递归函数
在函数内部,可以调用其他函数。如果一个函数在内部调用自身本身,这个函数就是递归函数。
函数实现过程
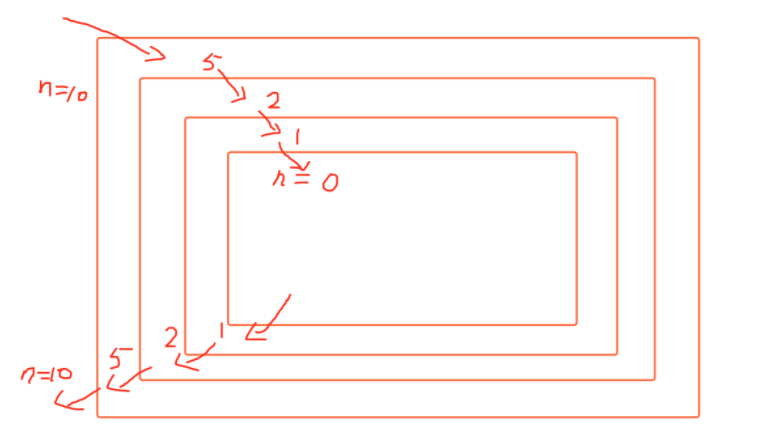
def calc(n): v = int(n//2) print(v) if v > 0: calc(v) print(n) calc(10)
输出结果
5
2
1
0
1
2
5
10
为什么是这个结果
递归特性:
- 必须有一个明确的结束条件
- 每次进入更深一层递归时,问题规模相比上次递归都应有所减少
- 一般通过return结束递归
- 递归效率不高,递归层次过多会导致栈溢出(在计算机中,函数调用是通过栈(stack)这种数据结构实现的,每当进入一个函数调用,栈就会加一层栈帧,每当函数返回,栈就会减一层栈帧。由于栈的大小不是无限的,所以,递归调用的次数过多,会导致栈溢出)
- 堆栈扫盲http://www.cnblogs.com/lln7777/archive/2012/03/14/2396164.html
递归深度
python默认对最大递归层数做了一个限制:997,但是也可以自己限制
import sys sys.setrecursionlimit(10000)#修改递归层数 n=0 def f(): global n n+=1 print(n) f() f()
递归应用
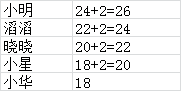
1.下面我们来猜一下小明的年龄
小明是新来的同学,丽丽问他多少岁了。
他说:我不告诉你,但是我比滔滔大两岁。
滔滔说:我也不告诉你,我比晓晓大两岁
晓晓说:我也不告诉你,我比小星大两岁
小星也没有告诉他说:我比小华大两岁
最后小华说,我告诉你,我今年18岁了
这个怎么办呢?当然,有人会说,这个很简单啊,知道小华的,就会知道小星的,知道小星的就会知道晓晓的,以此类推,就会知道小明的年龄啦。这个过程已经非常接近递归的思想了。
用递归实现
""" age(5) = age(4)+2 age(4) = age(3) + 2 age(3) = age(2) + 2 age(2) = age(1) + 2 age(1) = 18 """ def calc_age(n): if n == 1: return 18 else: return calc_age(n-1)+2 print(calc_age(5)) # 26
2.一个数,除2直到不能整除2
n = 100 def cal(n): if n == 0: return else: n = int(n // 2) print(n) cal(n) print("退出=", n) cal(100)
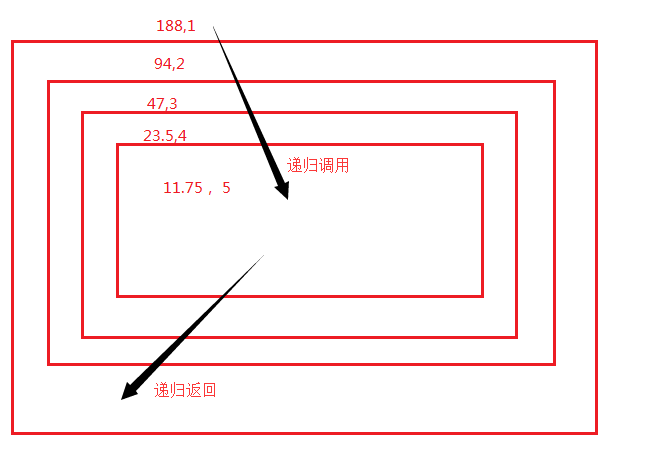
3.一个数,除2直到次数等于5退出
def calc(n,count): print(n, count) if count < 5: r = calc(n / 2, count + 1) return r # 里层返回为上层,此处不加return 返回None else: return n # 最里层返回 res = calc(188, 1) print('res ', res)
递归调用过程
4.深度查询
menus = [ { 'text': '北京', 'children': [ {'text': '朝阳', 'children': []}, {'text': '昌平', 'children': [ {'text': '沙河', 'children': []}, {'text': '回龙观', 'children': []}, ]}, ] }, { 'text': '上海', 'children': [ {'text': '宝山', 'children': []}, {'text': '金山', 'children': []}, ] } ] # 深度查询 #1. 打印所有的节点 #2. 输入一个节点名字,沙河, 你要遍历找,找到了,就打印它,并返回true,
实现
# 打印所有的节点 def recu_Menu(menu): for sub_menu in menu: menu_text = sub_menu['text'] menu_children = sub_menu['children'] print(menu_text) recu_Menu(menu_children) recu_Menu(menus) # 打印所有的节点,输入一个节点名字,沙河, 你要遍历找,找到了,就打印它,并返回true, def recu_Menu_node(menu, node, layer): # if len(menu)>0: for sub_menu in menu: menu_text = sub_menu['text'] menu_children = sub_menu['children'] print("menu_text=", menu_text) if node == menu_text: print("找到%s在第%s层" % (node, layer)) #返回到外层 return True else: if recu_Menu_node(menu_children, node, layer + 1) == True: #如果里层返回True,继续向上返回True return True else: recu_Menu_node(menu_children, node, layer + 1) node_str = input("输入一个节点名字-> ") print(recu_Menu_node(menus, node_str, 1))
-》回龙观
找到回龙观在第3层
True
5.猴子吃桃问题
# 题目:猴子吃桃问题:猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不瘾,又多吃了一个 # 第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,又多吃了一个。 # 以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下的一半零一个。 # 到第10天早上想再吃时,见只剩下一个桃子了。求第一天共摘了多少。 """ 下一天等于是前一天吃了一半还多一个剩下的。 所以f(n) = 2 * f(n - 1) + 2 """ def peach(n): if n == 1: return 1 else: return 2 * peach(n-1) + 2 print(peach(10)) # 1534
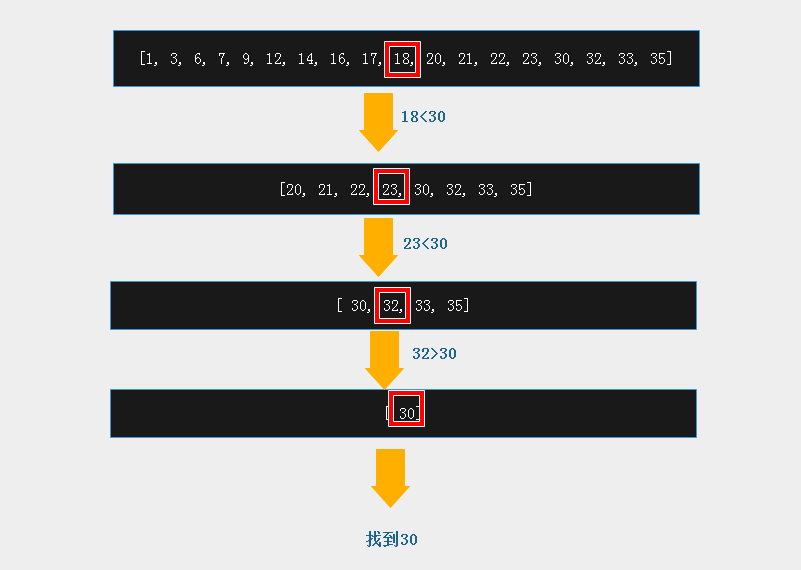
6.二分查找算法
从[1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 23, 30, 32, 33, 35]序列中找到30的位置
代码实现
data = [1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 23, 30, 32, 33, 35] print('start to find') # 递归二分查找 def binary_search(dataset, start, end, val): mid = int((start + end)/ 2) # 取中间数 # print(dataset, mid, start, end) if start <= end: if dataset[mid] == val: # 判断中间值和要找的那个值的大小关系 print("find val", dataset[mid]) return mid elif dataset[mid] > val: print('mid %s is bigger than %s, keep looking in left %s' % (dataset[mid], val, mid)) return binary_search(dataset, start, mid-1, val) else: # dataset[mid] < val: print('mid %s is smaller than %s, keep looking in right %s' % (dataset[mid], val, mid)) return binary_search(dataset, mid+1, end, val) else: # if dataset[start] == val: # print('finally find val:', dataset[start]) # return start # else: print("data %s doesn't exist in dataset " % val) return -1 print('start to find') print(binary_search(data,0,len(data)-1, 30))
输出结果
start to find mid 17 is smaller than 30, keep looking in right 8 mid 23 is smaller than 30, keep looking in right 13 mid 32 is bigger than 30, keep looking in left 15 find val 30 mid =14 #返回位置为14
另一种实现
data = [1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 23, 30, 32, 33, 35] print('start to find') def binary_search(dataset, val): mid = int(len(dataset)/ 2) # 取中间数 print(dataset) if mid > 0: if dataset[mid] == val: # 判断中间值和要找的那个值的大小关系 print("find n", dataset[mid]) elif dataset[mid] > val: new_dataset = dataset[:mid] # 顾头不顾尾 print('mid %s is bigger than %s, keep looking in left %s' % (dataset[mid], val, mid)) binary_search(new_dataset, val) else: # dataset[mid] < val: new_dataset = dataset[mid:] # 顾头不顾尾 print('mid %s is smaller than %s, keep looking in right %s' % (dataset[mid], val, mid)) binary_search(new_dataset, val) else: if dataset[0] == val: print('finally find val:', dataset[0]) else: print("data %s doesn't exist in dataset " % val) binary_search(data,30)