一、前言
前面我们已经分析了HashMap的源码,已经知道了HashMap可以用在哪种场合,如果这样一种情形,我们需要按照元素插入的顺序来访问元素,此时,LinkedHashMap就派上用场了,它保存着元素插入的顺序,并且可以按照我们插入的顺序进行访问。
二、LinkedHashMap用法

import java.util.Map;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> maps = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
maps.put("aa", "aa");
maps.put("bb", "bb");
maps.put("cc", "cc");
for (Map.Entry entry : maps.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
说明:以上是展示LInkedHashMap简单用法的一个示例,可以看到它确实按照元素插入的顺序进行访问,保持了元素的插入顺序。更具体的用户可以去参照API。
三、LinkedHashMap数据结构
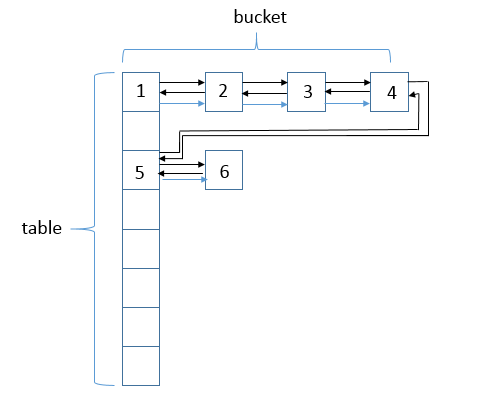
说明:LinkedHashMap会将元素串起来,形成一个双链表结构。可以看到,其结构在HashMap结构上增加了链表结构。数据结构为(数组 + 单链表 + 红黑树 + 双链表),图中的标号是结点插入的顺序。
四、LinkedHashMap源码分析
其实,在分析了HashMap的源码之后,我们来分析LinkedHashMap的源码就会容易很多,因为LinkedHashMap是在HashMap基础上进行了扩展,我们需要注意的就是两者不同的地方。
4.1 类的继承关系
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
说明:LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,所以HashMap的一些方法或者属性也会被继承;同时也实现了Map结构,关于HashMap类与Map接口,我们之前已经分析过,不再累赘。
4.2 类的属性

public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
// 版本序列号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
// 链表头结点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
// 链表尾结点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
// 访问顺序
final boolean accessOrder;
}
说明:由于继承HashMap,所以HashMap中的非private方法和字段,都可以在LinkedHashMap直接中访问。
4.3 类的构造函数
1. LinkedHashMap(int, float)型构造函数

public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
说明:总是会在构造函数的第一行调用父类构造函数,使用super关键字,accessOrder默认为false,access为true表示之后访问顺序按照元素的访问顺序进行,即不按照之前的插入顺序了,access为false表示按照插入顺序访问。
2. LinkedHashMap(int)型构造函数

public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
3. LinkedHashMap()型构造函数

public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
4. LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V>)型构造函数

public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
说明:putMapEntries是调用到父类HashMap的函数
5. LinkedHashMap(int, float, boolean)型构造函数

public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
说明:可以指定accessOrder的值,从而控制访问顺序。
4.4 类的重要函数分析
1. newNode函数

// 当桶中结点类型为HashMap.Node类型时,调用此函数
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
// 生成Node结点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
// 将该结点插入双链表末尾
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
说明:此函数在HashMap类中也有实现,LinkedHashMap重写了该函数,所以当实际对象为LinkedHashMap,桶中结点类型为Node时,我们调用的是LinkedHashMap的newNode函数,而非HashMap的函数,newNode函数会在调用put函数时被调用。可以看到,除了新建一个结点之外,还把这个结点链接到双链表的末尾了,这个操作维护了插入顺序。
其中LinkedHashMap.Entry继承自HashMap.Node

static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
// 前后指针
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
说明:在HashMap.Node基础上增加了前后两个指针域,注意,HashMap.Node中的next域也存在。
2. newTreeNode函数

// 当桶中结点类型为HashMap.TreeNode时,调用此函数
TreeNode<K,V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
// 生成TreeNode结点
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(hash, key, value, next);
// 将该结点插入双链表末尾
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
说明:当桶中结点类型为TreeNode时候,插入结点时调用的此函数,也会链接到末尾。
3. afterNodeAccess函数

void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
// 若访问顺序为true,且访问的对象不是尾结点
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
// 向下转型,记录p的前后结点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
// p的后结点为空
p.after = null;
// 如果p的前结点为空
if (b == null)
// a为头结点
head = a;
else // p的前结点不为空
// b的后结点为a
b.after = a;
// p的后结点不为空
if (a != null)
// a的前结点为b
a.before = b;
else // p的后结点为空
// 后结点为最后一个结点
last = b;
// 若最后一个结点为空
if (last == null)
// 头结点为p
head = p;
else { // p链入最后一个结点后面
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
// 尾结点为p
tail = p;
// 增加结构性修改数量
++modCount;
}
}
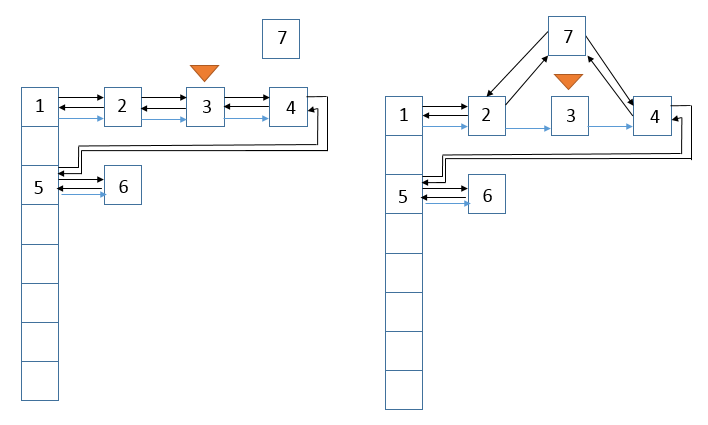
说明:此函数在很多函数(如put)中都会被回调,LinkedHashMap重写了HashMap中的此函数。若访问顺序为true,且访问的对象不是尾结点,则下面的图展示了访问前和访问后的状态,假设访问的结点为结点3

说明:从图中可以看到,结点3链接到了尾结点后面。
4. transferLinks函数

// 用dst替换src
private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> src,
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> dst) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> b = dst.before = src.before;
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> a = dst.after = src.after;
if (b == null)
head = dst;
else
b.after = dst;
if (a == null)
tail = dst;
else
a.before = dst;
}
说明:此函数用dst结点替换结点,示意图如下
说明:其中只考虑了before与after域,并没有考虑next域,next会在调用tranferLinks函数中进行设定。
5. containsValue函数

public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
// 使用双链表结构进行遍历查找
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
V v = e.value;
if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
说明:containsValue函数根据双链表结构来查找是否包含value,是按照插入顺序进行查找的,与HashMap中的此函数查找方式不同,HashMap是使用按照桶遍历,没有考虑插入顺序。
五、总结
在HashMap的基础上分析LinkedHashMap会容易很多,读源码好处多多,有时间的话,园友们也可以读读源码,感受一下来自java设计者的智慧。谢谢观看~
