写在前面
开学也有一周了,上了一个数据结构的小学期,让我们自助选题,我就选了如这篇题目所说的程序分析。废话不多说,开始正文。
需求分析
首先来看要求:
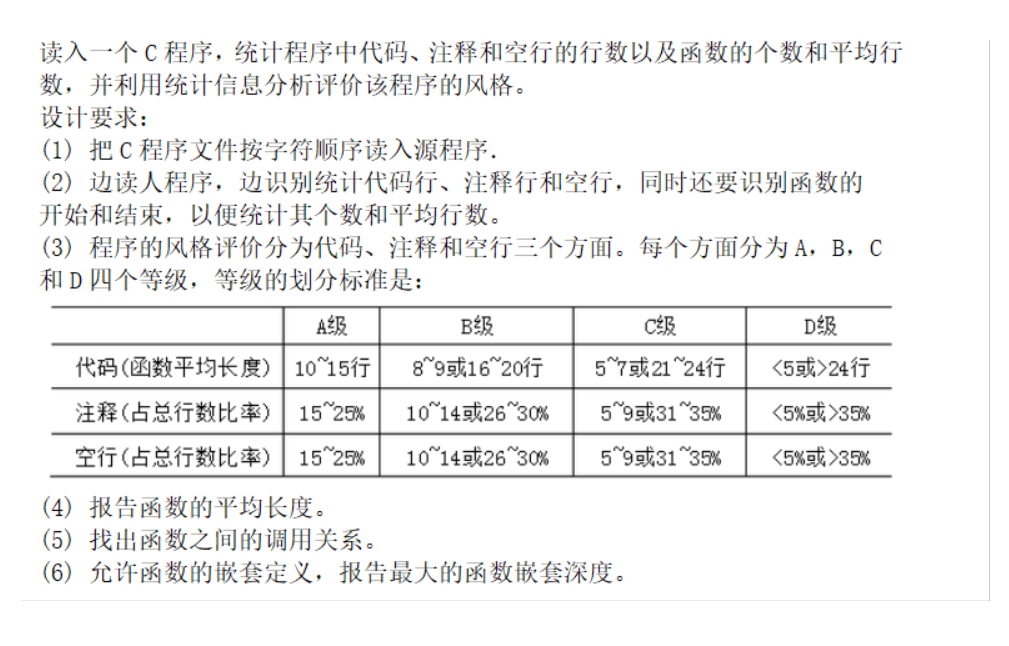
我们挨个分析需求:
首先,把C程序文件按字符顺序读入源程序。这个很好说,我们直接读取整个文件,按行读取即可。
第二个条件,统计代码行,注释行和空行,识别函数的开始和结束统计函数个数和平均行数。这就需要我们对读入的数据进行处理,识别出各种结果。
第三个条件,评分。这个在前面两个条件完成的基础上,就十分简单了。我们直接对读取的结果进行处理就好了。
第四个条件,报告平均长度,没什么好说的,前面求过了,直接输出即可。
第五个条件和第六个条件,一个是函数的调用关系,这就要求我们在统计的时候顺便搞一下函数的名称,识别出函数内调用的函数。
第六个条件,与第五个条件类似,我们直接在统计的过程中统计一下就好。
大概的需求看完后,就开始动手写代码吧。
开始前的准备
首先,我们要确定使用什么语言。看到第一个条件我的下意识反应就是使用Java,毕竟我就对Java熟悉了。而且Java里的很多API我都知道,敲起来也会很方便。之后就是创建项目,确定要使用的工具类了。这里我为了方便起见,创建了一个maven工程,然后导入了Hutools,这是一个工具类的整合包,里面有很多实用的工具类,直接导入坐标依赖就可:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
在这个项目里主要用到了字符串的处理工具。
编码
读取文件
首先就是读取文件了,我们先来看代码:
/**
* 读取文件流
*
* @return 读取完的文件流List
*/
private static List<String> getFileContent() {
// 将C程序作为流读入
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 使用一个List结构来存储读取的代码
List<String> fileContent = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("请输入要分析的C程序文件路径:");
String filePath = in.next();
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(filePath)) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的文件路径!");
System.exit(0);
}
File file = new File(filePath);
BufferedReader reader;
String line;
try {
reader = FileUtil.getReader(file, "UTF-8");
// 一次读入一行
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
fileContent.add(line);
}
// 读取完毕,关闭文件读入流和输入流
reader.close();
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("文件读写出错嘞~");
System.exit(0);
}
return fileContent;
}
这段代码不是很长,很好理解。我们首先使用了Scanner类来获取用户输入的文件路径,并且使用BufferReader进行文件的读取,每次读取一行,然后存储到一个List中供之后使用。这里要注意的是异常的处理,我们一定要处理好异常,不能再向上层抛出了。
统计代码行
/**
* 统计行数的方法
*
* @param fileContent
*/
private static void getLines(List<String> fileContent) {
boolean isInBlockNote = false;
for (String line : fileContent) {
// 位于段注释内,算段注释行
if (isInBlockNote) {
noteBlockLineCount++;
}
// 统计空行
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(line) && !isInBlockNote) {
emptyLineCount++;
}
// 统计行注释://
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "//")) {
noteLineCount++;
}
// 统计段注释:/* */
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "/*")) {
// 代表段注释开始了
noteBlockLineCount++;
isInBlockNote = true;
}
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "*/")) {
// 代表段注释结束了
isInBlockNote = false;
}
// 统计总行数
sumLineCount++;
}
// 统计代码行:总行数-空行-行注释-段注释
codeLineCount = sumLineCount - emptyLineCount - noteLineCount - noteBlockLineCount;
// 输出各个行数
System.out.println("总行数 = " + sumLineCount);
System.out.println("空行数 = " + emptyLineCount);
System.out.println("段注释行数 = " + noteBlockLineCount);
System.out.println("行注释行数 = " + noteLineCount);
System.out.println("代码行数 = " + codeLineCount);
}
这段代码也比较好理解,这里最关键的就是段注释了,段注释是有多行的情况的,所以这里我定义了一个标志变量来判断是否处在段注释内,这样就可以统计出段注释的长度了。
函数的读取
/**
* 统计函数的方法
* C程序里一个函数的特点:
* 返回值类型 函数名(参数){}
* 常见返回值类型:void int double float char
* 指针结构体等特殊函数不再统计
* 函数以'{' 作为开始,'}' 作为结束
* 需要排除if for while do 等的大括号
*
* @param fileContent
*/
private static void getMethods(List<String> fileContent) {
boolean isInMethod = false;
boolean isInOther = false;
String methodName = null;
for (String line : fileContent) {
if (isInMethod) {
// 在函数内,如果同时出现'('和')' 且不是while,if,for,证明调用了其他函数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "(")
