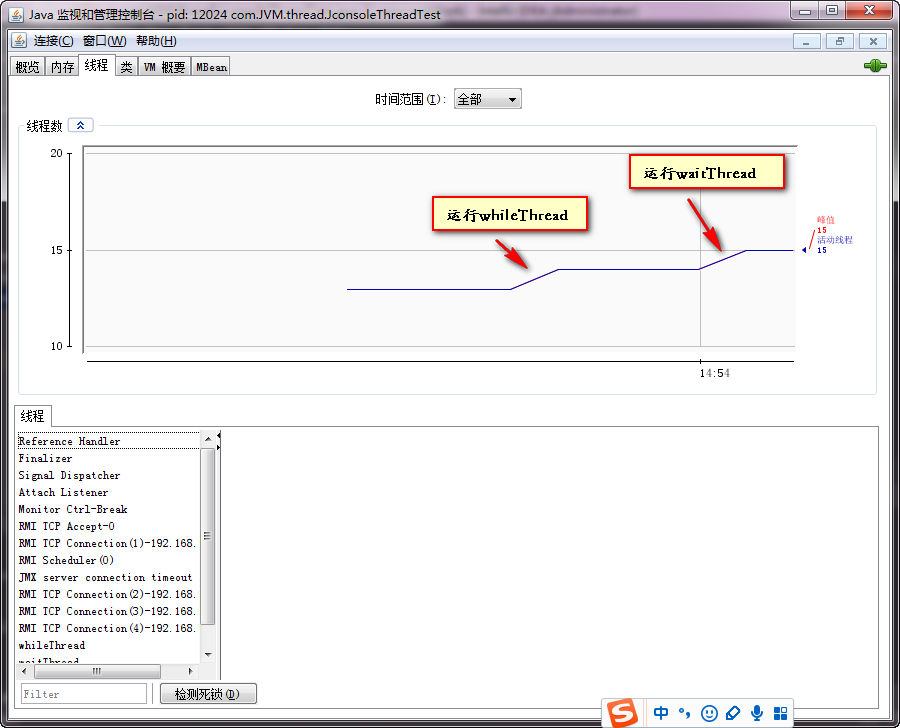
1、在命令行输入jconsole,然后选择需要连接的进程
2、内存分析
package com.JVM.thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @ClassName JconsoleHeapTest
* @Description 内存分析
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2019/5/26 14:39
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class JconsoleHeapTest {
public static final int _1MB = 1024*1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("method start");
fill(1000);
System.out.println("method end");
}
public static void fill(Integer cnt) {
List<JconsoleHeapTest> jconsoleHeapTests = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 不停创建对象
jconsoleHeapTests.add(new JconsoleHeapTest());
}
}
}

3、线程死锁分析
package com.JVM.thread;
/**
* @ClassName JconsoleSyncDeadLockTest
* @Description 线程死锁分析监控
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2019/5/26 14:30
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class JconsoleSyncDeadLockTest {
private static Object locka = new Object();
private static Object lockb = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程1
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (locka) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "get lockaing");
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" after sleep 500ms!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" need lockb!Just waiting!");
synchronized (lockb) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get lockb ing!");
}
}
}
}, "thread1");
// 线程2
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lockb) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "get lockb ing");
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" after sleep 500ms!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" need locka! Just waiting!");
synchronized (locka) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get locka ing!");
}
}
}
}, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
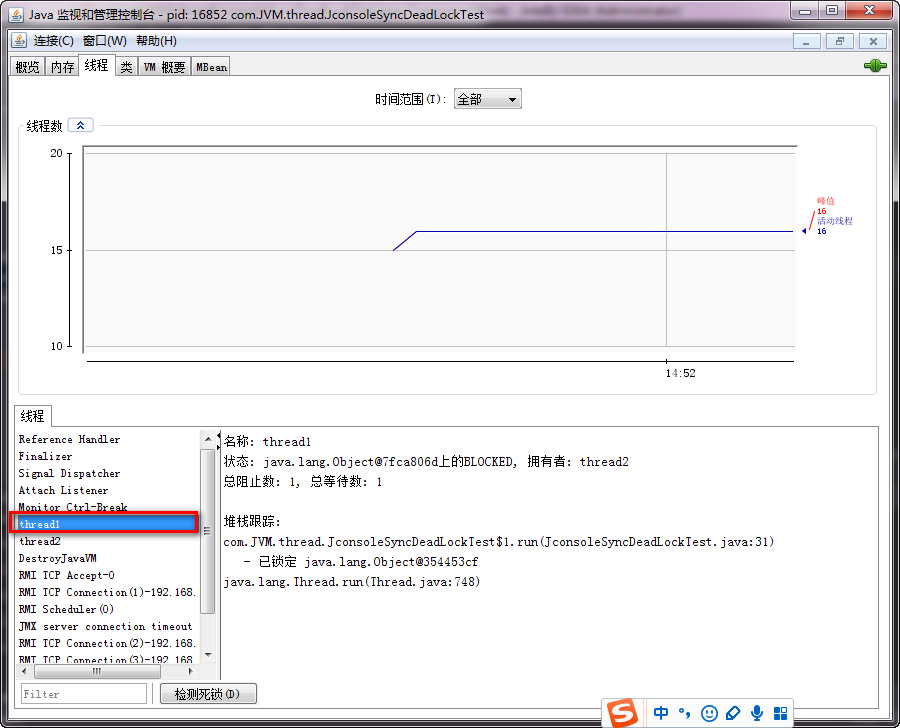
4、线程分析
package com.JVM.thread;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName JconsoleThreadTest
* @Description 线程分析
* @Author Administrator
* @Date 2019/5/26 14:19
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class JconsoleThreadTest {
public static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc.next();
// 控制台输入next,后执行whilleTread线程
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("start while Thread");
while(true) {
}
}, "whileThread").start();
sc.next();
// 控制台再次输入next,后执行waitTread线程
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("start waitThread");
Object o = new Object();
synchronized (o) {
try {
o.wait();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}, "waitThread").start();
}
}