一、确保你的python安装了这些包
# Check the versions of libraries # Python version import sys print('Python: {}'.format(sys.version)) # scipy import scipy print('scipy: {}'.format(scipy.__version__)) # numpy import numpy print('numpy: {}'.format(numpy.__version__)) # matplotlib import matplotlib print('matplotlib: {}'.format(matplotlib.__version__)) # pandas import pandas print('pandas: {}'.format(pandas.__version__)) # scikit-learn import sklearn print('sklearn: {}'.format(sklearn.__version__))
如果电脑都安装了,会有如下输出:
Python: 3.7.1 (default, Dec 10 2018, 22:54:23) [MSC v.1915 64 bit (AMD64)] scipy: 1.1.0 numpy: 1.15.4 matplotlib: 3.0.2 pandas: 0.23.4 sklearn: 0.20.1
Scipy是一个用于数学、科学、工程领域的常用软件包,可以处理插值、积分、优化、图像处理、常微分方程数值解的求解、信号处理等问题。它用于有效计算Numpy矩阵,使Numpy和Scipy协同工作,高效解决问题。
NumPy(Numerical Python) 是 Python 语言的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。
Matplotlib 是 Python 编程语言及其数值数学扩展包 NumPy 的可视化操作界面。它为利用通用的图形用户界面工具包。
pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。
sklearn是机器学习中常用的第三方模块,对常用的机器学习方法进行了封装,包括回归(Regression)、降维(Dimensionality Reduction)、分类(Classfication)、聚类(Clustering)等方法。
二、下面是鸢尾花的模型分析:
import pandas as pd from pandas.plotting import scatter_matrix import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import model_selection from sklearn.metrics import classification_report from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB from sklearn.svm import SVC import warnings #将鸢尾花数据集导入 input_file = "F://python入门//文件//Iris数据集//iris.csv" f = open(input_file) names = ['Sepal_Length','Sepal_Width','Petal_Length','Petal_Width','Species'] dataset = pd.read_csv(f, names=names) #查看数据的形状属性,多少行,多少列 print('查看数据的形状属性:') print(dataset.shape) #查看数据的前十行 print('查看数据的前十行:') print(dataset.head(10)) #查看数据的统计性描述 print('查看数据的统计性描述:') print(dataset.describe()) #输出箱线图 print('查看每个输入变量的箱线图:') dataset.plot(kind='box', subplots=True, layout=(2,2), sharex=False, sharey=False) plt.show() #输出一个直方图 print('查看每个输入变量的直方图:') dataset.hist() plt.show() #散点图 print('全部属性对的散点图:') scatter_matrix(dataset) plt.show() #将导入的数据集拆分为两部分,80% 用于训练模型,20% 用于验证模型。 array = dataset.values X = array[:,0:4] Y = array[:,4] validation_size = 0.20 seed = 7 #训练集和验证集 X_train, X_validation, Y_train, Y_validation = model_selection.train_test_split(X, Y,test_size=validation_size, random_state=seed) #每次运行算法前都要重新设置随机数量的种子,以确保是在用相同的数据拆分来评估每个算法 #现在我们用“准确率”这个维度去评估模型,也就是能正确预测出鸢尾花类别的比例 seed = 7 #用准确率这个维度评估模型 scoring = 'accuracy' #逻辑回归(LR) #线性判别分析(LDA) #K最近邻算法(KNN) #分类和回归树(CART) #高斯朴素贝叶斯(NB) #支持向量机(SVM) models = [] models.append(('LR', LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear'))) models.append(('LDA', LinearDiscriminantAnalysis())) models.append(('KNN', KNeighborsClassifier())) models.append(('CART', DecisionTreeClassifier())) models.append(('NB', GaussianNB())) models.append(('SVM', SVC())) # evaluate