2019春第十二周作业
| 这个作业属于那个课程 | C语言程序设计II |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/software-engineering-class2-2018/homework/3234 |
| 我在这个课程的目标是 | 熟悉链表 |
| 这个作业在那个具体方面帮助我实现目标 | 链表操作 |
| 参考文献 | 算法入门经典 |
第一题
6-1 计算最长的字符串长度 (15 分)
本题要求实现一个函数,用于计算有n个元素的指针数组s中最长的字符串的长度。
函数接口定义:
int max_len( char *s[], int n );
其中n个字符串存储在s[]中,函数max_len应返回其中最长字符串的长度。
裁判测试程序样例:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 #define MAXN 10 6 #define MAXS 20 7 8 int max_len( char *s[], int n ); 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 int i, n; 13 char *string[MAXN] = {NULL}; 14 15 scanf("%d", &n); 16 for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { 17 string[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*MAXS); 18 scanf("%s", string[i]); 19 } 20 printf("%d ", max_len(string, n)); 21 22 return 0; 23 } 24 25 /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
4 blue yellow red green
输出样例:
6
实验代码
1 int max_len( char *s[], int n ) 2 { 3 int MAX = strlen(s[0]) ; 4 for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++)if(strlen(s[i])>MAX)MAX = strlen(s[i]); 5 return MAX; 6 }
设计思路

本题调试过程中遇到的问题及解决方法
无
运行结果截图

第二题
6-2 统计专业人数 (15 分)
本题要求实现一个函数,统计学生学号链表中专业为计算机的学生人数。链表结点定义如下:
struct ListNode { char code[8]; struct ListNode *next; };
这里学生的学号共7位数字,其中第2、3位是专业编号。计算机专业的编号为02。
函数接口定义:
int countcs( struct ListNode *head );
其中head是用户传入的学生学号链表的头指针;函数countcs统计并返回head链表中专业为计算机的学生人数。
裁判测试程序样例:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 5 struct ListNode { 6 char code[8]; 7 struct ListNode *next; 8 }; 9 10 struct ListNode *createlist(); /*裁判实现,细节不表*/ 11 int countcs( struct ListNode *head ); 12 13 int main() 14 { 15 struct ListNode *head; 16 17 head = createlist(); 18 printf("%d ", countcs(head)); 19 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
1021202 2022310 8102134 1030912 3110203 4021205 #
输出样例:
3
实验代码
1 int countcs( struct ListNode *head ) 2 { 3 int conut = 0 ; 4 while(head) 5 { 6 if(head->code[1]=='0'&&head->code[2]=='2')conut++; 7 head = head -> next ; 8 } 9 10 return conut; 11 }
设计思路

本题调试过程中遇到的问题及解决方法
无
运行结果截图

第三题
6-3 删除单链表偶数节点 (20 分)
本题要求实现两个函数,分别将读入的数据存储为单链表、将链表中偶数值的结点删除。链表结点定义如下:
struct ListNode { int data; struct ListNode *next; };
函数接口定义:
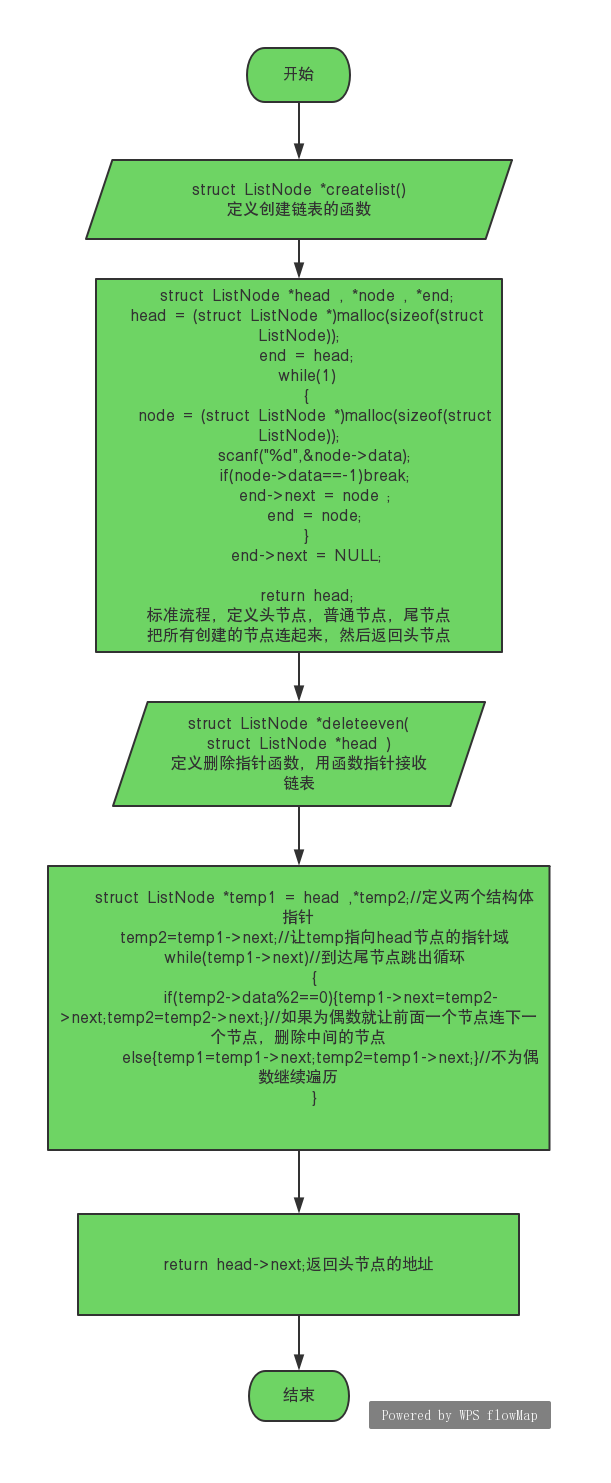
struct ListNode *createlist(); struct ListNode *deleteeven( struct ListNode *head );
函数createlist从标准输入读入一系列正整数,按照读入顺序建立单链表。当读到−时表示输入结束,函数应返回指向单链表头结点的指针。
函数deleteeven将单链表head中偶数值的结点删除,返回结果链表的头指针。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct ListNode { int data; struct ListNode *next; }; struct ListNode *createlist(); struct ListNode *deleteeven( struct ListNode *head ); void printlist( struct ListNode *head ) { struct ListNode *p = head; while (p) { printf("%d ", p->data); p = p->next; } printf(" "); } int main() { struct ListNode *head; head = createlist(); head = deleteeven(head); printlist(head); return 0; } /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1
输出样例:
1 3 5 7
实验代码
1 struct ListNode *createlist() 2 { 3 struct ListNode *head , *node , *end; 4 head = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 5 end = head; 6 while(1) 7 { 8 node = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); 9 scanf("%d",&node->data); 10 if(node->data==-1)break; 11 end->next = node ; 12 end = node; 13 } 14 end->next = NULL; 15 16 return head; 17 18 } 19 struct ListNode *deleteeven( struct ListNode *head ) 20 { 21 struct ListNode *temp1 = head ,*temp2; 22 temp2=temp1->next; 23 while(temp1->next) 24 { 25 if(temp2->data%2==0){temp1->next=temp2->next;temp2=temp2->next;} 26 else{temp1=temp1->next;temp2=temp1->next;} 27 } 28 29 return head->next; 30 }
