在我的项目里,树莓派主要作为中心节点,用于接收数据,Arduino作为子节点,用于发送数据,考虑到以后会有很多子节点,但又不至于使得代码过于繁琐,因此所有的传输数据添加一个头部编号用于区分不同节点。
nrf24l01支持的数据最大为4个字节,因此使用最高位的一个字节(8位)作为节点编号,剩余三个字节用于传输数据。以下为具体代码:
Arduino Leonardo程序
主要用于发送数据给树莓派,同时接收树莓派的响应数据。
#include <SPI.h> #include "RF24.h" #include <SPI.h> #include "RF24.h" #include <printf.h> /****************** User Config ***************************/ /*** Set this radio as radio number 0 or 1 ***/ bool radioNumber = 0; /* Hardware configuration: Set up nRF24L01 radio on SPI bus plus pins 7 & 8 */ RF24 radio(9,10); /**********************************************************/ byte addresses[][6] = {"1Node","2Node"}; // Used to control whether this node is sending or receiving bool role = 1; //这个是我们即将建立的传输渠道编码 //!!要和另一个模块的一致 const uint64_t pipes = 0xE8E8F0F0E1LL; //这个变量会保持我们接受到的信息 //变量类型一定要和传过来的一样 //要传输的数据 unsigned long sendData = 1; unsigned long head = 0x01000000;//高8位为头标志,根据标志不同区分不同发送源,0x00为中心主节点 unsigned long receData; void setup() { Serial.begin(57600); printf_begin(); Serial.println(F("RF24/examples/GettingStarted")); radio.begin(); radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MAX); radio.openWritingPipe(pipes); } void loop() { unsigned long data = sendData+head; Serial.print("Sending:"); Serial.println(data); bool ok = radio.write(&data,sizeof(unsigned long)); if(ok){ radio.startListening(); delay(925); //延时,用于响应返回时间 if(radio.available()){ radio.read(&receData,sizeof(unsigned long));//读取的数据为1时,表示正常 Serial.print("Response:"); Serial.println(receData); } radio.stopListening(); } } // Loop
结果如下:
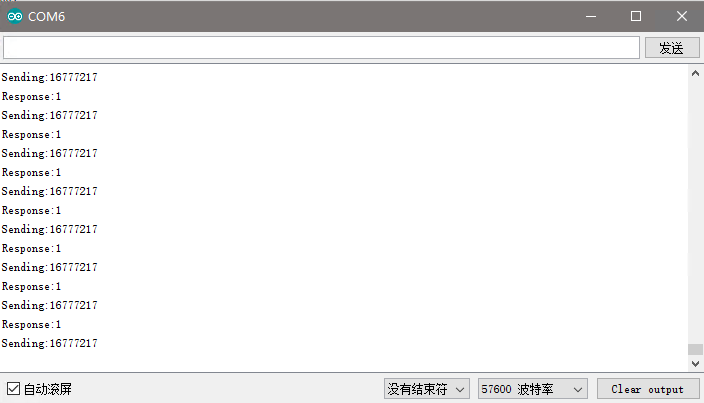
树莓派程序
树莓派主要用于接收数据,同时发出响应。
#include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <unistd.h> #include <RF24/RF24.h> using namespace std; // // Hardware configuration // Configure the appropriate pins for your connections /****************** Raspberry Pi ***********************/ // Radio CE Pin, CSN Pin, SPI Speed // Setup for GPIO 22 CE and CE0 CSN with SPI Speed @ 4Mhz //RF24 radio(RPI_V2_GPIO_P1_22, BCM2835_SPI_CS0, BCM2835_SPI_SPEED_4MHZ); // NEW: Setup for RPi B+ //RF24 radio(RPI_BPLUS_GPIO_J8_15,RPI_BPLUS_GPIO_J8_24, BCM2835_SPI_SPEED_8MHZ); // Setup for GPIO 15 CE and CE0 CSN with SPI Speed @ 8Mhz //RF24 radio(RPI_V2_GPIO_P1_15, RPI_V2_GPIO_P1_24, BCM2835_SPI_SPEED_8MHZ); // RPi generic: RF24 radio(22,0); /*** RPi Alternate ***/ //Note: Specify SPI BUS 0 or 1 instead of CS pin number. // See http://tmrh20.github.io/RF24/RPi.html for more information on usage //RPi Alternate, with MRAA //RF24 radio(15,0); //RPi Alternate, with SPIDEV - Note: Edit RF24/arch/BBB/spi.cpp and set 'this->device = "/dev/spidev0.0";;' or as listed in /dev //RF24 radio(22,0); /****************** Linux (BBB,x86,etc) ***********************/ // Setup for ARM(Linux) devices like BBB using spidev (default is "/dev/spidev1.0" ) //RF24 radio(115,0); //BBB Alternate, with mraa // CE pin = (Header P9, Pin 13) = 59 = 13 + 46 //Note: Specify SPI BUS 0 or 1 instead of CS pin number. //RF24 radio(59,0); /********** User Config *********/ // Assign a unique identifier for this node, 0 or 1 bool radioNumber = 1; /********************************/ // Radio pipe addresses for the 2 nodes to communicate. const uint64_t pipes = 0xE8E8F0F0E1LL; unsigned long receData; unsigned long respData=0x01; unsigned long head=0x00000000; int main(int argc, char** argv){ cout << "RF24/examples/GettingStarted/ "; // Setup and configure rf radio radio.begin(); // optionally, increase the delay between retries & # of retries radio.setRetries(15,15); // Dump the configuration of the rf unit for debugging radio.printDetails(); radio.openReadingPipe(1,pipes); /***********************************/ // This simple sketch opens two pipes for these two nodes to communicate // back and forth. radio.startListening(); cout << "Listening .... "; // forever loop while (1) { // Pong back role. Receive each packet, dump it out, and send it back // // if there is data ready if ( radio.available() ) { // Fetch the payload, and see if this was the last one. while(radio.available()){ radio.read( &receData, sizeof(unsigned long) ); } radio.stopListening(); unsigned long data = respData+head; radio.write( &data, sizeof(unsigned long) ); // Now, resume listening so we catch the next packets. radio.startListening(); // Spew it printf("Got payload(%d) %lu... ",sizeof(unsigned long), receData); delay(925); //Delay after payload responded to, minimize RPi CPU time } } // forever loop return 0; }
结果如下:

上图中数据“16777217”用八进制表示为“0x01000001”,第一个字节的0x01表示从节点head=0x01000000发来的数据,数据为data=0x000001。