一、上传文件
上传一个图片
使用input type="file",来上传一个文件。注意:form表单必须添加属性enctype="multipart/form-data"
在views.py视图函数中,获取文件对象,必须使用request.FILES.get
新建项目upload_file,在项目中新建static文件夹,在文件夹里面创建upload目录,用来保存上传的文件。
修改settings.py,定义static路径

STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), )
修改urls.py,增加路径

from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), ]
修改views.py,增加视图函数

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse import os from upload_file import settings # 导入settings。注意:upload_file为项目名 # Create your views here. def index(request): if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'index.html') user = request.POST.get('user') # 获取文件对象,必须使用request.FILES.get avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar') print(user) print(avatar,type(avatar)) print(avatar.__dict__) # 查看对象所有属性 # 文件存储的绝对路径 path = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, "static", "upload", avatar.name) with open(path,'wb') as f: # 将大文件分割成若干小文件处理,处理完每个小文件后释放该部分内存 for line in avatar.chunks(): f.write(line) # 写入文件 return HttpResponse('上传成功')
新建index.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> {#上传文件必须指定enctype="multipart/form-data"#} <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <lable>上传图片</lable> <input type="file" name="avatar"><br> <lable>用户名</lable> <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
启动项目,访问url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/
选择一个图片
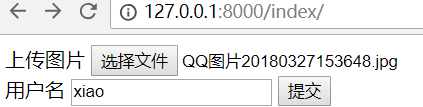
提示上传成功
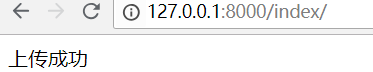
在upload目录,就会多出一个图片 QQ图片20180327153648.jpg
上传按钮美化
所有好看的上传按钮,都是经过修饰的。那么它是如何做到的呢!原理如下:

修饰的样式一般是用html做的,将前面的input上传控件变成透明。
那么用户看到的是一个经过修饰的按钮,实际点击的是input上传控件!
注意:上传控件的尺寸和后面的html控件,大小是一样的,比如div
举例:
修改index.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> {#上传文件必须指定enctype="multipart/form-data"#} <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <div style="position: relative;display: inline-block;height: 50px;min- 300px;overflow: hidden;"> <div style="position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;z-index: 1000;border: 1px dotted #9d9d9d;color: #9d9d9d;line-height: 50px;padding-left: 15px;"> <i class="fa fa-cloud-upload" aria-hidden="true"></i> <span>点击上传文件</span> </div> {#opacity表示设置透明度,0表示完全透明#} <input name="customer_excel" type="file" id="excelFile" style="position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;background-color: #333333;z-index: 1001;opacity: 0;filter:alpha(opacity=0);"> </div> <div> <lable>用户名: </lable><input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </div> </form> <script src="/static/js/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> $(function () { {#当元素的值发生改变时,会发生 change 事件#} $('#excelFile').change(function (e) { {#event.currentTarget 属性是在事件冒泡阶段内的当前 DOM 元素,通常等于 this#} {#:file 选择器选取带有 type=file 的 input 元素#} {#0表示获取第一个元素,name表示获取文件名#} var fileName = e.currentTarget.files[0].name; {#prev() 获得匹配元素集合中每个元素紧邻的前一个同胞元素,通过选择器进行筛选是可选的#} {#$(this)表示上传控件,那么它前一个同胞元素为div style="position:...#} {#find() 方法获得当前元素集合中每个元素的后代,通过选择器、jQuery 对象或元素来筛选。#} {#text() 方法方法设置或返回被选元素的文本内容#} $(this).prev().find('span').text(fileName); }) }) </script> </body> </html>
重新访问网页,效果如下:
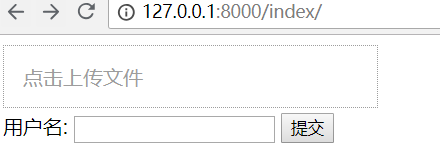
重新上传一个图片,效果如下:
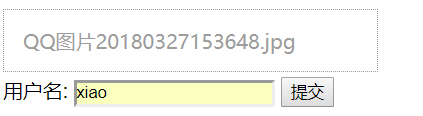
点击提交,提示上传成功!
这个是重点,考试必考!
二、上传头像
一般做上传头像功能,会有一个预览效果。总共有4种方法:
- createObjectURL
- FileReader
- FormData
- iframe
前2种,是在浏览器端可以做图片预览,没有上传图片到服务器!
后2种,图片需要上传到服务器。
兼容性效果对比: iframe > FormData > FileReader -> createObjectURL
iframe的兼容性是最好的,即使ie6也支持。FormData对浏览器,有一定要求
参考兼容性:
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/URL/createObjectURL
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/FileReader
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/FormData
createObjectURL
举例:
修改urls.py,增加路径

urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('upload_file/', views.upload_file), ]
修改views.py,增加视图函数

def upload_file(request): if request.method == "GET": print(11) return render(request,'upload_file.html') user = request.POST.get('user') avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar') # 文件存储的绝对路径 path = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, "static", "upload", avatar.name) with open(path,'wb') as f: for line in avatar.chunks(): f.write(line) return HttpResponse('上传成功')
创建upload_file.html,注意:不是所有浏览器都有createObjectURL

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <div style="height: 100px; 100px;padding: 2px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;position: relative;"> <img style="height: 100%; 100%;border: 0;overflow: hidden;border-radius: 50%;" id="previewImg" src="/static/images/default.png"> <input style="top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;opacity: 0;position: absolute;z-index: 102;" id="avatarImg" name="avatar" type="file" class="img-file"/> </div> <div>点击图片更换(<a href="#">撤销</a>)</div> <lable>用户名:</lable> <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> <script src="/static/js/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> {#浏览器加载资源完成后#} $(function () { {#执行函数#} bindChangeAvatar1(); }); function bindChangeAvatar1() { {#绑定change事件#} $('#avatarImg').change(function () { {#$(this)表示input上传控件,0表示第一个元素#} {#files[0] 获取file input中的File对象#} var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0]; console.log(file_obj); {#通过createObjectURL读取对象,生成url#} var blob = window.URL.createObjectURL(file_obj); {#修改src的值#} document.getElementById('previewImg').src = blob; {#load() 当资源加载完成之后才会执行#} $('#previewImg').load(function () { {#revokeObjectURL释放对象#} window.URL.revokeObjectURL(blob); }) }) } </script> </body> </html>
访问url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/upload_file/
上传一个图片

