这篇博文整理的很好,我网上看道 的,写的详细的都在这里面了!
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ch_soft/article/details/6945987。
首先、对UITableView进行讲解,下面有对它进行实际的应用
UITableView
显示大型内容的列表
单行,多列
垂直滚动,没有水平滚动
大量的数据集
性能强大,而且普遍存在于iPhone的应用程序中
TableView Styles
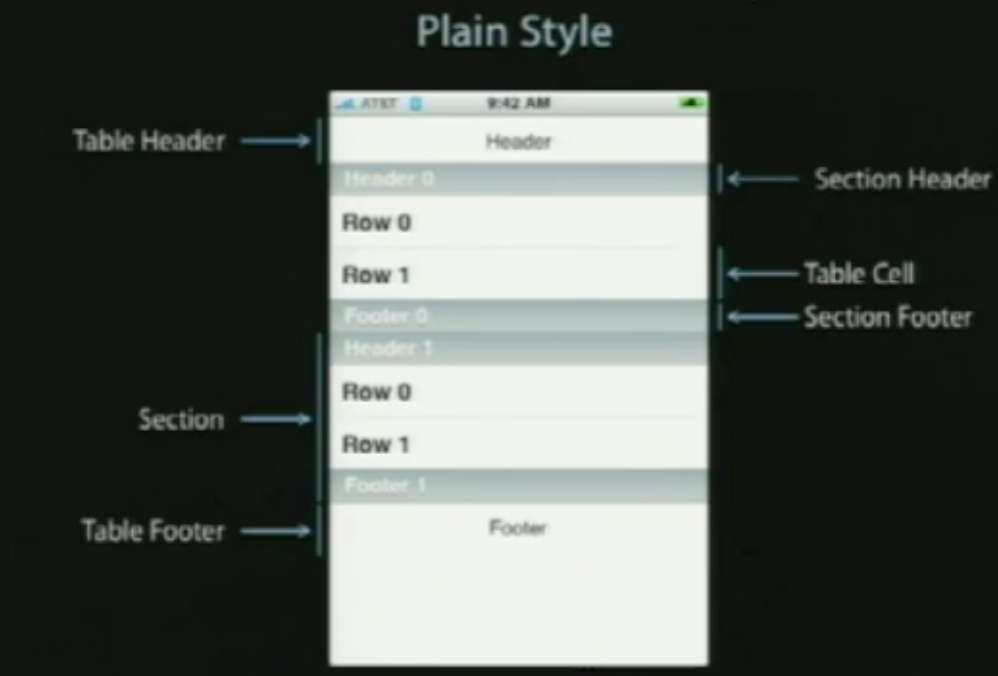
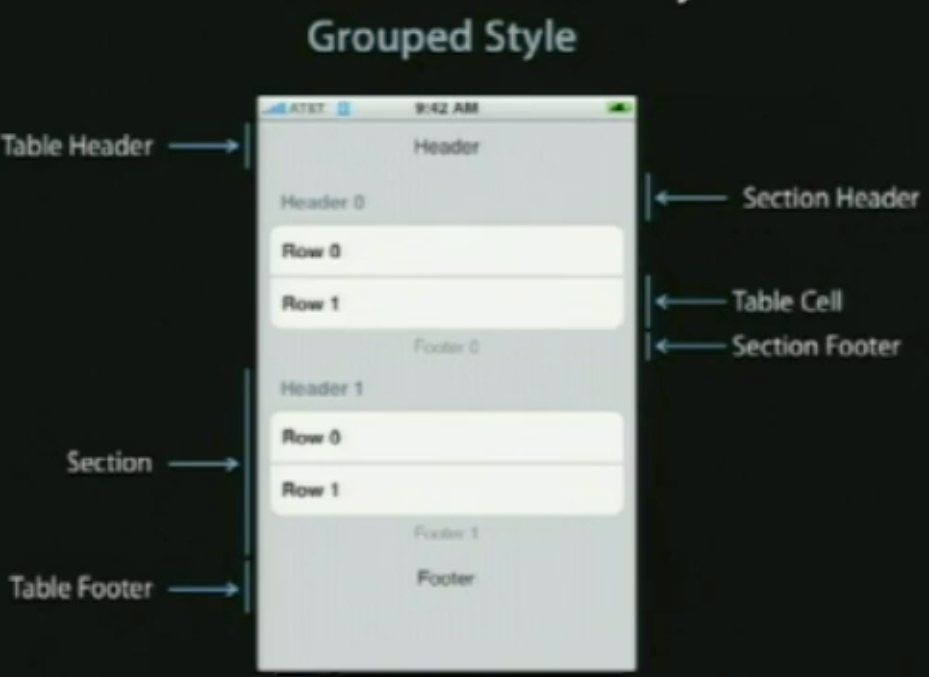
UITableView有两个默认的内置风格,第一个是UITableViewStylePlain(简明风格,简明风格表明表格视图自身没有真正地在你自己实际地提供任何外观之前提供很多的外观,大部分情况下,它会做的唯一的事情是它会给你这些header和footer,在顶部的章节header有章节F,它是当前固定在屏幕的顶部,即使你滚动那个内容章节的header F会保持在那里,直到所有F的内容都移走,然后它滚出去。表格视图还提供你在右边的索引部分,那只用在简易风格的表格视图中,你能够获取它。)另一种风格是UITableViewStyleGrouped风格(组团风格),UITableViewStyleGrouped表格视图是UIKit提供的另外一个默认风格,它给围绕章节分段的外观,它是垂直条纹的背景,顶部是白色圆形分段,你默认通过UITableView:StyleGrouped获得该类型的外观。
表格视图以及组成部分
在顶部,我们有表格header,它是UITableView上的一个可设置的属性,它只是个UIView,你能创建任何UIView子类或用UIImageView或UILable分配并设置它们为表格视图的tableheader view ,然后表格视图会安置它到你其余的内容之上,它会随着内容上下滚动。
在表格视图的内容底部,我们有表格footer,与header一样是UIView的任意子视图,它是你设置的UITableView的属性,然后表格视图会安置它到你其余的内容之下,在表格header和footer视图之间的是章节内容。
在章节中,有章节的header和章节的footer,在它们之间是所有的独立单元,就是Tablecell。如下图:
使用TableViews
在表格视图中显示数据
定制显示的外观和行为
一个直接的解决方法
表格视图用来显示一列数据,所以使用一个数组
[myTableView setList : myListOfStuff];//该方法不存在,想法比较天真
该方法争议性
所有的数据必须事先装载
所有的数据都装载在内存中
更加灵活的方案
另外一个对象为表格视图提供数据
不是一次性全部取得
只取现在需要展示的数据
像一个委托,它是纯粹的数据导向,它只向数据源询问数据
UITableViewDataSource(数据源协议)
提供章节和行的数目
//optionalmethod ,default to 1 if not implemented
-(NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView*)tableView;
//requiredmethod
-(NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section;
必要的时候向表格视图提供所要显示的cells
//required method
-(UITableViewCell*)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;//在该方法中,UITableViewCell是UIView的一个子类,它知道如何在表格视图滚轴,知道如何绘制分组风格表格视图和组群风格表格视图,它必须自己是一个UITableViewCell或者UITableViewCell的子类。
NSIndexPath
是Foundation框架中的一个普通的类,它提供了到嵌套数列的树中特定节点的路径,事实上,它是一个整数阵列,表格视图使用这个去表现在特定章节中的特定行,UITableView用的所有索引路径正好有两个元素,第一个是章节,第二个是行。
NSIndexPath和TableViews
@interfaceNSIndexPath (UITableView) {
}
+(NSIndexPath*)indexPathForRow:(NSUInteger)row inSection:(NSUInteger)section;
@property(nonatomic,readonly)NSUIntegerrow;
@property(nonatomic,readonly)NSUIntegersection;
@end
SingleSection Table View
返回行数
-(NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView*)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{
