aop( aspect oriented programming )

面向切面编程,是对所有对象或者是一类对象编程
几个重要的概念:
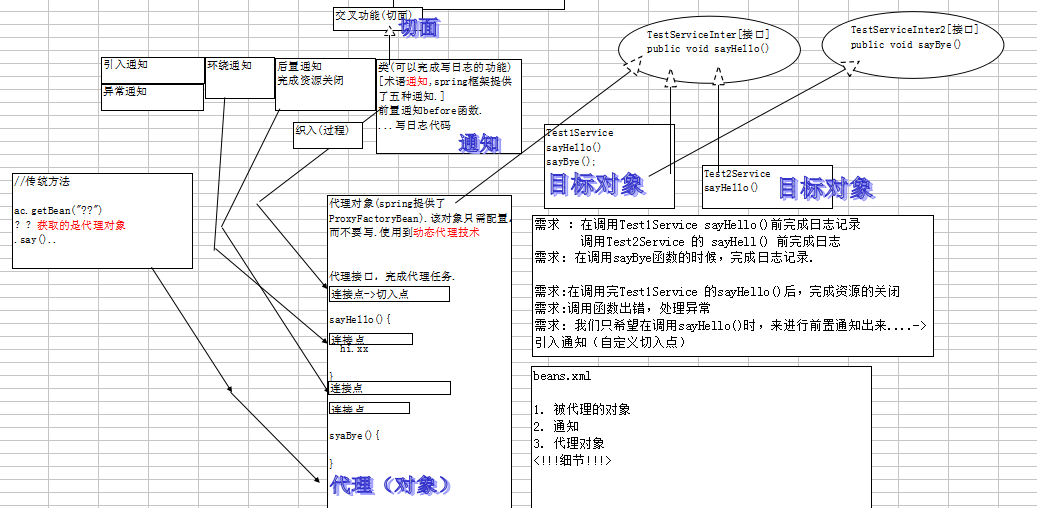
1.切面(aspect):要实现的交叉功能,是系统模块化的一个切面或领域。如日志记录。
2.连接点:应用程序执行过程中插入切面的地点,可以是方法调用,异常抛出,或者要修改的 字段。
3.通知:切面的实际实现,他通知系统新的行为。如在日志通知包含了实 现日志功能的代码,如向日志文件写日志。通知在连接点插入到应用系统中。
4.切入点:定义了通知应该应用在哪些连接点,通知可以应用到AOP框架支持的任何连接点。
5.引入:为类添加新方法和属性。
6.目标对象:被通知的对象。既可以是你编写的类也可以是第三方类。
7.代理:将通知应用到目标对象后创建的对象,应用系统的其他部分不用为了支持代理对象而 改变。
8.织入:将切面应用到目标对象从而创建一个新代理对象的过程。织入是一个过程。织入发生在目标 对象生命周期的多个点上:
编译期:切面在目标对象编译时织入.这需要一个特殊的编译器.
类装载期:切面在目标对象被载入JVM时织入.这需要一个特殊的类载入器.
运行期:切面在应用系统运行时织入.
创建切面的方式:
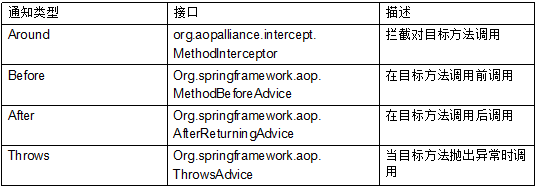
还有一种引用通知方式。总共五种类型,下面一一举例实现:
编程说明:
步骤:
1.定义接口
2.编写对象(被代理对象=目标对象)
3.编写通知(前置通知目标方法调用前调用)
4.在beans.xml文件配置
4.1 配置 被代理对象=目标对象
4.2 配置通知
4.3 配置代理对象 是 ProxyFactoryBean的对象实例
4.3.1 代理接口集
4.3.2 织入通知
4.3.3 配置被代理对象
一.定义接口:
接口1:
public interface TestServiceInter {
public void sayHello();
}
接口2:
public interface TestServiceInter2 {
public void sayBye();
}
二、编写对象
public class Test1Service implements TestServiceInter,TestServiceInter2 {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hi "+name);
}
public void sayBye() {
System.out.println("bye "+name);
//int i=9/0;
}
}
三、编写通知
1.前置通知
public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* method: 被调用方法名字
* args: 给method传递的参数
* target: 目标对象
*/
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("..............");
System.out.println("记录日志..."+method.getName());
}
}
该接口提供了获得目标方法、参数和目标对象的机会。不能够改变运行时参数,即不能替换参数对象和目标对象。
注意在方法结束后不返回任何值。原因是该接口返回后,目标方法将会被调用,应该返回目标对象的返回值。
该接口唯一能 阻止目标方法被调用的途径是抛出异常或(System.exit())。
2.后置通知
与前置通知类似
public class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method,
Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable
System.out.println("关闭资源。。。。");
}
}
3.环绕通知
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation arg0) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("调用方法前。。。");
Object obj=arg0.proceed(); //目标对象方法的调用执行
System.out.println("调用方法后。。。");
return obj;
}
}
该接口同前两种通知有两个重要区别:
1.该通知能够控制目标方法 是否真的被调用。通过invocation.proceed()方法来调用。
2.该通知可以控制返回的对象。可以返回一个与proceed()方法返回对象完全不同的对象。但要谨慎使用。
4.异常通知
public class MyThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
public void afterThrowing(Method m,Object[] os,Object target,Exception throwable){
System.out.println("出大事了"+throwable.getMessage());
}
}
public interface ThrowsAdvice{
}
该接口为标识性接口,没有任何方法,但实现该接口的类必须要有如下形式的方法:
public void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable);
public void afterThrowing(Method m,Object[] os,Object target,Exception throwable);
第一个方法只接受一个参数:需要抛出的异常。 第二个方法接受异常、被调用的方法、参数以及目标对象。
5.引入通知
如果不能表达在应用系统的什么地方应用 通知的话,通知将毫无用处,这就是切入点的用处。
