一、JDBC是什么
JDBC:java database connectivity
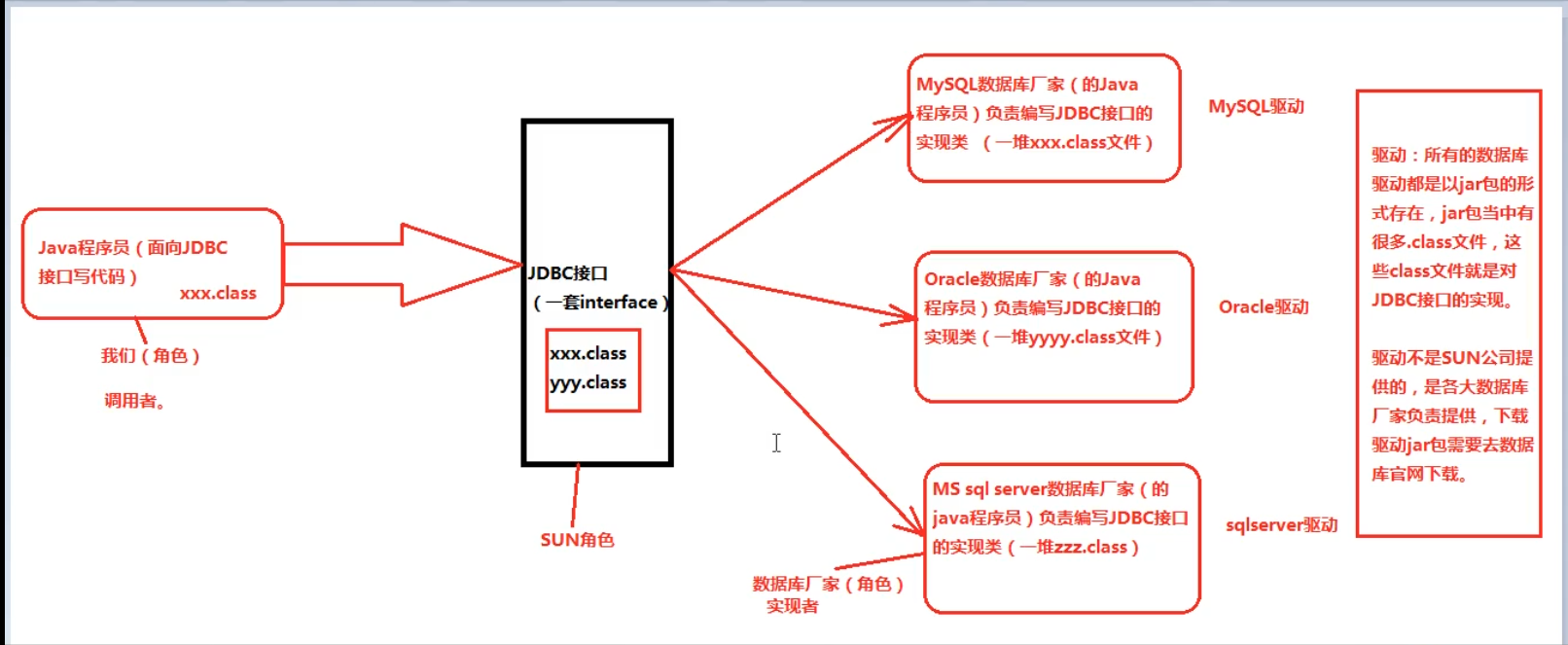
二、JDBC本质
JDBC 是sun公司提供的一套接口
接口都有调用者和实现者,面向接口调用,面向接口写实现类,都属于面向接口编程
为什么要面向接口编程:
为了解耦合,降低程序的耦合度,提高程序的扩展力。
比如:多态就是典型的面向抽象编程
Animal a = new Dog();
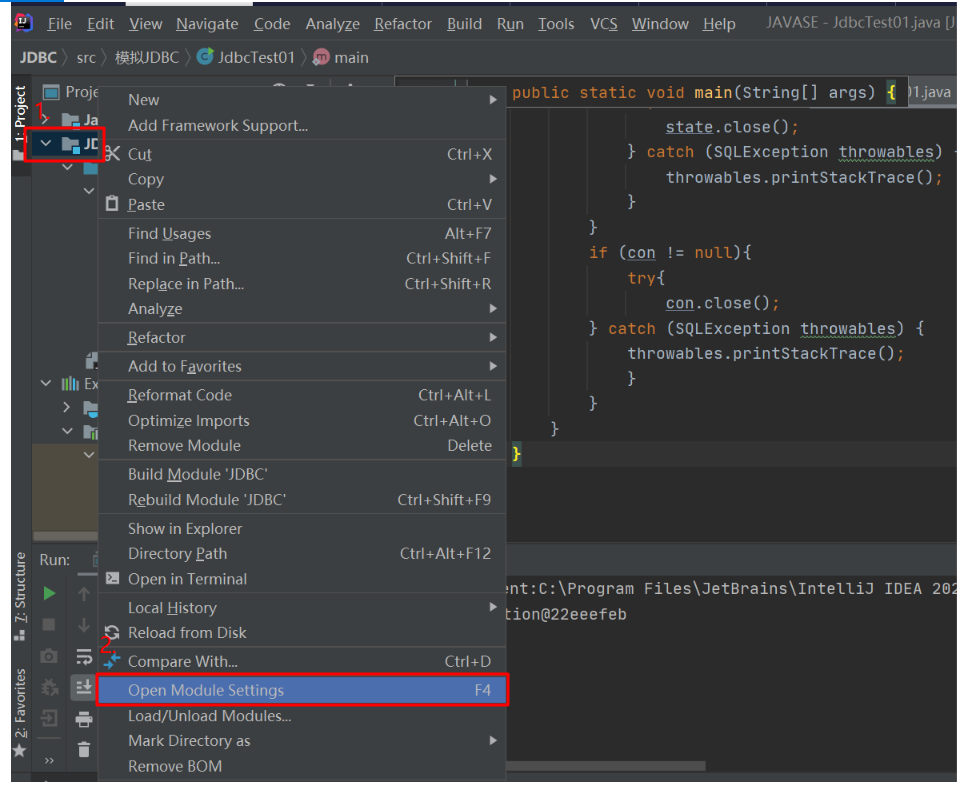
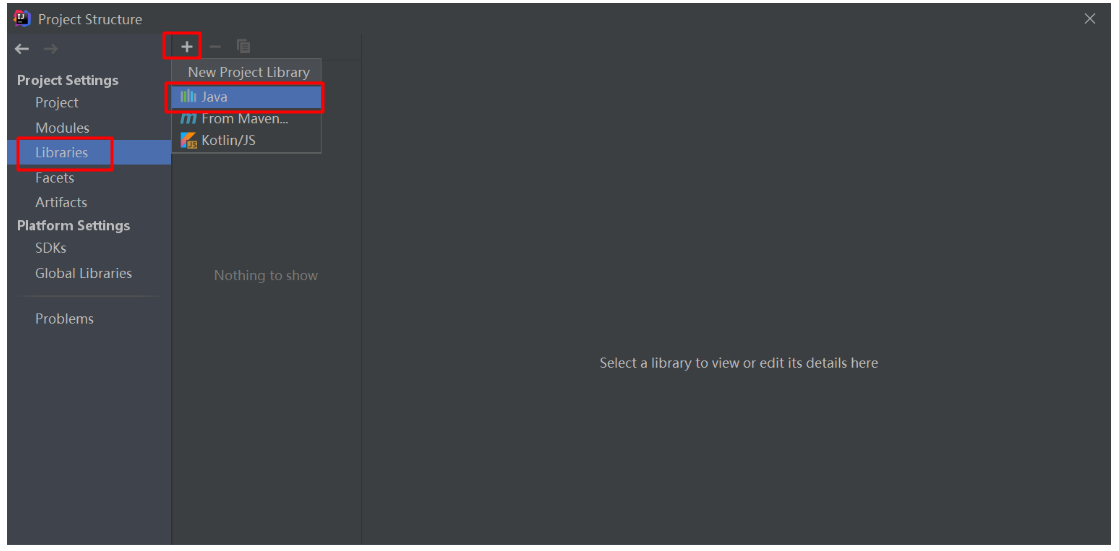
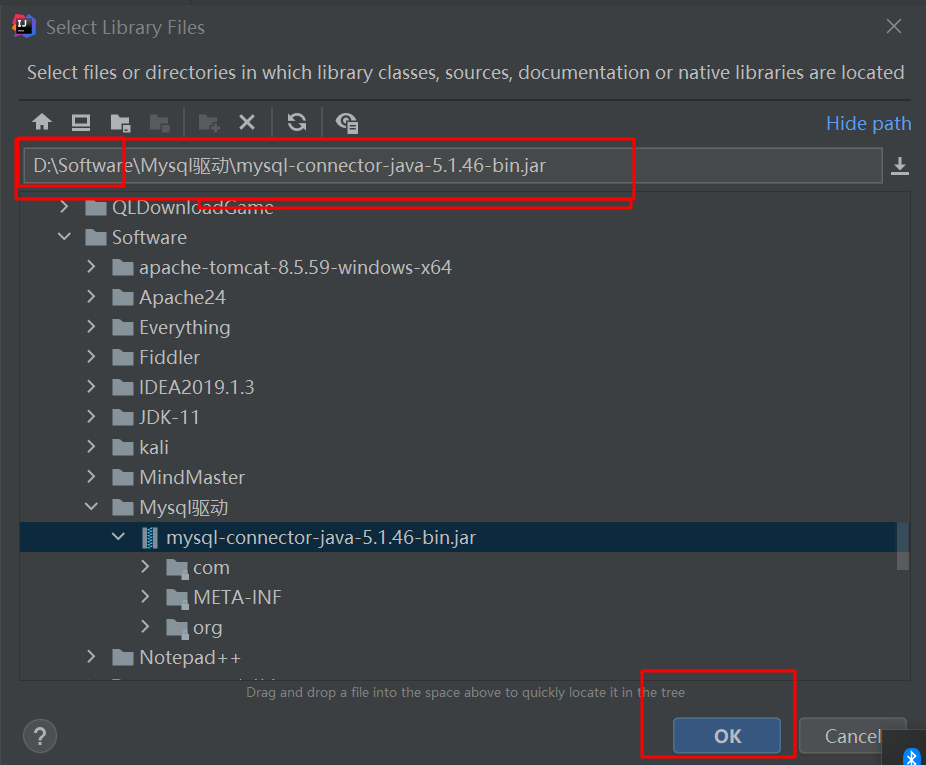
三、JDBC开发前的准备
先从对应的官网中下载对应的驱动jar包,配置到IDEA中
配置的截图
四、JDBC开发六步
1.注册驱动:告诉Java程序将要连接的是哪个品牌的数据库
2.获取连接:表示jvm和数据库之间的进程通道打开了,这属于进程之间的通信,使用之后一定要关闭
3.获取数据库操作对象(执行sql语句的对象)
4.执行sql语句
5.处理查询结果集:只有第四步执行的是select语句时才有第五步
6.释放资源:java程序和数据库是进程之间的通信,使用之后一定要关闭
// 示例1:sql语句是insert,所有没有上述第五步处理查询结果集
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.注册驱动,这里目的要把class文件加载一下,后续还有另外一种方式实现
java.sql.Driver driver = null;
// 写在这里是因为下边finally要用到,所以声明为全局的
Connection con = null;
Statement state = null;
try {
driver = new Driver(); //多态,父类型引用指向子类对象;java.sql.Driver是接口,jdbc中的Driver是实现类
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
//2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/firstbase";
String userName = "root";
String password = "123456";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
System.out.println("数据库连接对象是:" + con);
//3.获取数据库操作对象(专门执行sql语句的对象)
state = con.createStatement();
//4.执行sql语句
String sql = "insert into dept(deptno, dname, loc) values(60, 'SALES', 'NEWYORK')";
int count = state.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "保存成功" : "保存失败");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.释放资源,为了保证资源一定释放,在finally语句中关闭资源,并且遵循从小到大依次关闭,分别try catch
if (state != null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (con != null){
try{
con.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
// 示例2:delete 和 update
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Driver driver = null;
Connection con = null;
Statement state = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//2.获取连接
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/firstbase","root","123456");
//3.获取数据库执行对象
state = con.createStatement();
//4.执行sql语句;jdbc中sql语句不需要写分号
// String sql = "delete from dept where deptno = 50 "; //删除语句
String sql = "update dept set dname = 'zhangsan' where deptno = 10 "; // 修改语句
int count = state.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "删除成功" : "删除失败");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (state != null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (con != null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
//示例3:注册驱动的另一种常用的写法
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JdbcTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.注册驱动的另外一种方式(比较常用)
try {
//这里不需要接收返回值,因为只需要这个加载的动作,这个在源码中有静态代码块,只需要加载就执行了
//这种方式常用是因为接收的是一个字符串,可以写到配置文件.properities中
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/firstbase","root","123456");
System.out.println(con); //这里打印出con对象,表示获取连接成功
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//实例4:使用资源绑定器绑定属性文件
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用资源绑定器绑定属性配置文件
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String jdbc = bundle.getString("jdc");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String userName = bundle.getString("userName");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection con = null;
Statement state = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(jdbc);
//2.获取连接
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
//3.获取数据库操作对象
state = con.createStatement();
//4.执行sql语句
String sql = "insert into dept(deptno, dname, loc) values(60, 'SALES', 'NEWYORK')";
int count = state.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "保存成功" : "保存失败");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (state != null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (con != null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
// 实例5:处理查询结果集
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
Statement state = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/firstbase", "root", "123456");
state = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from dept";
rs = state.executeQuery(sql); //这里rs就是查询结果集
while(rs.next()) { //rs.next()返回布尔类型,如果rs一下行有数据返回true,否则返回false
String deptno = rs.getString("deptno"); //rs.getString()参数可以是数字1,2,3表示第几列,或者是传字段名
String dname = rs.getString("dname");
String loc = rs.getString("loc");
System.out.println(deptno + " " + dname + " " + loc);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (state != null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (con != null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}