选择结构语句
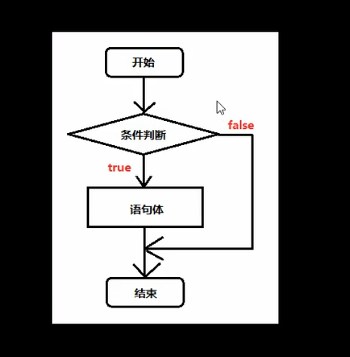
一、单if语句:
/*
if单循环的格式:
if(判断条件){
输出语句
}
单if语句就是满足条件执行它,不满足条件就跳过它。
*/
练习代码:
public class Demo12if{ public static void main(String[]args){ System.out.println("今天天气好,在外面闲逛,看到一家黑网吧!"); int age = 16; if (age >= 18){ System.out.println("进入网吧"); System.out.println("开始游戏"); System.out.println("队友太坑下机"); } System.out.println("回家吃饭"); } }
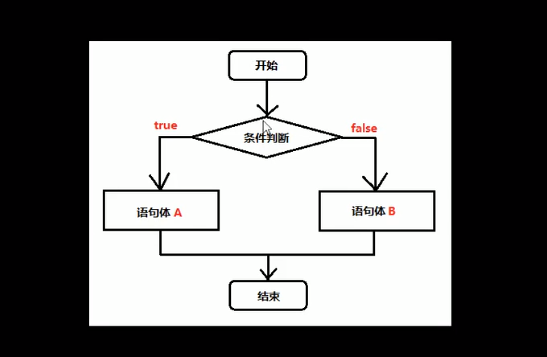
二、标准if..else:
/*
if..else两个的关系为,二者选一个执行。
语句格式:
if(关系表达式){
语句体1;
}else{
语句体2;
}
注意:if里的关系表达式成立(true)执行花括号中的语句,不成立(false)则执行else后花括号中的语句。
*/
练习代码
public class Demo13if_else{ public static void main(String[]args){ System.out.println("今天天气好,在外面闲逛,看到一家黑网吧!"); int age = 16; if(age >= 18){ System.out.println("我已经满18岁了可以去网吧嗨皮"); } else{ System.out.println("我没满18岁,还是回家去了吧。"); } System.out.println("溜了,溜了!"); } }
三、扩展if-else语句
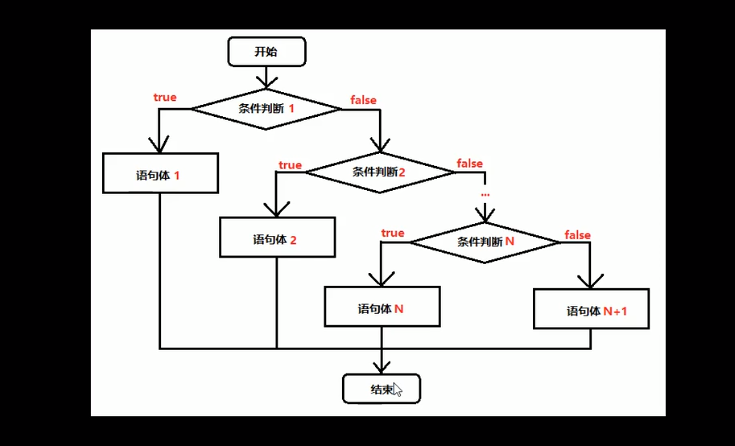
//x和y的关系满足如下:
//如果x >= 3,那么y = 2x + 1
//如果-1 < x < 3,那么y = 2x
//如果x <= -1 ,那么y = 2x - 1
练习代码:
public class Demo14ifElse{ public static void main(String[]args){ int x = 5; int y; if(x >= 3){ y = 2 * x + 1; }else if(-1 < x && x < 3){ y = 2 * x; } else { y = 2 * x - 1; } System.out.println("结果是:"+y);//输出结果为11,因为第一个条件就已经满足,系统直接执行第10行代码。 } }
代码练习2:
/*
90-100优秀
80-89-好
70-79良
60-69及格
60以下不及格
*/
public class Demo15kaoshi{ public static void main(String[] args){ int score = 120; if(score<0 || score>100){ System.out.println("你的成绩有误"); } else if (score >=90 && score <= 100){ System.out.println("你的成绩优秀"); } else if (score >=80 && score < 90){ System.out.println("你的成绩好"); } else if (score >=60 && score < 70){ System.out.println("你的成绩及格"); } else { System.out.println("你的成绩不及格"); } } }