---恢复内容开始---
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
|
|
作业学习目标 |
|
随笔博文正文内容包括:
实验内容和步骤
实验1:
在“System.out.println(...);”语句处按注释要求设计代码替换...,观察代码录入中IDE提示,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
|
class Parent { private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性"; public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性"; protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性"; String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性"; private void pMethod1() { System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void pMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void pMethod3() { System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void pMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } class Son extends Parent{ private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性"; public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性"; protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性"; String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性"; public void sMethod1() { System.out.println(...);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值 System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void sMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void sMethod() { System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void sMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); Son son=new Son(); System.out.println(...); //分别尝试用parent调用Paren类的方法、用son调用Son类的方法 } } |
将三个程序放入同一包中代码如下(parent类的private不可调用):
package project; class Parent { private String p1 "这是Parent的私有属性"; public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性"; protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性"; String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性"; private void pMethod1() { System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void pMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void pMethod3() { System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void pMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } class Son extends Parent{ private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性"; public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性"; protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性"; String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性"; public void sMethod1() { System.out.println(p2);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值 System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void sMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void sMethod() { System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void sMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); Son son=new Son(); System.out.println(parent.p2); System.out.println(parent.p3); System.out.println(parent.p4);//分别尝试用parent调用Paren类的方法、用son调用Son类的方法 System.out.println(son.p2); System.out.println(son.p3); System.out.println(son.p4); System.out.println(son.s2); System.out.println(son.s3); System.out.println(son.s4); parent.pMethod2(); son.pMethod2(); son.sMethod1(); } }
程序运行截图如下:
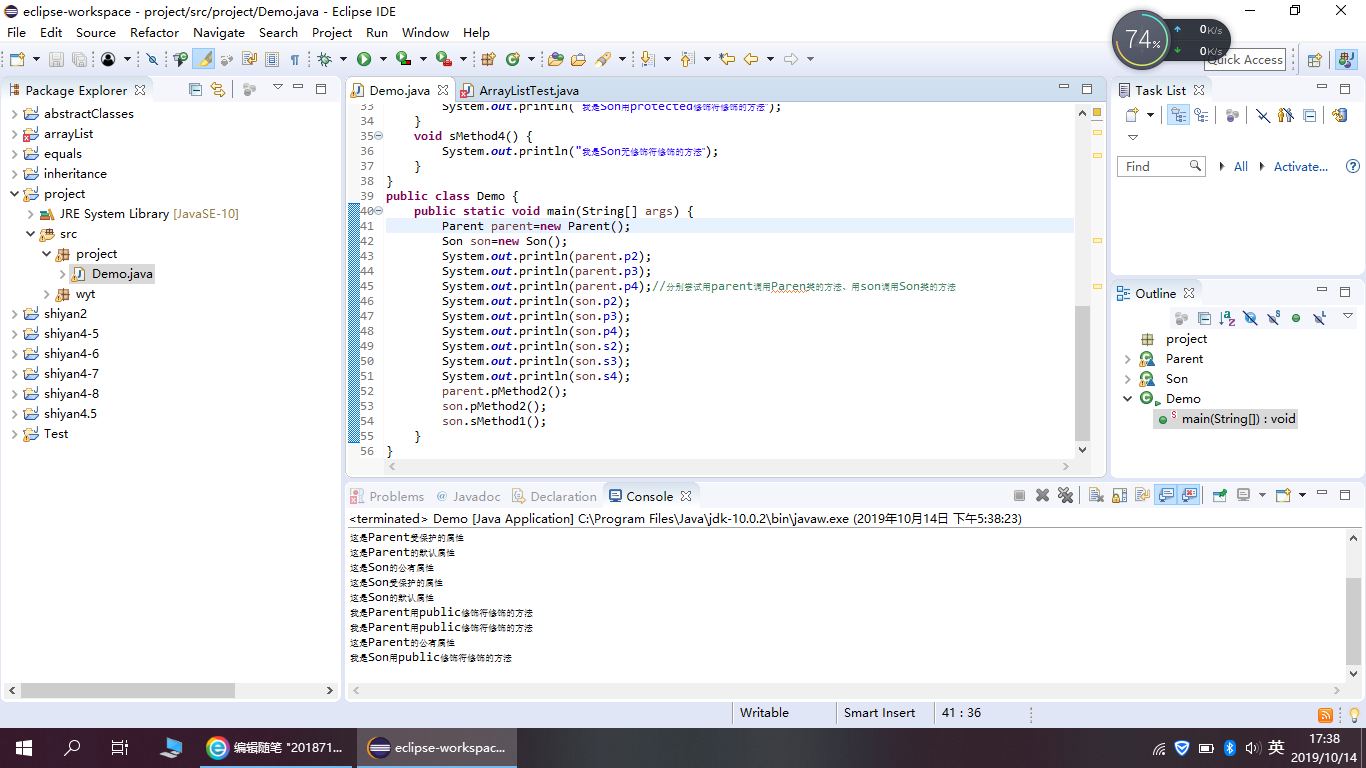
将parent类放入自己名字命名的包中,程序代码如下:
package wyt; public class Parent { private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性"; public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性"; protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性"; String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性"; private void pMethod1() { System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void pMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void pMethod3() { System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void pMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
程序运行截图如下:
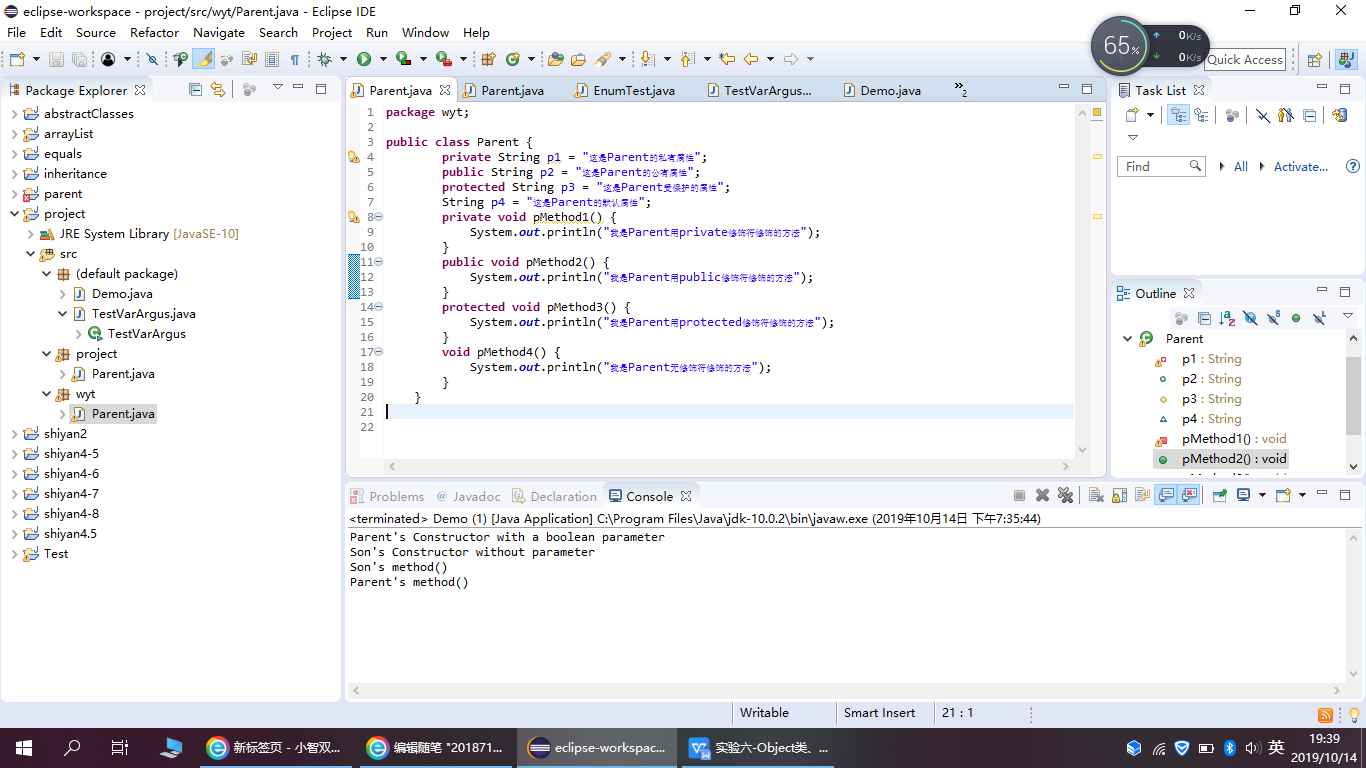
分开后实验代码如下:
package parent; public class Parent { private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性"; public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性"; protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性"; String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性"; private void pMethod1() { System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void pMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void pMethod3() { System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void pMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
package project; class Son extends Parent{ private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性"; public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性"; protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性"; String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性"; public void sMethod1() { System.out.println(p2);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值 System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void sMethod2() { System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void sMethod() { System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void sMethod4() { System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); Son son=new Son(); System.out.println(parent.p2); System.out.println(parent.p3); System.out.println(parent.p4);//分别尝试用parent调用Paren类的方法、用son调用Son类的方法 System.out.println(son.p2); System.out.println(son.p3); System.out.println(son.p4); System.out.println(son.s2); System.out.println(son.s3); System.out.println(son.s4); parent.pMethod2(); son.pMethod2(); son.sMethod1(); } }
程序运行结果如下:
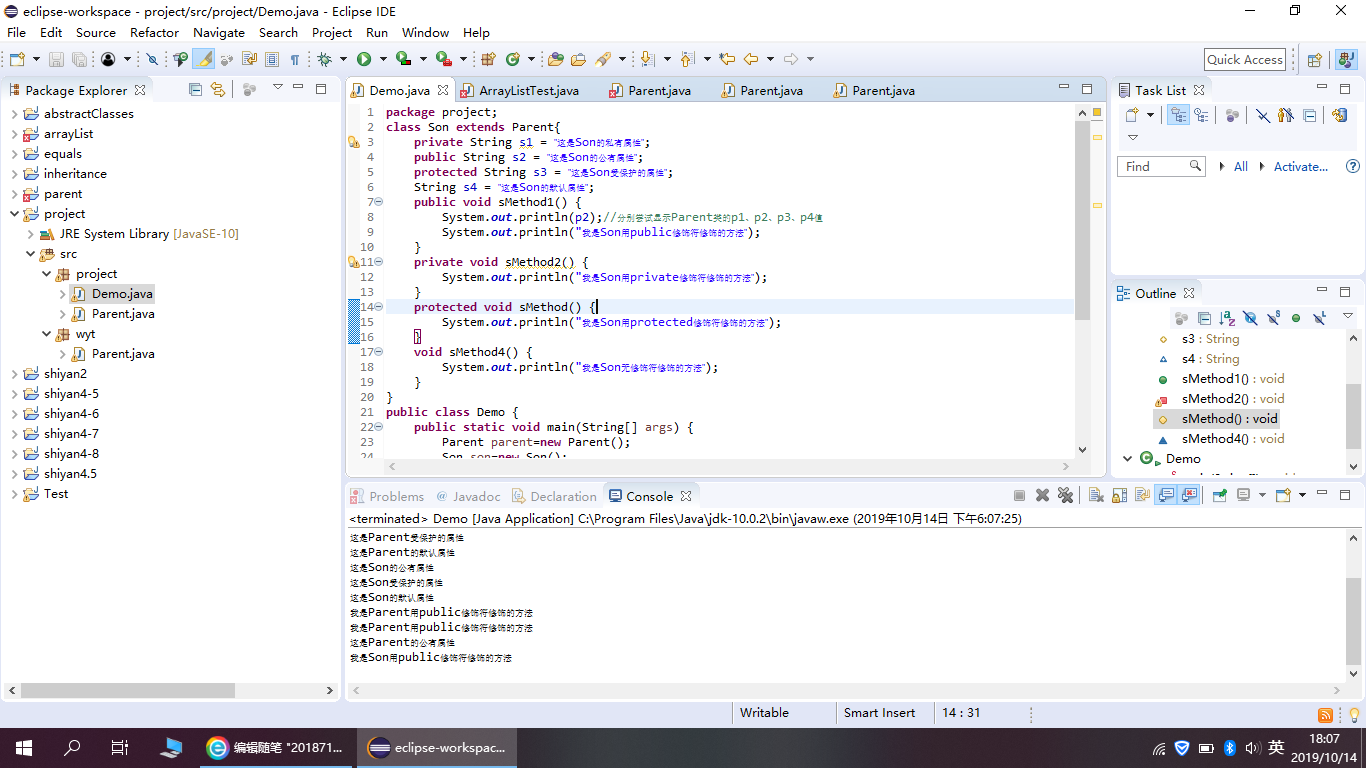
总结:Java四种权限修饰符包括:private、default、protected、public;
修饰符所能访问的目录结构如下图:
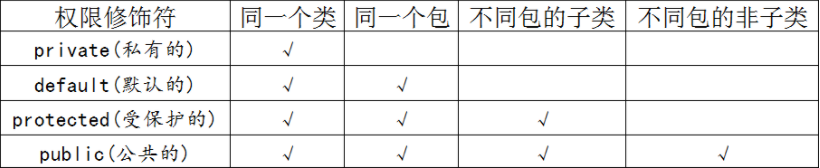
1)private: 私有权限修饰符,可以修饰构造方法、成员数据(成员变量和成员方法)、只能修饰内部类,不能修饰外部类。被private修饰的成员,只能在本类中使用,在其它类中不能被调用。
2)default:默认权限修饰符,默认权限即同包权限,同包权限的元素只能在本类或者同包的类中可以调用。
3)protected:受保护权限修饰符,被其修饰的类、属性以及方法只能被类本身的方法及子类访问,即使子类在不同的包中也可以访问。
4)public:公共权限,public可以修饰类、构造方法、成员数据(成员变量和成员方法),被public修饰的成员,可以在任何一个类中被调用,不管同包或不同包,是权限最大的一个修饰符。
测试程序1:实验2:导入第5章以下示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
l 运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
l 删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法,在代码录入中理解类中重写Object父类方法的技术要点。
例题5.8程序代码如下:
package equals; /** * This program demonstrates the equals method. * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { var alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);//对alice1进行初始化 var alice2 = alice1;//将alice1的值赋给alice2 var alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);//对alice3进行初始化 var bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); var carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000); System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); } }
程序运行截图如下:
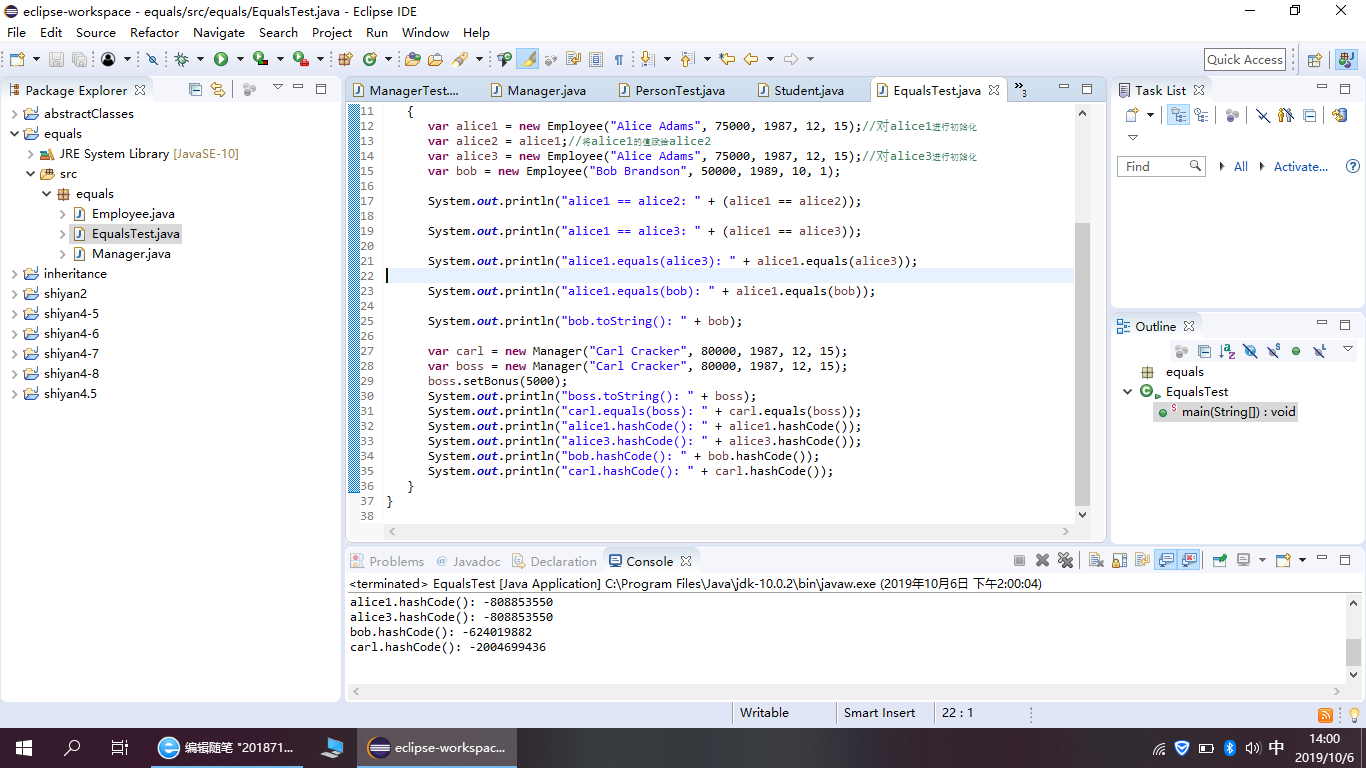
例题5.9程序代码如下