return[myStringcount];
}
请求时提供一个单元
-(UITableViewCell*)tableView:(UITableView*)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)indexPath {
UITableViewCell*cell = ......;
cell.textLabel.text=[myStringobjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
return[cell autorelease];
}
单元复用(cellreuse)
当你轻滑屏幕,你必须一次滚动上百行的文字,很多很多的不同单元,它不会完成的很好,每次一个消失,你破坏呢个表格视图单元,然后为下一个创建新的,我们最终会做的是当一个表格视图单元从顶部消失,它会放在一个复用队列中,并且在你的TableViewCellforRowIndexPath方法中,你可以选择,当然你应该总是这样做,你有机会去在分配新的单元前,向表格视图询问复用队列其中的一个单元,如果一个单元已经从顶部滚轴消失,对于显示当前可视的东西,它不会必须的,你能取得它改变它的内容为你所需要显示的新行而它会被重新滚进底部。(有点像循环瀑布)
-(UITableViewCell*)dequeueReusableCellWithindentifier:(NSString*)identifier;
//取回可复用的一个单元
-(UITableViewCell*)tableView:(UITableView*)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)indexPath {
UITableViewCell*cell = [tableViewdequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@"MyIdentifier"];
if(cell== nil){
cell=[[[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:.....reuseIdentifier:@"MyIdentifier"]autorelease];
}
cell.text= [myStringobjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
returncell;
}
触发一个更新
什么时候数据源会被请求数据
当一行变得可视
完全更新会被响应当使用reloadData
-(void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[superviewWillAppear:animated]; //所有的数据重新被加载,然后在放到复用队列中
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
章节和行进行重载数据
-(void)insertSections:(NSIndexSet*)sectionswithRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;//可以插入整个章节
-(void)ideleteSections:(NSIndexSet*)sectionswithRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;//可以删除整个章节
-(void)reloadSections:(NSIndexSet*)sections withRowAnimation:
(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;//在iPhoneos 3.0中重载章节数据(上面两个方法的合并)
它们能重载部分的数据,而不会把所有东西都丢掉
-(void)insertRowsAtIndexPaths:(NSArray*)indexPahts withRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;
-(void)deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:(NSArray*)indexPahts withRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;
-(void)reloadRowsAtIndexPaths:(NSArray*)indexPahts withRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAniamtion)animation;
其它的数据源方法