&& StrUtil.contains(line, ")")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "for")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "while")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "if")) {
String[] lineSplits = StrUtil.split(line, "(");
if (StrUtil.contains(lineSplits[0], "=")) {
// 包含等号,说明是有返回值的函数,再进行一次切割
String[] splits = StrUtil.split(line, "=");
String replaceWithFen = StrUtil.replace(splits[1], ";", "");
String replaceWithZuo = StrUtil.replace(replaceWithFen, "(", "");
System.out.println(methodName + "函数调用了名为" + StrUtil.replace(replaceWithZuo, ")", "") + "的函数");
} else {
// 不包含等号,说明是没有返回值的函数,直接输出
String replaceWithFen = StrUtil.replace(lineSplits[0], ";", "");
System.out.println(methodName + "函数调用了名为" + StrUtil.replace(replaceWithFen, " ", "") + "的函数");
}
}
// 在方法内,找到方法开始的标志行,开始统计函数行数
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "{")) {
methodLineCount++;
continue;
}
// 如果嵌套定义函数,增加嵌套层数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "void")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "int")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "float")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "double")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "char")) {
// 包含返回值,且有右括号或者{ 表示该行为函数嵌套定义
if (StrUtil.endWith(line, ")") || StrUtil.endWith(line, "{")) {
methodLoopCount++;
}
}
methodLineCount++;
}
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "void")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "int")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "float")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "double")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "char")) {
// 满足条件,说明这行是函数定义
isInMethod = true;
String[] splits = StrUtil.split(line, " ");
String[] split = StrUtil.split(splits[1], "(");
methodName = split[0];
// 统计函数个数
methodCount++;
// 如果这行有{ 说明是函数开始了,计数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "{")) {
methodLineCount++;
}
}
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "while")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "if")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "for")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "do")) {
// 证明是在其他大括号的结构里 (嵌套结构)
isInOther = true;
// 统计嵌套个数
loopCount++;
}
// 遇到了最后一个 } 代表该函数到结尾了 (排除while,if,for do的大括号)
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "}") && isInMethod && !isInOther) {
isInMethod = false;
methodLoopLayerCounts.add(methodLoopCount);
methodLineCounts.add(methodLineCount);
methodLineCount = 0;
methodLoopCount = 0;
}
// 在其他嵌套结构里,且到了尾部
if (isInOther) {
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "}")) {
isInOther = false;
methodLineCounts.add(loopCount);
loopCount = 0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("函数个数 = " + methodCount);
for (Integer lineCount : methodLineCounts) {
sumMethodLineCount += lineCount;
}
avrMethodLineCount = sumMethodLineCount / methodCount;
System.out.println("函数平均长度 = " + avrMethodLineCount);
// 输出函数最大嵌套层数
maxLayer = CollUtil.max(methodLoopLayerCounts);
System.out.println("函数最大嵌套层数 = " + maxLayer);
}
这段是全文的核心代码了,这里的难点有很多。这里要注意的是我没有统计类似struct,*等特殊的类型,毕竟要考虑的话确实比较多。
这里要注意的是,统计函数的长度的时候,会遇到类似while,do,for等结构,他们也有大括号,所以要确定好判断用的方法,这样才不会判断错误。
确定代码风格
这应该是所有代码中最简单的了,不再赘述,直接上代码:
/**
* 确定代码风格等级
*/
private static void getCodeStyle() {
// 代码等级 判断函数平均长度
if (avrMethodLineCount >= 10 && avrMethodLineCount <= 15) {
System.out.println("代码等级为A");
} else if ((avrMethodLineCount >= 8 && avrMethodLineCount <= 9) || (avrMethodLineCount >= 16 && avrMethodLineCount <= 20)) {
System.out.println("代码等级为B");
} else if ((avrMethodLineCount >= 5 && avrMethodLineCount <= 7) || (avrMethodLineCount >= 21 && avrMethodLineCount <= 26)) {
System.out.println("代码等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("代码等级为D");
}
// 注释等级 看注释行数占总行数的比例
int notePercent = (int) ((((float) (noteBlockLineCount + noteLineCount)) / sumLineCount) * 100);
if (notePercent >= 15 && notePercent <= 25) {
System.out.println("注释等级为A");
} else if ((notePercent >= 10 && notePercent <= 14) || (notePercent >= 26 && notePercent <= 30)) {
System.out.println("注释等级为B");
} else if ((notePercent >= 5 && notePercent <= 9) || (notePercent >= 31 && notePercent <= 35)) {
System.out.println("注释等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("注释等级为D");
}
// 空行等级 看空行行数占总行数的比例
int emptyPercent = (int) (((float) emptyLineCount / sumLineCount) * 100);
if (emptyPercent >= 15 && emptyPercent <= 25) {
System.out.println("空行等级为A");
} else if ((emptyPercent >= 10 && emptyPercent <= 14) || (emptyPercent >= 26 && emptyPercent <= 30)) {
System.out.println("空行等级为B");
} else if ((emptyPercent >= 5 && notePercent <= 9) || (emptyPercent >= 31 && emptyPercent <= 35)) {
System.out.println("空行等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("空行等级为D");
}
}
总结
总的来说,这次的小学期算是验证了我自己的水平,自己也是这么长时间以来第一次自己敲长一点的代码。这个程序的问题还是蛮多的,毕竟程序分析这个题目实在是太大了。如果读者有兴趣的话,可以自己去完善。
附录
这里附上全部代码:
/**
* @ClassName: AnalyzeMain
* @Description: 程序分析主函数
* 没有解决的问题:1.没有做到读取特殊返回类型的函数,如struct,指针等
* 2.代码如果不够规范的话,该程序就可能会失效 可适性不够强
* @author: LiuGe
* @date: 2020/9/10 9:07
*/
public class AnalyzeMain {
public static int emptyLineCount = 0;
public static int noteLineCount = 0;
public static int noteBlockLineCount = 0;
public static int sumLineCount = 0;
public static int codeLineCount = 0;
public static int methodCount = 0;
public static int loopCount = 0;
public static List<Integer> methodLineCounts = new ArrayList<>();
// 只存储 没有使用
public static List<Integer> methodLoopCounts = new ArrayList<>();
public static int methodLineCount = 0;
public static int sumMethodLineCount = 0;
public static int avrMethodLineCount = 0;
public static int methodLoopCount = 0;
public static List<Integer> methodLoopLayerCounts = new ArrayList<>();
public static int maxLayer = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取读取的文件流
List<String> fileContent = getFileContent();
// 行数统计
getLines(fileContent);
// 函数统计
getMethods(fileContent);
// 确定代码风格等级
getCodeStyle();
}
/**
* 读取文件流
*
* @return 读取完的文件流List
*/
private static List<String> getFileContent() {
// 将C程序作为流读入
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 使用一个List结构来存储读取的代码
List<String> fileContent = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("请输入要分析的C程序文件路径:");
String filePath = in.next();
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(filePath)) {
System.out.println("请输入正确的文件路径!");
System.exit(0);
}
File file = new File(filePath);
BufferedReader reader;
String line;
try {
reader = FileUtil.getReader(file, "UTF-8");
// 一次读入一行
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
fileContent.add(line);
}
// 读取完毕,关闭文件读入流和输入流
reader.close();
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("文件读写出错嘞~");
System.exit(0);
}
return fileContent;
}
/**
* 确定代码风格等级
*/
private static void getCodeStyle() {
// 代码等级 判断函数平均长度
if (avrMethodLineCount >= 10 && avrMethodLineCount <= 15) {
System.out.println("代码等级为A");
} else if ((avrMethodLineCount >= 8 && avrMethodLineCount <= 9) || (avrMethodLineCount >= 16 && avrMethodLineCount <= 20)) {
System.out.println("代码等级为B");
} else if ((avrMethodLineCount >= 5 && avrMethodLineCount <= 7) || (avrMethodLineCount >= 21 && avrMethodLineCount <= 26)) {
System.out.println("代码等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("代码等级为D");
}
// 注释等级 看注释行数占总行数的比例
int notePercent = (int) ((((float) (noteBlockLineCount + noteLineCount)) / sumLineCount) * 100);
if (notePercent >= 15 && notePercent <= 25) {
System.out.println("注释等级为A");
} else if ((notePercent >= 10 && notePercent <= 14) || (notePercent >= 26 && notePercent <= 30)) {
System.out.println("注释等级为B");
} else if ((notePercent >= 5 && notePercent <= 9) || (notePercent >= 31 && notePercent <= 35)) {
System.out.println("注释等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("注释等级为D");
}
// 空行等级 看空行行数占总行数的比例
int emptyPercent = (int) (((float) emptyLineCount / sumLineCount) * 100);
if (emptyPercent >= 15 && emptyPercent <= 25) {
System.out.println("空行等级为A");
} else if ((emptyPercent >= 10 && emptyPercent <= 14) || (emptyPercent >= 26 && emptyPercent <= 30)) {
System.out.println("空行等级为B");
} else if ((emptyPercent >= 5 && notePercent <= 9) || (emptyPercent >= 31 && emptyPercent <= 35)) {
System.out.println("空行等级为C");
} else {
System.out.println("空行等级为D");
}
}
/**
* 统计函数的方法
* C程序里一个函数的特点:
* 返回值类型 函数名(参数){}
* 常见返回值类型:void int double float char
* 指针结构体等特殊函数不再统计
* 函数以'{' 作为开始,'}' 作为结束
* 需要排除if for while do 等的大括号
*
* @param fileContent
*/
private static void getMethods(List<String> fileContent) {
boolean isInMethod = false;
boolean isInOther = false;
String methodName = null;
for (String line : fileContent) {
if (isInMethod) {
// 在函数内,如果同时出现'('和')' 且不是while,if,for,证明调用了其他函数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "(")
&& StrUtil.contains(line, ")")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "for")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "while")
&& !StrUtil.contains(line, "if")) {
String[] lineSplits = StrUtil.split(line, "(");
if (StrUtil.contains(lineSplits[0], "=")) {
// 包含等号,说明是有返回值的函数,再进行一次切割
String[] splits = StrUtil.split(line, "=");
String replaceWithFen = StrUtil.replace(splits[1], ";", "");
String replaceWithZuo = StrUtil.replace(replaceWithFen, "(", "");
System.out.println(methodName + "函数调用了名为" + StrUtil.replace(replaceWithZuo, ")", "") + "的函数");
} else {
// 不包含等号,说明是没有返回值的函数,直接输出
String replaceWithFen = StrUtil.replace(lineSplits[0], ";", "");
System.out.println(methodName + "函数调用了名为" + StrUtil.replace(replaceWithFen, " ", "") + "的函数");
}
}
// 在方法内,找到方法开始的标志行,开始统计函数行数
