一.背包
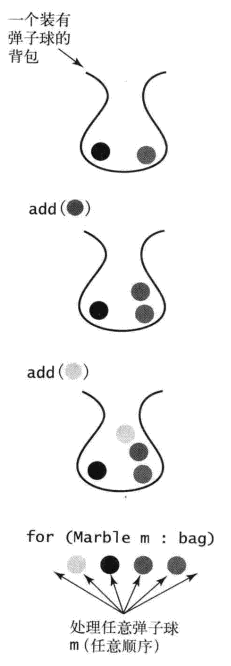
背包是一种不支持从中删除元素的集合数据类型,目的是帮助用例收集元素并迭代所有收集到的元素,也可以检查背包是否为空,或者获取背包中元素的数量。背包里面的元素的顺序不确定。
要理解背包的概念,可以想象一个喜欢收集弹珠球的人。他将所有的弹珠球都放在一个背包里,一次一个,并且会不时在所有的弹珠球中寻找某一颗;
1.用链表实现
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; private int n; private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty bag. */ public Bag() { first = null; n = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } public int size() { return n; } public void add(Item item) { Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; n++; } public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator(first); } private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Bag<String> bag = new Bag<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); bag.add(item); } StdOut.println("size of bag = " + bag.size()); for (String s : bag) { StdOut.println(s); } } }
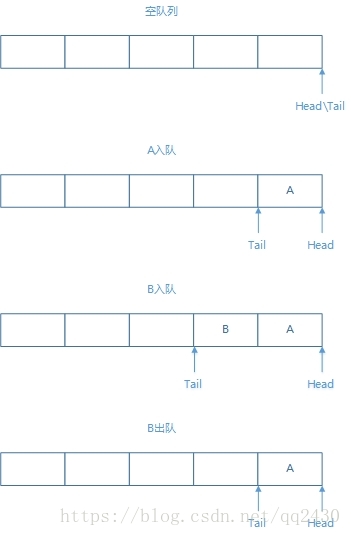
二.队列
队列的特性:
-
在队尾插入元素,在队首删除元素。
-
FIFO(先进先出),就向排队取票一样。
1.用链表实现
package structure; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; private Node<Item> last; private int n; private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } public Queue() { first = null; last = null; n = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } public int size() { return n; } public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); return first.item; } //增加元素 public void enqueue(Item item) { Node<Item> oldlast = last; last = new Node<Item>(); last.item = item; last.next = null; if (isEmpty()) first = last; else oldlast.next = last; n++; } //删除元素 public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); Item item = first.item; first = first.next; n--; if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering return item; } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator(first); } private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) queue.enqueue(item); else if (!queue.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + queue.size() + " left on queue)"); } }
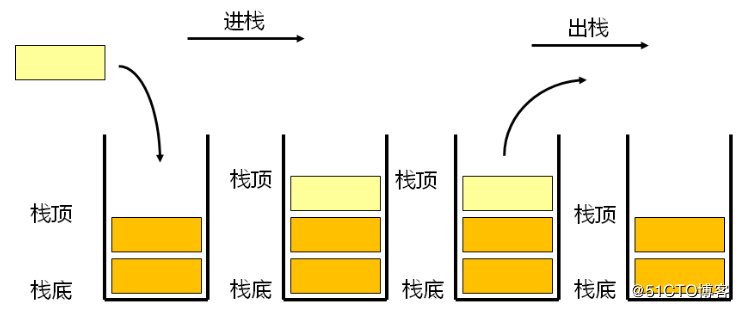
三.栈
(1)栈是一种线性结构,栈中的元素遵循先入后出的原则,最先进入的元素所在位置叫做栈底,最后放入的元素所在位置叫做栈顶。
这种结构类似于盛放羽毛球的圆筒,一端封闭,另一端开口,先放入的羽毛球位于筒的底部(即栈底),后放入的羽毛球位于筒的入口(即栈顶)。
(2)栈也是一种抽象的逻辑结构,依赖于物理结构(如数组、链表)而存在。既可以使用数组实现,也可以使用链表实现。
(3)出栈、入栈的时间复杂都是O(1)。
1.用数组实现
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class ResizingArrayStack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Item[] a;
private int n;
public ResizingArrayStack() {
a = (Item[]) new Object[2];
n = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
//重置数组大小
private void resize(int capacity) {
assert capacity >= n;
// textbook implementation
Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = a[i];
}
a = temp;
// alternative implementation
// a = java.util.Arrays.copyOf(a, capacity);
}
public void push(Item item) {
if (n == a.length) resize(2*a.length);
a[n++] = item;
}
public Item pop() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
Item item = a[n-1];
a[n-1] = null;
n--;
if (n > 0 && n == a.length/4) resize(a.length/2);
return item;
}
// 返回栈顶部数据,但不移除
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
return a[n-1];
}
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ReverseArrayIterator();
}
private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private int i;
public ReverseArrayIterator() {
i = n-1;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return i >= 0;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return a[i--];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResizingArrayStack<String> stack = new ResizingArrayStack<String>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String item = StdIn.readString();
if (!item.equals("-")) stack.push(item);
else if (!stack.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
StdOut.println("(" + stack.size() + " left on stack)");
}
}
2.用链表实现
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; private int n; private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } public Stack() { first = null; n = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } public int size() { return n; } public void push(Item item) { Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; n++; } public Item pop() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); Item item = first.item; // save item to return first = first.next; // delete first node n--; return item; // return the saved item } //返回栈顶部数据,但不移除 public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); return first.item; } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator(first); } private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) stack.push(item); else if (!stack.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(stack.pop() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + stack.size() + " left on stack)"); } }