oracle 12c, you might have problems in the other direction, since Oracle 12c prevents UTL_HTTP calls over HTTPS to anything older than TLSv1.2, as described here.
UTL_HTTPGives Error Over HTTPS Using RDBMS 12.1.0.1.0 (Doc ID 1675966.1) So you might have trouble accessing legacy systems, without reverting to HTTP.
For more information see:
Hope this helps. Regards Tim...