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "{")) {
methodLineCount++;
continue;
}
// 如果嵌套定义函数,增加嵌套层数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "void")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "int")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "float")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "double")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "char")) {
// 包含返回值,且有右括号或者{ 表示该行为函数嵌套定义
if (StrUtil.endWith(line, ")") || StrUtil.endWith(line, "{")) {
methodLoopCount++;
}
}
methodLineCount++;
}
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "void")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "int")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "float")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "double")
|| StrUtil.startWith(line, "char")) {
// 满足条件,说明这行是函数定义
isInMethod = true;
String[] splits = StrUtil.split(line, " ");
String[] split = StrUtil.split(splits[1], "(");
methodName = split[0];
// 统计函数个数
methodCount++;
// 如果这行有{ 说明是函数开始了,计数
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "{")) {
methodLineCount++;
}
}
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "while")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "if")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "for")
|| StrUtil.contains(line, "do")) {
// 证明是在其他大括号的结构里 (嵌套结构)
isInOther = true;
// 统计嵌套个数
loopCount++;
}
// 遇到了最后一个 } 代表该函数到结尾了 (排除while,if,for do的大括号)
if (StrUtil.startWith(line, "}") && isInMethod && !isInOther) {
isInMethod = false;
methodLoopLayerCounts.add(methodLoopCount);
methodLineCounts.add(methodLineCount);
methodLineCount = 0;
methodLoopCount = 0;
}
// 在其他嵌套结构里,且到了尾部
if (isInOther) {
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "}")) {
isInOther = false;
methodLineCounts.add(loopCount);
loopCount = 0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("函数个数 = " + methodCount);
for (Integer lineCount : methodLineCounts) {
sumMethodLineCount += lineCount;
}
avrMethodLineCount = sumMethodLineCount / methodCount;
System.out.println("函数平均长度 = " + avrMethodLineCount);
// 输出函数最大嵌套层数
maxLayer = CollUtil.max(methodLoopLayerCounts);
System.out.println("函数最大嵌套层数 = " + maxLayer);
}
/**
* 统计行数的方法
*
* @param fileContent
*/
private static void getLines(List<String> fileContent) {
boolean isInBlockNote = false;
for (String line : fileContent) {
// 位于段注释内,算段注释行
if (isInBlockNote) {
noteBlockLineCount++;
}
// 统计空行
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(line) && !isInBlockNote) {
emptyLineCount++;
}
// 统计行注释://
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "//")) {
noteLineCount++;
}
// 统计段注释:/* */
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "/*")) {
// 代表段注释开始了
noteBlockLineCount++;
isInBlockNote = true;
}
if (StrUtil.contains(line, "*/")) {
// 代表段注释结束了
isInBlockNote = false;
}
// 统计总行数
sumLineCount++;
}
// 统计代码行:总行数-空行-行注释-段注释
codeLineCount = sumLineCount - emptyLineCount - noteLineCount - noteBlockLineCount;
// 输出各个行数
System.out.println("总行数 = " + sumLineCount);
System.out.println("空行数 = " + emptyLineCount);
System.out.println("段注释行数 = " + noteBlockLineCount);
System.out.println("行注释行数 = " + noteLineCount);
System.out.println("代码行数 = " + codeLineCount);
}
}