cin.getline()和cin.get()
先说结论:
getline()位于#include<string>
getline()以回车作为结束,并在最后抛弃了作为回车
getline()主要用于输入字符串(string )
cin.getline()和cin.get()两者都主要用于输入字符型数组(位于#include<iostream>)
cin.getline()以回车结束输入,并且抛弃最后的回车;
cin.get()也是以回车结束输入,但最后回车会留在缓存区,如果下一次继续再次输入,回车会被读取;
解决方法:在cin.get()函数输入结束后紧跟着一个cin.get()接受回车;
拓展:
cin、scanf()也是会将回车留在缓存区,可以用getchar()接收回车
举例
1、
我的准备输入样例:
hello world
I love you
long time no see
实际输入
hello world
I love you
输入输出:

#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s,s1;
char s2[100],s3[100];
getline(cin, s);//读入了“hello world”
cin.get(s2, 20);//读入了“I love you”
cin.getline(s3, 20);//读入了回车(即上一次输入结束的标志:回车,留在了缓冲区被下一次读取)
//在第二次读入“I love you”回车后直接进行了输出,原本准备的“long time no see”没有机会输入直接输出,原因是回车被读入了s3
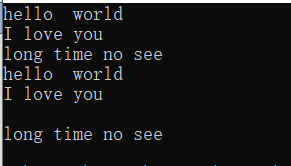
cout << s << endl;//输出了“hello world”再回车
cout << s2 << endl;//输出了“I love you”再回车
cout << s3 << endl;//输出了回车,再回车
return 0;
}
2、
我的实际输入:
hello world
I love you
long time no see
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s,s1;
char s2[100],s3[100],s4[100];
getline(cin, s);//读入了“hello world”
cin.get(s2, 20);//读入了“I love you”
cin.getline(s3, 20);//读入了回车(即上一次输入结束的标志:回车,留在了缓冲区被下一次读取)
cin.getline(s4, 20);//读入了“long time no see”
cout << s << endl;//输出了“hello world”再回车
cout << s2 << endl;//输出了“I love you”再回车
cout << s3 << endl;//输出了回车,再回车
cout << s4 << endl;//输出了“long time no see”
return 0;
}
输出结果: