树:
定义:
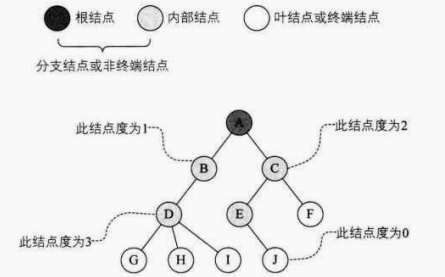
树是n个节点的有限集。n=0时称为空树。在任意一颗非空树中:(1)有且仅有一个特定的称为根(Root)的结点,(2)当n>1时,其余结点可分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1、T2、T3、……Tm,其中每一个集合本身又是一颗树,并称为根的子树,如下图
概念:
- 树的结点包含一个数据元素及若干指向其子树的分支。结点拥有的子树数称为结点的度(Degree)。度为0的结点称为叶结点(Leaf) 或终端结点;度不为0的结点称为非终端结点或分支结点。除根结点之外,分支结点也称为内部结点。树的度是树内各结点的度的最大值。因为这棵树结点的度的最大值是结点D的度为3,所以树的度也为3,如下图:
结点的子树的根称为该结点的孩子,相应的,该结点称为孩子的双亲。同一个双亲的孩子之间互称兄弟,如下图:
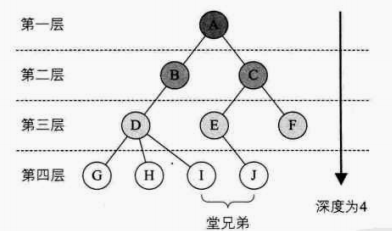
- 结点的层次从根开始,根为第一层,根的孩子为第二层。双亲在同一层的结点互为堂兄弟,树中结点的最大层次称为树的深度或者高度,如下图:
树的父节点表示法:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 5 /** 6 * 树的父节点表示法 7 * @author wydream 8 * 9 */ 10 11 public class TreeParent<E> { 12 13 //定义一个树类 14 public static class Node<T>{ 15 T data;//保存数据 16 int parent;//保存父节点的位置 17 public Node(){ 18 19 } 20 21 public Node(T data) { 22 this.data=data; 23 } 24 25 //指定根节点 26 public Node(T data,int parent) { 27 this.data=data; 28 this.parent=parent; 29 } 30 31 public String toString() { 32 return "TreeParent$Node[data=" + data + ", parent=" + parent + "]"; 33 } 34 } 35 36 private final int DEFAULT_TREE_SIZE=100;//树的默认大小 37 private int treeSize=0;//树的实际大小 38 //使用一个node数组来记录该树里的所有节点 39 private Node<E>[] nodes; 40 //记录树的节点数 41 private int nodeNums; 42 43 //以指定节点创建树 44 public TreeParent(E data) { 45 treeSize=DEFAULT_TREE_SIZE; 46 nodes=new Node[treeSize]; 47 nodes[0]=new Node<E>(data,-1); 48 nodeNums++; 49 } 50 51 //以指定根节点、指定treeSize创建树 52 public TreeParent(E data,int treeSize){ 53 this.treeSize=treeSize; 54 nodes=new Node[treeSize]; 55 nodes[0]=new Node<E>(data,-1); 56 nodeNums++; 57 } 58 59 //为指定节点添加子节点 60 public void addNode(E data,Node<E> parent) { 61 for(int i=0;i<treeSize;i++) { 62 // 找到数组中第一个为null的元素,该元素保存新节点 63 if(nodes[i]==null) { 64 nodes[i]=new Node<E>(data,pos(parent)); 65 nodeNums++; 66 return; 67 } 68 // 创建新节点,并用指定的数组元素保存它 69 } 70 throw new RuntimeException("该树已满"); 71 } 72 73 // 判断树是否为空 74 public boolean isEmpty() { 75 return nodes[0]==null; 76 } 77 78 // 返回根节点 79 public Node<E> root() { 80 return nodes[0]; 81 } 82 83 // 返回指定节点(非根结点)的父节点 84 public Node<E> parent(Node<E> node) { 85 return nodes[node.parent]; 86 } 87 88 // 返回指定节点(非叶子节点)的所有子节点 89 public List<Node<E>> children(Node<E> parent){ 90 List<Node<E>> list=new ArrayList<Node<E>>(); 91 for(int i=0;i<treeSize;i++) { 92 // 如果当前节点的父节点的位置等于parent节点的位置 93 if(nodes[i]!=null&&nodes[i].parent==pos(parent)) { 94 list.add(nodes[i]); 95 } 96 } 97 return list; 98 } 99 100 // 返回该树的深度 101 public int deep() { 102 //用于记录节点的最大深度 103 int max=0; 104 for(int i=0;i<treeSize&&nodes[i]!=null;i++) { 105 //初始化本节点的深度 106 int def=1; 107 //m 记录当前节点的父节点的位置 108 int m=nodes[i].parent; 109 //如果其父节点存在 110 while(m!=-1&&nodes[m]!=null) { 111 //向上继续搜索父节点 112 m=nodes[m].parent; 113 def++; 114 } 115 if(max<def) { 116 max=def; 117 } 118 } 119 return max; 120 } 121 122 //返回包含指定值的节点 123 public int pos(Node<E> node) { 124 for(int i=0;i<treeSize;i++) { 125 //找到指定节点 126 if(nodes[i]==node) { 127 return i; 128 } 129 } 130 return -1; 131 } 132 133 134 //测试 135 public static void main(String[] args) { 136 TreeParent<String> tp=new TreeParent<String>("root"); 137 TreeParent.Node root=tp.root(); 138 System.out.println(root); 139 tp.addNode("节点1", root); 140 System.out.println("此树的深度"+tp.deep()); 141 tp.addNode("节点2",root); 142 //获取根节点的所有子节点 143 List<TreeParent.Node<String>> nodes=tp.children(root); 144 System.out.println("根节点的第一个子节点为:"+nodes.get(0)); 145 // 为根节点的第一个子节点新增一个子节点 146 tp.addNode("节点3", nodes.get(0)); 147 System.out.println("此树的深度:" + tp.deep()); 148 149 } 150 }
程序运行结果:
TreeParent$Node[data=root, parent=-1] 此树的深度2 根节点的第一个子节点为:TreeParent$Node[data=节点1, parent=0] 此树的深度:3
树的子节点表示法:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 /** 5 * 树的子节点表示法 6 * @author wydream 7 * 8 */ 9 10 11 public class TreeChild<E> { 12 13 private static class SonNode{ 14 //记录当前节点的位置 15 private int pos; 16 private SonNode next; 17 18 public SonNode(int pos,SonNode next) { 19 this.pos=pos; 20 this.next=next; 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 public static class Node<T>{ 26 T data; 27 SonNode first;//记录第一个子节点 28 29 public Node(T data) { 30 this.data=data; 31 this.first=null; 32 } 33 34 public String toString() { 35 if (first != null) { 36 return "TreeChild$Node[data=" + data + ", first=" + first.pos + "]"; 37 } else { 38 return "TreeChild$Node[data=" + data + ", first=-1]"; 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 private final int DEFAULT_TREE_SIZE = 100; 44 private int treeSize=0; 45 46 // 使用一个Node[]数组来记录该树里的所有节点 47 private Node<E>[] nodes; 48 49 //记录节点数 50 private int nodeNums; 51 52 // 以指定根节点创建树 53 public TreeChild(E data) { 54 treeSize=DEFAULT_TREE_SIZE; 55 nodes=new Node[treeSize]; 56 nodes[0]=new Node<E>(data); 57 nodeNums++; 58 } 59 60 // 以指定根节点、指定treeSize创建树 61 public TreeChild(E data,int treeSize) { 62 this.treeSize=treeSize; 63 nodes=new Node[treeSize]; 64 nodes[0]=new Node<E>(data); 65 nodeNums++; 66 } 67 68 // 为指定节点添加子节点 69 public void addNode(E data,Node parent) { 70 for(int i=0;i<treeSize;i++) { 71 // 找到数组中第一个为null的元素,该元素保存新节点 72 if(nodes[i]==null) { 73 // 创建新节点,并用指定数组元素保存它 74 nodes[i]=new Node(data); 75 if(parent.first==null) { 76 parent.first=new SonNode(i, null); 77 }else { 78 SonNode next=parent.first; 79 while(next.next!=null) { 80 next=next.next; 81 } 82 next.next = new SonNode(i, null); 83 } 84 nodeNums++; 85 return; 86 } 87 } 88 throw new RuntimeException("该树已满,无法添加节点"); 89 } 90 91 //判断树是否为空 92 public boolean isEmpty() { 93 return nodes[0]==null; 94 } 95 96 //返回根节点 97 public Node<E> root(){ 98 return nodes[0]; 99 } 100 101 //返回指定节点的所有子节点 102 public List<Node<E>> children(Node<E> parent){ 103 List<Node<E>> list=new ArrayList<Node<E>>(); 104 // 获取parent节点的第一个子节点 105 SonNode next=parent.first; 106 // 沿着孩子链不断搜索下一个孩子节点 107 while(next!=null) { 108 list.add(nodes[next.pos]); 109 next=next.next; 110 } 111 return list; 112 } 113 114 // 返回指定节点(非叶子节点)的第index个子节点 115 public Node<E> child(Node parent,int index){ 116 // 获取parent节点的第一个子节点 117 SonNode next=parent.first; 118 // 沿着孩子链不断搜索下一个孩子节点 119 for(int i=0;next!=null;i++) { 120 if(index==i) { 121 return nodes[next.pos]; 122 } 123 next=next.next; 124 } 125 return null; 126 } 127 128 // 返回该树的深度 129 public int deep() { 130 // 获取该树的深度 131 return deep(root()); 132 } 133 134 // 这是一个递归方法:每棵子树的深度为其所有子树的最大深度 + 1 135 public int deep(Node node) { 136 if(node.first==null) { 137 return 1; 138 }else { 139 // 记录其所有子树的最大深度 140 int max=0; 141 SonNode next=node.first; 142 // 沿着孩子链不断搜索下一个孩子节点 143 while(next!=null) { 144 // 获取以其子节点为根的子树的深度 145 int tmp=deep(nodes[next.pos]); 146 if(tmp>max) { 147 max=tmp; 148 } 149 next=next.next; 150 } 151 // 最后,返回其所有子树的最大深度 + 1 152 return max + 1; 153 } 154 } 155 156 157 // 返回包含指定值得节点 158 public int pos(Node node) { 159 for (int i = 0; i < treeSize; i++) { 160 // 找到指定节点 161 if (nodes[i] == node) { 162 return i; 163 } 164 } 165 return -1; 166 } 167 168 //测试 169 public static void main(String[] args) { 170 171 TreeChild<String> tp = new TreeChild<String>("root"); 172 TreeChild.Node root = tp.root(); 173 System.out.println(root); 174 tp.addNode("节点1", root); 175 tp.addNode("节点2", root); 176 tp.addNode("节点3", root); 177 System.out.println("添加子节点后的根结点:" + root); 178 System.out.println("此树的深度:" + tp.deep()); 179 // 获取根节点的所有子节点 180 List<TreeChild.Node<String>> nodes = tp.children(root); 181 System.out.println("根节点的第一个子节点:" + nodes.get(0)); 182 // 为根节点的第一个子节点新增一个子节点 183 tp.addNode("节点4", nodes.get(0)); 184 System.out.println("此树第一个子节点:" + nodes.get(0)); 185 System.out.println("此树的深度:" + tp.deep()); 186 187 } 188 189 190 191 192 }
程序运行结果:
TreeChild$Node[data=root, first=-1] 添加子节点后的根结点:TreeChild$Node[data=root, first=1] 此树的深度:2 根节点的第一个子节点:TreeChild$Node[data=节点1, first=-1] 此树第一个子节点:TreeChild$Node[data=节点1, first=4] 此树的深度:3