深度卷积生成对抗网络
Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks
GANs如何工作的基本思想。可以从一些简单的,易于抽样的分布,如均匀分布或正态分布中提取样本,并将其转换成与某些数据集的分布相匹配的样本。虽然例子匹配一个二维高斯分布得到了交叉点,不是特别令人兴奋。
将演示如何使用GANs生成照片级真实感图像。将以深卷积GAN(DCGAN)为基础建立模型。将借用卷积体系结构,已经被证明在区分计算机视觉问题上是如此成功,并展示如何通过GANs来利用来生成真实感图像。
from mxnet import gluon, init, np, npx
from mxnet.gluon import nn
from d2l import mxnet as d2l
npx.set_np()
1. The Pokemon Dataset
将使用的数据集是从pokemondb获得的Pokemon精灵集合。首先下载、提取并加载此数据集。
#@save
d2l.DATA_HUB['pokemon'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'pokemon.zip',
'c065c0e2593b8b161a2d7873e42418bf6a21106c')
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('pokemon')
pokemon = gluon.data.vision.datasets.ImageFolderDataset(data_dir)
Downloading ../data/pokemon.zip from
http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/pokemon.zip...
将每个图像调整为64×64。ToTensor变换将像素值投影到[0,1],而生成器将使用tanh函数来获得[-1,1]。因此,用0.5平均值和0.5与值范围匹配的标准偏差。
batch_size = 256
transformer = gluon.data.vision.transforms.Compose([
gluon.data.vision.transforms.Resize(64),
gluon.data.vision.transforms.ToTensor(),
gluon.data.vision.transforms.Normalize(0.5, 0.5)
])
data_iter = gluon.data.DataLoader(
pokemon.transform_first(transformer), batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, num_workers=d2l.get_dataloader_workers())
让想象一下前20幅图像。
d2l.set_figsize((4, 4))
for X, y in data_iter:
imgs = X[0:20,:,:,:].transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)/2+0.5
d2l.show_images(imgs, num_rows=4, num_cols=5)
break

2. The Generator
生成器Generator需要映射噪声变量z∈Rd,一个length-d图像的宽度和宽度64×64。使用转置卷积层来扩大输入大小的全卷积网络。生成器的基本块包含一个转置卷积层,然后是批处理规范化和ReLU激活。
class G_block(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, channels, kernel_size=4,
strides=2, padding=1, **kwargs):
super(G_block, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.conv2d_trans = nn.Conv2DTranspose(
channels, kernel_size, strides, padding, use_bias=False)
self.batch_norm = nn.BatchNorm()
self.activation = nn.Activation('relu')
def forward(self, X):
return self.activation(self.batch_norm(self.conv2d_trans(X)))
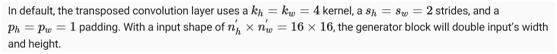
x = np.zeros((2, 3, 16, 16))
g_blk = G_block(20)
g_blk.initialize()
g_blk(x).shape
(2, 20, 32, 32)
如果将转置卷积层更改为4×4内核,1×1跨步和零填充。输入大小为1×1输出宽度和高度分别增加3。
x = np.zeros((2, 3, 1, 1))
g_blk = G_block(20, strides=1, padding=0)
g_blk.initialize()
g_blk(x).shape
(2, 20, 4, 4)
生成器由四个基本块组成,将输入的宽度和高度从1增加到32。同时,首先将潜在变量投影到64×8通道,然后每次将通道减半。最后,利用转置卷积层产生输出。进一步将宽度和高度加倍以匹配所需的64×64形状,并将通道大小减小到3。tanh激活函数用于将输出值投影到(-1,1)范围。
n_G = 64
net_G = nn.Sequential()
net_G.add(G_block(n_G*8, strides=1, padding=0), # output: (64*8, 4, 4)
G_block(n_G*4), # output: (64*4, 8, 8)
G_block(n_G*2), # output: (64*2, 16, 16)
G_block(n_G), # output: (64, 32, 32)
nn.Conv2DTranspose(
3, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding=1, use_bias=False,
activation='tanh')) # output: (3, 64, 64)
生成一个100维的潜在变量来验证生成器的输出形状。
x = np.zeros((1, 100, 1, 1))
net_G.initialize()
net_G(x).shape
(1, 3, 64, 64)
3. Discriminator
该鉴别器Discriminator是一个普通的卷积网络,但使用泄漏ReLU作为其激活函数。鉴于α∈[0,1]。R ReLU if α=0, and an identity function if α=1. For α∈(0,1), leaky ReLU。可以看出,如果α=0,以及如果α=1. 为α∈(0,1),leaky ReLU是一个非线性函数,对负输入给出非零输出。目的是解决“dying ReLU”问题,即神经元可能总是输出一个负值,因此由于ReLU的梯度为0,因此无法取得任何进展。
alphas = [0, 0.2, 0.4, .6, .8, 1]
x = np.arange(-2, 1, 0.1)
Y = [nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)(x).asnumpy() for alpha in alphas]
d2l.plot(x.asnumpy(), Y, 'x', 'y', alphas)

鉴别器的基本模块是卷积层,然后是批处理规范化层和泄漏ReLU激活。卷积层的超参数类似于生成块中的转置卷积层。
class D_block(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, channels, kernel_size=4, strides=2,
padding=1, alpha=0.2, **kwargs):
super(D_block, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2D(
channels, kernel_size, strides, padding, use_bias=False)
self.batch_norm = nn.BatchNorm()
self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)
def forward(self, X):
return self.activation(self.batch_norm(self.conv2d(X)))

x = np.zeros((2, 3, 16, 16))
d_blk = D_block(20)
d_blk.initialize()
d_blk(x).shape
(2, 20, 8, 8)
鉴别器是发生器的镜像。
n_D = 64
net_D = nn.Sequential()
net_D.add(D_block(n_D), # output: (64, 32, 32)
D_block(n_D*2), # output: (64*2, 16, 16)
D_block(n_D*4), # output: (64*4, 8, 8)
D_block(n_D*8), # output: (64*8, 4, 4)
nn.Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, use_bias=False)) # output: (1, 1, 1)
使用带输出通道的卷积层1作为最后一层获得单个预测值。
x = np.zeros((1, 3, 64, 64))
net_D.initialize()
net_D(x).shape
(1, 1, 1, 1)
4. Training
对生成器和鉴别器使用学习速率,改变β1在亚当中0.9到0.5。降低了动量的平滑度,即过去梯度的指数加权移动平均值,以处理快速变化的梯度,因为生成器和鉴别器相互竞争。另外,用随机产生的随机噪声来加速计算。
def train(net_D, net_G, data_iter, num_epochs, lr, latent_dim,
ctx=d2l.try_gpu()):
loss = gluon.loss.SigmoidBCELoss()
net_D.initialize(init=init.Normal(0.02), force_reinit=True, ctx=ctx)
net_G.initialize(init=init.Normal(0.02), force_reinit=True, ctx=ctx)
trainer_hp = {'learning_rate': lr, 'beta1': 0.5}
trainer_D = gluon.Trainer(net_D.collect_params(), 'adam', trainer_hp)
trainer_G = gluon.Trainer(net_G.collect_params(), 'adam', trainer_hp)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss',
xlim=[1, num_epochs], nrows=2, figsize=(5, 5),
legend=['discriminator', 'generator'])
animator.fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3)
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
# Train one epoch
timer = d2l.Timer()
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3) # loss_D, loss_G, num_examples
for X, _ in data_iter:
batch_size = X.shape[0]
Z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(batch_size, latent_dim, 1, 1))
X, Z = X.as_in_ctx(ctx), Z.as_in_ctx(ctx),
metric.add(d2l.update_D(X, Z, net_D, net_G, loss, trainer_D),
d2l.update_G(Z, net_D, net_G, loss, trainer_G),
batch_size)
# Show generated examples
Z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(21, latent_dim, 1, 1), ctx=ctx)
# Normalize the synthetic data to N(0, 1)
fake_x = net_G(Z).transpose(0, 2, 3, 1) / 2 + 0.5
imgs = np.concatenate(
[np.concatenate([fake_x[i * 7 + j] for j in range(7)], axis=1)
for i in range(len(fake_x)//7)], axis=0)
animator.axes[1].cla()
animator.axes[1].imshow(imgs.asnumpy())
# Show the losses
loss_D, loss_G = metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
animator.add(epoch, (loss_D, loss_G))
print('loss_D %.3f, loss_G %.3f, %d examples/sec on %s' % (
loss_D, loss_G, metric[2]/timer.stop(), ctx))
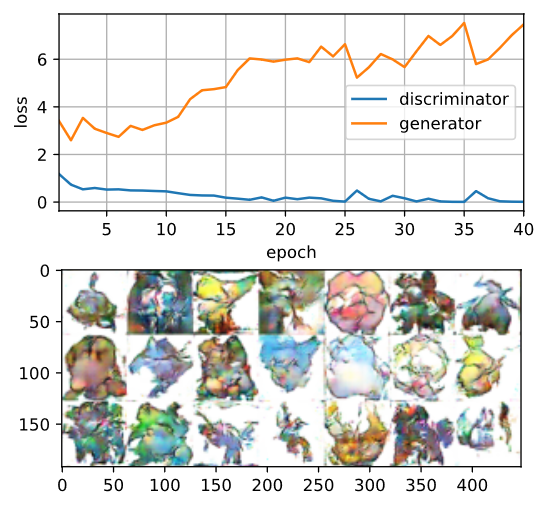
现在训练模型
latent_dim, lr, num_epochs = 100, 0.005, 40
train(net_D, net_G, data_iter, num_epochs, lr, latent_dim)
loss_D 0.011, loss_G 7.465, 2663 examples/sec on gpu(0)
5. Summary
· DCGAN architecture has four convolutional layers for the Discriminator and four “fractionally-strided” convolutional layers for the Generator.
· The Discriminator is a 4-layer strided convolutions with batch normalization (except its input layer) and leaky ReLU activations.
· Leaky ReLU is a nonlinear function that give a non-zero output for a negative input. It aims to fix the “dying ReLU” problem and helps the gradients flow easier through the architecture.