js 代码性能优化原理剖析与实战 All In One
fibonacci 性能优化
tail-call optimization / 尾调用优化
函数式编程,请注意 JavaScript 中递归的性能影响; 对于深度递归,请考虑使用迭代来避免堆栈溢出;
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Language_Overview

http://wiki.c2.com/?TailCallOptimization
https://webkit.org/blog/6240/ecmascript-6-proper-tail-calls-in-webkit/
In computer science, a tail call is a subroutine call performed as the final action of a procedure.
If the target of a tail is the same subroutine, the subroutine is said to be tail recursive, which is a special case of direct recursion.
Tail recursion (or tail-end recursion) is particularly useful, and is often easy to optimize in implementations.
在计算机科学中,尾调用是作为过程的最终操作执行的子例程调用。
如果尾的目标是同一个子程序,则称该子程序是尾递归的,这是直接递归的一种特殊情况。
尾递归(或尾端递归)特别有用,并且在实现中通常很容易优化。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tail_call
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/尾调用
性能优化
recursion / 递归 ❌ 简单好理解,但是性能不好
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/Recursion
memory cached / 内存缓存 ✅
iteration / 迭代替换递归
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/Iteration
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/search?q=Iteration
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Iterators_and_Generators
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/KeyframeEffect/iterationComposite
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Iteration_protocols
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Loops_and_iteration
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/caller
tail-call optimization / 尾调用优化
Hardware Acceleration / 硬件加速 ❓
WebAssembly / WebGL / Web API (requestAnimationFrame / cancelAnimationFrame ...)
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Performance/Animation_performance_and_frame_rate
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/window/requestAnimationFrame
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/cancelAnimationFrame
demos
fibonacci / 斐波那契
testCase fib(0) = 0
testCase fib(1) = 1
testCase fib(2) = 1
testCase fib(3) = 2
testCase fib(4) = 3
testCase fib(5) = 5
testCase fib(6) = 8
testCase fib(7) = 13
testCase fib(8) = 21
testCase fib(9) = 34
testCase fib(10) = 55
testCase fib(11) = 89
testCase fib(12) = 144
testCase fib(13) = 233
testCase fib(14) = 377
testCase fib(15) = 610
testCase fib(16) = 987
testCase fib(17) = 1597
testCase fib(18) = 2584
testCase fib(19) = 4181
testCase fib(20) = 6765
testCase fib(21) = 10946
testCase fib(22) = 17711
testCase fib(23) = 28657
testCase fib(24) = 46368
testCase fib(25) = 75025
testCase fib(26) = 121393
testCase fib(27) = 196418
testCase fib(28) = 317811
testCase fib(29) = 514229
testCase fib(30) = 832040
testCase fib(31) = 1346269
testCase fib(32) = 2178309
testCase fib(33) = 3524578
testCase fib(34) = 5702887
testCase fib(35) = 9227465
testCase fib(36) = 14930352
testCase fib(37) = 24157817
testCase fib(38) = 39088169
testCase fib(39) = 63245986
testCase fib(40) = 102334155
testCase fib(41) = 165580141
testCase fib(42) = 267914296
testCase fib(43) = 433494437
testCase fib(44) = 701408733
testCase fib(45) = 1134903170
testCase fib(46) = 1836311903
testCase fib(47) = 2971215073
testCase fib(48) = 4807526976
testCase fib(49) = 7778742049
testCase fib(50) = 12586269025
- recursion / 递归
// n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... n
// fib(n) 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 ... n
// 1. 递归
function fib(n) {
if(n < 2) {
return n;
}
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
function autoTest(fn, n) {
const testCases = [...new Uint8Array(n + 1)].map((item, i) => i);
console.clear();
const start = performance.now();
for (const testCase of testCases) {
console.log(`testCase fib(${testCase}) =`, fn(testCase));
}
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`total time used: ${(end - start) / 1000}s`);
}
// n <= 30
// n <= 60
// n <= 100
autoTest(fib, 50);
fib(49)
total time used: 306.43480000001193s ❌
fib(50)
total time used: 547.9031000000239s ❌
- iteration / 迭代
// n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... n
// fib(n) 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 ... n
// 2. 迭代
function fib(n) {
if(n < 2) {
return n;
}
let n1 = 0;
let n2 = 1;
while(n >= 2) {
// swap
[n2, n1] = [n1 + n2, n2];
n--;
}
return n2;
}
function autoTest(fn, n) {
const testCases = [...new Uint8Array(n + 1)].map((item, i) => i);
console.clear();
const start = performance.now();
for (const testCase of testCases) {
console.log(`testCase fib(${testCase}) =`, fn(testCase));
}
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`total time used: ${(end - start) / 1000}s`);
}
// n <= 30
// n <= 60
// n <= 100
autoTest(fib, 50);
total time used: 0.002100000023841858s

- memory cached
// n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... n
// fib(n) 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 ... n
// 3. 内存缓存
function fib(n, cache) {
cache = cache ?? {};
if(n < 2) {
return n;
}
if(!cache[n]) {
cache[n] = fib(n - 1, cache) + fib(n - 2, cache);
}
return cache[n];
}
function autoTest(fn, n) {
const testCases = [...new Uint8Array(n + 1)].map((item, i) => i);
console.clear();
const start = performance.now();
for (const testCase of testCases) {
console.log(`testCase fib(${testCase}) =`, fn(testCase));
}
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`total time used: ${(end - start) / 1000}s`)
}
// n <= 30
// n <= 60
// n <= 100
autoTest(fib, 50);
total time used: 0.001899999976158142s
- tail-call optimization
// n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... n
// fib(n) 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 ... n
// IIFE
(() => {
"use strict";
// 4. 尾调用优化
function fib(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
if (n === 0) {
return pre;
// return n;
}
if (n === 1) {
return cur;
}
return fib(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
function autoTest(fn, n) {
const testCases = [...new Uint8Array(n + 1)].map((item, i) => i);
console.clear();
const start = performance.now();
for (const testCase of testCases) {
console.log(`testCase fib(${testCase}) =`, fn(testCase));
}
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`total time used: ${(end - start) / 1000}s`)
}
// n <= 30
// n <= 60
// n <= 100
autoTest(fib, 50);
})();
total time used: 0.001699999988079071s
// IIFE
(() => {
"use strict";
// 4. 尾调用优化
function fib(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
if (n === 0) {
return pre;
// return n;
}
if (n === 1) {
return cur;
}
return fib(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
// function fib(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
// // ??? pre, cur 没有缓存 ❌
// if (n === 0) {
// return 0;
// }
// if (n === 1) {
// return 1;
// }
// return fib(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
// }
// function fib(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
// // ??? n 没有缓存 ❌
// if(n < 2) {
// return n;
// }
// return fib(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
// }
// function fib(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
// if(n < 2) {
// return n;
// }
// // swap
// [pre, cur] = [cur, cur + pre];
// return fib(n - 1, pre, cur);
// }
function autoTest(fn, n) {
const testCases = [...new Uint8Array(n + 1)].map((item, i) => i);
console.clear();
const start = performance.now();
for (const testCase of testCases) {
console.log(`testCase fib(${testCase}) =`, fn(testCase));
}
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`total time used: ${(end - start) / 1000}s`)
}
autoTest(fib, 50);
})();
total time used: 0.001599999964237213s
没有缓存 bug ??? stackoverflow ???
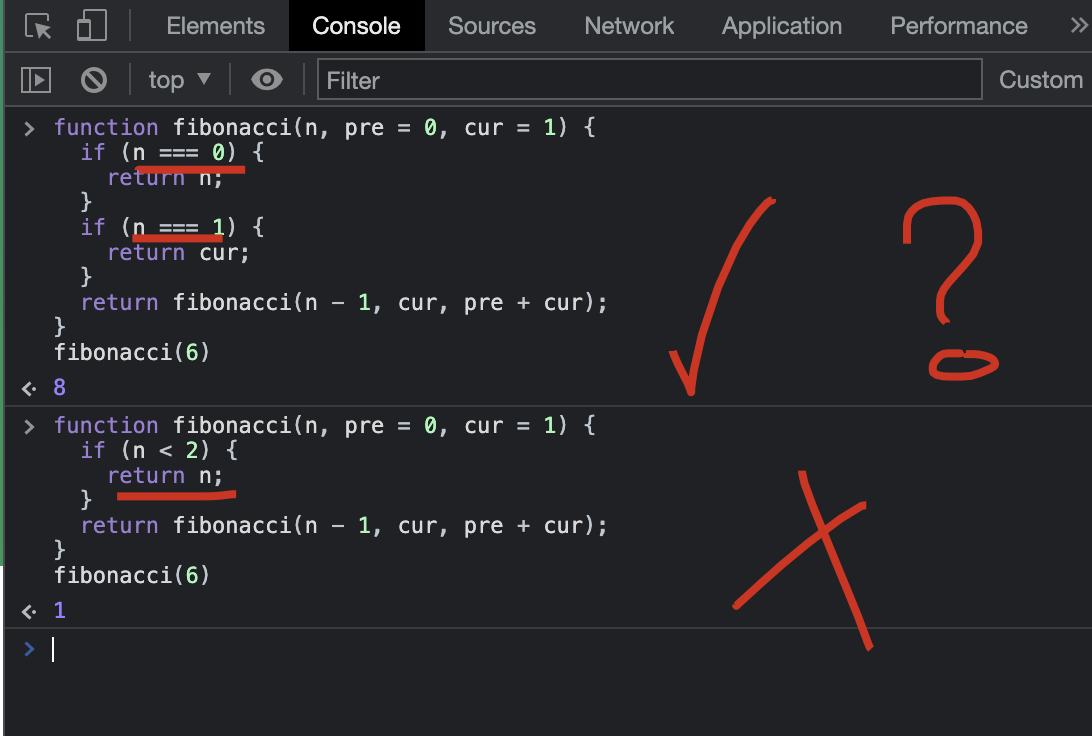
function fibonacci(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
// ✅
if (n === 0) {
return n;
}
// ✅
if (n === 1) {
return cur;
}
return fibonacci(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
fibonacci(6)
// 8 ✅
function fibonacci(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
// n 没有缓存 ❌
if (n < 2) {
return n;
}
return fibonacci(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
fibonacci(6)
// 1 ❌
js tail-call-optimization fibonacci
ES6
(function(){
function fib(n, sum=0, prev=1) {
if (n <= 1) return sum;
return fib(n-1, prev+sum, sum);
}
})();
https://medium.com/hackernoon/es6-tail-call-optimization-43f545d2f68b
// After modification
'use strict'
function fibonacci(n, pre, cur) {
if (n === 0) {
return n;
}
if (n === 1) {
return cur;
}
return fibonacci(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
// call
fibonacci(6, 0, 1)
'use strict'
function fibonacci(n, pre = 0, cur = 1) {
if (n === 0) {
return n;
}
if (n === 1) {
return cur;
}
return fibonacci(n - 1, cur, pre + cur);
}
fibonacci(6)
https://programmer.group/optimize-fibonacci-function-with-tail-recursion.html
ES5
function fib(n) {
return function(n,a,b) {
return n>0 ? arguments.callee(n-1, b, a+b) : a;
} (n,0,1);
}
function fib(n) {
function recur(n, a, b) {
if (n > 0) {
return recur(n - 1, b, a + b);
} else {
return a;
}
}
return recur(n, 0, 1);
}
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6877213/tail-recursion-and-fibonacci
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Fibonacci_sequence#JavaScript
严格模式 "use strict";
ES6 尾调用优化只在严格模式下开启,正常模式是无效的。
这是因为在正常模式下,函数内部有两个变量,可以跟踪函数的调用栈。
arguments:返回调用时函数的参数。
func.caller:返回调用当前函数的那个调用者函数。
尾调用优化发生时,函数的调用栈会改写,因此上面两个变量就会失真。
严格模式禁用这两个变量,所以尾调用模式仅在严格模式下生效。
factorial / 阶乘
https://www.shuxuele.com/numbers/factorial.html
// 阶乘函数(符号:!)的意思是把逐一减小的自然数序列相乘
function factorial(n) {
if(n === 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * factorial(n - 1);
};
// 尾调用优化 / 尾递归优化
function factorial(n, multi = 1) {
if(n === 1) {
return multi;
}
multi = n * multi;
return factorial(n - 1, multi);
};
阶乘,
科学计数法ebug ❌
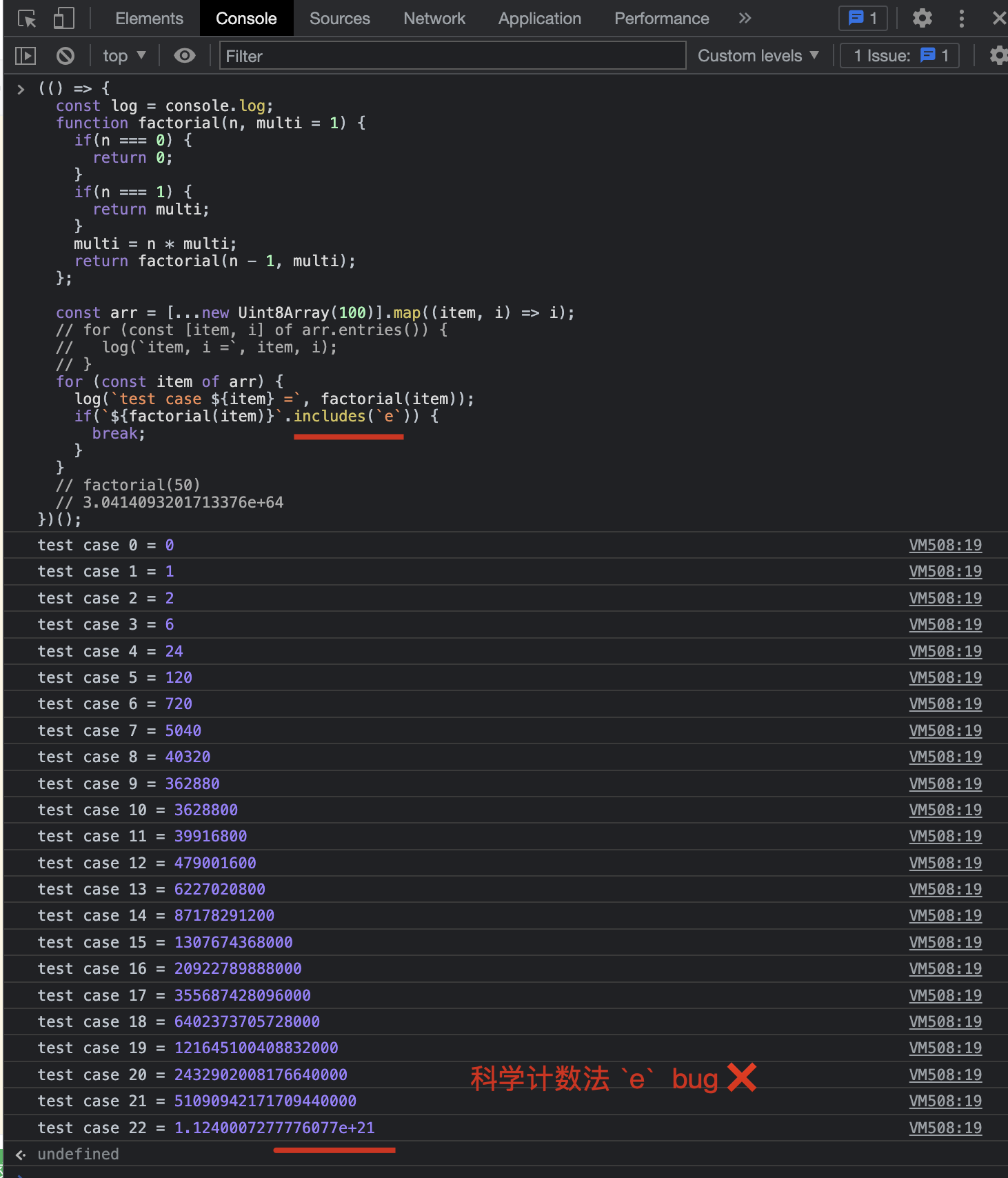
(() => {
const log = console.log;
function factorial(n, multi = 1) {
if(n === 0) {
return 0;
}
if(n === 1) {
return multi;
}
multi = n * multi;
return factorial(n - 1, multi);
};
const arr = [...new Uint8Array(100)].map((item, i) => i);
// for (const [item, i] of arr.entries()) {
// log(`item, i =`, item, i);
// }
for (const item of arr) {
log(`test case ${item} =`, factorial(item));
if(`${factorial(item)}`.includes(`e`)) {
break;
}
}
// factorial(50)
// 3.0414093201713376e+64
})();
(() => {
const log = console.log;
function factorial(n, multi = 1) {
if(n === 0) {
return 0;
}
if(n === 1) {
return multi;
}
multi = n * multi;
return factorial(n - 1, multi);
};
const arr = [...new Uint8Array(100)].map((item, i) => i);
// for (const [item, i] of arr.entries()) {
// log(`item, i =`, item, i);
// }
for (const item of arr) {
log(`testCase factorial(${item}) =`, factorial(item));
if(`${factorial(item)}`.includes(`e`)) {
break;
}
}
// factorial(50)
// 3.0414093201713376e+64
// 阶乘, `科学计数法` `e` bug ❌
})();
https://leetcode.cn/problems/factorial-trailing-zeroes/
https://leetcode.com/problems/factorial-trailing-zeroes/
refs
https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/04/tail-call.html
https://2ality.com/2015/06/tail-call-optimization.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37224520/are-functions-in-javascript-tail-call-optimized
https://javascript.plainenglish.io/javascript-optimizations-tail-call-optimization-tco-471b4f8e4f37
https://juejin.cn/post/6972036399503507487
©xgqfrms 2012-2020
www.cnblogs.com/xgqfrms 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 ️,侵权必究⚠️!