package equals; import java.time.*; import java.util.Objects; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; //构建成员变量 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } //域访问器 public String getName()//取得name这个属性的值 { return name; } public double getSalary()//取得Salary这个属性的值 { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { // a quick test to see if the objects are identical if (this == otherObject) return true;//判断两个引用是否是同一个 // must return false if the explicit parameter is null if (otherObject == null) return false;// // 若参数为空,则返回false // if the classes don't match, they can't be equal if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;//getClass():得到对象的类 // now we know otherObject is a non-null Employee var other = (Employee) otherObject; // test whether the fields have identical values return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); } public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]"; } }
程序运行截图如下:
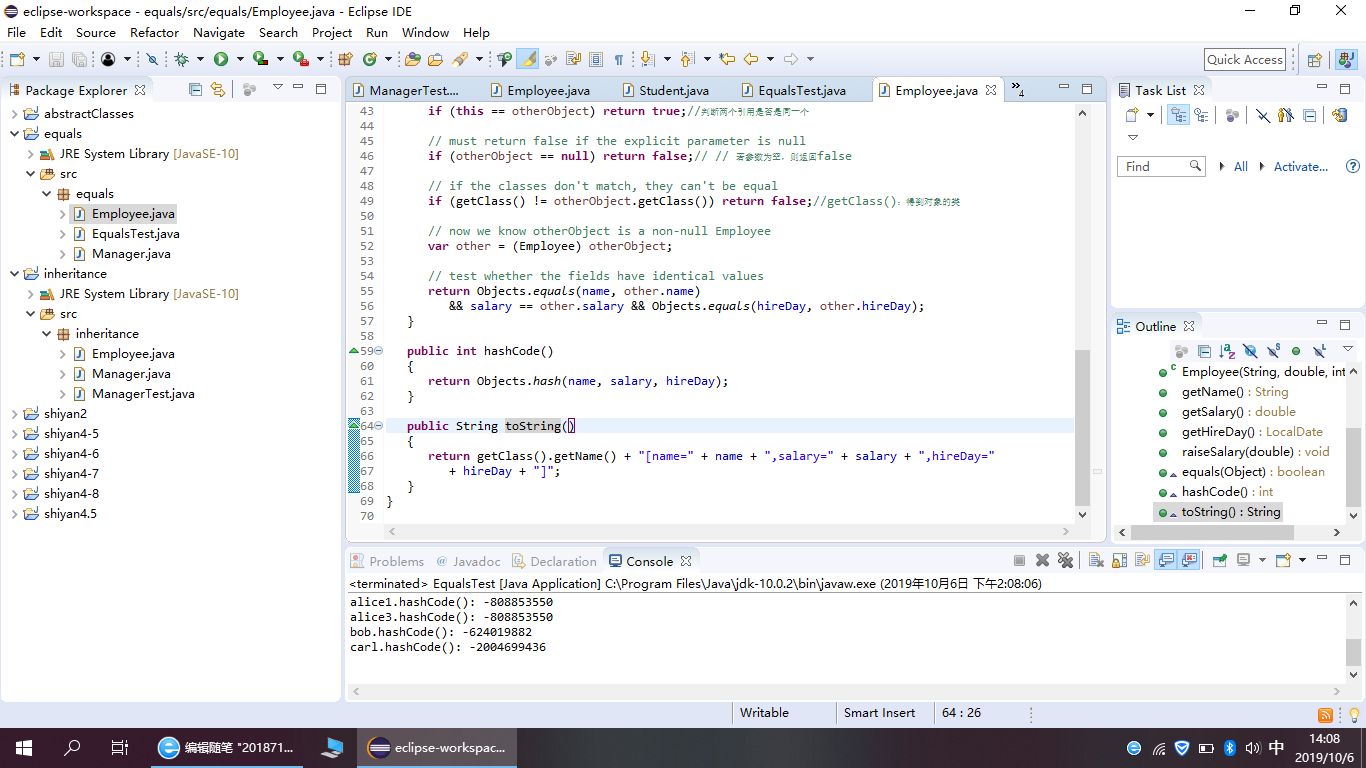
例题5.10程序代码如下:
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double bonus) { this.bonus = bonus; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; var other = (Manager) otherObject; // super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same classs //检查是否属于同一类 return bonus == other.bonus; } public int hashCode() { return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); } public String toString() { return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; } }
程序运行截图如下:
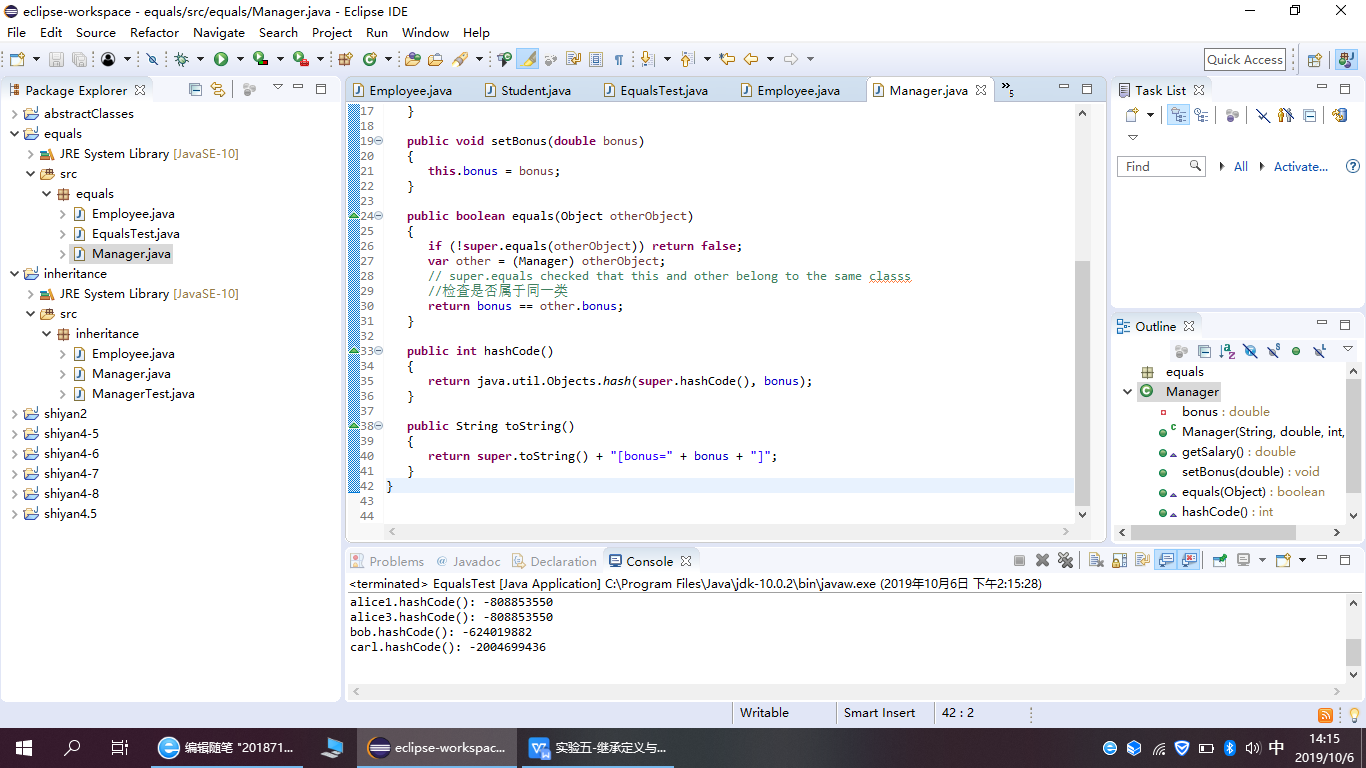
删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法,在代码录入中理解类中重写Object父类方法的技术要点。
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行程序5-11(教材182页),结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 设计适当的代码,测试ArrayList类的set()、get()、remove()、size()等方法的用法。
例题5.11程序代码如下(arrayList):
