List接口简介
List接口继承自Collection接口,是单列集合的一个重要分支,习惯性会将实现了List接口的对象成为List集合。在List集合中允许出现重复的元素,所有的元素是以一种线性方式进行储存的,在程序中可以通过索引来访问集合中的指定元素。另外,List集合还有一个特点就是元素有序,即元素的存入和取出顺序一样。
List作为Collection集合的子接口,不但继承了Collection接口中的全部方法,而且还增加了一些根据元素索引来操作集合的特有方法。
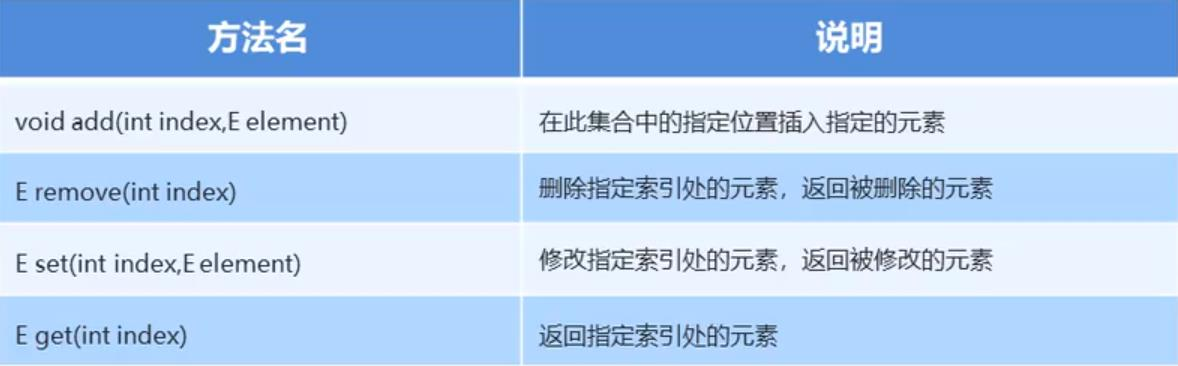
ArrayList集合
ArrayList是List接口的一个实现类,它是程序中最常见的一种集合。在ArrayList内部封装了一个长度可变的数组对象,当存入的数组长度超过数组长度时,ArrayList会在内存中分配一个更大的数组来储存这些元素,因此可以将ArrayList集合看做一个长度可变的数组。ArrayList集合中大部分方法都是从父接口Collection和List继承过来的。
1 public class Example01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//创建ArrayList集合 4 //向集合中添加元素 5 list.add("a"); 6 list.add("b"); 7 list.add("c"); 8 list.add("d"); 9 list.add(4,"e");//向集合的指定位置中插入指定的元素 10 list.set(3,"x");//将指定位置索引的元素替换 11 int i = list.size();//获取集合中元素的个数 12 list.get(1);//获取指定位置索引的元素 13 list.remove(4);//删除指定索引的元素 14 list.contains("c");//集合是否存在指定的元素 15 list.indexOf("b");//返回对象在集合中出现的位置索引 16 list.lastIndexOf("c");//返回对象在集合中最后一次出现的位置索引 17 } 18 }
这里只是列举了部分基本的方法,剩下的就不一样列举了。
需要注意的是索引的取值范围是从0开始的,最后一个索引是size-1,在访问元素时一定要注意索引不可超出此范围,否则会抛出角标越界异常IndexOutOfBoundsException。
由于ArrayList集合的底层是使用一个数组来保存元素,在增加或删除指定位置的元素时,会导致创建新的数组,效率比较低,因此不适合做大量的增删操作。但这种数组的结构运行程序通过索引的方式来访问元素,因此使用ArrayList集合查找元素很便捷。
LinkedList集合
前面提到ArrayList集合在查询元素时速度很快,但在增删元素时效率较低,为了克服这种局限性,可以使用List接口的另一个实现类LinkedList。该集合内部维护了一个双向循环链表,链表中的每一个元素都使用引用的方式来记住它的前一个元素和后一个元素,从而可以将所有的元素彼此连接起来。当插入一个新元素时,只需要修改元素之间的这种引用关系即可,删除一个节点也是如此。正因为这样的存储结构,所以LinkedList集合对于元素的增删操作具有很高的效率。
LinkedList是基于链表结构实现的,所以在类中包含了first和last两个指针(Node)。Node中包含了上一个节点和下一个节点的引用,这样就构成了双向的链表。每个Node只能知道自己的前一个例程和后一个节点,但对于链表来说,这已经足够了。

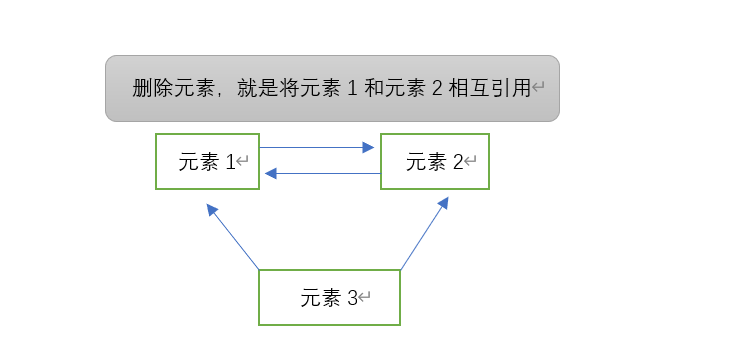
百度出来的答案基本都涉及底层原理,苦涩难懂,对于初学者来不太友好,简单点来说,新增一个元素时,元素1和元素2在集合中彼此互为前后关系,在它们之间新增一个元素时,只需要让元素1记住它后面的元素是新元素,让元素2记住它前面的元素为新元素就可以了;删除元素3时,只需要让元素1和元素2变成前后关系就可以了。(有兴趣的建议查阅官方文档或源码)
LinkedList集合除了具备增删元素效率高的特点,还专门针对元素的增删操作定义了一些特有的方法。

列出的方法主要针对集合中的元素进行增加、删除和获取操作。
1 public class Example { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 LinkedList link = new LinkedList();//创建LinkedList集合 4 //向集合中添加元素 5 link.add("stu1"); 6 link.add("stu2"); 7 link.add("stu3"); 8 link.add("stu4"); 9 System.out.println(link.toString());//取出并打印该集合中的元素 10 link.add(3,"student");//向集合中指定位置插入元素 11 link.addFirst("First");//向该集合第一个位置插入元素 12 System.out.println(link); 13 System.out.println(link.getFirst());//取出该集合中第一个元素 14 link.remove(3);//移除该集合中指定位置的元素 15 link.removeFirst();//移除该集合中的第一个元素 16 System.out.println(link); 17 } 18 }
运行结果:

LinkedList源码解析(1.6)
1 package java.util; 2 3 public class LinkedList<E> 4 extends AbstractSequentialList<E> 5 implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 6 { 7 // 链表的表头,表头不包含任何数据。Entry是个链表类数据结构。 8 private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null); 9 10 // LinkedList中元素个数 11 private transient int size = 0; 12 13 // 默认构造函数:创建一个空的链表 14 public LinkedList() { 15 header.next = header.previous = header; 16 } 17 18 // 包含“集合”的构造函数:创建一个包含“集合”的LinkedList 19 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 20 this(); 21 addAll(c); 22 } 23 24 // 获取LinkedList的第一个元素 25 public E getFirst() { 26 if (size==0) 27 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 28 29 // 链表的表头header中不包含数据。 30 // 这里返回header所指下一个节点所包含的数据。 31 return header.next.element; 32 } 33 34 // 获取LinkedList的最后一个元素 35 public E getLast() { 36 if (size==0) 37 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 38 39 // 由于LinkedList是双向链表;而表头header不包含数据。 40 // 因而,这里返回表头header的前一个节点所包含的数据。 41 return header.previous.element; 42 } 43 44 // 删除LinkedList的第一个元素 45 public E removeFirst() { 46 return remove(header.next); 47 } 48 49 // 删除LinkedList的最后一个元素 50 public E removeLast() { 51 return remove(header.previous); 52 } 53 54 // 将元素添加到LinkedList的起始位置 55 public void addFirst(E e) { 56 addBefore(e, header.next); 57 } 58 59 // 将元素添加到LinkedList的结束位置 60 public void addLast(E e) { 61 addBefore(e, header); 62 } 63 64 // 判断LinkedList是否包含元素(o) 65 public boolean contains(Object o) { 66 return indexOf(o) != -1; 67 } 68 69 // 返回LinkedList的大小 70 public int size() { 71 return size; 72 } 73 74 // 将元素(E)添加到LinkedList中 75 public boolean add(E e) { 76 // 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到表头(header)之前。 77 // 即,将节点添加到双向链表的末端。 78 addBefore(e, header); 79 return true; 80 } 81 82 // 从LinkedList中删除元素(o) 83 // 从链表开始查找,如存在元素(o)则删除该元素并返回true; 84 // 否则,返回false。 85 public boolean remove(Object o) { 86 if (o==null) { 87 // 若o为null的删除情况 88 for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { 89 if (e.element==null) { 90 remove(e); 91 return true; 92 } 93 } 94 } else { 95 // 若o不为null的删除情况 96 for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { 97 if (o.equals(e.element)) { 98 remove(e); 99 return true; 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 return false; 104 } 105 106 // 将“集合(c)”添加到LinkedList中。 107 // 实际上,是从双向链表的末尾开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。 108 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 109 return addAll(size, c); 110 } 111 112 // 从双向链表的index开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。 113 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 114 if (index < 0 || index > size) 115 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ 116 ", Size: "+size); 117 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 118 // 获取集合的长度 119 int numNew = a.length; 120 if (numNew==0) 121 return false; 122 modCount++; 123 124 // 设置“当前要插入节点的后一个节点” 125 Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index)); 126 // 设置“当前要插入节点的前一个节点” 127 Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous; 128 // 将集合(c)全部插入双向链表中 129 for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) { 130 Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor); 131 predecessor.next = e; 132 predecessor = e; 133 } 134 successor.previous = predecessor; 135 136 // 调整LinkedList的实际大小 137 size += numNew; 138 return true; 139 } 140 141 // 清空双向链表 142 public void clear() { 143 Entry<E> e = header.next; 144 // 从表头开始,逐个向后遍历;对遍历到的节点执行一下操作: 145 // (01) 设置前一个节点为null 146 // (02) 设置当前节点的内容为null 147 // (03) 设置后一个节点为“新的当前节点” 148 while (e != header) { 149 Entry<E> next = e.next; 150 e.next = e.previous = null; 151 e.element = null; 152 e = next; 153 } 154 header.next = header.previous = header; 155 // 设置大小为0 156 size = 0; 157 modCount++; 158 } 159 160 // 返回LinkedList指定位置的元素 161 public E get(int index) { 162 return entry(index).element; 163 } 164 165 // 设置index位置对应的节点的值为element 