each model in turn results = [] names = [] #遍历每个方法 print('输出每个方法的均值和标准差:') for name, model in models: kfold = model_selection.KFold(n_splits=10, random_state=seed) cv_results = model_selection.cross_val_score(model, X_train, Y_train, cv=kfold, scoring=scoring) results.append(cv_results) names.append(name) msg = "%s: %f (%f)" % (name, cv_results.mean(), cv_results.std()) print(msg) #消除警告 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #用箱线图将模型评估结果表示出来 fig = plt.figure() fig.suptitle('Algorithm Comparison') ax = fig.add_subplot(111) plt.boxplot(results) ax.set_xticklabels(names) print('利用箱线图衡量各模型方法的准确率:') plt.show() #经过验证,KNN 算法的准确率最高。现在我们看看该模型在验证集上的准确度。 knn = KNeighborsClassifier() knn.fit(X_train, Y_train) predictions = knn.predict(X_validation) #模型的准确率 print('模型的准确率:') print(accuracy_score(Y_validation, predictions)) #混淆矩阵 print('混淆矩阵:') print(confusion_matrix(Y_validation, predictions)) #分类报告显示了每个类别的精确率、召回率、F1 值 print('分类报告:') print(classification_report(Y_validation, predictions))
输出结果:
查看数据的形状属性: (150, 5) 查看数据的前十行: Sepal_Length Sepal_Width Petal_Length Petal_Width Species 0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa 2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa 3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa 4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa 5 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa 6 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa 7 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa 8 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 setosa 9 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 setosa 查看数据的统计性描述: Sepal_Length Sepal_Width Petal_Length Petal_Width count 150.000000 150.000000 150.000000 150.000000 mean 5.843333 3.057333 3.758000 1.199333 std 0.828066 0.435866 1.765298 0.762238 min 4.300000 2.000000 1.000000 0.100000 25% 5.100000 2.800000 1.600000 0.300000 50% 5.800000 3.000000 4.350000 1.300000 75% 6.400000 3.300000 5.100000 1.800000 max 7.900000 4.400000 6.900000 2.500000
查看每个输入变量的箱线图:
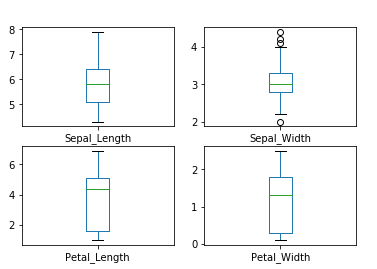
查看每个输入变量的直方图:
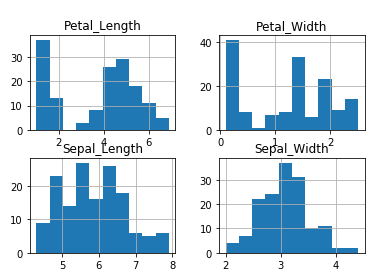
全部属性对的散点图:
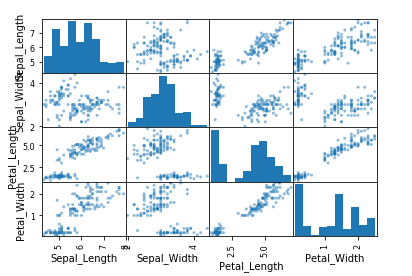
输出每个方法的均值和标准差: LR: 0.966667 (0.040825) LDA: 0.975000 (0.038188) KNN: 0.983333 (0.033333) CART: 0.966667 (0.040825) NB: 0.975000 (0.053359) SVM: 0.991667 (0.025000)
利用箱线图衡量各模型方法的准确率:
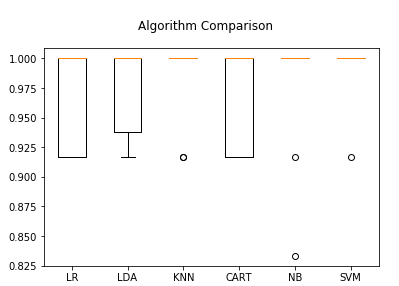
模型的准确率: 0.9 混淆矩阵: [[ 7 0 0] [ 0 11 1] [ 0 2 9]] 分类报告: precision recall f1-score support setosa 1.00 1.00 1.00 7 versicolor 0.85 0.92 0.88 12 virginica 0.90 0.82 0.86 11 micro avg 0.90 0.90 0.90 30 macro avg 0.92 0.91 0.91 30 weighted avg 0.90 0.90 0.90 30