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array list with three Employee objects // 声明和构造一个保存Employee对象的数组列表 var staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15));//添加元素 // raise everyone's salary by 5% //把每个人的工资提高5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects //打印有关所有员工对象的信息 for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }
实验运行截图如下:
例题5.11程序代码如下():
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; //构造器 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } //三个实例域用来存放将要操作的数据 public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
程序运行截图如下:
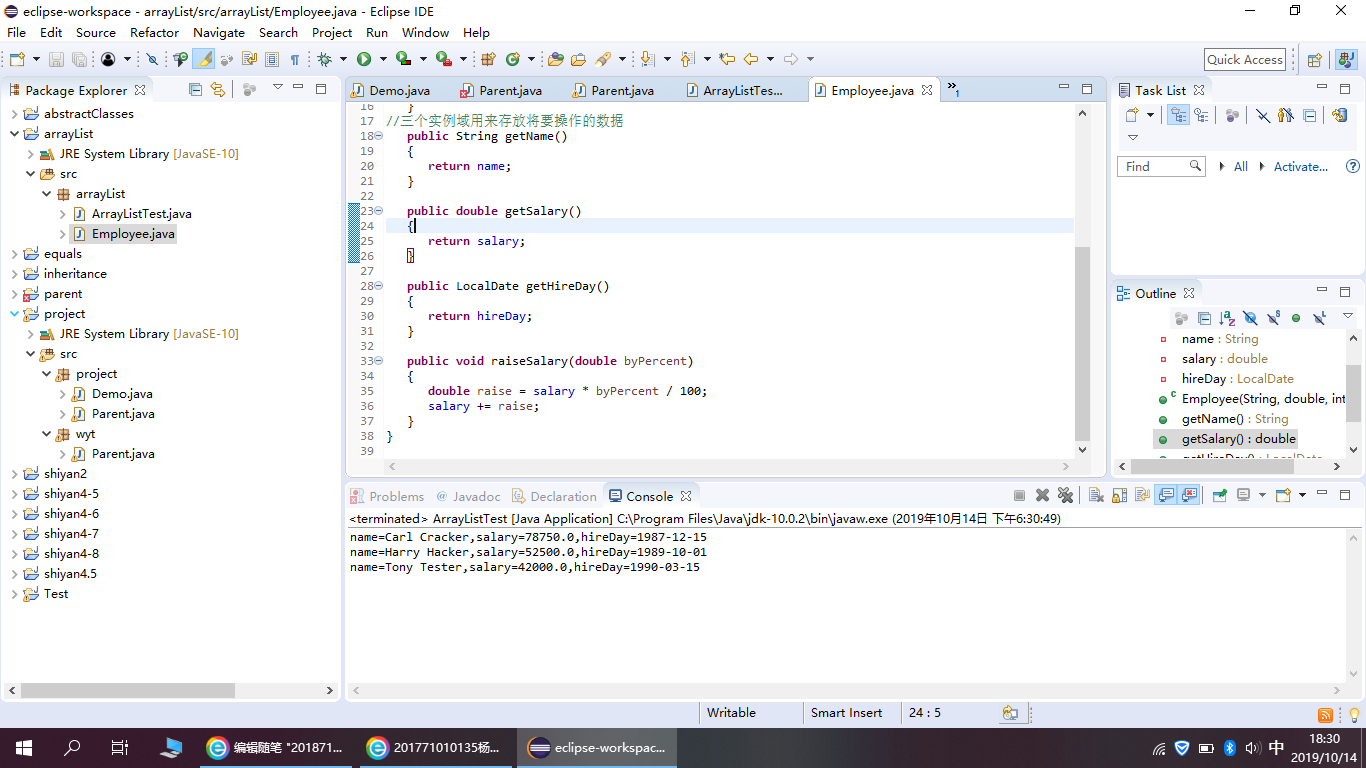
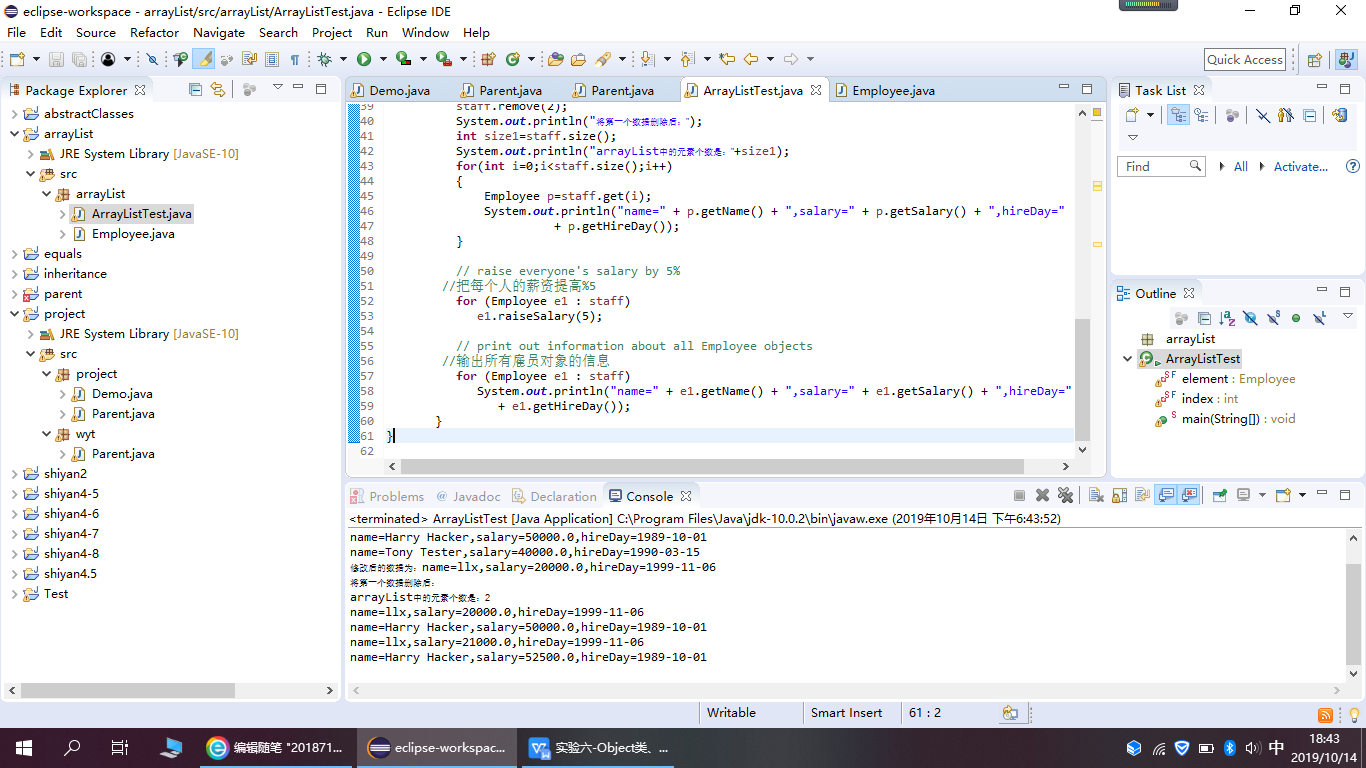
在ArrayList类的set()、get()、remove()、size()等方法,程序代码如下:
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { private static final Employee element = null; private static final int index = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array list with three Employee objects //用三个employee对象填充staff数组列表 ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15));//添加元素 ArrayList<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>(); int size=staff.size(); System.out.println("arrayList中的元素个数是:"+size); for(int i=0;i<staff.size();i++) { Employee e=staff.get(i); System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } staff.set(0, new Employee("llx", 20000, 1999, 11, 06)); Employee e=staff.get(0); System.out.println("修改后的数据为:name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); //remove()的用法 staff.remove(2); System.out.println("将第一个数据删除后:"); int size1=staff.size(); System.out.println("arrayList中的元素个数是:"+size1); for(int i=0;i<staff.size();i++) { Employee p=staff.get(i); System.out.println("name=" + p.getName() + ",salary=" + p.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + p.getHireDay()); } // raise everyone's salary by 5% //把每个人的薪资提高%5 for (Employee e1 : staff) e1.