166 public E set(int index, E element) { 167 Entry<E> e = entry(index); 168 E oldVal = e.element; 169 e.element = element; 170 return oldVal; 171 } 172 173 // 在index前添加节点,且节点的值为element 174 public void add(int index, E element) { 175 addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index))); 176 } 177 178 // 删除index位置的节点 179 public E remove(int index) { 180 return remove(entry(index)); 181 } 182 183 // 获取双向链表中指定位置的节点 184 private Entry<E> entry(int index) { 185 if (index < 0 || index >= size) 186 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ 187 ", Size: "+size); 188 Entry<E> e = header; 189 // 获取index处的节点。 190 // 若index < 双向链表长度的1/2,则从前先后查找; 191 // 否则,从后向前查找。 192 if (index < (size >> 1)) { 193 for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) 194 e = e.next; 195 } else { 196 for (int i = size; i > index; i--) 197 e = e.previous; 198 } 199 return e; 200 } 201 202 // 从前向后查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引” 203 // 不存在就返回-1 204 public int indexOf(Object o) { 205 int index = 0; 206 if (o==null) { 207 for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { 208 if (e.element==null) 209 return index; 210 index++; 211 } 212 } else { 213 for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { 214 if (o.equals(e.element)) 215 return index; 216 index++; 217 } 218 } 219 return -1; 220 } 221 222 // 从后向前查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引” 223 // 不存在就返回-1 224 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 225 int index = size; 226 if (o==null) { 227 for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) { 228 index--; 229 if (e.element==null) 230 return index; 231 } 232 } else { 233 for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) { 234 index--; 235 if (o.equals(e.element)) 236 return index; 237 } 238 } 239 return -1; 240 } 241 242 // 返回第一个节点 243 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 244 public E peek() { 245 if (size==0) 246 return null; 247 return getFirst(); 248 } 249 250 // 返回第一个节点 251 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则抛出异常 252 public E element() { 253 return getFirst(); 254 } 255 256 // 删除并返回第一个节点 257 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 258 public E poll() { 259 if (size==0) 260 return null; 261 return removeFirst(); 262 } 263 264 // 将e添加双向链表末尾 265 public boolean offer(E e) { 266 return add(e); 267 } 268 269 // 将e添加双向链表开头 270 public boolean offerFirst(E e) { 271 addFirst(e); 272 return true; 273 } 274 275 // 将e添加双向链表末尾 276 public boolean offerLast(E e) { 277 addLast(e); 278 return true; 279 } 280 281 // 返回第一个节点 282 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 283 public E peekFirst() { 284 if (size==0) 285 return null; 286 return getFirst(); 287 } 288 289 // 返回最后一个节点 290 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 291 public E peekLast() { 292 if (size==0) 293 return null; 294 return getLast(); 295 } 296 297 // 删除并返回第一个节点 298 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 299 public E pollFirst() { 300 if (size==0) 301 return null; 302 return removeFirst(); 303 } 304 305 // 删除并返回最后一个节点 306 // 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null 307 public E pollLast() { 308 if (size==0) 309 return null; 310 return removeLast(); 311 } 312 313 // 将e插入到双向链表开头 314 public void push(E e) { 315 addFirst(e); 316 } 317 318 // 删除并返回第一个节点 319 public E pop() { 320 return removeFirst(); 321 } 322 323 // 从LinkedList开始向后查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点 324 // 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点 325 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { 326 return remove(o); 327 } 328 329 // 从LinkedList末尾向前查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点 330 // 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点 331 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { 332 if (o==null) { 333 for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) { 334 if (e.element==null) { 335 remove(e); 336 return true; 337 } 338 } 339 } else { 340 for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) { 341 if (o.equals(e.element)) { 342 remove(e); 343 return true; 344 } 345 } 346 } 347 return false; 348 } 349 350 // 返回“index到末尾的全部节点”对应的ListIterator对象(List迭代器) 351 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 352 return new ListItr(index); 353 } 354 355 // List迭代器 356 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { 357 // 上一次返回的节点 358 private Entry<E> lastReturned = header; 359 // 下一个节点 360 private Entry<E> next; 361 // 下一个节点对应的索引值 362 private int nextIndex; 363 // 期望的改变计数。用来实现fail-fast机制。 364 private int expectedModCount = modCount; 365 366 // 构造函数。 367 // 从index位置开始进行迭代 368 ListItr(int index) { 369 // index的有效性处理 370 if (index < 0 || index > size) 371 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size); 372 // 若 “index 小于 ‘双向链表长度的一半’”,则从第一个元素开始往后查找; 373 // 否则,从最后一个元素往前查找。 374 if (index < (size >> 1)) { 375 next = header.next; 376 for (nextIndex=0; nextIndex<index; nextIndex++) 377 next = next.next; 378 } else { 379 next = header; 380 for (nextIndex=size; nextIndex>index; nextIndex--) 381 next = next.previous; 382 } 383 } 384 385 // 是否存在下一个元素 386 public boolean hasNext() { 387 // 通过元素索引是否等于“双向链表大小”来判断是否达到最后。 388 return nextIndex != size; 389 } 390 391 // 获取下一个元素 392 public E next() { 393 checkForComodification(); 394 if (nextIndex == size) 395 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 396 397 lastReturned = next; 398 // next指向链表的下一个元素 399 next = next.next; 400 nextIndex++; 401 return lastReturned.element; 402 } 403 404 // 是否存在上一个元素 405 public boolean hasPrevious() { 406 // 通过元素索引是否等于0,来判断是否达到开头。 407 return nextIndex != 0; 408 } 409 410 // 获取上一个元素 411 public E previous() { 412 if (nextIndex == 0) 413 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 414 415 // next指向链表的上一个元素 416 lastReturned = next = next.previous; 417 nextIndex--; 418 checkForComodification(); 419 return lastReturned.element; 420 } 421 422 // 获取下一个元素的索引 423 public int nextIndex() { 424 return nextIndex; 425 } 426 427 // 获取上一个元素的索引 428 public int previousIndex() { 429 return nextIndex-1; 430 } 431 432 // 删除当前元素。 