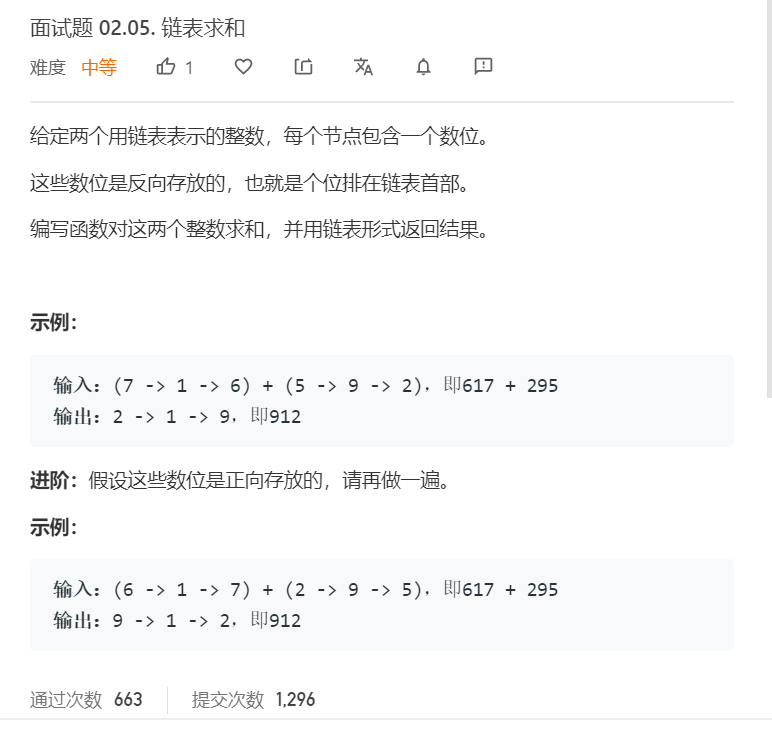
面试题 02.05. 链表求和
1、题目描述
-
给定两个用链表表示的整数,每个节点包含一个数位。
-
这些数位是反向存放的,也就是个位排在链表首部。
-
编写函数对这两个整数求和,并用链表形式返回结果。
试题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-lists-lcci/
2、java题解一(未通过):
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pCurrent = l1;
//遍历
int index = 0;
int num1 = 0;
while(pCurrent != null) {
int num = pCurrent.val; //个、十、百依次
num1 += num * Math.pow(10,index);
index++;
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
}
//重复
pCurrent = l2;
index = 0;
int num2 = 0;
while(pCurrent != null) {
int num = pCurrent.val; //个、十、百依次
num2 += num * Math.pow(10,index);
index++;
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
}
//进行相加
int sum = num1 + num2;
// System.out.println(sum);
//将数字拆分,转换为链表 912 2 91 1 9 9 0
ListNode listNode = new ListNode(sum % 10);
sum = sum / 10;
pCurrent = listNode;
while (sum != 0) {
int x = sum % 10;
pCurrent.next = new ListNode(x);
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
sum = sum / 10;
}
return listNode;
}
测试结果:
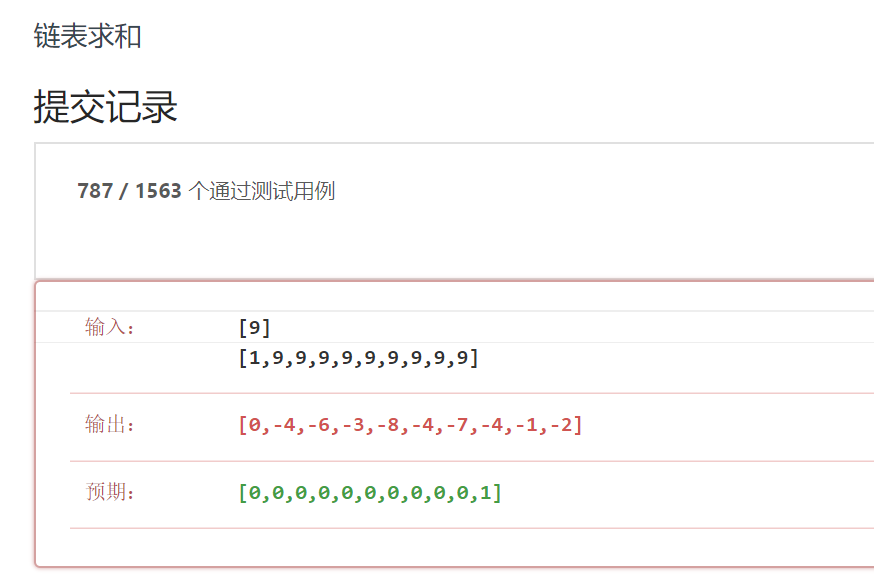
因为测试数值较大,int类型无法正确的进行保存,故出现了错误。将int类型改为long类型,在进行测试。
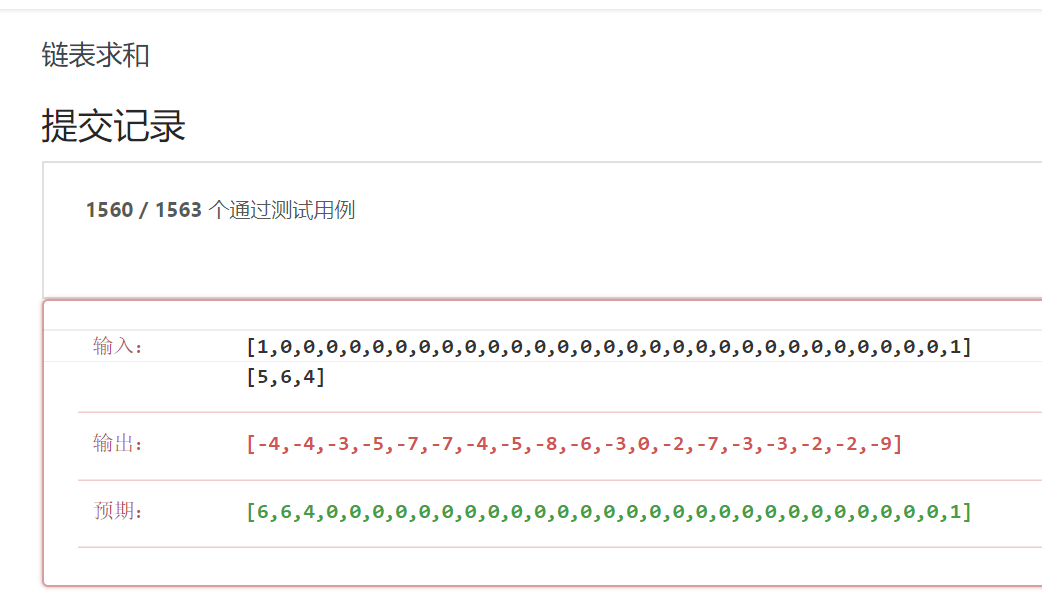
发现所测试的数据远远比我们想想的大,因此我们得另辟蹊径。
3、java题解二
考虑到该算法有超大规模的测试数据,我们引入了BigInteger这个类,来进行测试。
import java.math.BigInteger;
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pCurrent = l1;
//遍历
String num1 = "";
while(pCurrent != null) {
int num = pCurrent.val; //个、十、百依次
num1 += num;
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
}
//重复
pCurrent = l2;
String num2 = "";
while(pCurrent != null) {
int num = pCurrent.val; //个、十、百依次
num2 += num;
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
}
//逆序遍历,进行相加
String newNum1 = "";
for(int i = 0;i < num1.length();i++) {
newNum1 += num1.charAt(num1.length() - 1 - i);
}
String newNum2 = "";
for(int i = 0;i < num2.length();i++) {
newNum2 += num2.charAt(num2.length() - 1 - i);
}
// System.out.println(newNum1);
// System.out.println(newNum2);
BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger(newNum1);
BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger(newNum2);
BigInteger sum = bigInteger1.add(bigInteger2);
String sumStr = sum.toString();
ListNode saveNode = new ListNode(sumStr.charAt(sumStr.length() - 1) - 48);
pCurrent = saveNode;
for(int i = 1;i < sumStr.length();i++) {
pCurrent.next = new ListNode(sumStr.charAt(sumStr.length() - 1 - i) - 48);
pCurrent = pCurrent.next;
}
return saveNode;
}
}
测试结果:
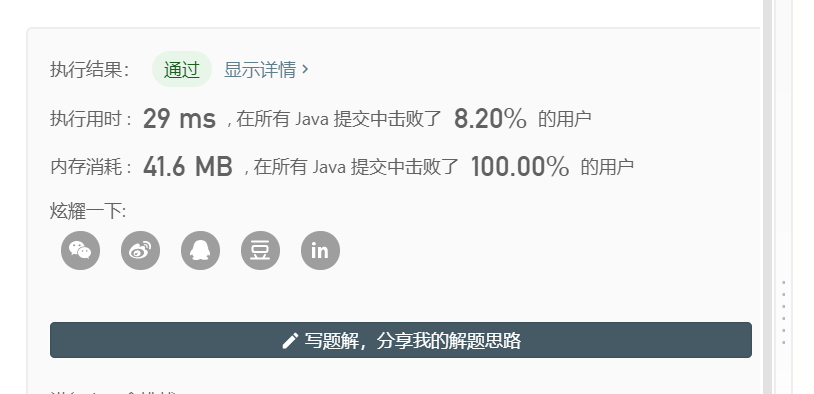
可以看到,该算法的用时较长,且如果改写成C语言代码时,我们并没有BigInteger这个类。
4、java题解三
对此,我们像将链表拆分,引入对位相加的计算策略。
ListNode list = new ListNode(-1); //定义输出链表
ListNode p = list;
int num = 0; //进位数字
int x = 0; //记录l1链表的值
int y = 0; //记录12链表的值
//遍历两个链表
while(l1 != null ||l2 != null) {
x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = x + y + num;
if(sum < 10) {
p.next = new ListNode(sum);
num = 0;
}else {
p.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
num = sum / 10;
}
if(l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
p = p.next;
}
if (num != 0) p.next = new ListNode(num);
return list.next;
测试结果:

可以看到,对于该算法,在java中的运行效率还是可以的。
5、C语言题解
struct ListNode* list = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
list->val = -1; //定义输出链表
list->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* p = list;
int num = 0; //进位数字
int x = 0; //记录l1链表的值
int y = 0; //记录12链表的值
//遍历两个链表
while(l1 != NULL ||l2 != NULL) {
x = l1 == NULL ? 0 : l1->val;
y = l2 == NULL ? 0 : l2->val;
int sum = x + y + num;
if(sum < 10) {
struct ListNode* temp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
temp->val = sum;
temp->next = NULL;
p->next = temp;
num = 0;
}else {
struct ListNode* temp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
temp->val = sum % 10;
temp->next = NULL;
p->next = temp;
num = sum / 10;
}
if(l1 != NULL) l1 = l1->next;
if(l2 != NULL) l2 = l2->next;
p = p->next;
}
if (num != 0) {
struct ListNode* temp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
temp->val = num;
temp->next = NULL;
p->next = temp;
}
return list->next;
测试结果:
可以看到,在C语言中,该算法的计算效率偏低。