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects //输出所有雇员对象的信息 for (Employee e1 : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e1.getName() + ",salary=" + e1.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e1.getHireDay()); } }
运行截图如下:
测试程序3:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页),结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 删除程序中Size枚举类,背录删除代码,在代码录入中掌握枚举类的定义要求。
例题5.12程序代码如下:
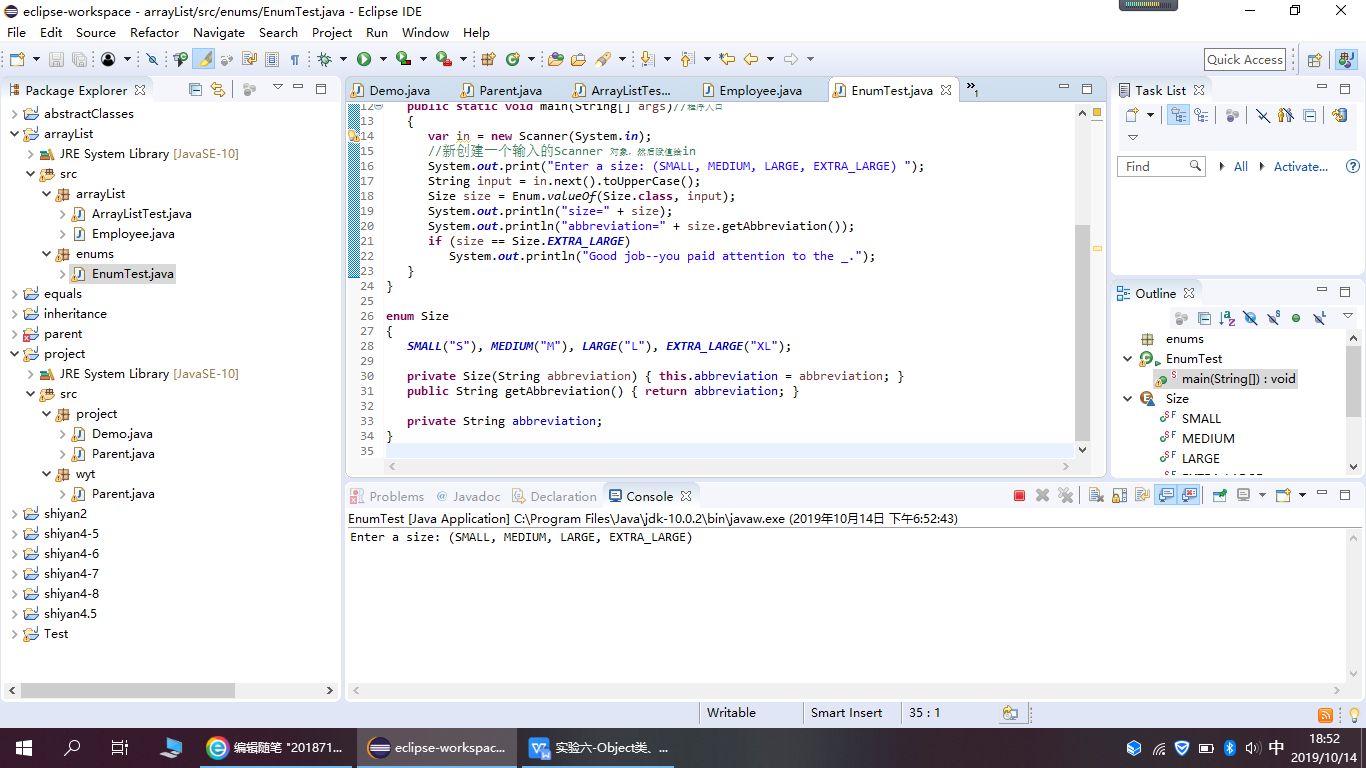
package enums; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates enumerated types. * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args)//程序入口 { var in = new Scanner(System.in); //新创建一个输入的Scanner 对象,然后赋值给in System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); System.out.println("size=" + size); System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); } } enum Size { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation; }
程序运行截图如下:
删除程序中Size枚举类override后代码如下:
package enums; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates enumerated types. * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args) { var in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); //静态方法valueOf System.out.println("size=" + size); System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); } } enum Size { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); //实例名 private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } @Override public String toString() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.toString(); } public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } public void setAbbreviation(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } private String abbreviation; }
测试程序4:录入以下代码,结合程序运行结果了解方法的可变参数用法
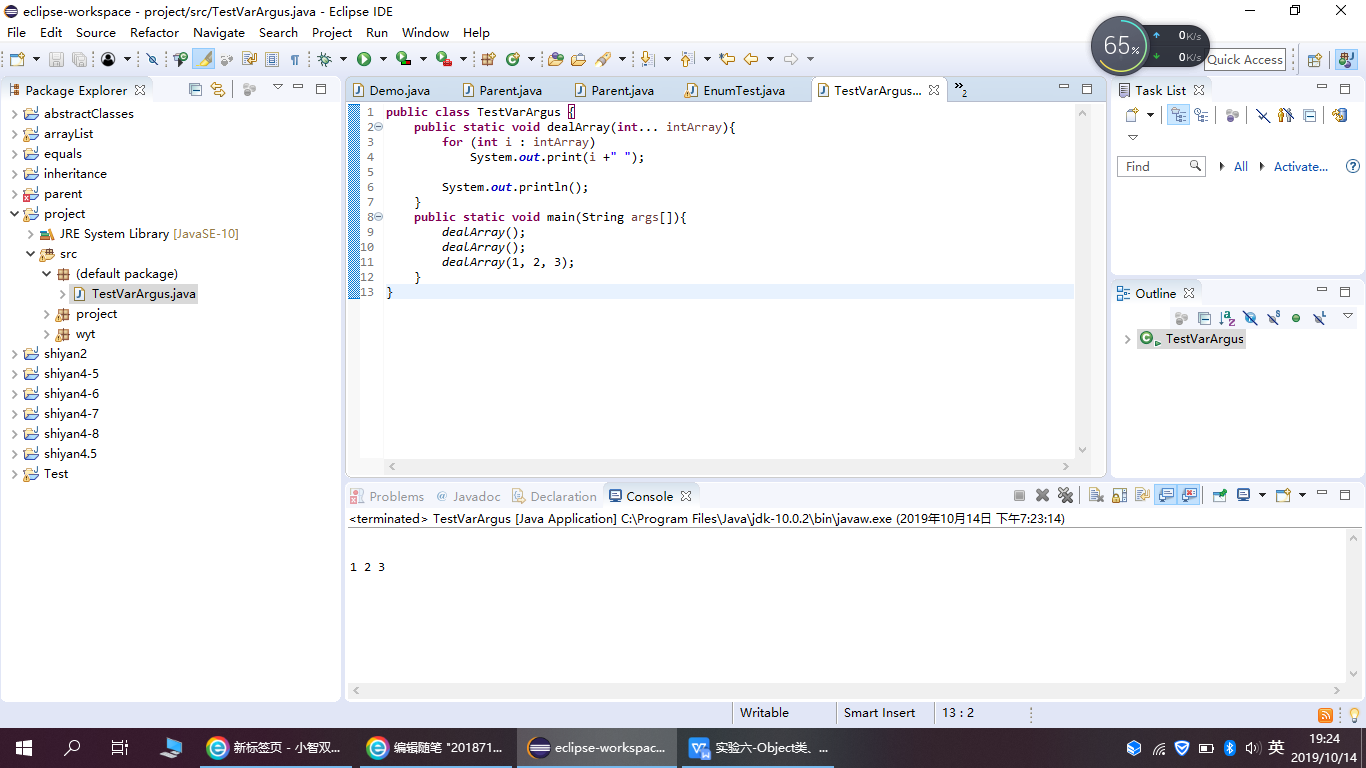
public class TestVarArgus { public static void dealArray(int... intArray){ for (int i : intArray) System.out.print(i +" "); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String args[]){ dealArray(); dealArray(); dealArray(1, 2, 3); } }
程序运行结果如下:
实验:3:编程练习:参照输出样例补全程序,使程序输出结果与输出样例一致。
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Son son = new Son(); son.method(); } } class Parent { Parent() { System.out.println("Parent's Constructor without parameter"); } Parent(boolean b) { System.out.println("Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter"); } public void method() { System.out.println("Parent's method()"); } } class Son extends Parent { //补全本类定义 }
程序运行结果如下:
Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter
Son's Constructor without parameter
Son's method()
Parent's method()
补全程序代码如下:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Son son = new Son(); son.method(); } } class Parent { Parent() { System.out.println("Parent's Constructor without parameter"); } Parent(boolean b) { System.out.println("Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter"); } public void method() { System.out.println("Parent's method()"); } } class Son extends Parent { Son(){ super(false); System.out.println("Son's Constructor without parameter"); System.out.println("Son's method()"); } }
程序输出截图如下:

第二部分:实验总结:
1)通过本周的学习,我们掌握了四种访问权限修饰符的使用特点;了解Object类的用途及常用API和ArrayList类的定义方法及用法;掌握枚举类定义方法及用途;
2):在实验课上通过老师的讲解,对四种权限修饰符有了初步的理解;课后在学长的讲解下有了更深入的掌握与理解;通过几次实验及程序的运行我对eclipse的使用有了更深入的掌握及包的建立类的建立过程中会遇到的基本问题有了一定的解决能力。
3):对于这周的实验在做的过程中我意识到自己的不足,应在课后多学习多动手从而加强自己的编程能力。