这章内容就是“provides a whirlwind tour of the UNIX System from a programmer's perspective”。
其实在看这章内容的时候,已经先看过了Chapter7~Chapter13,回头再看看这样的综述介绍。
1.2 UNIX Architecture
主要就了解下面这张图即可:
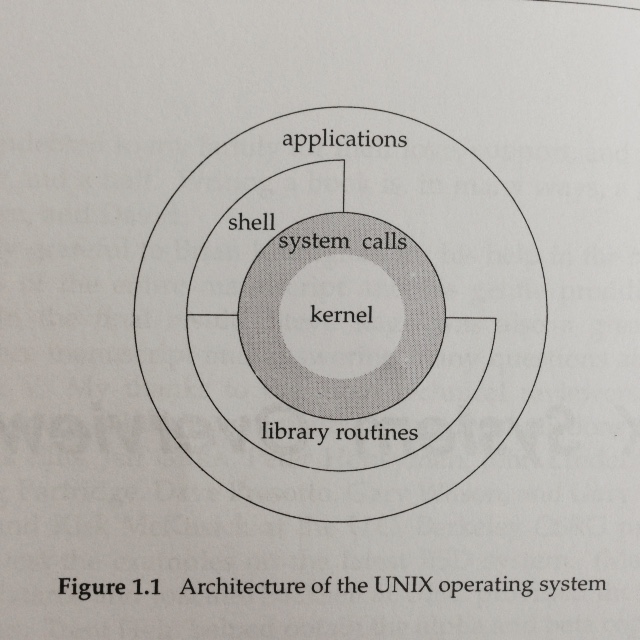
在一般UNIX operating system中谁在哪层来调用谁。
1.3 Logging In
操作系统根据/etc/passwd中的信息来判断logging in信息是否匹配。
每一行代表一个用户登录信息,举例:

一般分为七个部分,用冒号分割:
login name
encrypted password
numeric user ID
numeric group ID
a comment field(这个field在例子中为空)
home directory
shell programm
1.4 Files and Directories
这个部分给出了第一份代码的例子。通过这个20行代码的例子,交代了不少东西:
man命令怎么用
头文件apue.h是干啥的
错误处理函数err_sys和err_quit函数都是干啥的
...
看了之后,给我的感觉是作者安排每个例子都是用心的,尤其在书一开始的地方都把一些书上之后常用的内容交代清楚,让人看的很明白。
1.5 Input and Output
(1)File Descriptors定义(先记着,有个念想): "normally small non-negative integers that the kernel uses to identify the files accessed by a process. Whenever it opens an existing file or creates a new file, the kernel returns a file descriptor that we use when we want to read or write the file."
(2)Standard Input , Standard Output & Standard Error
(3)Unbuffered I/O:open read write lseek close都是,并且这些函数都跟file descriptors协作。看到这里对书上的例子瞬间产生了一个误解:不是说是unbuffered了么,怎么还有read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, BUFFSIZE)这样的形式呢?我没有看过后面的部分,但是猜测这里说的unbuffered是不用fflush刷新缓冲区的,具体的后面再看。
(4)Standard I/O:就是提供了一个buffered的接口来调用各种unbuffered I/O函数,函数包含在头文件<stdio.h>中。
1.6 Programs and Processes
(1)Program:磁盘上的可执行文件;执行的时候先读入内存,然后由kernel调用exec函数执行之。
(2)Processes and Process ID:正在执行的program示例就叫process;unix系统的进程号非负整数
(3)Process Control:fork ,exec, waitpid
(4)Thread and Thread IDs
1.7 Error Handling
(1)一般遇到error了,unix系统就返回一个负整数;不同的负整数标示不同类型的错误
(2)<errno.h>头文件中有“symbol errno and constants for each value that errno can assume”,每个符号都以E开头;可以用man 3 errno来查看具体代表意思。
(3)考虑到多线程的情况,是贡献进程中的address space的,每个线程要有独立的errno就需要其他的定义方法,如下图:
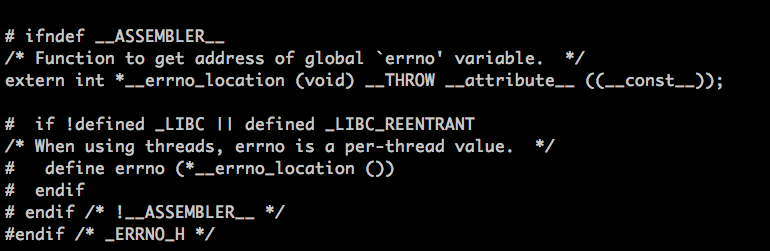
具体参考的是/usr/includes/bits/errno.h头文件中的定义
(4)strerror函数把错误变量映射到错误信息字符串;perror可以接受一个参数(一般是program的名),并将出错信息输出到standard error上。
(5)error recovery。fatal error么有recovery action;nonfatal error有recovery action。跟资源相关的nonfatal error的recovery的策略分两种:一种是等;一种是重试。
1.8 User Identification
1.9 Sginals
Signals are a technique used to notify a process that some condition has occurred
1.10 Time Values
unix系统有两类不同的时间变量:
(1)Calendar time:1970.1.1零点开始到现在的秒数
(2)Process time:CPU time(在多线程那章的时候用到过)
注意相对时间和绝对时间;另外如果是多核的条件,时间统计时候与单核的情况可能不一样
1.11 System Calls and Library Functions
具体可以参照1.2中的那张图理解。对于application的级别来说,即可以直接用system call也可以用libarary functions。
书上举了一个内存分配的malloc(2)函数与sbrk(3)的例子。