trie树(字典树)
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
bool wrd, vis;
int ch[26];
}trie[500009];
int siz = 1;
inline void insert(char* str)
{
int t = 1, len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(!trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'])
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'] = ++siz;
else
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'];
}
trie[t].wrd = true;
}
inline int search(char* str)
{
int t = 1, len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(!trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'])
return 0;
else
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'];
}
if(trie[t].wrd)
{
if(trie[t].vis) return -1;
trie[t].vis = true;
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
int n, m;
char str[55];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%s", str);
insert(str);
}
scanf("%d", &m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%s", str);
int res = search(str);
if(res == 1) printf("OK
");
else if(res == -1) printf("REPEAT
");
else printf("WRONG
");
}
return 0;
}
前置
大概没有
原理
结构
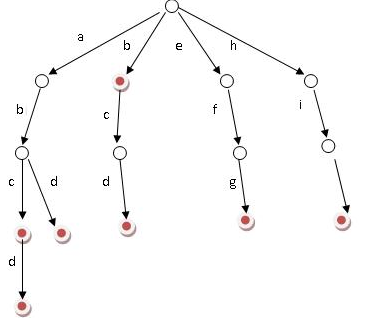
如上图,这就是一棵Trie树。这个Trie树中包含的单词有abc、abd、abcd、b、bcd、efg和hij。可以看到,Trie的字母并不存在结点上,而是存在边上。每个结点的儿子表示以这个结点对应的前缀的字符串的延续。结点的标记代表字符串的终止。这就是一棵Trie树的结构。
查找
从节点开始逐字符下跳, 直到没有对应的字符出现或在无结束标记情况下终止,代表查找失败
反之一直有对应字符并且在有标记情况下结束代表查找成功
插入
和查找相同的下跳,如果出现了没有的字符就创建新节点,并在结束时打上结束标记
分步实现
准备
一个结构体储存信息, wrd表示结束标记,siz表示当前节点数
struct node
{
bool wrd, vis;
int ch[26];
}trie[500009];
int siz = 1;
查找
vis可以判断是否找过
inline int search(char* str)
{
int t = 1, len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(!trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'])
return 0;
else
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'];
}
if(trie[t].wrd)
{
if(trie[t].vis) return -1;
trie[t].vis = true;
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
插入
inline void insert(char* str)
{
int t = 1, len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(!trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'])
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'] = ++siz;
else
t = trie[t].ch[str[i] - 'a'];
}
trie[t].wrd = true;
}
然后就没了
11.4更新
可持久化trie树
可持久化字典树就是记录 在字典树上有相同前缀 的前缀和(节点的个数),然后通过取差值(右边界减去左边界)判断一段区间内是否有字典树上的前缀
类似于主席树(毕竟都是可持久化操作)
求异或的最大值可以用01-trie树解决(用相同的深度存树,查询时从最高位贪心)
因此区间求异或最大值我们一般选择可持久化01-trie树
例题1:
概述:求区间异或最大值
显然直接暴力不能a,考虑可持久化tire树
插入
void insert(ll x, ll t, ll &z) {//t为上一个版本,z为当前版本
z = ++siz;//记录根节点
trie[z].init();//初始化
trie[z].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;//节点数++
ll k = z;
for(ll j = 31; j >= 0; j--) {//按位存入新的版本
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << j) & x);
trie[k].ch[nx ^ 1] = trie[t].ch[nx ^ 1];//当前版本与上一个版本重复的地方直接指向历史版本以节约空间
trie[k].ch[nx] = ++siz;
k = siz;
t = trie[t].ch[nx];
trie[k].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;//节点数
}
}
查询
ll search(ll l, ll r, ll x) {
ll ans = 0;
for(ll j = 31; j >= 0; j--) {
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << j) & x);//按位查询
ll nl = trie[l].ch[nx ^ 1];
ll nr = trie[r].ch[nx ^ 1];//
ll z = trie[nr].sum - trie[nl].sum;//如果z > 0判断是否存在(存在说明当前的x异或后可以找到一个1)
if(z) {
ans += 1LL * 1 << j;//累计答案
l = nl, r = nr;
}
else {
l = trie[l].ch[nx];
r = trie[r].ch[nx];
}
}
return ans;
}
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#define ll long long
ll n, q;
struct node {
ll ch[3], sum;
// bool wrd;
void init() {
sum = 0;
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(ch));
}
}trie[200000 * 40];
ll siz, root[600000];
void init() {
memset(trie, 0, sizeof(trie));
siz = 0;
memset(root, 0, sizeof(root));
}
void insert(ll x, ll t, ll &z) {
z = ++siz;
trie[z].init();
trie[z].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;
ll k = z;
for(ll j = 31; j >= 0; j--) {
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << j) & x);
trie[k].ch[nx ^ 1] = trie[t].ch[nx ^ 1];
trie[k].ch[nx] = ++siz;
k = siz;
t = trie[t].ch[nx];
trie[k].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;
}
}
ll search(ll l, ll r, ll x) {
ll ans = 0;
for(ll j = 31; j >= 0; j--) {
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << j) & x);
ll nl = trie[l].ch[nx ^ 1];
ll nr = trie[r].ch[nx ^ 1];
ll z = trie[nr].sum - trie[nl].sum;
if(z) {
ans += 1LL * 1 << j;
l = nl, r = nr;
}
else {
l = trie[l].ch[nx];
r = trie[r].ch[nx];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
freopen("hugclose.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("hugclose.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &q);
init();
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ll a;
scanf("%lld", &a);
insert(a, root[i - 1], root[i]);
}
for(ll j = 1; j <= q; j++) {
ll l, r, x;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &x, &l, &r);
printf("%lld
", search(root[l], root[r + 1], x));
}
return 0;
}
例题2
异或有可减性,因此可以求出前缀异或和,以此构建trie树
(本题luogu需要玄学卡常,也可能是我trie树常熟实在太大)
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
const int MAXN = 600000;
using namespace std;
int n, q, root[MAXN * 23 + 200000], siz, ret[MAXN + 7];//数组范围再开大会T
struct node {
int ch[2], sum;
void init() {
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(ch));
sum = 0;
}
}trie[MAXN * 23 + 300000];
inline void init() {
memset(trie, 0, sizeof(trie));
siz = 0;
memset(root, 0, sizeof(root));
}
inline void insert(int x, int t, int &z) {
z = ++siz;
trie[z].init();
trie[z].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;
int k = z;
for(register int i = 23; i >= 0; i--) {
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << i) & x);
trie[k].ch[nx ^ 1] = trie[t].ch[nx ^ 1];
trie[k].ch[nx] = ++siz;
k = siz;
t = trie[t].ch[nx];
trie[k].sum = trie[t].sum + 1;
}
}
inline int search(int l, int r, int x){
int ans = 0;
for(register int i = 23; i >= 0; i--) {
bool nx = ((1LL * 1 << i) & x);
int nl = trie[l].ch[nx ^ 1];
int nr = trie[r].ch[nx ^ 1];
int z = (trie[nr].sum - trie[nl].sum);
if(z) {
ans += (1LL * 1 << i);
l = nl, r = nr;
}
else {
l = trie[l].ch[nx];
r = trie[r].ch[nx];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
int x;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
init();
insert(ret[1], root[1], root[1]);//空节点插入
for(register int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
ret[i] = ret[i - 1] ^ x;//前缀和
insert(ret[i], root[i - 1], root[i]);
}
int h = n + 1;
for(register int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
char op;
int l, r, x;
scanf("
");
scanf("%c", &op);
if(op == 'A') {
scanf("%d", &x);
++h;
ret[h] = ret[h - 1] ^ x;
insert(ret[h], root[h - 1], root[h]);
}
else {
scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &x);
printf("%d
", search(root[l - 1], root[r], ret[h] ^ x));
}
}
}