在Java中,经常会需要新建一个对象,很多情况下,需要这个新建的对象和现有的某个对象保持属性一致。
那么,就有两种方式来实现这个对象的构造:
①通过新建一个对象,为这个对象的属性根据原有对象的属性来进行赋值
②调用clone方法,来实现实例对象的克隆
对于Java的clone方法,需要注意的就是它实际上是一种“浅克隆”(Shallow Clone),对于int、double这种基本数据类型,直接拷贝值;对于String这样的类对象,则是直接拷贝引用。因此对于通过clone得到的对象来说,它很大程度上还是和原有被克隆对象之间有着很大的联系(例如修改clone对象的String属性,则原有对象的String属性也会变化)。
于是,为了得到两个完全“独立”的具有相同属性的实例对象,就涉及到“深克隆”(Deep Clone)。至于如何来编写实现“深克隆”,可参考这篇博客(来自大学同学朱大佬分享): https://blog.csdn.net/zhangjg_blog/article/details/18369201
当然,至此要说明的重点并不是如何实现“深克隆”和“浅克隆”,而是要比较一下上面提到的①②两种方法,哪种效率更高一些。
首先,对于“浅克隆”来进行测试:
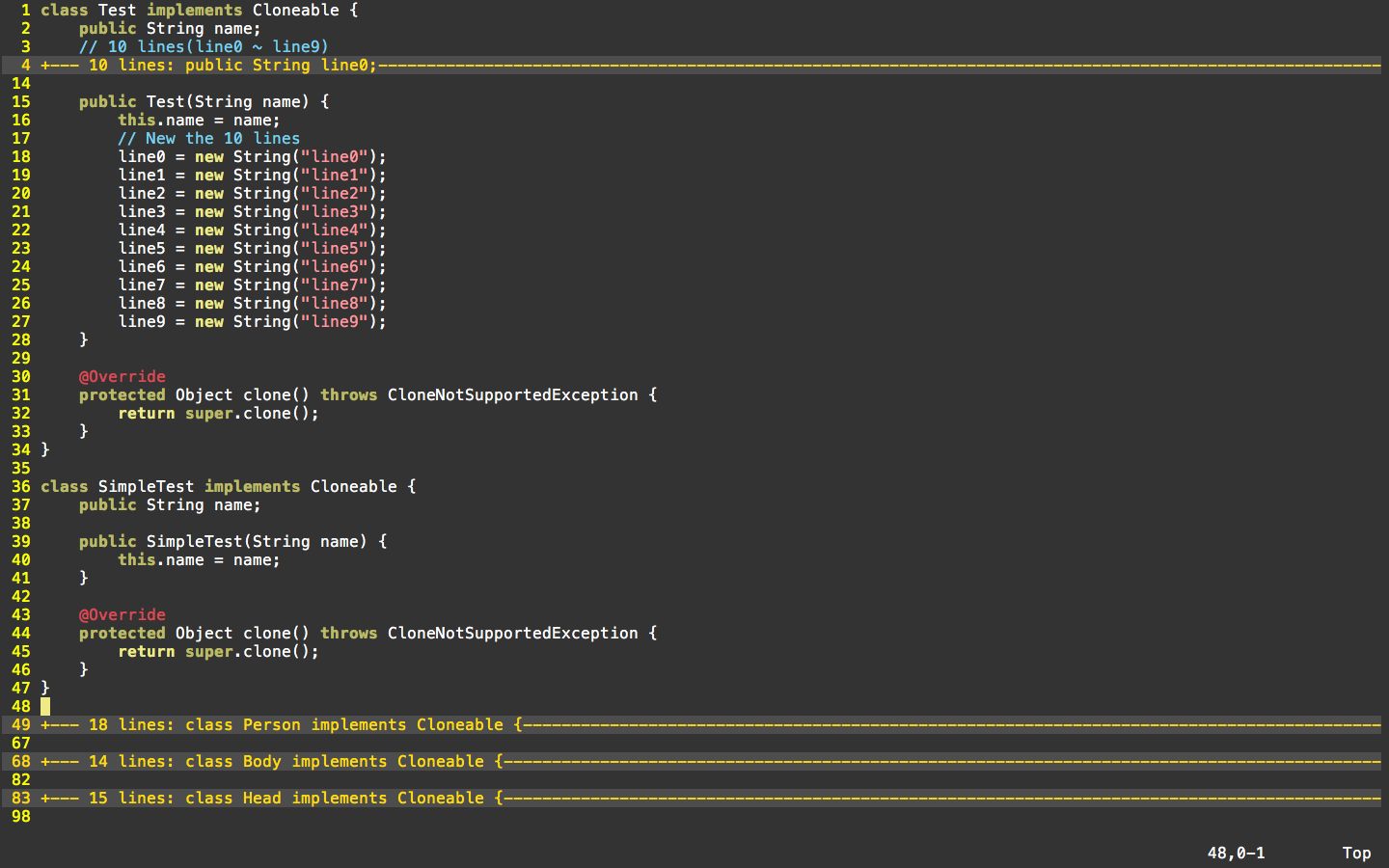
注:这里的SimpleTest类只包含一个name属性(String型),而Test类则包括name以及line0~line9这11个属性(均为String型)。这里让这些属性值在构造器中完成初始化。
测试代码:
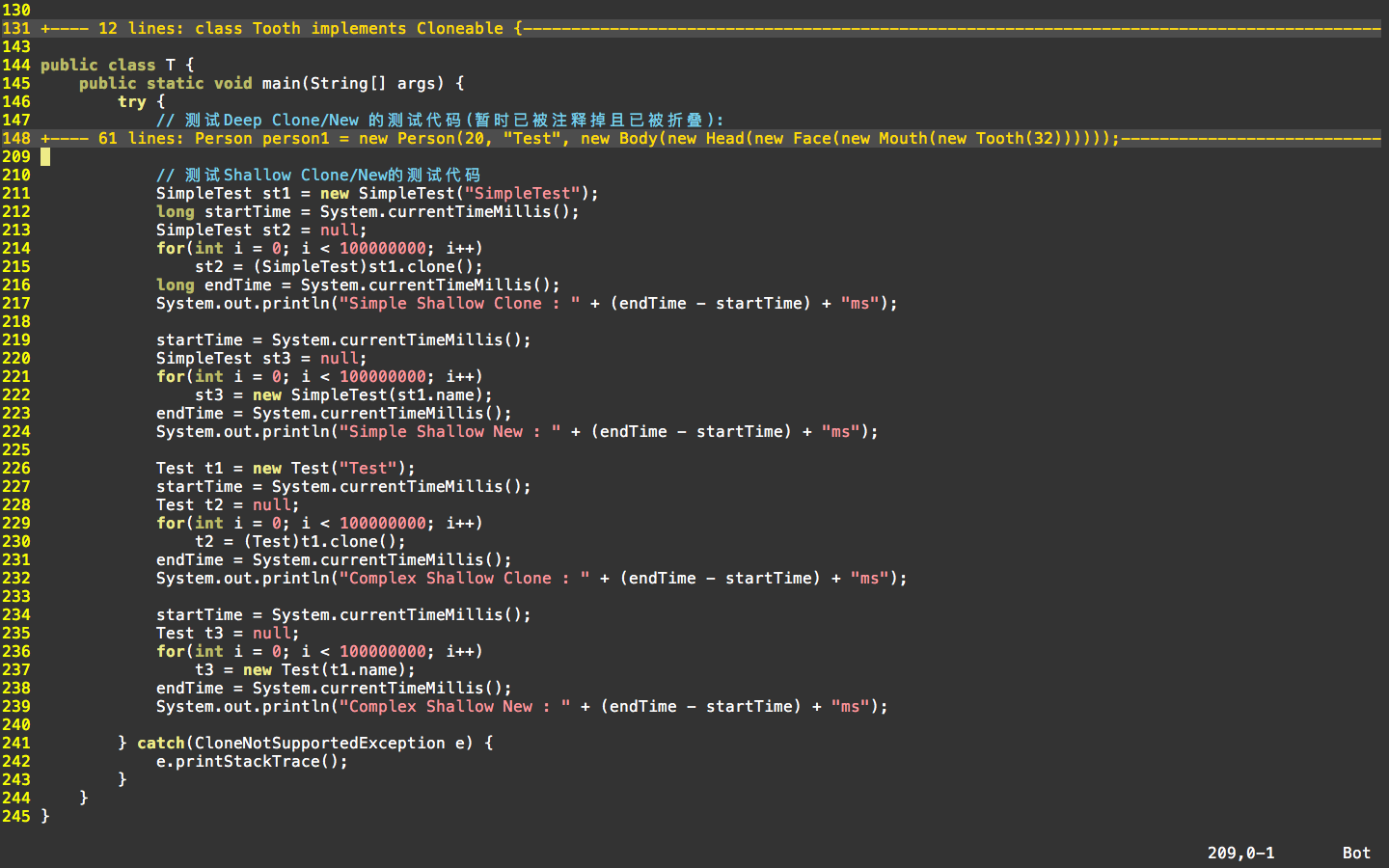
说明: 这里分别对四种情况进行测试:
1). 简单的“浅克隆”,通过用SimpleTest的“浅克隆”来进行测试
2). 简单的“构造”,通过用SimpleTest的构造器来实例对象,其name值,直接通被克隆对象的name值来获取
3). 复杂的“浅克隆”,通过Test的“浅克隆”来进行测试
4). 复杂的“构造”,通过正常构造Test,来获得Test实例,需要注意的就是,此时Test的构造器内涉及到一系列的new操作(代表复杂构造操作)
测试结果:
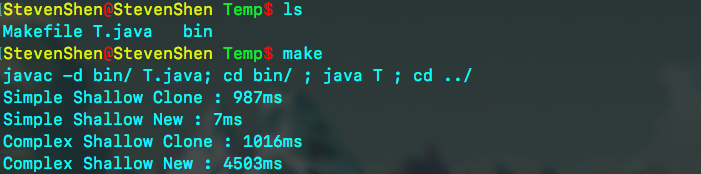
结果说明:
①对于轻量型的类对象,通过new操作来构造,效率会更高(对比987ms和7ms)。
②对于重量型的类对象,通过clone操作来进行构造,效率会更高(对比1016ms和4503ms)。
原因分析:
①对于轻量型的类对象,通过new操作即可很快地进行构造,而clone方法依旧涉及到new操作,但其会进行更多的方法调用,执行流程会消耗一些时间
②对于重量型的类对象,new操作则需要构造相当多的对象,从而会消耗很多时间;但clone方法(这里是“浅克隆”)只需要拷贝引用给新的对象即可,因此消耗的时间会更少
但是,这只是对于“浅克隆”来说,clone的构造效率会更高,但对于“深克隆”来说,情况却并不乐观。
首先,按照前面提到的那篇博客,来进一步构造深克隆:

class Person implements Cloneable { public int age; public String name; public Body body; public Person(int age, String name, Body body) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.body = body; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Person newPerson = (Person)super.clone(); newPerson.body = (Body)body.clone(); return newPerson; } } class Body implements Cloneable { public Head head; public Body(Head head) { this.head = head; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Body newBody = (Body)super.clone(); newBody.head = (Head)head.clone(); return newBody; } } class Head implements Cloneable { public Face face; public Head(Face face) { this.face = face; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Head newHead = (Head)super.clone(); newHead.face = (Face)face.clone(); return newHead; } } class Face implements Cloneable { public Mouth mouth; public Face(Mouth mouth) { this.mouth = mouth; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Face newFace = (Face)super.clone(); newFace.mouth = (Mouth)mouth.clone(); return newFace; } } class Mouth implements Cloneable { public Tooth tooth; public Mouth(Tooth tooth) { this.tooth = tooth; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Mouth newMouth = (Mouth)super.clone(); newMouth.tooth = (Tooth)tooth.clone(); return newMouth; } } class Tooth implements Cloneable { public final int number; public Tooth(int number) { this.number = number; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
测试代码: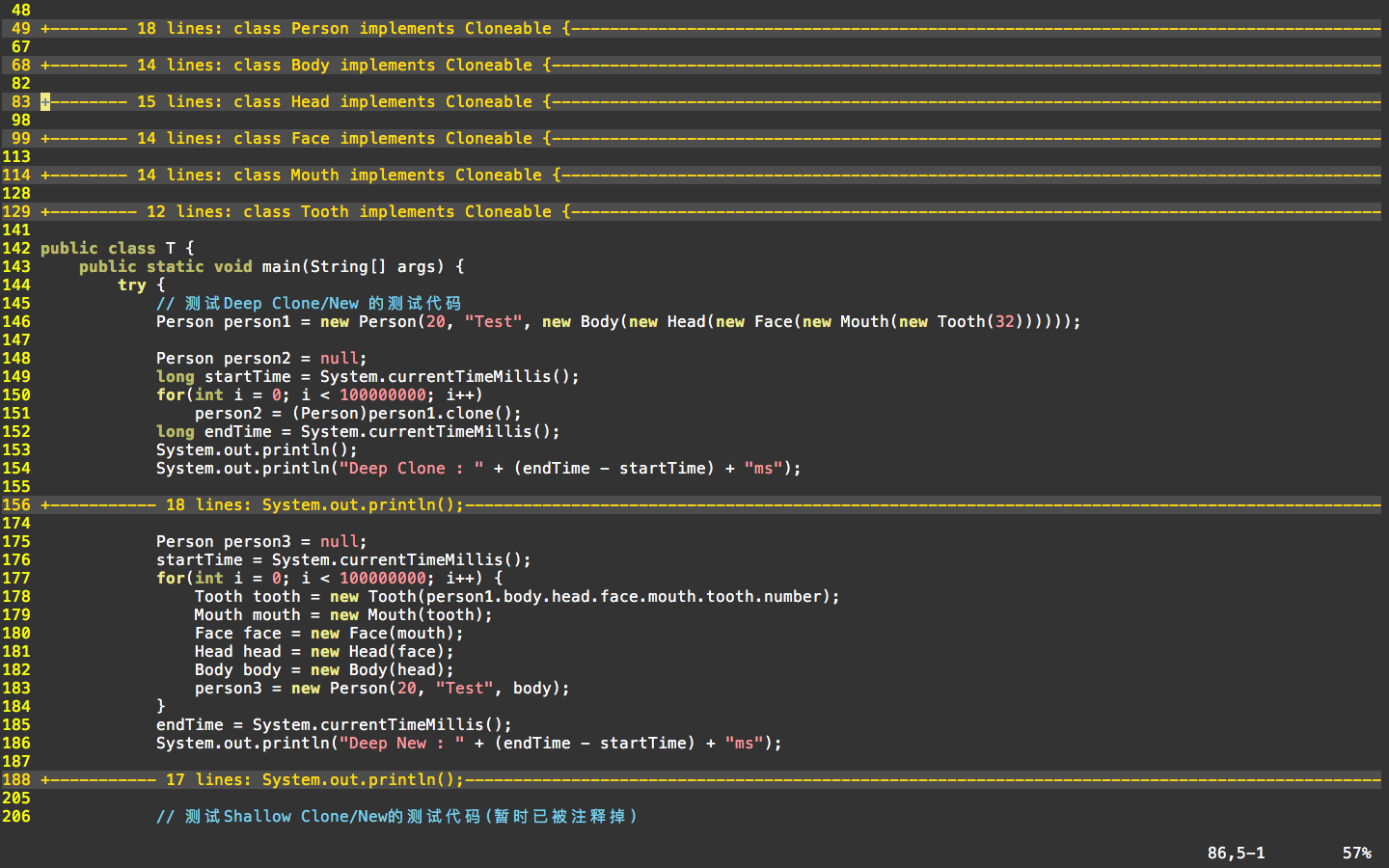

// 测试Deep Clone/New 的测试代码 Person person1 = new Person(20, "Test", new Body(new Head(new Face(new Mouth(new Tooth(32)))))); Person person2 = null; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) person2 = (Person)person1.clone(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Deep Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1 == person2: " + (person1 == person2)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person2.age: " + (person1.age == person2.age)); System.out.println("person1.name == person2.age: " + (person1.name == person2.name)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person2.body: " + (person1.body == person2.body)); System.out.println("person1.body.head == person2.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person2.body.head)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number)); System.out.println(); Person person3 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { Tooth tooth = new Tooth(person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number); Mouth mouth = new Mouth(tooth); Face face = new Face(mouth); Head head = new Head(face); Body body = new Body(head); person3 = new Person(20, "Test", body); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Deep New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1 == person3: " + (person1 == person3)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person3.age: " + (person1.age == person3.age)); System.out.println("person1.name == person3.age: " + (person1.name == person3.name)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person3.body: " + (person1.body == person3.body)); System.out.println("person1.body.head == person3.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person3.body.head)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number)); System.out.println();
按照这个结构,深克隆得到的对象和原有对象的关系如图:
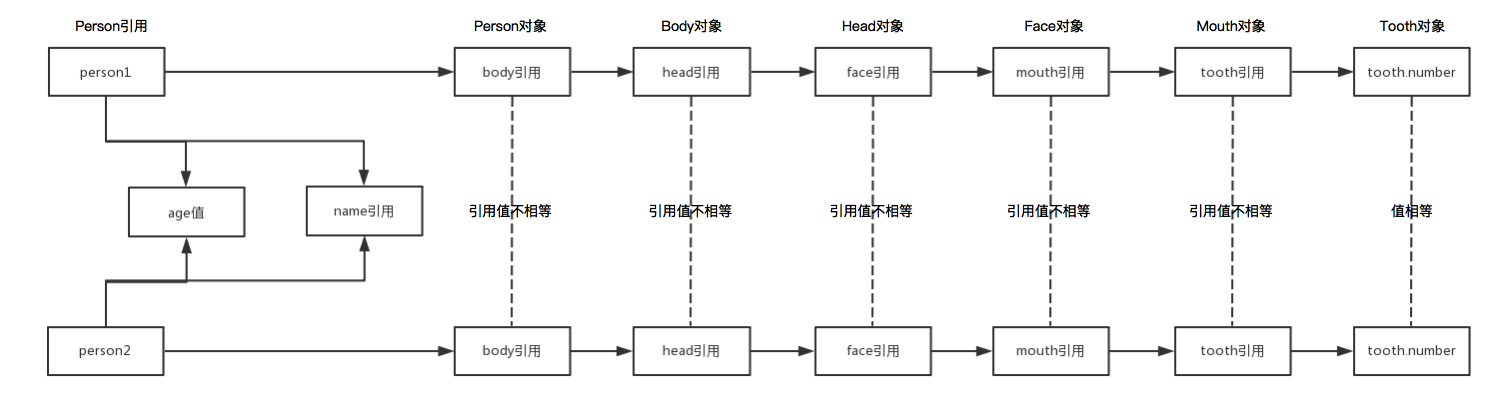
测试结果:
注: 这里的person3是通过new来构造的对象,其内部包含的每个引用对象(不包括其name),均是通过new来进行构造的。
结论: 可以发现,“深克隆”并没有提高克隆的效率!相反,这种方法此时比通过new构造对象的方法效率还低。
原因分析: 就和上面的测试一样: 此处的“深克隆”依旧会通过new的方法来不断构造对象,因而本质上并没有提高效率(不似“浅克隆”一般直接复制引用即可),反而由于操作流程的层层调用,使得其执行速度不如new构造对象的方法快。
至此,基本可以确定,clone方法只有在进行复杂的“浅克隆”时效率才会明显高于new构造方式,但由于此时的克隆本质上依旧是“浅克隆”,因此需要注意引用的指向问题,避免错误更改关联的信息值。
但是,对于测试一来说,这个比较是不全面的。因为浅克隆本质上,只是把类中的引用复制到新的对象属性中,而该测试中,new构造的对象的内部引用则是完全“独立”的。
因此,为了测试clone方法的“浅克隆”方式是否真正会提高效率,还要进行测试:
这里,更改了Test类的代码,为Test新增了一种构造器,便于构造对象;为Test新增了copy方法,该方法只是构建一个新的Test对象,并将自身的所有属性引用拷贝到这个新的对象属性中。
代码如图:
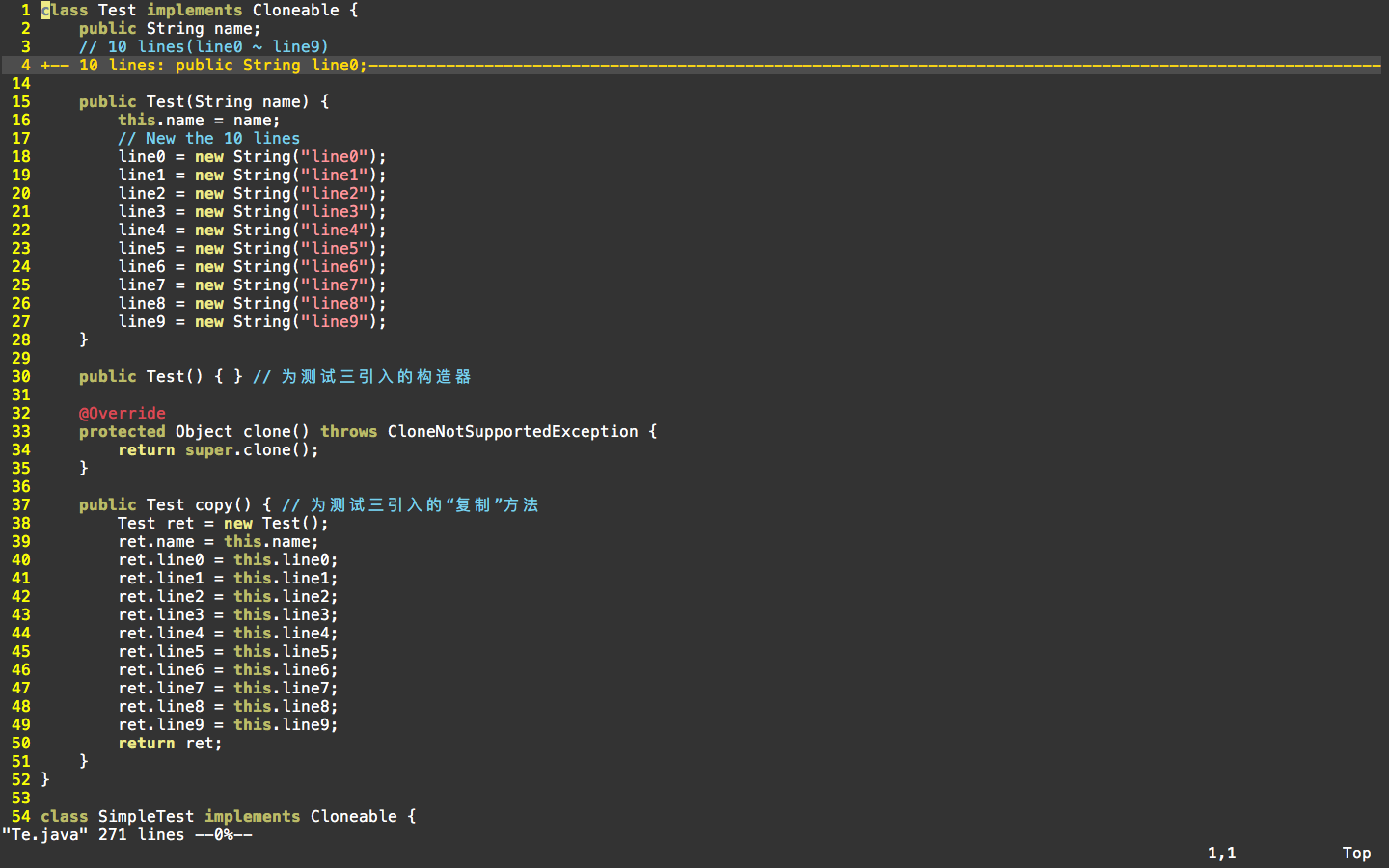
测试代码: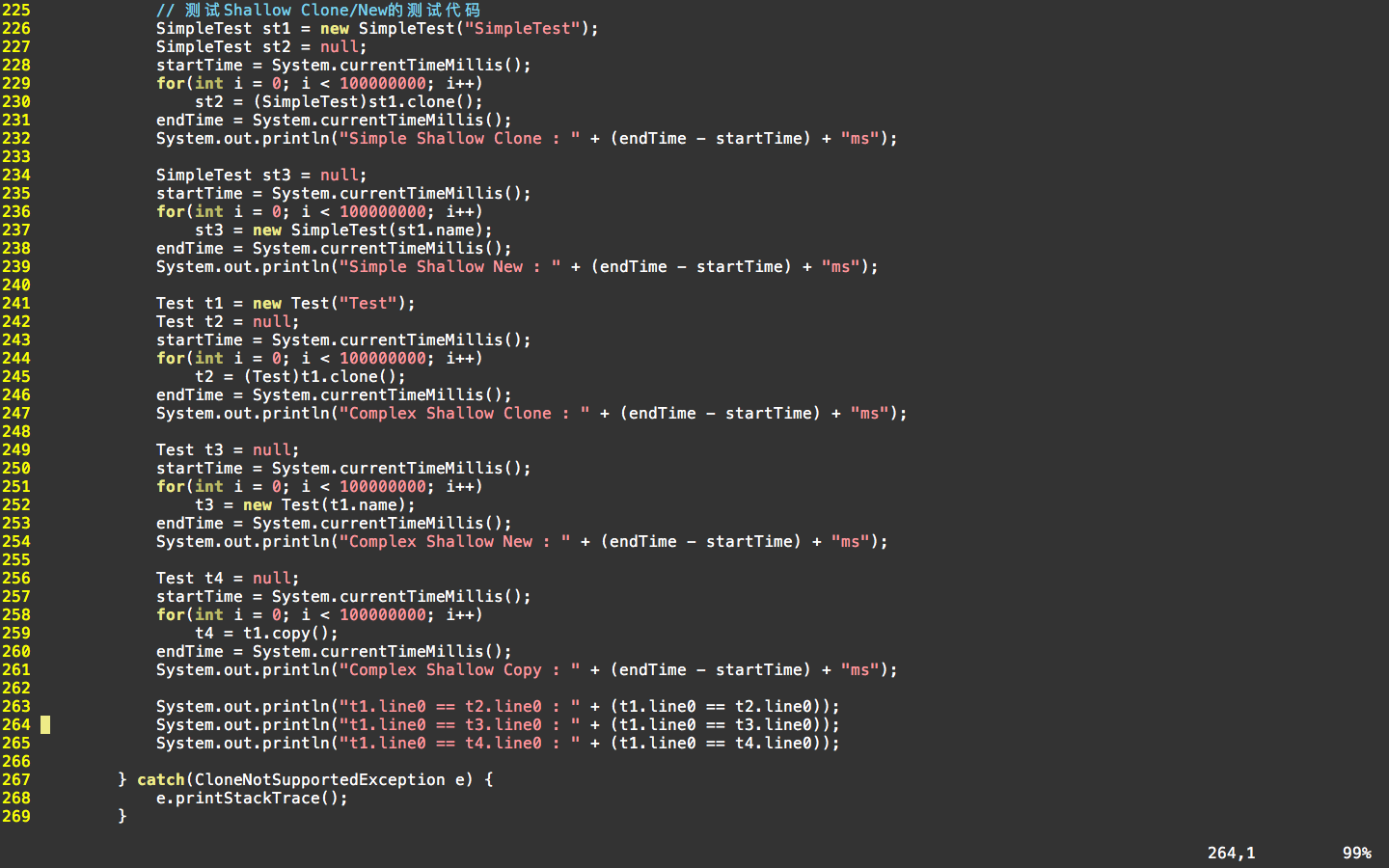
说明: 在原有测试代码的基础上,新增了测试对象t4,该对象的属性值通过调用copy方法来获得。当然,这里的copy实现的就是“浅克隆”的过程,即仅仅复制引用。
最后会打印三行信息:反映对于类内属性是否为真正的克隆。如果返回值为true,则表明line0引用指向的是相同空间,为“浅克隆”;如果返回值为false,则表明为真克隆,即对象真正隔离。
测试结果:

结论: 对于复杂的“浅克隆”,通过Copy的方式可实现类似Clone的实现(可以看到,Copy方法和Clone方法都是将引用直接拷贝),但是效率并没有Clone高(多次测试都是如此),这才是真正体现了Clone方法效率高的测试。
需要注意的是,clone尽管默认是“浅克隆”,但是依旧有很多应用情况。clone方法,可以将原有对象的private属性的信息也克隆下来,需要对此注意。
通过查阅stackoverflow,可以看到更多关于这方面的内容,其中也包括clone方法的应用场合(例如GUI面板等)。
最后,附上这篇博客的所有代码:

class Test implements Cloneable { public String name; // 10 lines(line0 ~ line9) public String line0; public String line1; public String line2; public String line3; public String line4; public String line5; public String line6; public String line7; public String line8; public String line9; public Test(String name) { this.name = name; // New the 10 lines line0 = new String("line0"); line1 = new String("line1"); line2 = new String("line2"); line3 = new String("line3"); line4 = new String("line4"); line5 = new String("line5"); line6 = new String("line6"); line7 = new String("line7"); line8 = new String("line8"); line9 = new String("line9"); } public Test() { } // 为测试三引入的构造器 @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } public Test copy() { // 为测试三引入的“复制”方法 Test ret = new Test(); ret.name = this.name; ret.line0 = this.line0; ret.line1 = this.line1; ret.line2 = this.line2; ret.line3 = this.line3; ret.line4 = this.line4; ret.line5 = this.line5; ret.line6 = this.line6; ret.line7 = this.line7; ret.line8 = this.line8; ret.line9 = this.line9; return ret; } } class SimpleTest implements Cloneable { public String name; public SimpleTest(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } class Person implements Cloneable { public int age; public String name; public Body body; public Person(int age, String name, Body body) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.body = body; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Person newPerson = (Person)super.clone(); newPerson.body = (Body)body.clone(); return newPerson; } } class Body implements Cloneable { public Head head; public Body(Head head) { this.head = head; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Body newBody = (Body)super.clone(); newBody.head = (Head)head.clone(); return newBody; } } class Head implements Cloneable { public Face face; public Head(Face face) { this.face = face; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Head newHead = (Head)super.clone(); newHead.face = (Face)face.clone(); return newHead; } } class Face implements Cloneable { public Mouth mouth; public Face(Mouth mouth) { this.mouth = mouth; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Face newFace = (Face)super.clone(); newFace.mouth = (Mouth)mouth.clone(); return newFace; } } class Mouth implements Cloneable { public Tooth tooth; public Mouth(Tooth tooth) { this.tooth = tooth; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Mouth newMouth = (Mouth)super.clone(); newMouth.tooth = (Tooth)tooth.clone(); return newMouth; } } class Tooth implements Cloneable { public final int number; public Tooth(int number) { this.number = number; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class T { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // 测试Deep Clone/New 的测试代码 Person person1 = new Person(20, "Test", new Body(new Head(new Face(new Mouth(new Tooth(32)))))); Person person2 = null; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) person2 = (Person)person1.clone(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Deep Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1 == person2: " + (person1 == person2)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person2.age: " + (person1.age == person2.age)); System.out.println("person1.name == person2.age: " + (person1.name == person2.name)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person2.body: " + (person1.body == person2.body)); System.out.println("person1.body.head == person2.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person2.body.head)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number)); System.out.println(); Person person3 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { Tooth tooth = new Tooth(person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number); Mouth mouth = new Mouth(tooth); Face face = new Face(mouth); Head head = new Head(face); Body body = new Body(head); person3 = new Person(20, "Test", body); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Deep New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1 == person3: " + (person1 == person3)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person3.age: " + (person1.age == person3.age)); System.out.println("person1.name == person3.age: " + (person1.name == person3.name)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person3.body: " + (person1.body == person3.body)); System.out.println("person1.body.head == person3.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person3.body.head)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth)); System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: " + (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number)); System.out.println(); // 测试Shallow Clone/New的测试代码 SimpleTest st1 = new SimpleTest("SimpleTest"); SimpleTest st2 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) st2 = (SimpleTest)st1.clone(); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Simple Shallow Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); SimpleTest st3 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) st3 = new SimpleTest(st1.name); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Simple Shallow New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); Test t1 = new Test("Test"); Test t2 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) t2 = (Test)t1.clone(); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Complex Shallow Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); Test t3 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) t3 = new Test(t1.name); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Complex Shallow New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); Test t4 = null; startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) t4 = t1.copy(); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Complex Shallow Copy : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println("t1.line0 == t2.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t2.line0)); System.out.println("t1.line0 == t3.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t3.line0)); System.out.println("t1.line0 == t4.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t4.line0)); } catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