为章节的header和footer设置标题(表格的header和footer是表格视图上的属性,你只分配那些视图章节header和footer是依据章节的,因此它们由委派功能所提供)
允许编辑和重排单元
外观和行为
UITableViewDelegate
可定制外观和行为
逻辑独立于视图
数据源和委派经常是相同的对象(事实上,很少情况下数据源不是委派)
表格视图的外观和行为
定制表格视图单元的外观
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *) tableView willDisplayCell:(UITableViewCell *)cellforRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;
这个会在表格视图的其中一个单元变为可视前立刻被调用,它是你在表格视图单元显示在屏幕上之前的外观定制的最后机会,它保证一旦你调用这个方法,我们不会涉及任何单元的外观,这之后,你改变的任何东西都会显示在屏幕上,如果有一些东西你可能在TableViewcellForRowAtIndexPath方法中不知道,你想稍微懒惰地做这个,这会在那之后最后的机会去修改外观。
验证和响应所选择的变化
使用表格视图委派功能,对于选择会有不同的功能
-(NSIndexPath*)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewwillSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)indexPath;//用户选择完成抬起手指,在该方法中,你可能决定去分配新的UIViewController,然后推它到self.navigationContrller,因此一些新事物滑进来,行选择通常会触发一个事件。选择通常不是一个持续的事情,它通常不会在你轻敲之后保持选择状态,通常会谈出选择然后完成一个行为,或者你把它滑出屏幕,当然滑回来时会淡出。在iphone应用程序中你也会看到连续的选择,我们在表格试图中是支持持续选择的,如果用户选择一行而你没有反选它,我们不会替你反选,过去在iPhoneOS 2.0中不是这样的,如果你不反选它,这个行为是不确定的,我们现在支持这个持续选择行为。
响应选择
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)indexPath {
NSIntegerrow = indexPath.row ;
idobjectToDispaly = [myObjects ObjectAtIndex:row ];
MyViewController* myViewController = …....;
myViewController.object = objectToDispaly ;
[self.navigationControllerpushViewController: myViewController animated:YES];
}
修改和禁用选择
-(NSIndexPath*)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewwillSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
if(indexPath.row== ….) {
returnnil;
}
else{ return indexPath ;}
}
UITableViewController
是UIViewController的子类,如果你想用全屏表格试图风格,它会是很便利的起点,表格试图会被自动创建,这包括控制器,表格视图,数据源和委派,它在你第一次出现时替你调用reloadData,它在用户导航回去时反选,会知道你之前所选的item。UITableViewController在正确的时间替你处理反选的事情,它还会闪烁滚动指示条,实际上这是iPhone人机界面的一部分。
TableView cells
指定的初始化程序
-(id)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame reuseIdentifier:(NSString *)reuseIdentifier ;
//旧的版本,现在已经不是默认的初始化程序了
-(id)initWithStyle:(UITableviewCellStyle)style reuseIdentifier:(NSString *)reuseIdentifier ;
//新版本
单元风格(cellstyle)
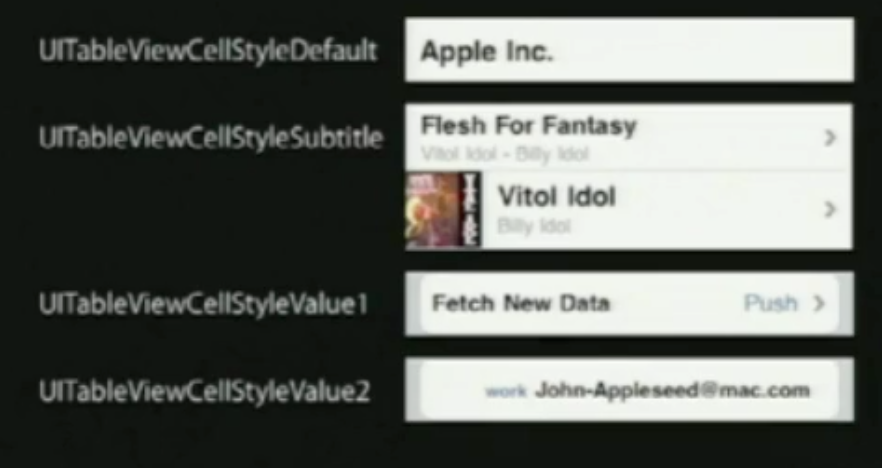
基本属性
UITableViewCell有一个图像视图和一到两个的文本标签
cell.imageView.image= [UIImage imageNamed:@”vitolidok.png”];
cell.textLabel.text= @”Vitol Idol”;
cell.detailTextLabel.text=@”Billy Idol”;
效果如图:

如果你在表格视图单元的默认风格上设置detailTextLabel.text,它是不会做任何事情,因为它不显示一个额外的detailText。
附件类型
//UITableView委托方法
-(UITableViewCellAccessoryType)tableView:(UITableView*)table accessoryTypeForRowWithIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *) indexPath;

-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewaccessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *) indexPath {
//只有是在蓝色描述的按钮(也就是上面的第二个)
NSIntegerrow = indexPath.row.
}
定制内容视图
在有些情况下,简单的图像和文本是不够的
UITableViewCell有一个contentview 属性
为contentview 添加额外的视图
-(UITableViewCell*) tableView :(UITableView) tableViewcellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell*cell = ….......;
CGRectframe = cell.contentView.bounds;
UILabel*myLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame :frame];
myLabel.text= ….;
[cell.contentViewaddSubview : myLabel];
[myLabelrelease];
}
其次,实际的使用方法
第一种,正常的使用方法
//
// TableViewViewController.m
// TableView
//
// Created by ch_soft on 11-11-7.
// Copyright 2011年 __MyCompanyName__. All rights reserved.
//
#import "TableViewViewController.h"
@implementation TableViewViewController
- (void)dealloc
{
[super dealloc];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
{
// Releases the view if it doesn't have a superview.
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Release any cached data, images, etc that aren't in use.
}
#pragma mark - View lifecycle
// Implement viewDidLoad to do additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
dataArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"1",@"2",@"3",@"4",@"5",nil];
edit=NO;
[super viewDidLoad];
UIButton * button=[UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeCustom];
button.frame=CGRectMake(10,10, 60,20);
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(edit:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[button setTitle:@"eidt" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[self.view addSubview:button];
//创建一个tableview
tableview=[[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(10, 40, 300, 400) style:UITableViewStylePlain];
[self.view addSubview:tableview];
tableview.delegate=self;
tableview.dataSource=self;
[tableview release];
}
-(void)edit:(id)sender
{
[tableview setEditing:!tableview.editing animated:YES];
if (edit) {
edit=NO;
[tableview setEditing:NO];
}else
{
edit=YES;
[tableview setEditing:YES];
}
}
#pragma mark TableView Delegate
//对编辑的状态下提交的事件响应
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"commond eidting style ");
if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete) {
[dataArray removeObjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
// Delete the row from the data source.
[tableview deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationFade];
}
else if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleInsert) {
// Create a new instance of the appropriate class, insert it into the array, and add a new row to the table view.
}
}
//响应选中事件
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
NSLog(@"did selectrow");
}
//行将显示的时候调用
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView willDisplayCell:(UITableViewCell *)cell forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"will display cell");
}
//点击了附加图标时执行
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath");
}
//开始移动row时执行
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView moveRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)sourceIndexPath toIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)destinationIndexPath
{
NSLog(@"moveRowAtIndexPath");
}
//开发可以编辑时执行
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView willBeginEditingRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"willBeginEditingRowAtIndexPath");
}
//选中之前执行
-(NSIndexPath*)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView willSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"willSelectRowAtIndexPath");
return indexPath;
}
//将取消选中时执行
-(NSIndexPath *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView willDeselectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"willDeselectRowAtIndexPath");
return indexPath;
}
//移动row时执行
-(NSIndexPath *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView targetIndexPathForMoveFromRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)sourceIndexPath toProposedIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)proposedDestinationIndexPath
{
NSLog(@"targetIndexPathForMoveFromRowAtIndexPath");
//用于限制只在当前section下面才可以移动
if(sourceIndexPath.section != proposedDestinationIndexPath.section){
return sourceIndexPath;
}
return proposedDestinationIndexPath;
}
//删除按钮的名字
-(NSString*)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForDeleteConfirmationButtonForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
return @"删除按钮的名字";
}
//让表格可以修改,滑动可以修改
-(BOOL)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView canEditRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
return YES;
}
//让行可以移动
-(BOOL)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView canMoveRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
return YES;
}
-(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView editingStyleForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
//
NSLog(@"手指撮动了");
return UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete;
}
#pragma mark TableView DataSource
-(NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView{
return 1;
}
-(NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{
return [dataArray count];
}
-(UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSString * indetify=@"cell";
UITableViewCell *cell=[tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:indetify];
if (cell==nil) {
cell=[[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:indetify];
}
cell.textLabel.text=[dataArray objectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
cell.accessoryType=UITableViewCellAccessoryCheckmark;//添加附加的样子
return cell;
}
- (void)viewDidUnload
{
[super viewDidUnload];
// Release any retained subviews of the main view.
// e.g. self.myOutlet = nil;
}
- (BOOL)shouldAutorotateToInterfaceOrientation:(UIInterfaceOrientation)interfaceOrientation
{
// Return YES for supported orientations
return (interfaceOrientation == UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait);
}
@end
第二种,使用自定义UITbaleViewCell方法。
其实很简单,只需要定义一个UItableViewCell的子类,然后在初始化cell的时候,使用自定义的cell生成cell就可以了。
@interface CustomTableCell :UITableViewCell {
}
@end
上篇文章介绍了如何用UITableView显示表格,并讲了几种UITableViewCell的风格。不过有时候我们需要自己定义UITableViewCell的风格,其实就是向行中添加子视图。添加子视图的方法主要有两种:使用代码以及从.xib文件加载。当然后一种方法比较直观。
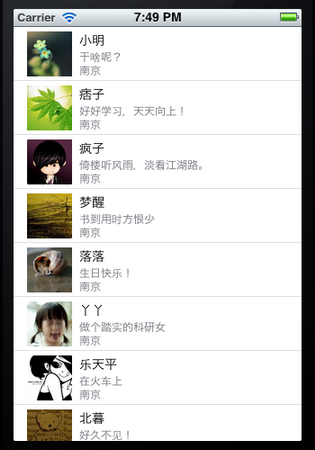
我们这次要自定义一个Cell,使得它像QQ好友列表的一行一样:左边是一张图片,图片的右边是三行标签:

当然,我们不会搞得这么复杂,只是有点意思就行。
1、运行Xcode 4.2,新建一个Single View Application,名称为Custom Cell:

2、将图片资源导入到工程。为此,我找了14张50×50的.png图片,名称依次是1、2、……、14,放在一个名为Images的文件夹中。将此文件夹拖到工程中,在弹出的窗口中选中Copy items into…

添加完成后,工程目录如下:
3、创建一个UITableViewCell的子类:选中Custom Cell目录,依次选择File — New — New File,在弹出的窗口,左边选择Cocoa Touch,右边选择Objective-C class:

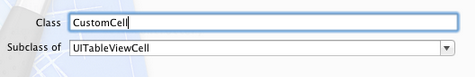
单击Next,输入类名CustomCell,Subclass of选择UITableViewCell:
之后选择Next和Create,就建立了两个文件:CustomCell.h和CustomCell.m。
4、创建CustomCell.xib:依次选择File — New — New File,在弹出的窗口,左边选择User Interface,右边选择Empty:

单击Next,选择iPhone,再单击Next,输入名称为CustomCell,选择好位置:

单击Create,这样就创建了CustomCell.xib。
5、打开CustomCell.xib,拖一个Table View Cell控件到面板上:

选中新加的控件,打开Identity Inspector,选择Class为CustomCell;然后打开Size Inspector,调整高度为60。
6、向新加的Table View Cell添加控件:拖放一个ImageView控件到左边,并设置大小为50×50。然后在ImageView右边添加三个Label,设置标签字号,最上边的是14,其余两个是12:

接下来向CustomCell.h添加Outlet映射,将ImageView与三个Label建立映射,名称分别为imageView、nameLabel、decLabel以及locLable,分别表示头像、昵称、个性签名,地点。
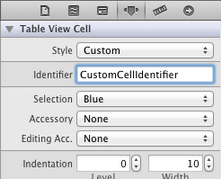
选中Table View Cell,打开Attribute Inspector,将Identifier设置为CustomCellIdentifier:
为了充分使用这些标签,还要自己创建一些数据,存在plist文件中,后边会做。
7、打开CustomCell.h,添加属性:
@property (copy, nonatomic) UIImage *image; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *dec; @property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *loc;
8、打开CustomCell.m,向其中添加代码:
8.1 在@implementation下面添加代码:
@synthesize image; @synthesize name; @synthesize dec; @synthesize loc;
8.2 在@end之前添加代码:
- (void)setImage:(UIImage *)img {
if (![img isEqual:image]) {
image = [img copy];
self.imageView.image = image;
}
}
-(void)setName:(NSString *)n {
if (![n isEqualToString:name]) {
name = [n copy];
self.nameLabel.text = name;
}
}
-(void)setDec:(NSString *)d {
if (![d isEqualToString:dec]) {
dec = [d copy];
self.decLabel.text = dec;
}
}
-(void)setLoc:(NSString *)l {
if (![l isEqualToString:loc]) {
loc = [l copy];
self.locLabel.text = loc;
}
}
这相当于重写了各个set函数,从而当执行赋值操作时,会执行我们自己写的函数。
好了,现在自己定义的Cell已经可以使用了。
不过在此之前,我们先新建一个plist,用于存储想要显示的数据。建立plist文件的方法前面的文章有提到。我们建好一个friendsInfo.plist,往其中添加数据如下:

注意每个节点类型选择。
9、打开ViewController.xib,拖一个Table View到视图上,并将Delegate和DataSource都指向File’ Owner,就像上一篇文章介绍的一样。
10、打开ViewController.h,向其中添加代码:
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface ViewController : UIViewController<UITableViewDelegate, UITableViewDataSource> @property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray *dataList; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray *imageList; @end
11、打开ViewController.m,添加代码:
11.1 在首部添加:
#import "CustomCell.h"
11.2 在@implementation后面添加代码:
@synthesize dataList; @synthesize imageList;
11.3 在viewDidLoad方法中添加代码:
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
//加载plist文件的数据和图片
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
NSURL *plistURL = [bundle URLForResource:@"friendsInfo" withExtension:@"plist"];
NSDictionary *dictionary = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfURL:plistURL];
NSMutableArray *tmpDataArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
NSMutableArray *tmpImageArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for (int i=0; i<[dictionary count]; i++) {
NSString *key = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"%i", i+1];
NSDictionary *tmpDic = [dictionary objectForKey:key];
[tmpDataArray addObject:tmpDic];
NSString *imageUrl = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"%i.png", i+1];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:imageUrl];
[tmpImageArray addObject:image];
}
self.dataList = [tmpDataArray copy];
self.imageList = [tmpImageArray copy];
}
11.4 在ViewDidUnload方法中添加代码:
self.dataList = nil; self.imageList = nil;
11.5 在@end之前添加代码:
#pragma mark -
#pragma mark Table Data Source Methods
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return [self.dataList count];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
static NSString *CustomCellIdentifier = @"CustomCellIdentifier";
static BOOL nibsRegistered = NO;
if (!nibsRegistered) {
UINib *nib = [UINib nibWithNibName:@"CustomCell" bundle:nil];
[tableView registerNib:nib forCellReuseIdentifier:CustomCellIdentifier];
nibsRegistered = YES;
}
CustomCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CustomCellIdentifier];
NSUInteger row = [indexPath row];
NSDictionary *rowData = [self.dataList objectAtIndex:row];
cell.name = [rowData objectForKey:@"name"];
cell.dec = [rowData objectForKey:@"dec"];
cell.loc = [rowData objectForKey:@"loc"];
cell.image = [imageList objectAtIndex:row];
return cell;
}
#pragma mark Table Delegate Methods
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
return 60.0;
}
- (NSIndexPath *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView
willSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
return nil;
}
12、运行:
第三部分:加强理解
看TableView的资料其实已经蛮久了,一直想写点儿东西,却总是因为各种原因拖延,今天晚上有时间静下心来记录一些最近学习的TableView的知识。下面进入正题,UITableView堪称UIKit里面最复杂的一个控件了,使用起来不算难,但是要用好并不容易。当使用的时候我们必须要考虑到后台数据的设计,tableViewCell的设计和重用以及tableView的效率等问题。
下面分9个方面进行介绍:
一、UITableView概述
UITableView继承自UIScrollView,可以表现为Plain和Grouped两种风格,分别如下图所示:


其中左边的是Plain风格的,右边的是Grouped风格,这个区别还是很明显的。
查看UITableView的帮助文档我们会注意到UITableView有两个Delegate分别为:dataSource和delegate。
dataSource是UITableViewDataSource类型,主要为UITableView提供显示用的数据(UITableViewCell),指定UITableViewCell支持的编辑操作类型(insert,delete和reordering),并根据用户的操作进行相应的数据更新操作,如果数据没有更具操作进行正确的更新,可能会导致显示异常,甚至crush。
delegate是UITableViewDelegate类型,主要提供一些可选的方法,用来控制tableView的选择、指定section的头和尾的显示以及协助完成cell的删除和排序等功能。
提到UITableView,就必须的说一说NSIndexPath。UITableView声明了一个NSIndexPath的类别,主要用来标识当前cell的在tableView中的位置,该类别有section和row两个属性,前者标识当前cell处于第几个section中,后者代表在该section中的第几行。
UITableView只能有一列数据(cell),且只支持纵向滑动,当创建好的tablView第一次显示的时候,我们需要调用其reloadData方法,强制刷新一次,从而使tableView的数据更新到最新状态。
二、UITableViewController简介
UITableViewController是系统提供的一个便利类,主要是为了方便我们使用UITableView,该类生成的时候就将自身设置成了其包含的tableView的dataSource和delegate,并创建了很多代理函数的框架,为我们大大的节省了时间,我们可以通过其tableView属性获取该controller内部维护的tableView对象。默认情况下使用UITableViewController创建的tableView是充满全屏的,如果需要用到tableView是不充满全屏的话,我们应该使用UIViewController自己创建和维护tableView。
UITableViewController提供一个初始化函数initWithStyle:,根据需要我们可以创建Plain或者Grouped类型的tableView,当我们使用其从UIViewController继承来的init初始化函数的时候,默认将会我们创建一个Plain类型的tableView。
UITableViewController默认的会在viewWillAppear的时候,清空所有选中cell,我们可以通过设置self.clearsSelectionOnViewWillAppear = NO,来禁用该功能,并在viewDidAppear中调用UIScrollView的flashScrollIndicators方法让滚动条闪动一次,从而提示用户该控件是可以滑动的。
三、UITableViewCell介绍
UITableView中显示的每一个单元都是一个UITableViewCell对象,看文档的话我们会发现其初始化函数initWithStyle:reuseIdentifier:比较特别,跟我们平时看到的UIView的初始化函数不同。这个主要是为了效率考虑,因为在tableView快速滑动的滑动的过程中,频繁的alloc对象是比较费时的,于是引入了cell的重用机制,这个也是我们在dataSource中要重点注意的地方,用好重用机制会让我们的tableView滑动起来更加流畅。
我们可以通过cell的selectionStyle属性指定cell选中时的显示风格,以及通过accessoryType来指定cell右边的显示的内容,或者直接指定accessoryView来定制右边显示的view。
系统提供的UITableView也包含了四种风格的布局,分别是:
typedef enum { UITableViewCellStyleDefault, UITableViewCellStyleValue1, UITableViewCellStyleValue2, UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle } UITableViewCellStyle;
这几种文档中都有详细描述,这儿就不在累赘。然而可以想象系统提供的只是最常用的几种类型,当系统提供的风格不符合我们需要的时候,我们就需要对cell进行定制了,有以下两种定制方式可选:
1、直接向cell的contentView上面添加subView
这是比较简单的一种的,根据布局需要我们可以在不同的位置添加subView。但是此处需要注意:所有添加的subView都最好设置为不透明的,因为如果subView是半透明的话,view图层的叠加将会花费一定的时间,这会严重影响到效率。同时如果每个cell上面添加的subView个数过多的话(通常超过3,4个),效率也会受到比较大的影响。
下面我们看一个例子:
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; static NSString *reuseIdetify = @"SvTableViewCell"; UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuseIdetify]; if (!cell) { cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:reuseIdetify]; cell.accessoryType = UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator; cell.showsReorderControl = YES; for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100 + 15 * i, 0, 30, 20)]; label.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor]; label.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", i]; [cell.contentView addSubview:label]; [label release]; } } cell.textLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; cell.textLabel.text = [sectionModal.cityNames objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; return cell; }
在上面这个例子中,我往每个cell中添加了6个subView,而且每个subView都是半透明(UIView默认是半透明的),这个时候滑动起来明显就可以感觉到有点颤抖,不是很流畅。当把每一个subView的opaque属性设置成YES的时候,滑动会比之前流畅一些,不过还是有点儿卡。
2、从UITableViewCell派生一个类
通过从UITableViewCell中派生一个类,可以更深度的定制一个cell,可以指定cell在进入edit模式的时候如何相应等等。最简单的实现方式就是将所有要绘制的内容放到一个定制的subView中,并且重载该subView的drawRect方法直接把要显示的内容绘制出来(这样可以避免subView过多导致的性能瓶颈),最后再将该subView添加到cell派生类中的contentView中即可。但是这样定制的cell需要注意在数据改变的时候,通过手动调用该subView的setNeedDisplay方法来刷新界面,这个例子可以在苹果的帮助文档中的TableViewSuite工程中找到,这儿就不举例了。
观看这两种定制cell的方法,我们会发现subView都是添加在cell的contentView上面的,而不是直接加到cell上面,这样写也是有原因的。下面我们看一下cell在正常状态下和编辑状态下的构成图:
cell在正常状态下的构成图如下:

进入编辑状态下cell的构成图如下:

通过观察上面两幅图片我们可以看出来,当cell在进入编辑状态的时候,contentView会自动的缩放来给Editing control腾出位置。这也就是说如果我们把subView添加到contentView上,如果设置autoresizingMask为更具父view自动缩放的话,cell默认的机制会帮我们处理进入编辑状态的情况。而且在tableView是Grouped样式的时候,会为cell设置一个背景色,如果我们直接添加在cell上面的话,就需要自己考虑到这个背景色的显示问题,如果添加到contentView上,则可以通过view的叠加帮助我们完成该任务。综上,subView最好还是添加到cell的contentView中。
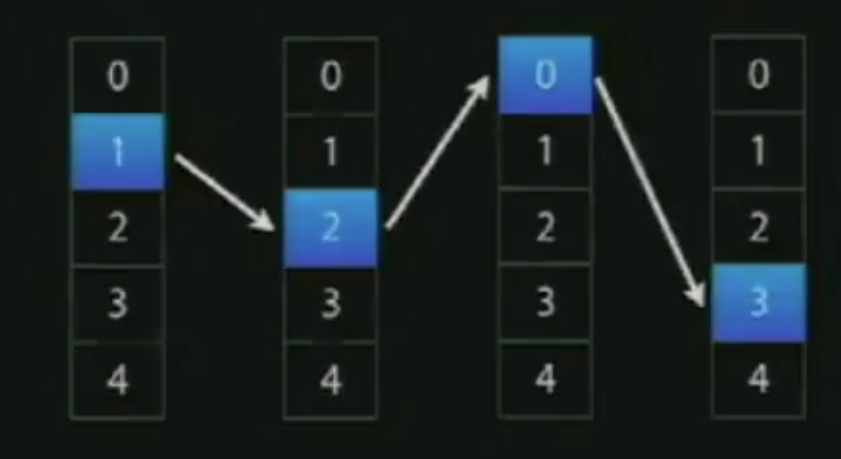
四、Reordering
为了使UITableVeiew进入edit模式以后,如果该cell支持reordering的话,reordering控件就会临时的把accessaryView覆盖掉。为了显示reordering控件,我们必须将cell的showsReorderControl属性设置成YES,同时实现dataSource中的tableView:moveRowAtIndexPath:toIndexPath:方法。我们还可以同时通过实现dataSource中的 tableView:canMoveRowAtIndexPath:返回NO,来禁用某一些cell的reordering功能。
下面看苹果官方的一个reordering流程图:

上图中当tableView进入到edit模式的时候,tableView会去对当前可见的cell逐个调用dataSource的tableView:canMoveRowAtIndexPath:方法(此处官方给出的流程图有点儿问题),决定当前cell是否显示reoedering控件,当开始进入拖动cell进行拖动的时候,每滑动过一个cell的时候,会去掉用delegate的tableView:targetIndexPathForMoveFromRowAtIndexPath:toProposedIndexPath:方法,去判断当前划过的cell位置是否可以被替换,如果不行则给出建议的位置。当用户放手时本次reordering操作结束,调用dataSource中的tableView:moveRowAtIndexPath:toIndexPath:方法更新tableView对应的数据。
此处给个我写demo中的更新数据的小例子:
// if you want show reordering control, you must implement moveRowAtndexPath, or the reordering control will not show // when use reordering end, this method is invoke - (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView moveRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)sourceIndexPath toIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)destinationIndexPath { // update DataModal NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.section]; NSString *city = [[sourceSectionModal.cityNames objectAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.row] retain]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames removeObject:city]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; SvSectionModal *desinationsSectionModal= [[SvTableViewDataModal sections] objectAtIndex:destinationIndexPath.section]; [desinationsSectionModal.cityNames insertObject:city atIndex:destinationIndexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:destinationIndexPath.section withSection:desinationsSectionModal]; [city release]; }
上面代码中首先拿到源cell所处的section,然后从该section对应的数据中移除,然后拿到目标section的数据,然后将源cell的数据添加到目标section中,并更新回数据模型,如果我们没有正确更新数据模型的话,显示的内容将会出现异常。
五、Delete & Insert
cell的delete和insert操作大部分流程都是一样的,当进入编辑模式的时候具体的显示是delete 还是insert
还是insert 取决与该cell的editingStyle的值,editStyle的定义如下:
取决与该cell的editingStyle的值,editStyle的定义如下:
typedef enum { UITableViewCellEditingStyleNone, UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete, UITableViewCellEditingStyleInsert } UITableViewCellEditingStyle;
当tableView进入编辑模式以后,cell上面显示的delete还是insert除了跟cell的editStyle有关,还与 tableView的delegate的tableView:editingStyleForRowAtIndexPath:方法的返回值有关(在这里唠叨一句,其实delegate提供了很多改变cell属性的机会,如非必要,还是不要去实现这些方法,因为执行这些方法也造成一定的开销)。
delete和insert的流程如下苹果官方文档中给出的图所示:

下面是我写的demo中删除和添加部分的代码:
#pragma mark - - (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { NSLog(@"commit editStyle: %d", editingStyle); if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete) { NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames removeObjectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:indexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; [tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationRight]; } else { // do something for add it NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames insertObject:@"new City" atIndex:indexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:indexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; [tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationRight]; } }
代码中首先判断当前操作是delete操作还是insert操作,相应的更新数据,最后根据情况调用tableView的insertRowsAtIndexPaths:withRowAnimation:或者deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:withRowAnimation:方法,对tableView的视图进行更新。cell的删除和添加操作相对还是比较简单的。
六、Cell的Select操作
当我们在tableView中点击一个cell的时候,将会调用tableView的delegate中的tableView:didSelectRowAtIndexPath:方法。
关于tableView的cell的选中,苹果官方有以下几个建议:
1、不要使用selection来表明cell的选择状态,而应该使用accessaryView中的checkMark或者自定义accessaryView来显示选中状态。
2、当选中一个cell的时候,你应该取消前一个cell的选中。
3、如果cell选中的时候,进入下一级viewCOntroller,你应该在该级菜单从navigationStack上弹出的时候,取消该cell的选中。
这块儿再提一点,当一个cell的accessaryType为UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator的时候,点击该accessary区域通常会将消息继续向下传递,即跟点击cell的其他区域一样,将会掉delegate的tableView:didSelectRowAtIndexPath:方法,当时如果accessaryView为 UITableViewCellAccessoryDetailDisclosureButton的时候,点击accessaryView将会调用delegate的 tableView:accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath:方法。
七、批量插入,删除,部分更新操作
UITableView提供了一个批量操作的特性,这个功能在一次进行多个row或者scetion的删除,插入,获取更新多个cell内容的时候特别好用。所有的批量操作需要包含在beginUpdates和endUpdates块中,否则会出现异常。
下面请看我demo中的一个批量操作的例子:
- (void)groupEdit:(UIBarButtonItem*)sender { [_tableView beginUpdates]; // first update the data modal [_tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:0 inSection:0]] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationTop]; [_tableView deleteSections:[NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndex:0] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationTop]; [SvTableViewDataModal deleteSectionAtIndex:0]; SvSectionModal *section = [[SvTableViewDataModal sections] objectAtIndex:0]; [section.cityNames insertObject:@"帝都" atIndex:0]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:0 withSection:section]; [_tableView endUpdates]; }
上面的例子中我们可以看到先往tableView的第0个section的第0行添加一个cell,然后将第0个section删掉。按照我们程序中写的顺序,那么新添加进去的“帝都”,将不在会显示,因为包含它的整个section都已经被删除了。
执行程序前后结果如下图:


demo中第0个section是陕西省的城市,第1个section是北京。左边是执行前的截图,右边是执行后的截图,观察发现结果并不像我们前面推测的那样。那是因为在批量操作时,不管代码中先写的添加操作还是删除操作,添加操作都会被推出执行,直到这个块中所有的删除操作都执行完以后,才会执行添加操作,这也就是上面苹果官方图片上要表达的意思。
苹果官方文档有一副图可以帮助我们更好的理解这一点:

原图中操作是:首先删除section 0中的row 1,然后删除section 1,再向section 1中添加一行。执行完批量更新以后就得到右半边的结果。
八、IndexList
当我们tableView中section有很多,数据量比较大的时候我们可以引入indexList,来方便完成section的定位,例如系统的通讯录程序。我们可以通过设置tableView的sectionIndexMinimumDisplayRowCount属性来指定当tableView中多少行的时候开始显示IndexList,默认的设置是NSIntegerMax,即默认是不显示indexList的。
为了能够使用indexlist我们还需要实现dataSource中一下两个方法:
- (NSArray *)sectionIndexTitlesForTableView:(UITableView *)tableView;
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView sectionForSectionIndexTitle:(NSString *)title atIndex:(NSInteger)index;
第一个方法返回用于显示在indexList中的内容的数组,通常为A,B,C...Z。第二个方法的主要作用是根据用户在indexList中点击的位置,返回相应的section的index值。这个例子可以在苹果官方给出的TableViewSuite中找到,实现起来还是很简单的。
九、其他
1、分割线
我们可以通过设置tableView的separatorStyle属性来设置有无分割线以及分割线的风格,其中style定义如下:
typedef enum { UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleNone, UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleSingleLine, UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleSingleLineEtched } UITableViewCellSeparatorStyle;
同时还可以通过tableView的separatorColor属性来设置分割线的颜色。
2、如何提高tableView的性能
a、重用cell
我们都知道申请内存是需要时间,特别是在一段时间内频繁的申请内存将会造成很大的开销,而且上tebleView中cell大部分情况下布局都是一样的,这个时候我们可以通过回收重用机制来提高性能。
b、避免content的重新布局
尽量避免在重用cell时候,对cell的重新布局,一般情况在在创建cell的时候就将cell布局好。
c、使用不透明的subView
在定制cell的时候,将要添加的subView设置成不透明的会大大减少多个view层叠加时渲染所需要的时间。
d、如果方便,直接重载subView的drawRect方法
如果定制cell的过程中需要多个小的元素的话,最好直接对要显示的多个项目进行绘制,而不是采用添加多个subView。
e、tableView的delegate的方法如非必要,尽量不要实现
tableView的delegate中的很多函数提供了对cell属性的进一步控制,比如每个cell的高度,cell是否可以编辑,支持的edit风格等,如非必要最好不要实现这些方法因为快速的调用这些方法也会影响性能。
(以上5点建议,前三点来自苹果官方文档,后两点我自己加的,有什么不对的地方,欢迎指正)
小结:UITableView本身是很复杂的,本片博客只起到抛砖引玉的作用,欢迎大家补充。想用好UITableView,还是需要实际项目中的锻炼的
