1. Bipartite:
Determine if an undirected graph is bipartite. A bipartite graph is one in which the nodes can be divided into two groups such that no nodes have direct edges to other nodes in the same group.
Examples
1 -- 2
/
3 -- 4
is bipartite (1, 3 in group 1 and 2, 4 in group 2).
1 -- 2
/ |
3 -- 4
is not bipartite.
Assumptions
- The graph is represented by a list of nodes, and the list of nodes is not null.
分析:
- 假设两个组:0和1
- 定义一个hashmap来存放graphNode和组号,并且可以用.containskey()来确定它有没有被访问过
- 从第一个Node开始expand,然后去看它的邻居是否被visited过:1. 如果有那就看它的key(组号)是不是和这个Node相等,如果相等,直接返回false;如果不想等,ignore;
2. 如果没有,那就把它存入hashmap中,它的key(组号)和这个Node相反
- 有任何一个node返回false就可以直接返回false了
- 全部走完,都没有false,那就true
代码如下:

public class GraphNode { public int key; public List<GraphNode> neighbors; public GraphNode(int key) { this.key = key; this.neighbors = new ArrayList<GraphNode>(); } } public class Solution { public boolean isBipartite(List<GraphNode> graph) { // write your solution here HashMap<GraphNode, Integer> visited = new HashMap<GraphNode, Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++) { boolean res = BFS(graph.get(i), visited); if(res == false) { return false; } } return true; } private boolean BFS(GraphNode node, HashMap<GraphNode, Integer> visited) { //if this node has been searched, then it does not need to be searched again if(visited.containsKey(node)) { return true; } //two group:0,1 Queue<GraphNode> q = new LinkedList<GraphNode>(); q.offer(node); visited.put(node, 0);//mark the node as group 0 //generate its neighbor while(!q.isEmpty()) { GraphNode cur = q.poll(); for(GraphNode neighbor : cur.neighbors) { if(!visited.containsKey(neighbor)) { if(visited.get(cur) == 0) { visited.put(neighbor, 1); }else { visited.put(neighbor, 0); } q.offer(neighbor); }else { if(visited.get(neighbor) == visited.get(cur)) { return false; } } } } return true; } }
2. Dijkstra's Algorithm:
find the shortest path cost from a single node to any other nodes in that graph
主要用到的数据结构是priority queue
Initial state: start node
Node expansion/generation node:这里的expansion相当于pop,generation相当于push
termination condition:所有点都计算完毕,也就是p_queue为空
具体思路如下:
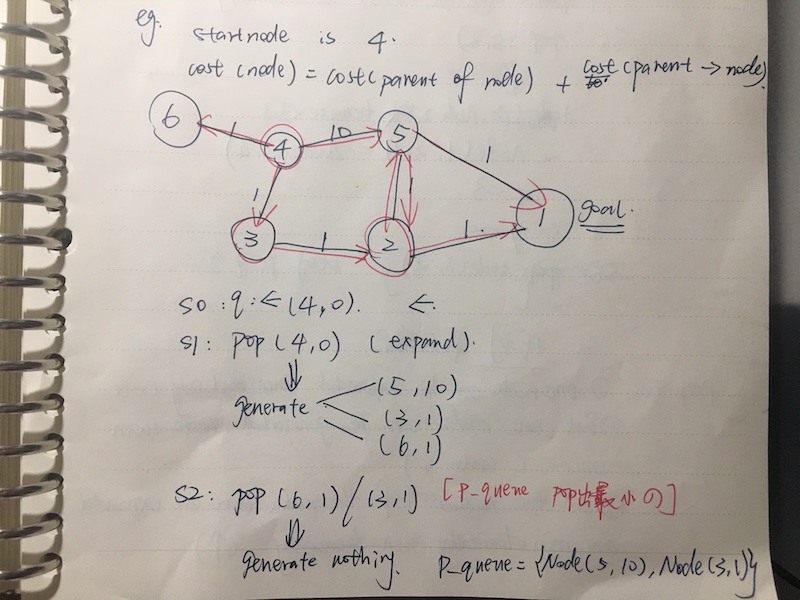

特性:1. 一个node只能被expand有且只有一次
2. 但是一个node可以被generate多次,且每次cost都减少
3. 所有被expanded的node都是单调递增的:因为每次pop()出来最小的元素,所以按从小到大pop
4. TC=O(nlogn),n个node,pop n次,每次logn
5. 当一个node被pop出来的时候,它的cost是它的最短距离
* how to find the shortest path between a pair of node: terminate condition: when the targer node is expanded
应用:Kth smallest number in sorted matrix
Given a matrix of size N x M. For each row the elements are sorted in ascending order, and for each column the elements are also sorted in ascending order. Find the Kth smallest number in it.
例如:
{ {1, 3, 5, 7},
{2, 4, 8, 9},
{3, 5, 11, 15},
{6, 8, 13, 18} }
- the 5th smallest number is 4
- the 8th smallest number is 6
思路:
1. Initial state:matrix[0][0]
2. node expansion/generate rule:
expand node[i][j]
generate node[i+1][j] node[i][j+1]
3. terminate condition:Kth smallest number pop出
- 由于可能有重复元素,我们定义一个boolean[][] visited来记录这个点是否被visited过
- 为了方便记录每一个元素的坐标,写一个class graph,里面有这个点的横纵坐标和大小
- 因为要用minHeap,所以要override比较器
- BFS
- generate node的条件是1. 不越界 2. 没有被visited过
代码如下:

public class kSmalleasMatrix { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //[[[1,3,5,7],[2,4,8,9],[3,5,11,15],[6,8,13,18]],16] int[][] matrix = {{1,3,5,7}, {2,4,8,9}, {3,5,11,15}, {6,8,13,18}}; int k = 16; System.out.println(kthSmallest(matrix, k)); } public static int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) { int col = matrix[0].length; int row = matrix.length; Queue<graph> heap=new PriorityQueue<>(new MyComparator()); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[row][col]; int count = 1; heap.offer(new graph(0, 0, matrix[0][0])); visited[0][0] = true; while(count < k) { graph cur = heap.poll(); if(cur.row + 1 < row && !visited[cur.row + 1][cur.col]) { heap.offer(new graph(cur.row + 1, cur.col, matrix[cur.row + 1][cur.col])); visited[cur.row + 1][cur.col] = true; } if(cur.col + 1 < col && !visited[cur.row][cur.col + 1]) { heap.offer(new graph(cur.row, cur.col + 1, matrix[cur.row][cur.col + 1])); visited[cur.row][cur.col + 1] = true; } count++; } return heap.poll().value; } } class graph { int row; int col; int value; graph(int row, int col, int value) { this.row = row; this.col = col; this.value = value; } } class MyComparator implements Comparator<graph>{ @Override//Annotation,告诉编译器这是一个重写的 public int compare(graph c1, graph c2) { if(c1.value == c2.value) { return 0; } return c1.value < c2.value ? -1 : 1; } }