设计思路
本题调试过程中遇到的问题及解决方法
循环条件弄错差点把电脑内存挤爆
运行结果截图
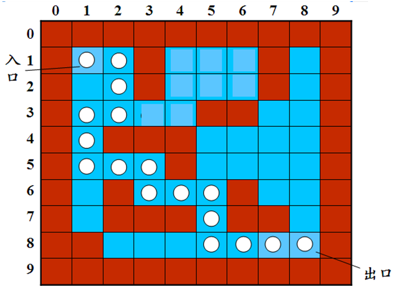
挑战题(迷宫)//八皇后在上一周的博客中
迷宫这道题是一道BFS(宽度搜索)的裸题,并且没有什么特殊条件,所以BFS能够很快找出最短路径。
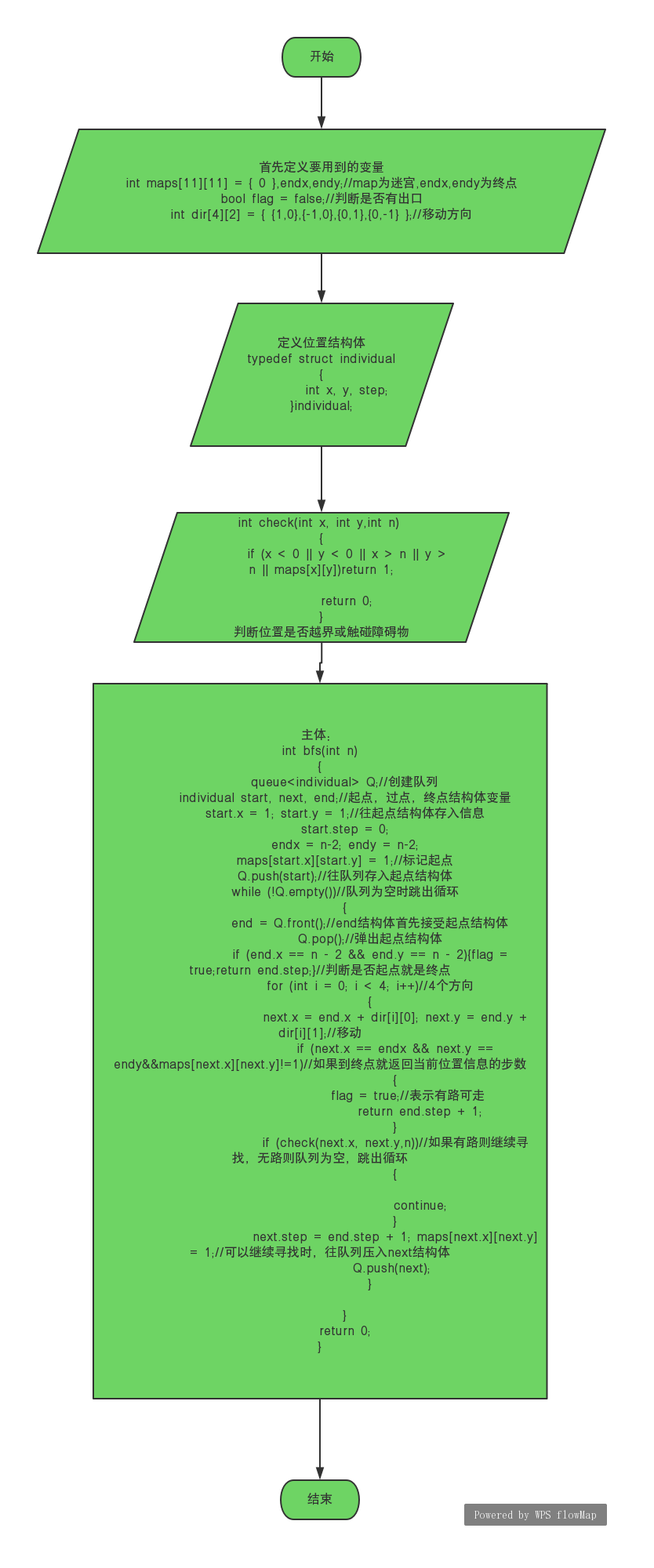
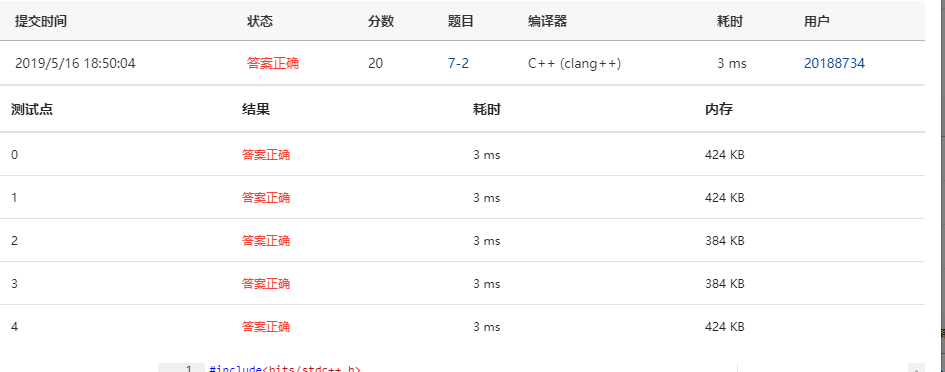
7-2 求迷宫最短通道 (20 分)
递归求解迷宫最短通道的总步长。输入一个迷宫,求从入口通向出口的可行路径中最短的路径长度。为简化问题,迷宫用二维数组 int maze[10][10]来存储障碍物的分布,假设迷宫的横向和纵向尺寸的大小是一样的,并由程序运行读入, 若读入迷宫大小的值是n(3<n<=10),则该迷宫横向或纵向尺寸都是n,规定迷宫最外面的一圈是障碍物,迷宫的入口是maze[1][1],出口是maze[n-2][n-2], 若maze[i][j] = 1代表该位置是障碍物,若maze[i][j] = 0代表该位置是可以行走的空位(0<=i<=n-1, 0<=j<=n-1)。求从入口maze[1][1]到出口maze[n-2][n-2]可以走通的路径上经历的最短的总步长。要求迷宫中只允许在水平或上下四个方向的空位上行走,走过的位置不能重复走。
输入格式:
输入迷宫大小的整数n, 以及n行和n列的二维数组(数组元素1代表障碍物,0代表空位)
输出格式:
若有可行的通道则输出一个整数,代表求出的通道的最短步长;若没有通道则输出"No solution"
输入样例:
10 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
上述输入代表的是如下这样一个迷宫:
其中红色的小方块是障碍物,蓝色的小方块是空位,白色的小圆连起来是一条从入口到出口的通道,两个圆之间代表一个步长。
输出样例:
14
实验代码
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int maps[11][11] = { 0 },endx,endy; 5 bool flag = false; 6 int dir[4][2] = { {1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} }; 7 8 typedef struct individual 9 { 10 int x, y, step; 11 }individual; 12 13 int check(int x, int y,int n) 14 { 15 if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x > n || y > n || maps[x][y])return 1; 16 17 return 0; 18 } 19 int bfs(int n) 20 { 21 queue<individual> Q; 22 individual start, next, end; 23 start.x = 1; start.y = 1; 24 start.step = 0; 25 endx = n-2; endy = n-2; 26 maps[start.x][start.y] = 1; 27 Q.push(start); 28 while (!Q.empty()) 29 { 30 end = Q.front(); 31 Q.pop(); 32 if (end.x == n - 2 && end.y == n - 2){flag = true;return end.step;} 33 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 34 { 35 next.x = end.x + dir[i][0]; next.y = end.y + dir[i][1]; 36 if (next.x == endx && next.y == endy&&maps[next.x][next.y]!=1) 37 { 38 flag = true; 39 return end.step + 1; 40 } 41 if (check(next.x, next.y,n)) 42 { 43 44 continue; 45 } 46 next.step = end.step + 1; maps[next.x][next.y] = 1; 47 Q.push(next); 48 } 49 50 } 51 return 0; 52 } 53 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) 54 { 55 int n; 56 cin >> n; 57 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 58 { 59 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 60 cin >> maps[i][j]; 61 } 62 int step = bfs(n); 63 if (flag==false)cout << "No solution"; 64 else cout << step; 65 return 0; 66 }
设计思路
本题调试过程中遇到的问题及解决方法
本来能一次过的,结果脑袋懵了明明是主函数建立的迷宫,却在BFS中把迷宫又初始化了,醉了。
运行结果截图
| 学习总结: | 存在的问题 | 心得 | 完成作业消耗时间 | 本周学习内容 |
| 第四周 | 对文件读取数据的运用不是很熟练 | 多去看关于刷题的书籍,有助于提高自己写题能力,实在不会的可以参考大佬的代码,加以自己理解之后去默写几遍 | 半个小时左右 | 文件输入,BFS,DFS,PARTITION算法及简单的贪心算法 |
| 第五周 | 对单纯用数组完成双向链表的操作还是太生疏了,说明对双向链表的运作原理不熟 | 推荐两本比较好的书《挑战程序设计》《算法竞赛》 | 半个小时左右 | vector数组及list双向链表操作 |
|
第六周 |
指针的概念太久没记有点生疏了 | 对vector数组使用愈加熟练 | 一小时左右 | 数据结构 |
| 第七周 | 对联通二维数组的最大子数和自闭了 | 多看些算法,不然写题目用什么方法去解决都弄不清 | 基础题目10分钟,挑战作业现在都在自闭中 | 迭代器 |
| 第八周 | 最小权值路径最优解该用什么解法 | 多思考一下如何优化自己的代码,会有新的收获 | 一个小时 | 递归和分治法 |
| 第九周 | 指针类型的转换 | 能用数据结构解决的问题就用数据结构 | 半小时 | windows函数 |
| 第十周 | 指针结构体 | 对地址的概念要熟悉才能更好的运用指针和结构体 | 十分钟 | 依然是windows函数 |
| 第十一周 | 数论,递归 | 多看数论就会变得很牛B | 2天 |
经典数论 |
| 第十二周 | 链表 | 把指针域和数据域搞清,还有结构体的知识多看点 | 两个小时 |
链表,python语法 |
结对编程感想:本周因为搭档有事,所以没有结对编程
系列一:代码函数 系列二:博客字数
预习作业:
从第十三周开始,将进入课程设计阶段,请在本次作业中给出:
1.所在小组想要开发的项目的名称和目标;
2.项目主体功能的描述;
3.现阶段已做的准备工作;
4.小组成员名单和进度安排。(课程设计阶段:13-17周)