433 // 删除双向链表中的当前节点 434 public void remove() { 435 checkForComodification(); 436 Entry<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; 437 try { 438 LinkedList.this.remove(lastReturned); 439 } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { 440 throw new IllegalStateException(); 441 } 442 if (next==lastReturned) 443 next = lastNext; 444 else 445 nextIndex--; 446 lastReturned = header; 447 expectedModCount++; 448 } 449 450 // 设置当前节点为e 451 public void set(E e) { 452 if (lastReturned == header) 453 throw new IllegalStateException(); 454 checkForComodification(); 455 lastReturned.element = e; 456 } 457 458 // 将e添加到当前节点的前面 459 public void add(E e) { 460 checkForComodification(); 461 lastReturned = header; 462 addBefore(e, next); 463 nextIndex++; 464 expectedModCount++; 465 } 466 467 // 判断 “modCount和expectedModCount是否相等”,依次来实现fail-fast机制。 468 final void checkForComodification() { 469 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 470 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 471 } 472 } 473 474 // 双向链表的节点所对应的数据结构。 475 // 包含3部分:上一节点,下一节点,当前节点值。 476 private static class Entry<E> { 477 // 当前节点所包含的值 478 E element; 479 // 下一个节点 480 Entry<E> next; 481 // 上一个节点 482 Entry<E> previous; 483 484 /** 485 * 链表节点的构造函数。 486 * 参数说明: 487 * element —— 节点所包含的数据 488 * next —— 下一个节点 489 * previous —— 上一个节点 490 */ 491 Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) { 492 this.element = element; 493 this.next = next; 494 this.previous = previous; 495 } 496 } 497 498 // 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到entry节点之前。 499 private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) { 500 // 新建节点newEntry,将newEntry插入到节点e之前;并且设置newEntry的数据是e 501 Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous); 502 newEntry.previous.next = newEntry; 503 newEntry.next.previous = newEntry; 504 // 修改LinkedList大小 505 size++; 506 // 修改LinkedList的修改统计数:用来实现fail-fast机制。 507 modCount++; 508 return newEntry; 509 } 510 511 // 将节点从链表中删除 512 private E remove(Entry<E> e) { 513 if (e == header) 514 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 515 516 E result = e.element; 517 e.previous.next = e.next; 518 e.next.previous = e.previous; 519 e.next = e.previous = null; 520 e.element = null; 521 size--; 522 modCount++; 523 return result; 524 } 525 526 // 反向迭代器 527 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { 528 return new DescendingIterator(); 529 } 530 531 // 反向迭代器实现类。 532 private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator { 533 final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size()); 534 // 反向迭代器是否下一个元素。 535 // 实际上是判断双向链表的当前节点是否达到开头 536 public boolean hasNext() { 537 return itr.hasPrevious(); 538 } 539 // 反向迭代器获取下一个元素。 540 // 实际上是获取双向链表的前一个节点 541 public E next() { 542 return itr.previous(); 543 } 544 // 删除当前节点 545 public void remove() { 546 itr.remove(); 547 } 548 } 549 550 551 // 返回LinkedList的Object[]数组 552 public Object[] toArray() { 553 // 新建Object[]数组 554 Object[] result = new Object[size]; 555 int i = 0; 556 // 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到Object[]数组中 557 for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) 558 result[i++] = e.element; 559 return result; 560 } 561 562 // 返回LinkedList的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型 563 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 564 // 若数组a的大小 < LinkedList的元素个数(意味着数组a不能容纳LinkedList中全部元素) 565 // 则新建一个T[]数组,T[]的大小为LinkedList大小,并将该T[]赋值给a。 566 if (a.length < size) 567 a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( 568 a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); 569 // 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到数组a中 570 int i = 0; 571 Object[] result = a; 572 for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) 573 result[i++] = e.element; 574 575 if (a.length > size) 576 a[size] = null; 577 578 return a; 579 } 580 581 582 // 克隆函数。返回LinkedList的克隆对象。 583 public Object clone() { 584 LinkedList<E> clone = null; 585 // 克隆一个LinkedList克隆对象 586 try { 587 clone = (LinkedList<E>) super.clone(); 588 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 589 throw new InternalError(); 590 } 591 592 // 新建LinkedList表头节点 593 clone.header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null); 594 clone.header.next = clone.header.previous = clone.header; 595 clone.size = 0; 596 clone.modCount = 0; 597 598 // 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到克隆对象中 599 for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) 600 clone.add(e.element); 601 602 return clone; 603 } 604 605 // java.io.Serializable的写入函数 606 // 将LinkedList的“容量,所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中 607 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 608 throws java.io.IOException { 609 // Write out any hidden serialization magic 610 s.defaultWriteObject(); 611 612 // 写入“容量” 613 s.writeInt(size); 614 615 // 将链表中所有节点的数据都写入到输出流中 616 for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) 617 s.writeObject(e.element); 618 } 619 620 // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式反向读出 621 // 先将LinkedList的“容量”读出,然后将“所有的元素值”读出 622 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 623 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 624 // Read in any hidden serialization magic 625 s.defaultReadObject(); 626 627 // 从输入流中读取“容量” 628 int size = s.readInt(); 629 630 // 新建链表表头节点 631 header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null); 632 header.next = header.previous = header; 633 634 // 从输入流中将“所有的元素值”并逐个添加到链表中 635 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 636 addBefore((E)s.readObject(), header); 637 } 638 639 }
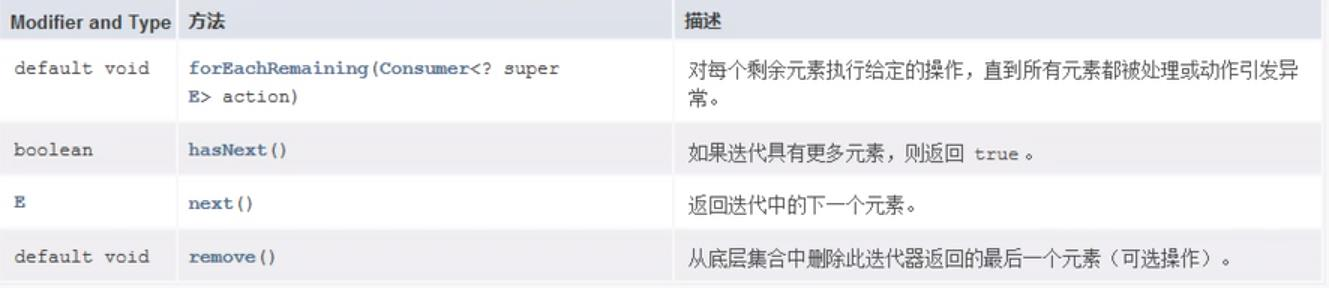
迭代器
通常情况下,你会希望遍历一个集合中的元素。例如,显示集合中的每个元素。
一般遍历数组都是采用for循环或者增强for,这两个方法也可以用在集合框架,但是还有一种方法是采用迭代器遍历集合框架,它是一个对象,实现了Iterator 接口或 ListIterator接口。
迭代器,使你能够通过循环来得到或删除集合的元素。ListIterator 继承了 Iterator,以允许双向遍历列表和修改元素。
1 public class Example01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();//创建ArrayList集合 4 //向集合中添加元素 5 list.add("stu1"); 6 list.add("stu2"); 7 list.add("stu3"); 8 list.add("stu4"); 9 //第一种方法,把链表变为数组相关内容进行遍历 10 String[] strArray = new String[list.size()]; 11 list.toArray(strArray); 12 for (int i = 0; i <strArray.length ; i++) { 13 System.out.println(strArray[i]); 14 } 15 //第二种遍历方法使用 For-Each 遍历 List 16 for (String str : list) { 17 System.out.println(str); 18 } 19 //第三种遍历 使用迭代器进行相关遍历 20 Iterator it = list.iterator(); //获取Iterator对象 21 while (it.hasNext()){ //判断ArrayList集合中是否存在下一个元素 22 Object obj = it.next(); //取出ArrayList集合中的元素 23 System.out.println(obj); 24 } 25 } 26 }