(本人)魏修祺 201421122008
二、题目描述:
在个人作业1中,用各种语言实现了一个命令行的四则运算小程序。进一步,本次要求把这个程序做成GUI,成为一个有基本功能、一定价值的程序。在下面的功能需求中实现两个:
-
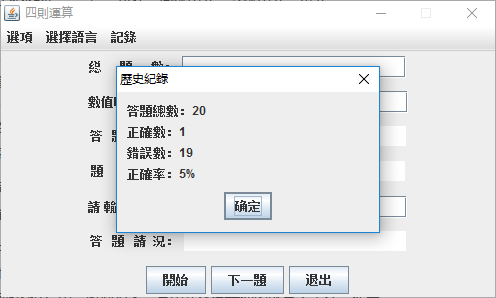
记录用户的对错总数,程序退出再启动的时候,能把以前的对错数量保存并在此基础上增量计算。
-
有计时功能,能显示用户开始答题后的消耗时间。
-
界面支持中文简体/中文繁体/英语,用户可以选择一种;
三、项目实现:
1、需求分析
- 在题目描述3个功能中,我和队友分工完成,我完成的是界面语言选择和错题记录;
- 针对于所要完成的功能,首先要设计一个GUI,友好的界面,方便用户体会各种功能;
- 对于不同地区,可以有不同语言的选择,按要求只完成3个语言选择;
- 错题记录,记录用户使用过程产生的错题,方便用户学习。
2、程序设计
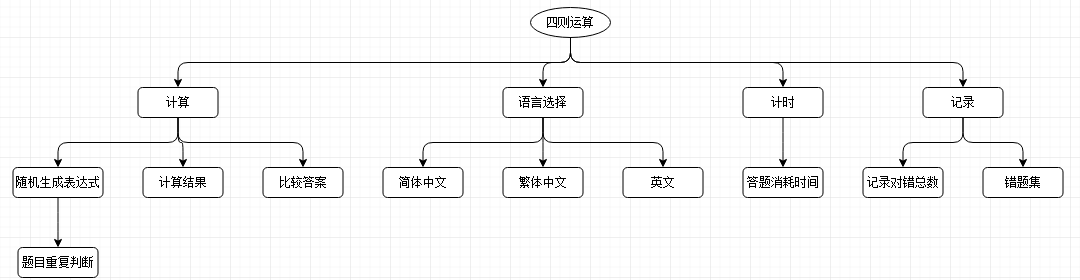
说明:四则远算主要功能分为,计算、语言选择、计时、记录。其中计算是最核心最重要的部分,但在个人作业1中已经有过详细说明,这里不再细说。语言选择提高三种语言选择,初始默认为简体中文。计时功能,记录用户在开始答题直到答题结束消耗时间。记录主要是对答题结束之后,将对错总数和错题写到文件里。
3、代码展示
1.主界面
public MainFrame(int oper) { // 创建组件 jb1 = new JButton(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jb1")); jb2 = new JButton(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jb2")); jb3 = new JButton(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jb3")); // 设置监听 jb1.addActionListener(this); jb2.addActionListener(this); jb3.addActionListener(this); jmb = new JMenuBar(); // JMenuBar指菜单栏 jm1 = new JMenu(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jm1")); // JMenu是菜单栏中的选项栏 jm2 = new JMenu(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jm2")); jm3 = new JMenu(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jm3")); jmi1 = new JMenuItem(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jmi1")); // JMenuItem指选项栏中的选项 jmi1.addActionListener(this); jmi2 = new JMenuItem(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jmi2")); jmi2.addActionListener(this); jmi3 = new JMenuItem("简体中文"); jmi3.addActionListener(this); jmi4 = new JMenuItem("繁體中文"); jmi4.addActionListener(this); jmi5 = new JMenuItem("English"); jmi5.addActionListener(this); jmi6 = new JMenuItem(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jmi6")); jmi6.addActionListener(this); jmi7 = new JMenuItem(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jmi7")); jmi7.addActionListener(this); jm1.add(jmi1); jm1.add(jmi2); ... jp1 = new JPanel(); ... jlb1 = new JLabel(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jlb1")); ... jtf1 = new JTextField(20); jtf2 = new JTextField(20); ... // 加入到JPanel中 jp1.add(jlb1); jp1.add(jtf1); ... // 加入JFrame中 this.setJMenuBar(jmb); this.add(jp1); ... // 设置布局管理器 this.setLayout(new GridLayout(7, 1)); // 给窗口设置标题 this.setTitle(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jf")); // 设置窗体大小 this.setSize(500, 300); // 设置窗体初始位置 this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); // 设置当关闭窗口时,保证JVM也退出 this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 显示窗体 this.setVisible(true); this.setResizable(false); }
2.语言选择实现 参考博客:[http://blog.csdn.net/wendy432/article/details/52494064]
2.1语言选择监听
1 // 切换到中文 2 if (e.getSource().equals(jmi3)) { 3 this.dispose(); 4 new MainFrame(0); 5 }// 切换到英文 6 else if (e.getSource().equals(jmi4)) { 7 this.dispose(); 8 MainFrame mf = new MainFrame(2); 9 mf.setOper(2); 10 }// 切换到繁体 11 else if (e.getSource().equals(jmi5)) { 12 this.dispose(); 13 MainFrame mf = new MainFrame(1); 14 mf.setOper(1); 15 }
2.2根据不同参数获取地区
1 public static ResourceBundle locale(int m) { 2 ResourceBundle bundle = null; 3 switch (m) { 4 case 0: 5 bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("mess", Locale.CHINESE); 6 break; 7 case 1: 8 bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("mess", Locale.US); 9 break; 10 case 2: 11 bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("mess", Locale.TAIWAN); 12 } 13 return bundle; 14 } 15 }
2.3根据获取的地区语言调用不同资源文件,实现语言替换

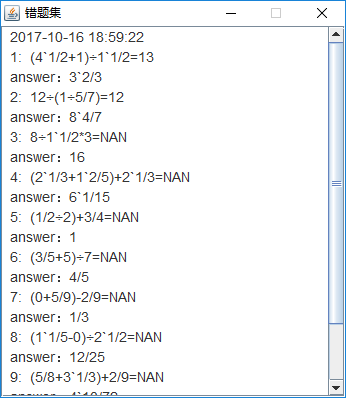
3.错题集的实现
3.1每次答错会将错误的题目、正确答案和答错的答案存到一个List中。err为错误个数,question为题目,message为错误答案,answer为正确答案。
1 errList.add(err + ": " + question + "=" + message +"
"+"answer:"+ answer);
3.2当所有题目答完之后,将错误的所有合集写到文件error.txt中
1 ErrorOutPut.outPut(errList);
1 public static void outPut(List<Object> errList) { 2 String filepath = "errList.txt"; 3 File file = new File(filepath); 4 BufferedWriter out = null; 5 if (file.exists()) { 6 try { 7 out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter( 8 new FileOutputStream(file, true))); 9 // 输出时间 10 Date now = new Date(); 11 String date = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(now); 12 out.write("DATE:" + date); 13 out.newLine(); 14 // 输出错题集 15 while (errList.size() != 0) { 16 String err = (String) errList.remove(0); 17 out.write(err); 18 out.newLine(); 19 } 20 } catch (IOException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } finally { 23 try { 24 out.close(); 25 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 } else { 31 try { 32 file.createNewFile(); 33 out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter( 34 new FileOutputStream(file, true))); 35 // 输出时间 36 Date now = new Date(); 37 String date = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(now); 38 out.write(date); 39 out.newLine(); 40 // 输出错题集 41 while (errList.size() != 0) { 42 String err = (String) errList.remove(0); 43 out.write(err); 44 out.newLine(); 45 } 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } finally { 49 try { 50 out.close(); 51 } catch (IOException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 }
3.3主界面监听触发查看错题集
1 // 错题集 2 else if (e.getSource().equals(jmi6)) { 3 new ErrListFrame(getOper()); 4 }
3.4先将文件中内容读取出来存放在errList中,在一个新界面显示
1 public static List<Object> readErrList() { 2 String filepath = "errList.txt"; 3 File file = new File(filepath); 4 String lineTex = null; 5 List<Object> errList = new ArrayList<Object>(); 6 try { 7 if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) { 8 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 9 while ((lineTex = br.readLine()) != null) { 10 errList.add(lineTex); 11 } 12 br.close(); 13 } else { 14 System.out.println("文件不存在!"); 15 } 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 System.out.println("文件读取错误!"); 18 } 19 return errList; 20 }
1 public ErrListFrame(int oper) { 2 jta = new JTextArea(); 3 scroll = new JScrollPane(jta); 4 // jta.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(350,400)); 5 jta.setFont(new Font("标楷体", Font.PLAIN, 14)); // 设置当前字体。 6 jta.setEditable(false); 7 jta.setBackground(Color.white); 8 scroll.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(JScrollPane.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS); 9 List<Object> readErrList = ReadErrList.readErrList(); 10 for (int i = 0; i < readErrList.size(); i++) { 11 errList = errList + (String) readErrList.get(i) + " " + " "; 12 } 13 jta.setText(errList); 14 15 this.add(scroll); 16 // 给窗口设置标题 17 this.setTitle(Lovo.locale(oper).getString("jmi6")); 18 // 设置窗体大小 19 this.setSize(350, 400); 20 // 设置窗体初始位置 21 this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); 22 // 显示窗体 23 this.setVisible(true); 24 this.setResizable(false); 25 26 }
4、程序运行
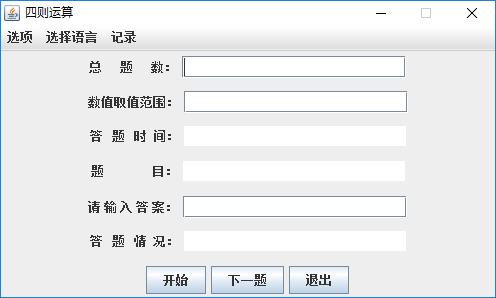
1.主界面
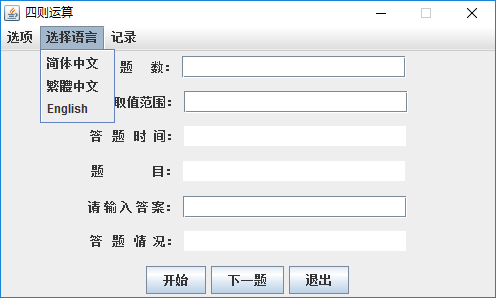
2.选择语言(默认是简体中文)
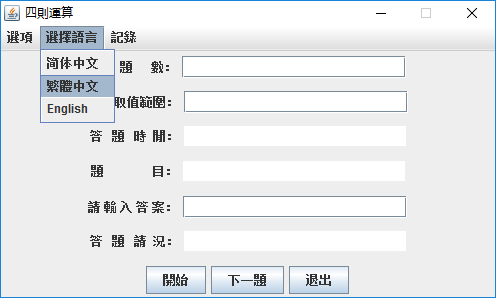
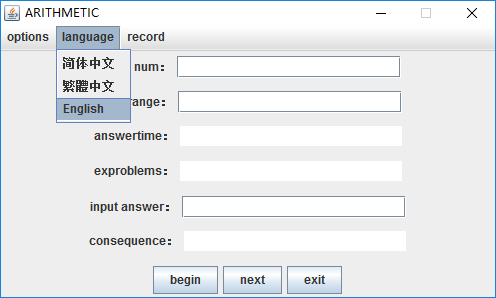
3.计算及结果展示(第二张图表示不同语言效果)
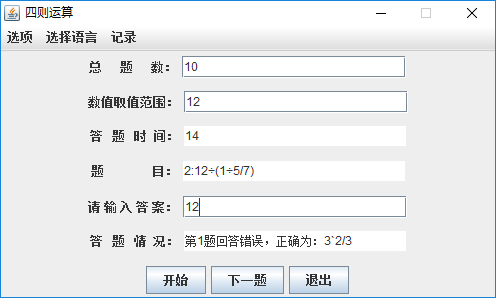
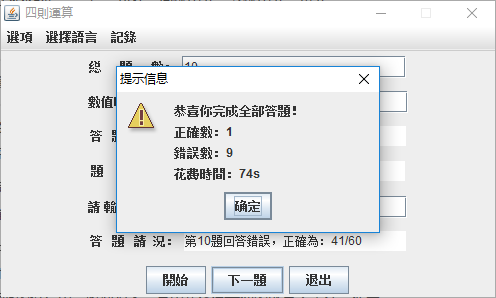
4.记录功能:错题集和历史记录
5、小结感受
- 本次结对编程是在个人作业1基础上进行增量,队友作业1功能完成比较完善,在他的个人作业1上增量开发,不用再次去大量完善个人作业1的功能,容易了很多。
- 结对编程的队友是同宿舍的,过去也有一起结对编程经历,队友之间很熟悉,配合起来相对默契。
- 结对编程分工,根据自己想要完成和自己有能力完成的功能来分配,编程过程中遇到问题相互沟通,很快就解决。
- 对于结对编程真的能带来1+1>2的效果吗? 这个问题我觉得是要在双方具有默契的时候,比如编程过程中采用标准化,java编程命名采用驼峰命名法等,并且队友之间沟通顺畅,遇到问题能够一起解决,这样的结对编程才能带来1+1>2的效果。
四、运用“汉堡包”的方式,评价结对伙伴:
优点:对于问题的处理非常快,解决思路很清晰,非常值得学习。
缺点:有些方法没标明用途,代码的注释有点欠缺。
希望他提高的地方:对一些方法尽量标明用途,以便以后容易重新查阅。
五、描述结对过程:
1.读完题目,明确任务需求。这次结对编程需要在个人作业1上增加3个功能。
2.根据任务需求和自身条件分配任务,比如这次结对编程我要完成的任务是主界面设计、语言选择和错题集。
3.独自完成自己任务,遇到问题时一起沟通解决。比如在做语言选择时,语言切换使用关掉上个界面,启用新界面来处理的,实际操作中新界面弹窗出现问题,在讨论中发现新界面弹窗语言切换参数是旧界面的而非新界面的。自己独立最终也能发现问题,但不会如此快速。
4.完成功能后,相互互省代码,调试功能。
5.整合所有功能代码,调试功能是否冲突。
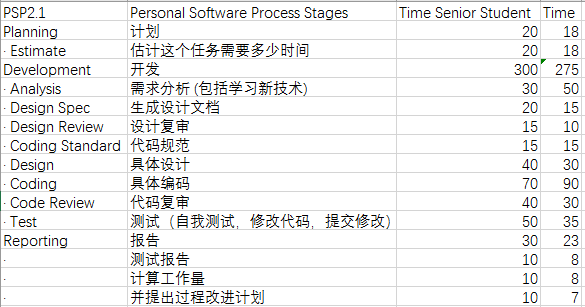
六、展示PSP: