如果一个构造函数的第一个参数是自身类类型的引用,且任何额外参数都有默认值,则此构造函数是拷贝构造函数
class numbered{ public : numbered(){//构造函数 mysn = 0; } numbered(const numbered& inputOne){//拷贝构造函数 mysn = inputOne.mysn; mysn = mysn +1; }int mysn; };
拷贝构造函数发生以下情况:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; class numbered{ public : numbered(){//构造函数 mysn = 0; } numbered(const numbered& inputOne){//拷贝构造函数 mysn = inputOne.mysn; mysn = mysn +1; }int mysn; }; void f(numbered s){ cout<<s.mysn<<endl; } int main() { numbered a;//构造函数 numbered b=a;//【1】拷贝构造函数 f(a);//【2】将a赋给函数f过程中,发生了拷贝构造 //【3】从一个返回类型为非引用的函数返回一个对象--类似第二点 //【4】用花括号列表(C++11)初始化一个数组中的对象或一个聚合类中的成员 system("pause"); return 0; }
运行结果:
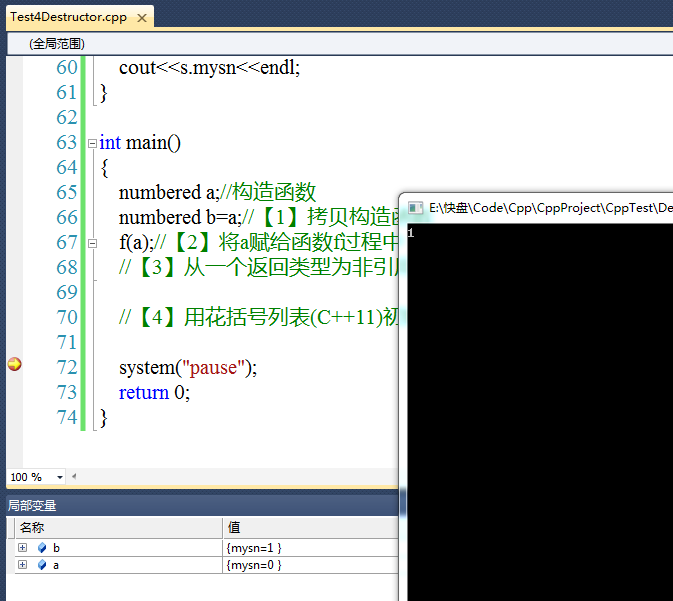
从watch窗口可以看到:b.mysn比a.mysn多1,这是由于拷贝构造函数造成的
从输出中可以看出,f(a)输出了1,这也是由于拷贝构造函数造成的。
关于拷贝构造函数发生的四种情况:
numbered b=a;//【1】拷贝构造函数
f(a);//【2】将a赋给函数f过程中,发生了拷贝构造
//【3】从一个返回类型为非引用的函数返回一个对象--类似第二点
//【4】用花括号列表(C++11)初始化一个数组中的对象或一个聚合类中的成员
第二点,第三点最容易忽略,应该注意。
以上是拷贝构造函数的基本内容,下面用一个比较复杂的例子来分析拷贝构造函数,构造函数等的区别
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class A { public: A(){ cout << "constructor called!" << endl; } A(int i) : x(i){ cout << i << " constructor called!" << endl; } A(const A &a){ x = a.x+1; cout << x << " copy constructor called!" << endl; } A &operator=(const A &a){ x = a.x+10; cout << x << " 拷贝赋值函数called!" << endl; return *this; } ~A(){cout << x << " destructor called" << endl;} private: //A(const A &a){cout << "copy constuctor called!" << endl;} int x; }; A get_A() { A a(5); return a; } int main() { cout<<"-----1-----"<<endl; A a = 1; // 1 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----2-----"<<endl; A b = get_A(); // 2 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----3-----"<<endl; b = a; // 3 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----4-----"<<endl; A c = A(2); // 4 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----5-----"<<endl; b = 3; // 5 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----6-----"<<endl; A d = b; // 6 cout<<endl; cout<<"-----7-----"<<endl; A e(b); // 7 cout<<endl; return 0; }
运行结果

关于第1点和第4点,为何没有拷贝构造函数这个操作??
这个地方不是很明白?
也请高手指教。我如果搞清楚了,也会及时更新