切入点决定了一个特定的类的特定方法是否满足一定的规则。若符合,通知就应用到该方法上。
引入通知只需要在beans.xml中自定义切入点来控制通知。
四、beans.xml配置
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"
>
<!-- 配置被代理的对象 -->
<bean id="test1Service" class="com.hsp.aop.Test1Service">
<property name="name" value="顺平" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置前置通知 -->
<bean id="MyMethodBeforeAdvice" class="com.hsp.aop.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" />
<!-- 配置后置通知 -->
<bean id="myAfterReturningAdvice" class="com.hsp.aop.MyAfterReturningAdvice"/>
<!-- 配置环绕通知 -->
<bean id="myMethodInterceptor" class="com.hsp.aop.MyMethodInterceptor" />
<!-- 配置异常通知 -->
<bean id="myThrowsAdvice" class="com.hsp.aop.MyThrowsAdvice"/>
<!-- 定义前置通知的切入点 -->
<bean id="myMethodBeforeAdviceFilter" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor" >
<property name="advice" ref="MyMethodBeforeAdvice" />
<property name="mappedNames">
<list>
<value>sayHello</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 代理对象的实现原理.实现接口
proxyFactoryBean implements TestServiceInter,TestServiceInter2{
public void sayHello();
}
思考:多态下接口类型的转换
interface Inter1{};
class A implements Inter1,Inter2{
}
Inter1 a=new A();
Inter2 b=(Inter2)a;
-->
<!-- 配置代理对象,只需配置而不要写 -->
<bean id="proxyFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 代理接口集 这里name值是固定的-->
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>com.hsp.aop.TestServiceInter</value>
<value>com.hsp.aop.TestServiceInter2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 把通知织入到代理对象 这里name值是固定的 -->
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<!-- 相当于把MyMethodBeforeAdvice前置通知和代理对象关联,我们也
可以把通知看成拦截器,struts2核心拦截器 -->
<!-- 相当于自定义切入点来控制前置通知的使用 -->
<value>myMethodBeforeAdviceFilter</value>
<!-- 织入后置通知 -->
<value>myAfterReturningAdvice</value>
<!-- 织入环绕通知 -->
<value>myMethodInterceptor</value>
<!-- 织入异常通知 -->
<value>myThrowsAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 配置被代理对象,可以指定 -->
<property name="target" ref="test1Service"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/hsp/aop/beans.xml");
TestServiceInter ts=(TestServiceInter) ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean");
ts.sayHello();
((TestServiceInter2)ts).sayBye();
}
执行结果:

现在加入打印代理对象的类型的语句:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/hsp/aop/beans.xml");
TestServiceInter ts=(TestServiceInter) ac.getBean("proxyFactoryBean");
System.out.println("ts的类型是"+ts);
ts.sayHello();
((TestServiceInter2)ts).sayBye();
}
执行结果:

ts是个代理对象,从中还可以看出只要代理对象被调用就会执行织入通知。
提问? 说spring的aop中,当你通过代理对象去实现aop的时候,获取的ProxyFactoryBean是什么类型?
答: 返回的是一个代理对象,如果目标对象实现了接口,则spring使用jdk 动态代理技术,如果目标对象没有实现接口,则spring使用CGLIB技术.