0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结(0-5分)
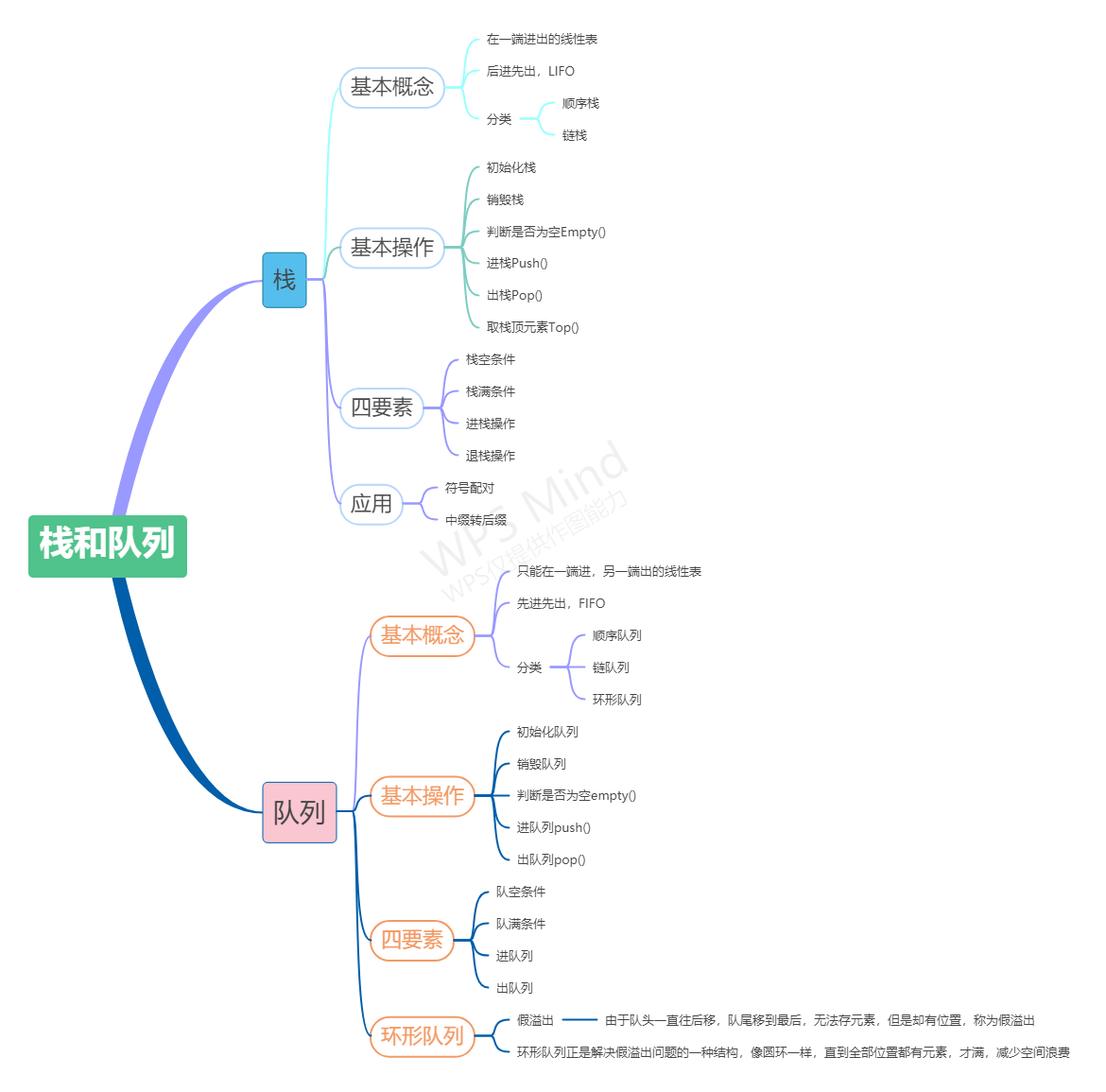
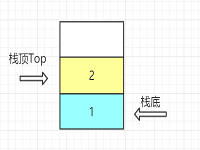
1.1 栈
- 定义:栈是一种只能在一端进行插入删除操作的线性表。
- 组成:栈顶--Top进行操作; 栈底--不能进行任何操作
- 特性:先进后出,后进先出;线性关系
- 基本操作:初始化,销毁,判断是否为空,进栈,出栈,取栈顶元素
- 存储结构:顺序栈与链栈,两者的不同与其存储结构有关
1.1.1 顺序栈
- 四要素:
1. 栈空:top=-1
2. 栈满:top=MaxSize-1
3. 进栈:S.data[++S.top]=e
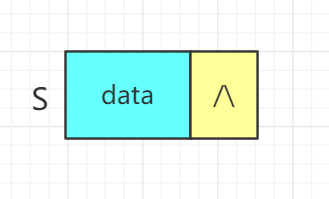
4. 出栈:e=S.data[S.top--] - 结构体
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top; //栈顶指针
}Stack,*SqStack;
- 初始化
void CreatStack(SqStack s) {
s = new Stack;
s->top = -1;
}
- 是否为空
看top是否有增加即可判断
bool StackEmpty(SqStack s) {
return (s->top == -1);
}
- 进栈
元素e进栈,先将top++腾出空位,再将e放到栈顶
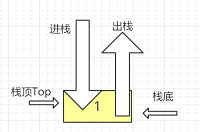
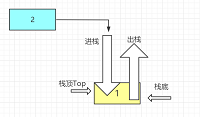

bool Push(SqStack s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == MaxSize-1) {
cout << "栈满";
return false;
}
s->data[++s->top] = e;
return true;
}
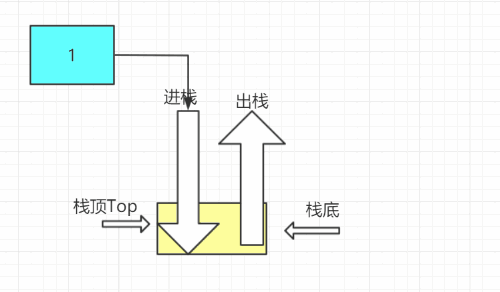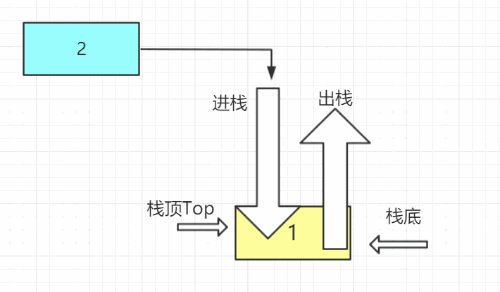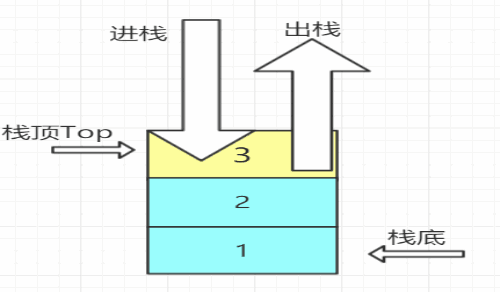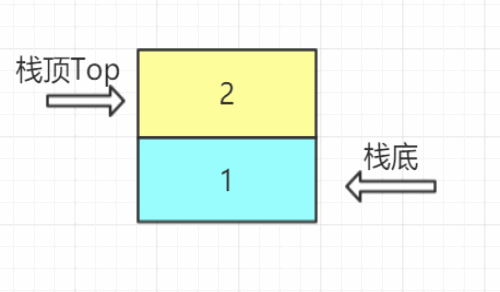
- 出栈
直接让栈顶top--,即可,但不是物理删除
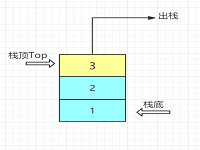
bool Pop(SqStack s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == -1) {
cout << "栈空";
return false;
}
e=s->data[s->top--];
return true;
}
- 取栈顶元素

bool GetTop(SqStack s, ElemType e) {
if (s->top == -1) {
cout << "栈空";
return false;
}
e = s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
1.1.2 链栈
- 四要素:
1. 栈空:S->next=NULL
2. 栈满:不考虑
3. 进栈:头插法
4. 出栈:e=S->next->data,并删除结点 - 结构体
typrdef struct linkNode
{
ElemType data;
struct linkNode *next;
}LiNode,*Listack;
- 初始化
void CreatStack(LiStack &s)
{
s=new LiNode;
s->next=NULL;
}
- 是否为空
bool StackEmpty(LiStack S)
{
return (S->next == NULL);
}
- 进栈
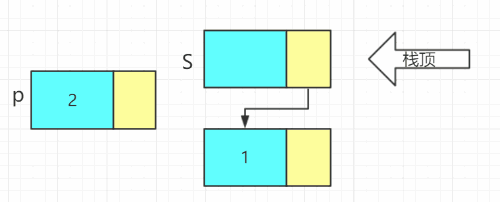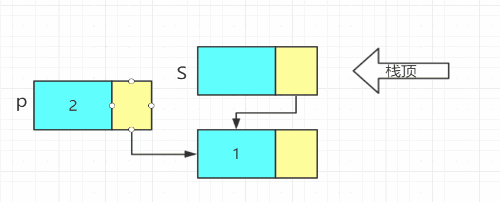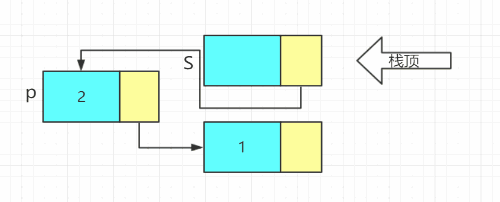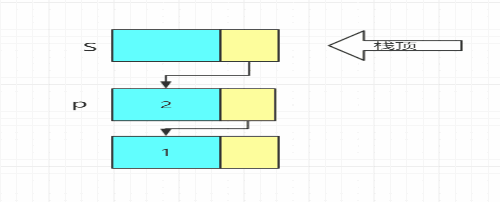
void Push(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
LiStack p;
p = new LiNode;
p->data = e;
p->next = S->next;//头插法
S->next = p;
}
- 出栈
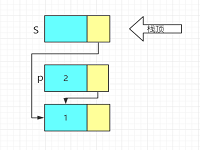
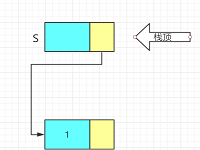
bool Pop(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
LiStack p;
if (S->next == NULL)return false;
p = S->next;
e = p->data;
S->next = p->next;
delete p;
return true;
}
- 取栈顶元素
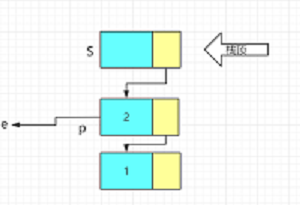
bool DetTop(LiStack& S, ElemType e)
{
if (S->next == NULL)return false;
e = S->next->data;
return true;
}
1.1.3C++中的stack库
| 函数 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| stack<int>S | 定义int类型的栈 |
| S.push(x) | X进栈 |
| S.pop() | 弹出栈顶元素 |
| e=S.top() | 取栈顶元素赋给e |
| S.empty() | 判断栈是否为空 |
| S.size() | 判断栈的长度 |
使用时加上头文件#include<stack>
采用链栈的方式存储
1.1.4 栈的应用
1. 中缀表达式转后缀表达式
- 数字:碰到数字就输出,对于多位数或小数采取循环解决
- 正负号:开头正负号,flag标记,正号不输出,后面的正负号和前面一样
- 加减号:优先级最低,所以进栈的时候,必须是空栈,除非是左括号
- 乘除号:优先级最高,但栈顶如果也是乘除,则先弹出,再入栈
- 左括号:进栈前优先级最高,直接进栈,进栈后优先级最低
- 右括号:不入栈,将栈中元素弹出,直到碰到左括号
代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
stack<char>S;
int main()
{
int flag=0;
string str;
cin >> str;
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {//对字符进行遍历
/*判断有负号*/
if ((str[i] == '-'||str[i]=='+') && flag == 0){
if(str[i]=='+') continue;//加号不输出
cout << str[i];//对第一个字符进行判断有无负号
}
else if ((str[i] == '-'||str[i]=='+') && i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == '(') {//对后面数据进行判断,是否有负号
if(str[i]=='+'){ cout<<" ";
flag = 0;
continue;
}
cout << " " << str[i];
}
/*判断是否是数字,包括小数*/
else if ((str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')||str[i]=='.') {
if (flag)cout << " ";
while ((str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') || str[i] == '.') cout << str[i++];
i--;//避免下一个数据被埋没
flag = 1;//除去第一个数不带空格,后面都要带
}
/*判断运算符*/
else if (str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+') {//加减优先级相同,且优先级低
if (S.empty())S.push(str[i]);//当栈为空时,进行入栈
else {//栈顶优先级高,进行出栈,直到空栈
while (!S.empty()) {
if (S.top() == '(')break;//左括号进栈后优先级最低
cout << " " << S.top();
S.pop();
}
S.push(str[i]);
}
}
else if (str[i] == '(')S.push(str[i]);//左括号进栈前优先级最高,直接入栈
else if (str[i] == '*' || str[i] == '/') {//遇到乘与除,优先级高,如果栈顶为乘或除,需要将它们输出,再入栈
while (!S.empty() && (S.top() == '*' || S.top() == '/')) {
cout << " " << S.top();
S.pop();
}
S.push(str[i]);
}
else if (str[i] == ')') {//遇到右括号,就让左括号上面的全部输出,并将左括号弹出
while (S.top() != '(') {
cout << " " << S.top();
S.pop();
}
S.pop();
}
}
while (!S.empty()) {//将栈中剩余输出
cout << " " << S.top();
S.pop();
}
return 0;
}
2. 符号配对
- 当遇到左符号时:进行入栈,对于/*只需要入/即可
- 当遇到右符号时:判断是否为空,不为空在进行符号匹配
- 对/* 和*/特判
- 匹配:1.匹配成功;2.栈空,缺少左符号;3.栈不空,缺少右符号
代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
stack<char>S;
int IsMatch(char a, char b);
int main()
{
string s, str;
int len;
while (1) {//读入字符
getline(cin, s);
if (s == ".")break;
str += s;
}
len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{') S.push(str[i]);//左符号入栈
else if (str[i] == '/' && i + 1 < len && str[i + 1] == '*')S.push(str[i++]); //左符号入栈
else if (str[i] == ')' || str[i] == ']' || str[i] == '}') {//右符号进行匹配
if (!S.empty() && IsMatch(S.top(),str[i]))//匹配成功
S.pop();
else if (S.empty()) {//栈空
cout << "NO" << endl;
if(str[i]=='*')cout<<"?-*/";
else cout<<"?-"<<str[i];
return 0;
}
else if(!S.empty()){
cout << "NO" << endl;
if(S.top()=='/')cout<<"/*-?";
else cout<<S.top()<<"-?";
return 0;
}
}
else if (str[i] == '*' && str[i + 1] == '/' && (i + 1 < len)) {// /*进行匹配
if (!S.empty() && S.top() == '/')//匹配
S.pop();
else if (S.empty()) {//栈空
cout << "NO" << endl;
if(str[i]=='*')cout<<"?-*/";
else cout<<"?-"<<str[i];
return 0;
}
else if(!S.empty()){
cout << "NO" << endl;
if(S.top()=='/')cout<<"/*-?";
else cout<<S.top()<<"-?";
return 0;
}
i++;
}
}
if (S.empty())cout << "YES";
else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
if(S.top()=='*'||S.top()=='/') cout <<"/*-?";
else cout << S.top() << "-?";
}
return 0;
}
int IsMatch(char a, char b)
{
if (a == '[' && b == ']')return 1;
else if (a == '(' && b == ')')return 1;
else if (a == '{' && b == '}')return 1;
else return 0;
}
3. 迷宫求解
深度搜索(DFS),又称回溯法。
从上一个节点开始,任意找下一个能走的点,当找不到能走的点时,退回上一个点寻找是否有其他方向的点。
使用栈存储当前路径。后进先出,方便回退到上一个点。
这种找到的不是最短路,但却效率高
#include <stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 100
#define M 8
#define N 8
int mg[M + 2][N + 2] =
{
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
};
typedef struct
{
int i; //当前方块的行号
int j; //当前方块的列号
int di; //di是下一可走相邻方位的方位号
} Box;
typedef struct
{
Box data[MaxSize];
int top; //栈顶指针
} StType; //定义栈类型
int mgpath(int xi, int yi, int xe, int ye) //求解路径为:(xi,yi)->(xe,ye)
{
int i, j, k, di, find;
StType st; //定义栈st
st.top = -1; //初始化栈顶指针
st.top++; //初始方块进栈
st.data[st.top].i = xi; st.data[st.top].j = yi; st.data[st.top].di = -1;
mg[xi][yi] = -1;
while (st.top > -1) //栈不空时循环
{
i = st.data[st.top].i; j = st.data[st.top].j; di = st.data[st.top].di; //取栈顶方块
if (i == xe && j == ye) //找到了出口,输出路径
{
printf("迷宫路径如下:
");
for (k = 0; k <= st.top; k++)
{
printf(" (%d,%d)", st.data[k].i, st.data[k].j);
if ((k + 1) % 5 == 0) //每输出每5个方块后换一行
printf("
");
}
printf("
");
return(1); //找到一条路径后返回1
}
find = 0;
while (di < 4 && find == 0) //找下一个可走方块
{
di++;
switch (di)
{
case 0:i = st.data[st.top].i - 1; j = st.data[st.top].j; break;
case 1:i = st.data[st.top].i; j = st.data[st.top].j + 1; break;
case 2:i = st.data[st.top].i + 1; j = st.data[st.top].j; break;
case 3:i = st.data[st.top].i, j = st.data[st.top].j - 1; break;
}
if (mg[i][j] == 0) find = 1; //找到下一个可走相邻方块
}
if (find == 1) //找到了下一个可走方块
{
st.data[st.top].di = di; //修改原栈顶元素的di值
st.top++; //下一个可走方块进栈
st.data[st.top].i = i; st.data[st.top].j = j; st.data[st.top].di = -1;
mg[i][j] = -1; //避免重复走到该方块
}
else //没有路径可走,则退栈
{
mg[st.data[st.top].i][st.data[st.top].j] = 0;//让该位置变为其他路径可走方块
st.top--; //将该方块退栈
}
}
return(0); //表示没有可走路径,返回0
}
int main()
{
mgpath(1, 1, 7, 5);
return 0;
}
1.3 队列
- 定义:队列是一种只能在一端进行插入,另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
- 组成:队头--front进行删除操作; 队尾--rear进行插入操作
- 特性:先进先出,后进后出;线性关系
- 基本操作:初始化,销毁,判断是否为空,进队列,出队列,取队头(或队尾)元素
- 分类:顺序队列,环形队列,链队列
1.3.1顺序队列

- 四要素:
1. 队空:front=rear
2. 队满:rear=MaxSize-1
3. 进队:Q->data[++Q->rear]=e
4. 出队:e=Q->data[Q->front--] - 结构体
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
ElemType front, rear;
}Queue,*SqQueue;
- 初始化队列
void CreatQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{
Q == new Queue;
Q->front = Q->rear = -1;
}
- 判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue& Q)
{
return (Q->front == Q->rear);
}
- 进队列
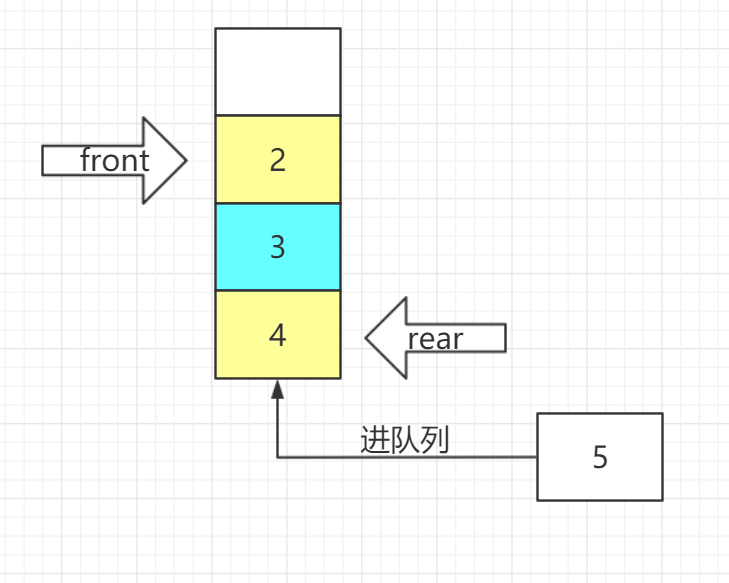

bool EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType e)
{
if (Q->rear + 1 == MaxSize)return false;
Q->data[++Q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
- 出队列
bool DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType& e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)return false;
e = Q->data[Q->front--];
return true;
}
1.3.2环形队列
由于顺序队列中,队头进行删除后,并不是物理删除,只是front指针后移,会导致前面空间的浪费,
最后的结果是,当达到front=rear时,很大的空间并没有数据,造成假溢出,此时就要用环形队列啦!!!
环形队列就像是一个大圆桌,有人来就找空位,有人走腾出空位,直到全部坐满。

其存储结构与顺序表相同,在某些地方发生一些改变
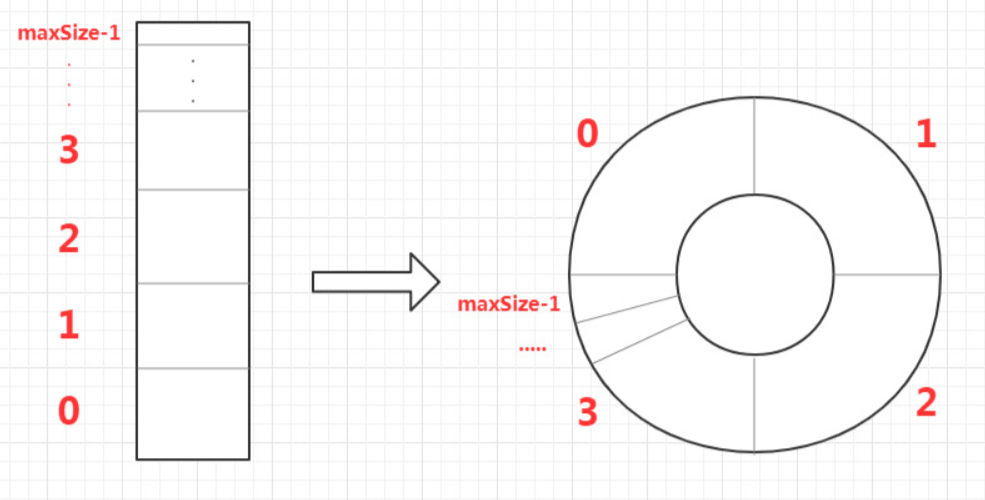
| 不同 | 顺序队列 | 循环队列 |
|---|---|---|
| 初始化 | rear=front=-1 | rear=front=0 |
| 队满 | rear=front | (rear+1)%MaxSize=front |
| 进队 | rear++ | rear=(rear+1)%MaxSize |
| 出队 | front++ | front=(front+1)%MaxSize |
1.3.1链队列

- 结构体
//定义节点结构
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}QueueNode;
//定义头节点
typedef struct {
QueueNode* front;
QueueNode* rear;
}LinkQueue;
- 初始化队列
初始化链队列,头节点置空
void InitQueue(LinkQueue* Q)
{
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
}
- 判断是否为空
int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue* Q)
{
return(Q->front == NULL && Q->rear == NULL);
}
- 进队列
void EnLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType v)
{
QueueNode* p;
p = new QueueNode;//为新的节点分配空间
p->data = v;
p->next = NULL;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))
Q->front = Q->rear = p;
else
{
Q->rear->next = p; //将新的节点连接到队列
Q->rear = p; //指向队列尾
}
}
- 出队列
bool DeLinkQueue(LinkQueue* Q, ElemType &e)
{
QueueNode* s;
if (QueueEmpty(Q))return false; //判断队列是否为空
s = Q->front;
e = s->data;
if (Q->front == Q->rear) //判断队列是否只有一个节点
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
else
Q->front = s->next;
delete s;
return true;
}
1.3.4C++中的queue库
| 函数 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| queue<int>Q | 定义一个队列 |
| Q.push(X) | X元素进队列尾 |
| Q.pop() | 弹出队头元素 |
| e=Q.front() | 队头元素赋给e |
| e=Q.back() | 队尾元素赋给e |
| Q.empty() | 判断是否尾空 |
| Q.size() | 计算队列长度 |
使用时加上头文件#include<queue>
采用链式存储
1.3.5队列应用
1.报数问题
运用的数据结构:环形队列
只要不是出队列的数据,都先出队列,再进队列;
满足要求就输出
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
queue<int>q;
int main()
{
int n,m,t;
cin>>n>>m;
if(m>n){
cout<<"error!";
return 0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) q.push(i);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<m;j++){
t=q.front();//保存
q.pop();//弹出
q.push(t);//进入
}
t=q.front();//第m个数
cout<<t<<" ";
q.pop();
}
cout<<q.front();
}
2.迷宫之最短路
队列解决迷宫问题,广度搜索(BFS),能够找到最短路,效率不如DFS
从一个节点开始,寻找所有接下来能继续走的点,继续不断寻找,直到找到出口。
使用队列存储当前正在考虑的节点。
#include <stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 100
#define M 8
#define N 8
int mg[M+2][N+2]=
{
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
};
typedef struct
{ int i,j; //方块的位置
int pre; //本路径中上一方块在队列中的下标
} Box; //方块类型
typedef struct
{
Box data[MaxSize];
int front,rear; //队头指针和队尾指针
} QuType; //定义顺序队类型
void print(QuType qu,int front) //从队列qu中输出路径
{
int k=front,j,ns=0;
printf("
");
do //反向找到最短路径,将该路径上的方块的pre成员设置成-1
{ j=k;
k=qu.data[k].pre;
qu.data[j].pre=-1;
} while (k!=0);
printf("迷宫路径如下:
");
k=0;
while (k<MaxSize) //正向搜索到pre为-1的方块,即构成正向的路径
{ if (qu.data[k].pre==-1)
{ ns++;
printf(" (%d,%d)",qu.data[k].i,qu.data[k].j);
if (ns%5==0) printf("
"); //每输出每5个方块后换一行
}
k++;
}
printf("
");
}
int mgpath(int xi,int yi,int xe,int ye) //搜索路径为:(xi,yi)->(xe,ye)
{
int i,j,find=0,di;
QuType qu; //定义顺序队
qu.front=qu.rear=-1;
qu.rear++;
qu.data[qu.rear].i=xi; qu.data[qu.rear].j=yi; //(xi,yi)进队
qu.data[qu.rear].pre=-1;
mg[xi][yi]=-1; //将其赋值-1,以避免回过来重复搜索
while (qu.front!=qu.rear && !find) //队列不为空且未找到路径时循环
{
qu.front++; //出队,由于不是环形队列,该出队元素仍在队列中
i=qu.data[qu.front].i; j=qu.data[qu.front].j;
if (i==xe && j==ye) //找到了出口,输出路径
{
find=1;
print(qu,qu.front); //调用print函数输出路径
return(1); //找到一条路径时返回1
}
for (di=0;di<4;di++) //循环扫描每个方位,把每个可走的方块插入队列中
{
switch(di)
{
case 0:i=qu.data[qu.front].i-1; j=qu.data[qu.front].j;break;
case 1:i=qu.data[qu.front].i; j=qu.data[qu.front].j+1;break;
case 2:i=qu.data[qu.front].i+1; j=qu.data[qu.front].j;break;
case 3:i=qu.data[qu.front].i, j=qu.data[qu.front].j-1;break;
}
if (mg[i][j]==0)
{ qu.rear++; //将该相邻方块插入到队列中
qu.data[qu.rear].i=i; qu.data[qu.rear].j=j;
qu.data[qu.rear].pre=qu.front; //指向路径中上一个方块的下标
mg[i][j]=-1; //将其赋值-1,以避免回过来重复搜索
}
}
}
return(0); //未找到一条路径时返回1
}
int main()
{
mgpath(1,1,M,N);
return 1;
}
2.PTA实验作业(4分)
2.1 7-3 符号配对

2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
- 思路
- 当遇到左符号时:进行入栈,对于/*只需要入/即可
- 当遇到右符号时:判断是否为空,不为空在进行符号匹配
- 对/* 和*/特判
- 匹配:1.匹配成功;2.栈空,缺少左符号;3.栈不空,缺少右符号
- 伪代码
stack<char>S
将字符读入str字符数据中
for i = 0 to str.length()
if str[i]是(, [, { then S.push(str[i])
else if str[i] = / && i + 1 < str.length() && str[i + 1] = *
then S.push(str[i++])
else if str[i] = ),], }
if S不空且S.top()与str[i]匹配,弹出栈顶S.pop()
else if S空
cout << "NO"<<endl
if str[i]=* cout<<"?-*/"
else cout<<"?-"<<str[i]
return 0
else if
cout << "NO"<<endl
if S.top()=/ cout<<"/*-?"
else cout<<S.top()<<"-?"
return 0
else if str[i] = *&&i + 1 < str.length() && str[i + 1] = /
if S不空且S.top() = / thenS.pop()//匹配成功
else if S空
cout << "NO"<<endl
if str[i]=* cout<<"?-*/"
else cout<<"?-"<<str[i]
return 0
else if
cout << "NO"<<endl
if S.top()=/ cout<<"/*-?"
else cout<<S.top()<<"-?"
return 0
i++
end for
if 栈空 cout<<"YES"
else
cout<<"NO"
if top是/ cout<<"/*-?"
else cout<<S.top()<<"-?"
return 0
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
利用栈的先进后出特点,最顶端一定是和右符号最近的左符号,进行比对,判断是否匹配
利用stack库,使得操作更快
学会思考多种情况和特殊情况的处理,将/左符号只留一个/右符号留一个 -
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
- 思路
输入时,将a,b客户分别入队到对应的队列中
开始循环输出,a,输出两个,b,输出一个
最后输出剩余队列的元素 - 伪代码
queue<int>a, b;//a,b分别代表两个银行,将数据入队
while a,b都不为空
// 输出两个a,一个b
if flag=1 cout<<a.front() flag=0//进行空格处理
else cout<<" "<<a.front()
a.pop()
if a不为空,cout << " " << a.front() a.pop()
cout << " " << b.front() b.pop()
end while
while a不为空
if flag = 1 cout << a.front() flag = 0//没有b的元素进行空格处理
else cout << " " << a.front()
a.pop()
end while
while b不为空
if flag = 1 cout << b.front() flag = 0//没有a的元素进行空格处理
else cout << " " << b.front()
b.pop()
end while
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
根据队列先进先出,可以将不同银行客户按顺序输出,
直接使用C++中的queue库,更加快捷方便
3.阅读代码(0--1分)
3.1 题目及解题代码
class DinnerPlates {
public:
int cap;
set<int> notFullStack;
map<int, stack<int>> stackCont;
DinnerPlates(int capacity) {
cap = capacity;
}
void push(int val) {
// 正常情况下 stackCont 为空时 notFullStack 也为空
if(stackCont.size() == 0 ){
stackCont[0].push(val);
if(stackCont[0].size() < cap) notFullStack.insert(0);
}
else if(stackCont.size() != 0 && notFullStack.size() == 0){
int lastStackIndex = stackCont.rbegin()->first ;
// 不需要 判断最后一个 stack 是否 满了
stackCont[lastStackIndex + 1].push(val);
if(stackCont[lastStackIndex + 1].size() < cap) notFullStack.insert(lastStackIndex + 1);
}
else if( stackCont.size() != 0 && notFullStack.size() != 0 ){
int firstNotFullFromLeft = *notFullStack.begin();
stackCont[firstNotFullFromLeft].push(val);
if(stackCont[firstNotFullFromLeft].size() >= cap) notFullStack.erase(firstNotFullFromLeft);
}
}
int pop() {
if(stackCont.size() == 0) return -1;
int lastStackIndex = stackCont.rbegin()->first ;
int val = stackCont[lastStackIndex].top();
stackCont[lastStackIndex].pop();
int lastStackSize = stackCont[lastStackIndex].size();
// 没有满的 stack
notFullStack.insert(lastStackIndex);
if(lastStackSize == 0) {
stackCont.erase(lastStackIndex);
notFullStack.erase(lastStackIndex);
}
return val;
}
int popAtStack(int index) {
if( stackCont.find(index) == stackCont.end() ) return -1;
// 最大的栈 index
int lastStackIndex = stackCont.rbegin()->first ;
int val = stackCont[index].top();
stackCont[index].pop();
int thisStackSize = stackCont[index].size();
notFullStack.insert(index);
if(thisStackSize == 0) {
stackCont.erase(index);
if(lastStackIndex == index) notFullStack.erase(index);
}
return val;
}
};
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
利用了C++中的STL库的set和map;
set记录未满的栈的index序列,set可以使之有序
map 记录栈index 以及对应的 stack
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点
名称过于冗长,阅读有点麻烦。。。