点击提交,提示上传成功
在upload目录,会有一个文件 QQ图片20180327153648.jpg
FileReader
举例:
修改upload_file.html里面的js代码即可,readAsDataURL也有兼容问题

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <div style="height: 100px; 100px;padding: 2px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;position: relative;"> <img style="height: 100%; 100%;border: 0;overflow: hidden;border-radius: 50%;" id="previewImg" src="/static/images/default.png"> <input style="top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;opacity: 0;position: absolute;z-index: 102;" id="avatarImg" name="avatar" type="file" class="img-file"/> </div> <div>点击图片更换(<a href="#">撤销</a>)</div> <lable>用户名:</lable> <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> <script src="/static/js/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> $(function () { bindChangeAvatar2(); }); function bindChangeAvatar2() { $('#avatarImg').change(function () { var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0]; //使用fileReader对文件对象进行操作 var reader = new FileReader(); //readAsDataURL 将文件读取为 DataURL reader.readAsDataURL(file_obj); //onload 事件会在页面或图像加载完成后立即发生 reader.onload = function (e) { // 修改src属性 $('#previewImg')[0].src = this.result; }; }) } </script> </body> </html>
上传一个图片
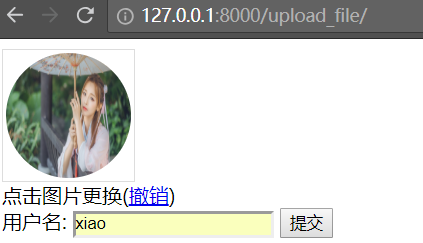
点击提交,提示上传成功
在upload目录,会有一个文件 59fffde43ed74.jpg
FormData
上面的保存图片方式有问题,因为用户上传的图片,可能会重名。为了解决这个问题,需要使用uuid模块。
uuid
UUID是128位的全局唯一标识符,通常由32字节的字符串表示。
它可以保证时间和空间的唯一性,也称为GUID,全称为:
UUID —— Universally Unique IDentifier。Python 中叫 UUID
它通过MAC地址、时间戳、命名空间、随机数、伪随机数来保证生成ID的唯一性。
UUID主要有五个算法,也就是五种方法来实现:

1、uuid1()——基于时间戳 由MAC地址、当前时间戳、随机数生成。可以保证全球范围内的唯一性, 但MAC的使用同时带来安全性问题,局域网中可以使用IP来代替MAC。 2、uuid2()——基于分布式计算环境DCE(Python中没有这个函数) 算法与uuid1相同,不同的是把时间戳的前4位置换为POSIX的UID。 实际中很少用到该方法。 3、uuid3()——基于名字的MD5散列值 通过计算名字和命名空间的MD5散列值得到,保证了同一命名空间中不同名字的唯一性, 和不同命名空间的唯一性,但同一命名空间的同一名字生成相同的uuid。 4、uuid4()——基于随机数 由伪随机数得到,有一定的重复概率,该概率可以计算出来。 5、uuid5()——基于名字的SHA-1散列值 算法与uuid3相同,不同的是使用 Secure Hash Algorithm 1 算法
使用方面:

首先,Python中没有基于DCE的,所以uuid2可以忽略;
其次,uuid4存在概率性重复,由无映射性,最好不用;
再次,若在Global的分布式计算环境下,最好用uuid1;
最后,若有名字的唯一性要求,最好用uuid3或uuid5。
编码方法:

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import uuid name = "test_name" namespace = "test_namespace" print(uuid.uuid1()) # 带参的方法参见Python Doc print(uuid.uuid3(namespace, name)) print(uuid.uuid4()) print(uuid.uuid5(namespace, name))
修改urls.py,增加路径form_data_upload,用来和ajax交互的

urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('upload_file/', views.upload_file), path('form_data_upload/', views.form_data_upload), ]
修改upload_file视图函数,使用uuid,完整代码如下:

import os import json import uuid from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from upload_file import settings # 导入settings。注意:upload_file为项目名 # Create your views here. def index(request): if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'index.html') user = request.POST.get('user') # 获取文件对象,必须使用request.FILES.get avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar') print(user) print(avatar,type(avatar)) print(avatar.__dict__) # 查看对象所有属性 # 文件存储的绝对路径 path = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, "static", "upload", avatar.name) with open(path,'wb') as f: # 将大文件分割成若干小文件处理,处理完每个小文件后释放该部分内存 for line in avatar.chunks(): f.write(line) # 写入文件 return HttpResponse('上传成功') def upload_file(request): if request.method == "GET": return render(request, 'upload_file.html') # 直接获取图片地址即可,因为ajax已经将图片上传了 avatar = request.POST.get('avatar') user = request.POST.get('user') print(avatar,user) return HttpResponse("上传成功") def form_data_upload(request): """ ajax上传文件 :param request: :return: """ img_upload = request.FILES.get('img_upload') # 获取文件对象 # 生成随机文件名 file_name = str(uuid.uuid4()) + "." + img_upload.name.rsplit('.', maxsplit=1)[1] # 文件保存到static下的images目录 img_file_path = os.path.join('static', 'images', file_name) with open(img_file_path, 'wb') as f: # 写入问题 for line in img_upload.chunks(): f.write(line) # 因为ajax发送的图片路径的static前面没有带/,所以这里要拼接一下 return HttpResponse(os.path.join("/",img_file_path))
修改upload_file.html,要全部修改

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> {% csrf_token %} <div style="height: 100px; 100px;padding: 2px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;position: relative;"> <img style="height: 100%; 100%;border: 0;overflow: hidden;border-radius: 50%;" id="previewImg" src="/static/images/default.png"> <input style="top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;opacity: 0;position: absolute;z-index: 102;" id="avatarImg" name="avatar_img" type="file" class="img-file"/> </div> <div>点击图片更换(<a href="#">撤销</a>)</div> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <div> <input type="hidden" name="avatar" id="avatar"> <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </div> </form> <script src="/static/js/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> $(function () { bindChangeAvatar3(); }); function bindChangeAvatar3() { $('#avatarImg').change(function () { var csrf = $("[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val(); var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0]; var formdata = new FormData(); formdata.append('img_upload', file_obj); formdata.append("csrfmiddlewaretoken",csrf); $.ajax({ url: '/form_data_upload/', type:'POST', data: formdata, processData: false, // tell jQuery not to process the data contentType: false, // tell jQuery not to set contentType success: function (arg) { // 给img标签设置src属性,预览 console.log(arg); $('#previewImg').attr('src',arg); console.log(arg); var avatar = $('#avatar').val(arg); console.log(avatar); //打印头像地址,用于后续表单提交 } }) }) } </script> </body> </html>
访问网页,上传一张图片
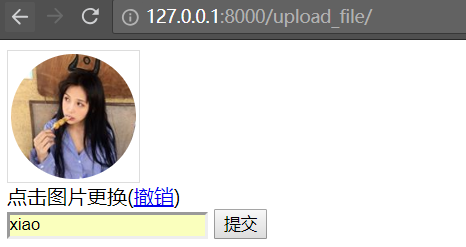
点击提交,提示上传成功
查看upload目录,会多一个文件 d405ecde-59bc-40f0-a2eb-c8dfe8c8645f.jpg
注意:form_data_upload和upload_file虽然都处理了POST数据。但是它们接收的数据是不一样的!
用户点击上传时,走form_data_upload视图函数,将图片上传到服务器
用户点击提交时,将服务器的图片url地址和用户名提交给upload_file视图函数。
为什么呢?因为用户点击上传时,已经将图片上传到服务器了。所以点击提交按钮时,需要再将图片上传一次。
只需要将图片的url地址传给服务器即可!
iframe
所有浏览器都支持 <iframe> 标签,它是兼容性最好的一种方式
iframe 元素会创建包含另外一个文档的内联框架(即行内框架)
举例:内嵌汽车之家
创建文件iframe.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <iframe style=" 960px;height: 800px;" src="https://www.autohome.com.cn/beijing/" frameborder="0"></iframe> </body> </html>
直接使用谷歌浏览器打开,效果如下:
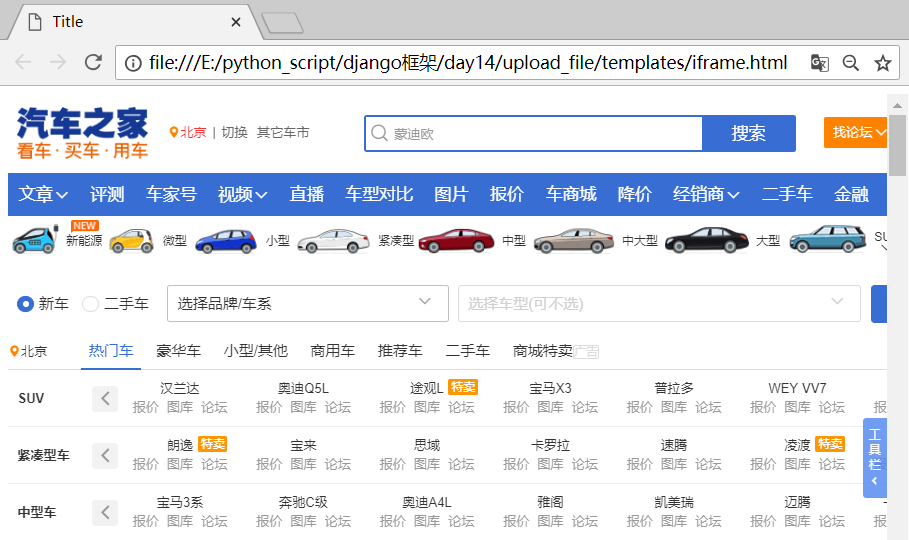
它直接内嵌了一个网页,如果width和height设置合理的话,打开网页,将会和汽车直接,是一摸一样的。
举例2:输入什么地址,就跳转什么地址
修改iframe.html,增加一个输入框,加入一段js代码。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" id="addr"> <input type="submit" onclick="changeUrl()" value="访问"> <iframe id="ifr" style=" 960px;height: 800px;" src="https://www.autohome.com.cn/beijing/" frameborder="0"></iframe> <script> function changeUrl() { //获取输入框的值 var addr = document.getElementById("addr").value; //修改iframe的src的值 document.getElementById("ifr").src = addr; } </script> </body> </html>
访问页面,效果如下:
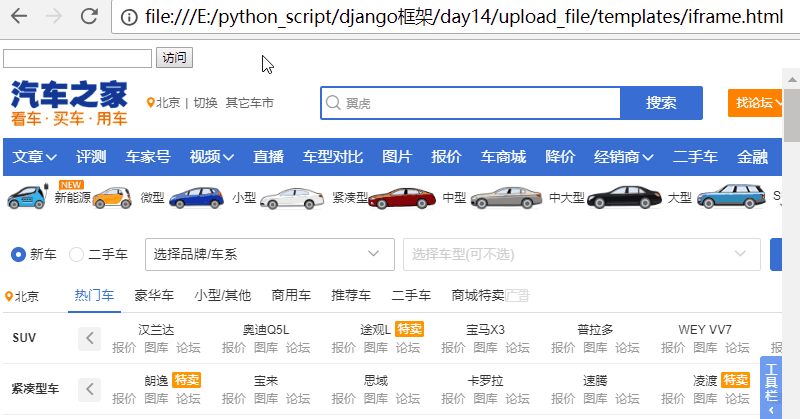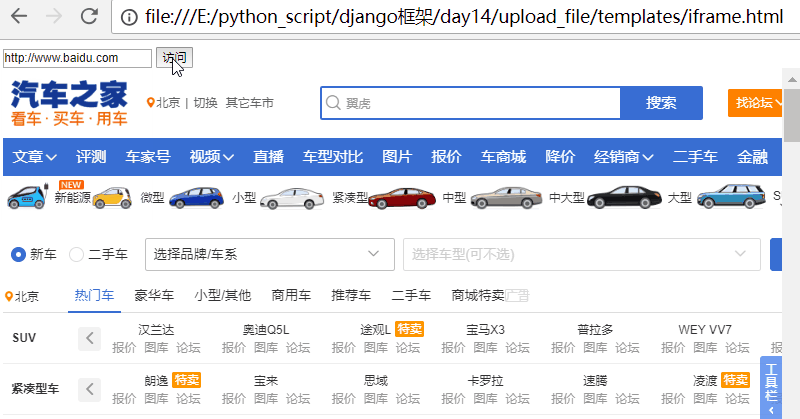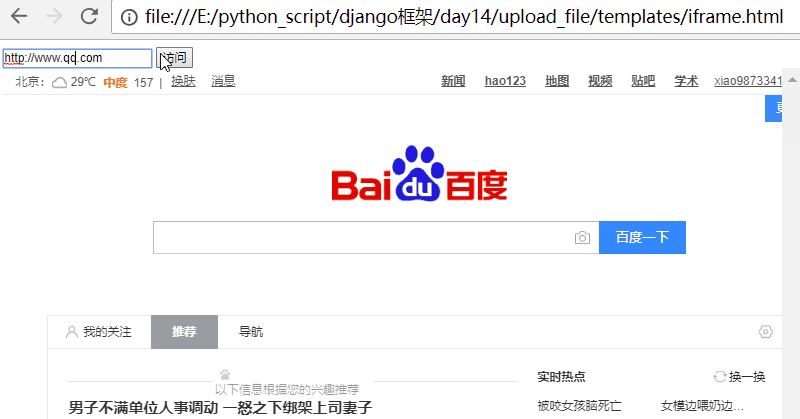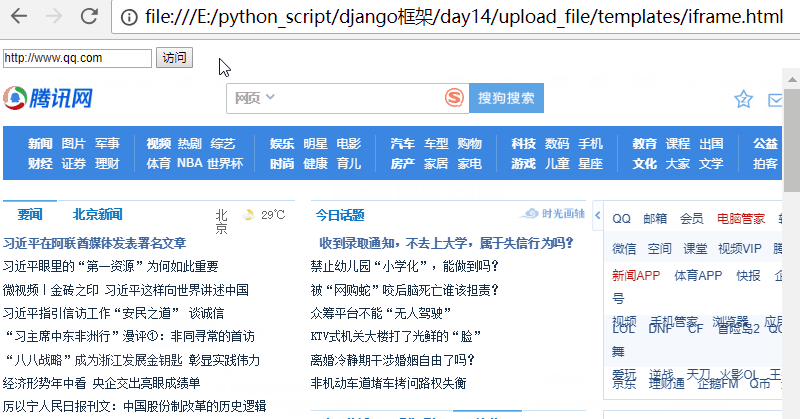
注意:整体页面并没有刷新,只是iframe里面刷新了!
它有2个应用场景:
1. iframe标签
可以修改src,且页面不刷新
2. form表单
提交表单数据,但刷新数据
修改urls.py,增加路径

urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('upload_file/', views.upload_file), path('form_data_upload/', views.form_data_upload), path('iframe_upload_img/', views.iframe_upload_img), path('upload_iframe/', views.upload_iframe), ]
修改views.py,增加视图函数

def iframe_upload_img(request): if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'iframe_upload_img.html') USER_LIST = [] # 空列表 user = request.POST.get('user') pwd = request.POST.get('pwd') avatar = request.POST.get('avatar') # 最加到列表中 USER_LIST.append( { 'user':user, 'pwd':pwd, 'avatar':avatar } ) return HttpResponse("上传成功") def upload_iframe(request): # iframe post提交 ret = {'status':True,'data':None} try: avatar = request.FILES.get('avatar') file_name = str(uuid.uuid4()) + "." + avatar.name.rsplit('.', maxsplit=1)[1] img_file_path = os.path.join('static', 'upload', file_name) with open(img_file_path, 'wb') as f: for line in avatar.chunks(): f.write(line) ret['data'] = os.path.join("/",img_file_path) except Exception as e: ret['status'] = False ret['error'] = '上传失败' return HttpResponse(json.dumps(ret))
增加iframe_upload_img.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div style="height: 100px; 100px;padding: 2px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;position: relative;"> <iframe style="display: none;" id="ifr" name="fffff"></iframe> <form method="POST" action="/upload_iframe/" enctype="multipart/form-data" target="fffff"> {% csrf_token %} <img style="height: 100px; 100px;border: 0;overflow: hidden;border-radius: 50%;" id="prevImg" src="/static/images/default.png"> <input style="top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;opacity: 0;position: absolute;z-index: 102;" id="avatar" name="avatar" type="file" class="img-file"/> </form> </div> <form method="post" action="/iframe_upload_img/"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="avatar" id="formAvatar" style="display: none"> <input type="text" name="user" placeholder="请输入用户名"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> <script src="/static/js/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> $(function () { bindChangeAvatar4(); }); function bindChangeAvatar4() { $('#avatar').change(function () { //parent该变量指的是包含当前分割窗口的父窗口 $(this).parent().submit(); //onload 事件会在页面或图像加载完成后立即发生 $('#ifr')[0].onload = function (){ //获取post返回值,比如{"status": true, "data": "/static\upload\bc72823e-b274-4a76-8ec2-af844a738959.jpg"} var iframeContents = $('#ifr')[0].contentWindow.document.body.innerText; console.log(iframeContents); //反向序列化数据 iframeContents = JSON.parse(iframeContents); if (iframeContents.status) { //修改图片的src属性 $('#prevImg').attr('src', iframeContents.data); //修改隐藏输入框的值 $('#formAvatar').val(iframeContents.data); } } }) } </script> </body> </html>
访问url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/iframe_upload_img/
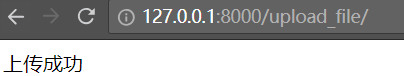
上传一个图片
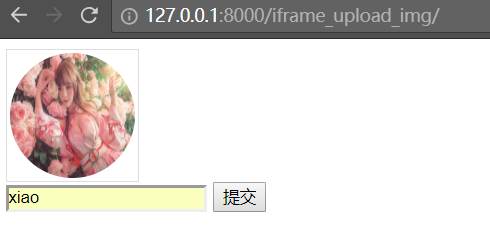
点击提交,提示上传成功
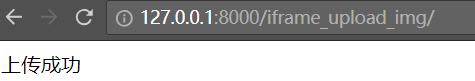
查看upload目录,会多一个文件 de83205e-2e8b-4839-a1c4-19656df9c49f.jpg
总结:
1. 在浏览器端可以做图片预览 - createObjectURL - FileReader 2. 使用Ajax上传文件: - FormData对象 3. 伪ajax上传文件: - iframe - form 4. 图片预览 本质就是修改img的src数据 5. 使用场景: a. 文件上传 - FormData对象 - iframe b. 图片预览 - createObjectURL、FileReader - iframe
文件上传场景:
假如是政府,或者传统企业,使用最后一种
假如是互联网企业,使用第3种!
三、CBV
CBV(class base views) 就是在视图里使用类处理请求
之前我们写的视图函数,都是FBV(function base views)
路径url的配置
cbv 顾名知义就是通过类的方法来调用,我们在url中配置为如下路径
path('user/', views.UserView.as_view()),
这里的UserView是一个class 类,View不是必须的。一般约定成俗,会加一个View!
要想使用此方法,这个路径后面还得必须有一个as_view()这个是必须的固定格式
views里面函数的格式
在views里面配置类,需要导入一个模块View

from django.views import View #这里必须要继承View这个类,只有继承了这个url那里的as_view()才会有这个方法 class UserView(View): def get(self, request): return HttpResponse('cbv-get') def post(self, request): return HttpResponse('cbv-post')
注意:get和post的方法名,必须是小写。因为在源码中,使用了request.method.lower(),通过反射来找到类中的方法!
详情请参考下面的内容
get方式访问
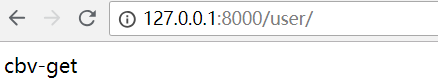
post方式访问
login登陆页面
修改views.py

from django.views import View #这里必须要继承View这个类,只有继承了这个url那里的as_view()才会有这个方法 class UserView(View): def get(self, request): # return HttpResponse('cbv-get') return render(request, 'login.html') # 发送到login.html def post(self, request): return HttpResponse('cbv-post')
新建login.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="username"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
访问页面,点击提交

输出:
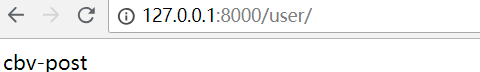
这里通过查看View的源码,可以看到里面会有很多种提交方法 http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace'] 使用ajax的时候这些方法都是可以使用的。
cbv匹配原理
这种根据url来匹配方法的是通过反射方法(getattr)来做的。请求过来后先走dispatch这个方法,这个方法存在View类中。
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist, # defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the # request method isn't on the approved list. if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: handler = self.http_method_not_allowed return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.method.lower() 将请求方式变成小写。通过反射来找到类中对应的方法!
所有的框架,本质都是通过请求方式,反射不同的函数!
所以CBV的本质,实际还是用的FBV,只不过了类封装而已!
定制dispatch
如果需要批量对方法,例如get,post等方法做一些操作的时候,这里我们可以手动写一个dispatch,这个dispatch就和装饰器的效果一样。因为请求来的时候总是先走的dispatch。

from django.views import View #这里必须要继承View这个类,只有继承了这个url那里的as_view()才会有这个方法 class UserView(View): def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print('操作前的代码...') obj = super(UserView, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) print('操作后的代码...') return obj def get(self, request): # return HttpResponse('cbv-get') return render(request, 'login1.html') # 发送到login.html def post(self, request): return HttpResponse('cbv-post')
这次我们再通过浏览器访问的时候,发现不管get或者post方法,都会走print代码

四、python读写Excel
python操作excel主要用到xlrd和xlwt这两个库,即xlrd是读excel,xlwt是写excel的库。
需要安装2个模块
pip3 install xlrd
pip3 install xlwt
读excel-->xlrd
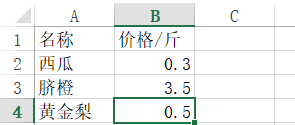
新建一个excel,文件名为fruits.xlsx,内容如下:
抛开django框架,新建一个test.py文件

import xlrd #打开excel文件,创建一个workbook对象,book对象也就是fruits.xlsx文件,表含有sheet名 rbook=xlrd.open_workbook(r'C:UsersxiaoDesktopfruits.xlsx') #sheets方法返回对象列表,[<xlrd.sheet.Sheet object at 0x103f147f0>] rbook.sheets() # xls默认有3个工作簿,Sheet1,Sheet2,Sheet3 rsheet=rbook.sheet_by_index(0) # 取第一个工作簿 #获取总行数 rows=rsheet.nrows #获取总列数 cols=rsheet.ncols print('行数:',rows,'列数',cols) #通过cell的位置坐标取得cell值 cell=rsheet.cell(0,0) print('0,0坐标的值是:',cell.value) print('3,1坐标的值是:',rsheet.cell(3,1).value) #取得第二行的值,参数是(行数,起点,终点) row1=rsheet.row_values(1) print('第一行的值是:',row1)
执行输出:
行数: 4 列数 2
0,0坐标的值是: 名称
3,1坐标的值是: 0.5
第一行的值是: ['西瓜', 0.3]
注意:a1单元格的坐标为0,0。在xlrd模块里面,坐标都是数字,所以不能用a1表示。
坐标如下:
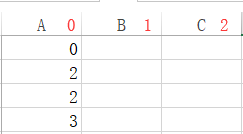
A,B,C纵坐标分别为0,1,2
所以3,1坐标的值是最后一行的价格,也就是0.5
循环工作簿的所有行和列
在末尾增加以下代码

# 循环工作簿的所有行 for row in rsheet.get_rows(): # 循环一行的所有列 for col in row: # 获取一个单元格中的值 print(col.value)
执行输出:
名称
价格/斤
西瓜
0.3
脐橙
3.5
黄金梨
0.5
写excel-->xltw

import xlwt f = xlwt.Workbook() sheet1 = f.add_sheet('学生',cell_overwrite_ok=True) row0 = ["姓名","年龄","出生日期","爱好"] colum0 = ["张三","李四","王五"] #写第一行 for i in range(0,len(row0)): sheet1.write(0,i,row0[i]) #写第一列 for i in range(0,len(colum0)): sheet1.write(i+1,0,colum0[i]) # 写入一行数据 sheet1.write(1,1,"23") sheet1.write(1,2,"1990") sheet1.write(1,3,"女") f.save('test.xls')
执行程序,查看excel文件

OpenPyXL
由于xlrd不能对已存在的xlsx文件,进行修改!所以必须使用OpenPyXL
OpenPyXL:较好的支持对xlsx文件的修改,功能比较强大,适用于需要处理XLSX文件,需要修改XLSX文件中的值,最后生成xlsx。openpyxl(可读写excel表)专门处理Excel2007及以上版本产生的xlsx文件,xls和xlsx之间转换容易
注意:如果文字编码是“gb2312” 读取后就会显示乱码,请先转成Unicode。
官网上最推荐的是openpyxl:
综上,所以选择使用OpenPyX来做一个修改excel的小程序。
OpenPyXL的官网参考:
https://openpyxl.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html
https://openpyxl.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
1、OpenPyXL模块的安装
pip3 install openpyxl
2、快速实现xlsx文件的单元格修改
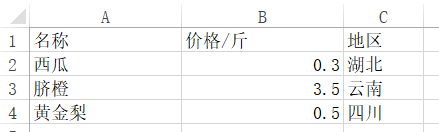
举例:增加一列地区,并增加相应的值

from openpyxl import load_workbook #excel文件绝对路径 file_home = r'C:UsersxiaoDesktopfruits.xlsx' wb = load_workbook(filename= file_home) # 打开excel文件 sheet_ranges = wb['Sheet1'] print(sheet_ranges['A1'].value) # 打印A1单元格的值 ws = wb['Sheet1'] #根据Sheet1这个sheet名字来获取该sheet ws["C1"] = '地区' #修改C1的值为LJK5679842 ws['C2'] = '湖北' ws['C3'] = '云南' ws['C4'] = '四川' wb.save(file_home) #保存修改后的excel
执行代码,查看excel文件
五、虚拟环境virtualenv
windows 安装
安装模块virtualenv
pip3 install virtualenv
安装纯净环境
–no-site-packages表示不包括系统全局的Python安装包,这样会更令环境更干净
E:python_script>virtualenv --no-site-packages pure_venv Using base prefix 'c:\python35' New python executable in E:python_scriptpure_venvScriptspython.exe Installing setuptools, pip, wheel...done.
E:python_script>cd pure_venv
E:python_scriptpure_venv>cd Scripts
激活虚拟环境
E:python_scriptpure_venvScripts>activate.bat
查看当前模块列表
(pure_venv) E:python_scriptpure_venvScripts>pip3 list Package Version ---------- ------- pip 10.0.1 setuptools 40.0.0 wheel 0.31.1
安装指定版本的django
(pure_venv) E:python_scriptpure_venvScripts>pip3 install django==1.11
打开Pcharm,新建一个django项目
点击...
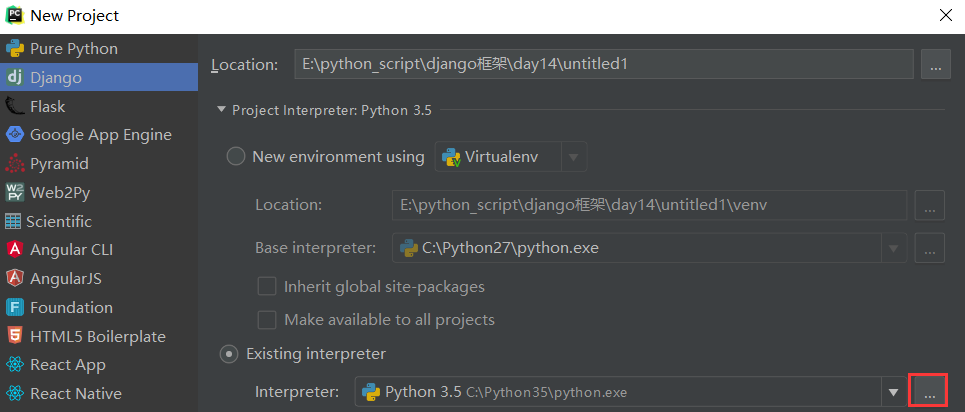
选择虚拟环境,点击...
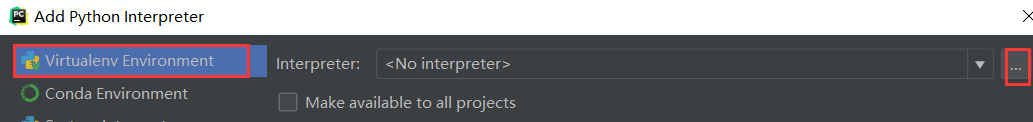
选择虚拟目录的python.exe
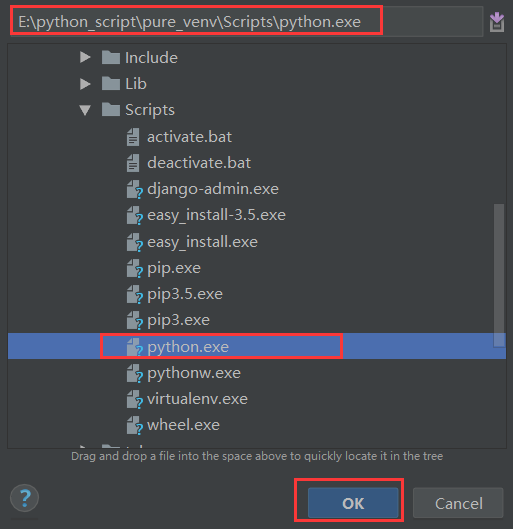
选择刚才添加的虚拟环境
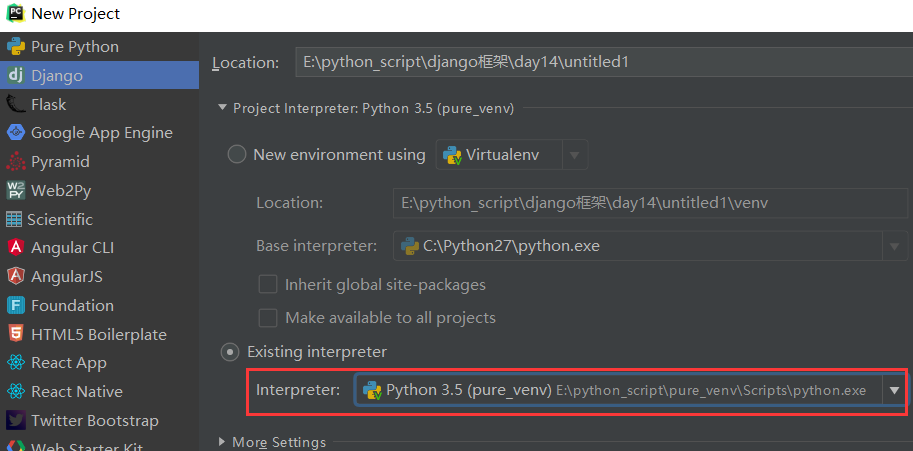
创建项目之后,发现url就是老版本的了!
pip安装包临时指定 从国内的清华pip源下载:
pip install django==1.11.11 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
将虚拟环境的依赖包关系导出到requirements.txt
pip freeze > requirements.txt
注意:约定成熟使用requirements.txt,一些开源的django项目,里面一般使用这个名字!
查看requirements.txt文件,内容如下:
Django==1.11.11 pytz==2018.5
如果需要按照 requirements.txt 安装项目依赖的第三方包,使用命令:
pip install -r requirements.txt
新建一个虚拟环境,测试一下,就可以了!
linux安装
# 安装virtualenv /usr/local/python3.5/bin/pip3 install virtualenv # 创建虚拟目录 mkdir /virtualenvs cd /virtualenvs # 创建虚拟环境 # -p 指定python版本 # –no-site-packages表示不包括系统全局的Python安装包,这样会更令环境更干净 /usr/local/python3.5/bin/virtualenv -p /usr/local/python3.5/bin/python3.5 --no-site-packages venv
指定豆瓣源
#创建目录 mkdir ~/.pip # 编辑配置文件 vi ~/.pip/pip.conf
内容如下:
[global] index-url = http://pypi.douban.com/simple trusted-host = pypi.douban.com
安装相关模块
# django指定版本为1.11 /virtualenvs/venv/bin/pip3 install django==1.11 # rest-framework /virtualenvs/venv/bin/pip3 install djangorestframework # 监控内存模块 /virtualenvs/venv/bin/pip3 install memory_profiler
作业:
1.客户表,放到excel文件中。使用excel上传,将数据导入到数据中!
2.增加登录页面
答案:
1.excel文件上传
新建一个excel文件,比如客户表.xlsx,内容如下:
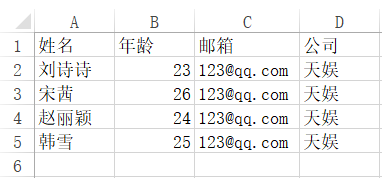
新建一个项目excel_upload
操作excel,需要安装2个模块。xlrd用来读取,xlwt用来写入!
pip3 install xlrd
pip3 install xlwt
修改settings.py,增加static路径

STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), )
新建目录static,在里面创建2个目录,js和file。file用来存放上传的excel文件
将jquery.min.js放到js目录中!
修改models.py,增加客户表模型

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Customer(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name="姓名") age = models.IntegerField(verbose_name="年龄") email = models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name="邮箱") company = models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name="公司")
使用2个命令,生成表
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
修改urls.py,增加2个路径

from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('upload_file/', views.upload_file), path('index/', views.index), ]
修改views.py,增加视图函数

import os import uuid import xlrd from app01 import models from excel_upload import settings from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect from django.core.paginator import Paginator, EmptyPage, PageNotAnInteger # Create your views here. def upload_file(request): # 上传文件 if request.method == "GET": return render(request, 'upload_file.html') user = request.POST.get('user') file_upload = request.FILES.get('customer_excel') # 获取excel文件对象 # 判断上传的文件后缀 if file_upload.name.rsplit('.', maxsplit=1)[1] not in ['xls','xlsx']: return HttpResponse('上传失败,只能上传xls格式') # 生成唯一的文件名 file_name = str(uuid.uuid4()) + '.' + file_upload.name.rsplit('.', maxsplit=1)[1] # 拼接路径 img_file_path = os.path.join('static', 'files', file_name) print(img_file_path) with open(img_file_path, 'wb') as f: # 写入文件 for line in file_upload.chunks(): f.write(line) # 拼接excel文件的绝对路径 file_path = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, img_file_path) print(file_path) # 打开excel表 data = xlrd.open_workbook(file_path) table = data.sheet_by_index(0) # 读取第一个sheet nrows = table.nrows # 获得总行数 date_list = [] # 定义空列表,用来批量插入 try: for i in range(1, nrows): # 读取每一行数据 rows = table.row_values(i) # 行的数据放在数组里 # 生成对象 obj_list = models.Customer(name=rows[0], age=rows[1], email=rows[2], company=rows[3], ) # 追加到列表中 date_list.append(obj_list) # 使用bulk_create批量插入 models.Customer.objects.bulk_create(date_list) except Exception as e: return HttpResponse('批量添加失败{}'.format(e)) return redirect('/index/') # 跳转首页 def index(request): # 首页展示数据 customer_list = models.Customer.objects.all() # 读取表中的所有数据 # print() paginator = Paginator(customer_list, 20) # 每页显示2条 # 异常判断 try: # 当前页码,如果取不到page参数,默认为1 current_num = int(request.GET.get("page", 1)) # 当前页码 customer_list = paginator.page(current_num) # 获取当前页码的数据 except EmptyPage: # 页码不存在时,报EmptyPage错误 customer_list = paginator.page(1) # 强制更新为第一页 # 如果页数十分多时,换另外一种显示方式 if paginator.num_pages > 9: # 一般网页展示11页,左5页,右5页,加上当前页,共11页 if current_num - 4 < 1: # 如果前5页小于1时 pageRange = range(1, 9) # 页码的列表:范围是初始状态 elif current_num + 4 > paginator.num_pages: # 如果后5页大于总页数时 # 页码的列表:范围是(当前页-5,总页数+1)。因为range顾头不顾尾,需要加1 pageRange = range(current_num - 4, paginator.num_pages + 1) else: # 页码的列表:后5页正常时,页码范围是(当前页-5,当前页+6)。注意不是+5,因为range顾头不顾尾! pageRange = range(current_num - 4, current_num + 5) else: pageRange = paginator.page_range # 页码的列表 data = {"customer_list": customer_list, "paginator": paginator, "current_num": current_num, "pageRange": pageRange} return render(request, "index.html", data)
创建文件index.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> {#数据展示#} <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-8"> <table class="table table-bordered"> <thead> <tr> <th>编号</th> <th>姓名</th> <th>年龄</th> <th>邮箱</th> <th>公司</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for customer in customer_list %} <tr> <th scope="row">{{ forloop.counter }}</th> <td>{{ customer.name }}</td> <td>{{ customer.age }}</td> <td>{{ customer.email }}</td> <td>{{ customer.company }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> {#分页展示#} <nav aria-label="Page navigation"> <ul class="pagination"> <li><a href="?page=1" aria-label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">首页</span></a></li> {#has_previous 判断是否有上一页#} {% if customer_list.has_previous %} {#previous_page_number 上一页的页码#} <li><a href="?page={{ customer_list.previous_page_number }}" aria-label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">上一页</span></a></li> {% else %} {#class="disabled" 禁止用户点击#} <li class="disabled"><a href="" aria-label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">上一页</span></a> </li> {% endif %} {#遍历页码的列表#} {% for i in pageRange %} {#判断当前页码数等于底部页码时#} {% if current_num == i %} {#增加class,加深按钮#} <li class="active"><a href="?page={{ i }}">{{ i }}</a></li> {% else %} {#href参数为简写,它会自动获取当前路径,并拼接参数#} <li><a href="?page={{ i }}">{{ i }}</a></li> {% endif %} {% endfor %} {#has_next 判断是否有下一页#} {% if customer_list.has_next %} {#next_page_number 下一页的页码#} <li><a href="?page={{ customer_list.next_page_number }}" aria-label="Next"><span aria-hidden="true">下一页</span></a></li> {% else %} {#class="disabled" 禁止用户点击#} <li class="disabled"><a href="" aria-label="Next"><span aria-hidden="true">下一页</span></a></li> {% endif %} <li><a href="?page={{ paginator.num_pages }}" aria-label="Next"><span aria-hidden="true">最后一页</span></a> </li> </ul> </nav> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
创建文件upload_file.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> {% csrf_token %} <div style="position: relative;display: inline-block;height: 50px;min- 300px;overflow: hidden;"> <div style="position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;z-index: 1000;border: 1px dotted #9d9d9d;color: #9d9d9d;line-height: 50px;padding-left: 15px;"> <i class="fa fa-cloud-upload" aria-hidden="true"></i> <span>点击上传文件</span> </div> <input name="customer_excel" type="file" id="excelFile" style="position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;background-color: #333333;z-index: 1001;opacity: 0;filter:alpha(opacity=0);"> </div> <div> <input type="text" name="user"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </div> </form> <script src="/static/js/1jquery.min.js"></script> <script> !window.jQuery && alert('jQuery未导入!请确认路径是否正确'); $(function () { $('#excelFile').change(function (e) { var fileName = e.currentTarget.files[0].name; $(this).prev().find('span').text(fileName); }) }) </script> </body> </html>
启动django项目,访问页面
上传一个excel文件
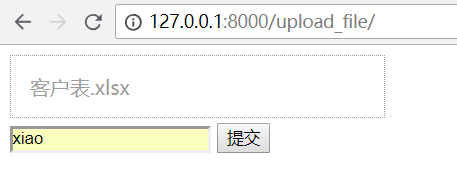
成功后,会跳转首页
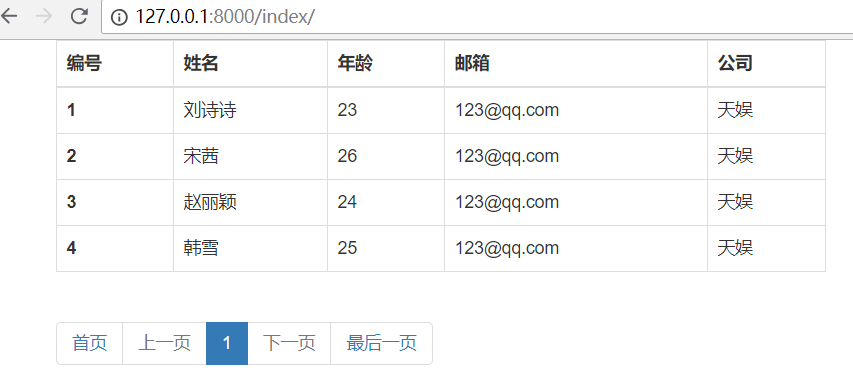
2.登录页面
创建超级用户
python manage.py createsuperuser
完整代码在github:
https://github.com/987334176/excel_upload
登录效果如下:

