1.回顾单例模式(Singleton Pattern)
设置一个静态的构造函数,让Student仅能被new一个,给所有调用返回一个相同的实例
StudentPrototype类代码如下:
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Prototype { class StudentPrototype { public String Name="kxy"; private StudentPrototype() { Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("执行StudentPrototype构造函数"); } private static StudentPrototype _studentPrototype=null; static StudentPrototype() { _studentPrototype = new StudentPrototype(); } public static StudentPrototype GetStudent() { return _studentPrototype; } } }
Program代码如下:
using System; namespace Prototype { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StudentPrototype studentPrototype1 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype1.Name = "flt";//赋新值之前,Name的值为kxy StudentPrototype studentPrototype2 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"; StudentPrototype studentPrototype3 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); StudentPrototype studentPrototype4 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); Console.Read(); } } }
因为studentPrototype1和studentPrototype2是调用了同个实例,所以
当执行studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"时,studentPrototype1的Name属性也会变成wzz
同理,studentPrototype3、studentPrototype4也是使用这个实例
2.原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
原型模式是对一个原型的Clone,并返回一个新的实例
可理解为,在单例的基础上,Clone这个单例,并返回Clone出来的新实例,这个单例就是原型
StudentPrototype类代码如下:
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Prototype { class StudentPrototype { public String Name="kxy"; private StudentPrototype() { Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("执行StudentPrototype构造函数"); } private static StudentPrototype _studentPrototype=null; static StudentPrototype() { _studentPrototype = new StudentPrototype(); } public static StudentPrototype GetStudent() { return (StudentPrototype)_studentPrototype.MemberwiseClone();//返回一个Clone的例子 } } }
这时候因为studentPrototype1和studentPrototype2不是使用同一个实例,所以
当执行studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"时,studentPrototype1的Name并不会受到影响,依旧是flt
同理,studentPrototype3、studentPrototype4也是使用了Clone出来的新实例
3.Clone的缺陷
MemberwiseClone是一种浅克隆,无法克隆引用参数
如,在StudentPrototype类中引入StuScore
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Prototype { class StudentPrototype { public String Name = "kxy"; private static StudentPrototype _studentPrototype = null; public StuScore stuScore; private StudentPrototype() { Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("执行StudentPrototype构造函数"); } static StudentPrototype() { _studentPrototype = new StudentPrototype(); _studentPrototype.stuScore = new StuScore();//实例化_studentPrototype这个实力中StuScore的实例,外面函数才能赋值 } public static StudentPrototype GetStudent() { return (StudentPrototype)_studentPrototype.MemberwiseClone(); } } class StuScore { public int Number = 0; public double Score = 0; } }
Program
using System; namespace Prototype { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StudentPrototype studentPrototype1 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype1.Name = "flt"; studentPrototype1.stuScore.Number = 108; studentPrototype1.stuScore.Score = 95; StudentPrototype studentPrototype2 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"; studentPrototype2.stuScore.Number = 124; studentPrototype2.stuScore.Score = 85; StudentPrototype studentPrototype3 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); StudentPrototype studentPrototype4 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); Console.Read(); } } }
这时候因为studentPrototype1和studentPrototype2不是使用同一个实例,所以
当执行studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"时,studentPrototype1的Name并不会受到影响,依旧是flt
这个和上述一样
但是当执行
studentPrototype2.stuScore.Number = 124;
studentPrototype2.stuScore.Score = 85;
时,studentPrototype1的stuScore的属性值会被改变
因为浅克隆并不会克隆出一个新的StuScore的实例,而是所有克隆出来的StudentPrototype实力都引用同一个StuScore实例
即引用类型的对象并不会被Clone出一个新的实例
4.浅克隆缺陷的解决方法
借助序列化、反序列化实现深度Clone
新建一个类SerializeHelper,用来对对象进行序列化和反序列化
代码如下:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; namespace Prototype { public class SerializeHelper { public static string Serializable(object target)//序列化,把对象序列化为一个字符串 { using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream()) { new BinaryFormatter().Serialize(stream, target); return Convert.ToBase64String(stream.ToArray()); } } public static T Derializable<T>(string target)//反序列化,把字符串反序列化成一个对象 { byte[] targetArray = Convert.FromBase64String(target); using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(targetArray)) { return (T)(new BinaryFormatter().Deserialize(stream)); } } public static T DeepClone<T>(T t)//用序列化和反序列化实现深克隆 { return Derializable<T>(Serializable(t)); } } }
在对对象进行序列化时,对象所对应的类要有一个序列化的特性,即在类名上面加上[Serializable]
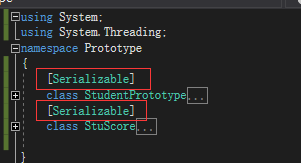
Program代码如下:
using System; namespace Prototype { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StudentPrototype studentPrototype1 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype1.Name = "flt"; studentPrototype1.stuScore.Number = 108; studentPrototype1.stuScore.Score = 95;
StudentPrototype studentPrototype2 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); studentPrototype2.Name = "wzz"; studentPrototype2.stuScore.Number = 124; studentPrototype2.stuScore.Score = 85; StudentPrototype studentPrototype3 = SerializeHelper.DeepClone(StudentPrototype.GetStudent()); studentPrototype3.Name = "zjx"; studentPrototype3.stuScore.Number = 223; studentPrototype3.stuScore.Score = 90; StudentPrototype studentPrototype4 = StudentPrototype.GetStudent(); Console.Read(); } } }
studentPrototype3 是深度克隆的对象,连stuScore也是一个新的Clone实例,所以执行
studentPrototype3.stuScore.Number = 223;
studentPrototype3.stuScore.Score = 90;
并不会影响到studentPrototype1和studentPrototype2的stuScore