备忘录模式
意图:
在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可将改对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
适用性:
1、必须保存一个对象在某一个时刻的部分状态,这样以后需要时它才能恢复到先前的状态。
2、如果一个用接口来让其它对象直接得到这些状态,将会暴露对象的实现细节并破坏对象的封装性。
UML:
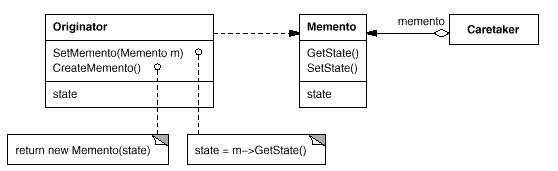
代码实现:实现保存游戏中英雄的不同状态,并能恢复到对应状态。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "memento.h" 3 #include <string> 4 #include <time.h> 5 #include <map> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 class Memento{ 10 public: 11 Memento(int hp=0, int mp=0, int atk=0) 12 { 13 mHp = hp; 14 mMp = mp; 15 mAttack = atk; 16 } 17 18 public: 19 int mHp; 20 int mMp; 21 int mAttack; 22 }; 23 24 class Caretaker 25 { 26 public: 27 Memento* GetState(string key) 28 { 29 return mData[key]; 30 } 31 void SetState(string key, Memento* pMemento) 32 { 33 mData[key] = pMemento; 34 } 35 ~Caretaker() 36 { 37 auto it = mData.begin(); 38 for(; it != mData.end(); it++) 39 { 40 if(mData.count("he") && it->second != nullptr) 41 { 42 delete it->second; 43 } 44 } 45 mData.clear(); 46 } 47 48 private: 49 map<string, Memento*> mData; 50 }; 51 52 class Hero{ 53 public: 54 Hero(int hp=100, int mp=100, int at=100):mHp(hp), mMp(mp), mAttack(at), mCaretaker(new Caretaker){} 55 56 void saveState(string key) 57 { 58 Memento* pMemento = new Memento(mHp, mMp, mAttack); 59 mCaretaker->SetState(key, pMemento); 60 } 61 62 void resumeState(string key) 63 { 64 auto mmt = mCaretaker->GetState(key); 65 mHp = mmt->mHp; 66 mMp = mmt->mMp; 67 mAttack = mmt->mAttack; 68 } 69 70 void battle() 71 { 72 mHp = rand()%100; 73 mMp = rand()%100; 74 mAttack = rand()%100; 75 } 76 77 void showState() 78 { 79 cout<<"血量:"<<mHp<<endl 80 <<"蓝量:"<<mMp<<endl 81 <<"攻击:"<<mAttack<<endl; 82 } 83 84 private: 85 int mHp; 86 int mMp; 87 int mAttack; 88 Caretaker* mCaretaker; 89 }; 90 91 void main() 92 { 93 srand((unsigned int) time(NULL)); 94 95 Caretaker ctk; 96 Hero hero; 97 Memento mmt; 98 99 cout<<"----战斗前-----"<<endl; 100 hero.showState(); 101 cout<<endl; 102 hero.saveState("战斗前"); 103 104 hero.battle(); 105 cout<<"-----战斗1后-----"<<endl; 106 hero.showState(); 107 cout<<endl; 108 hero.saveState("战斗1后"); 109 110 hero.battle(); 111 cout<<"-----战斗2后-----"<<endl; 112 hero.showState(); 113 hero.saveState("战斗2后"); 114 cout<<endl; 115 116 hero.battle(); 117 cout<<"-----战斗3后-----"<<endl; 118 hero.showState(); 119 hero.saveState("战斗3后"); 120 cout<<endl; 121 122 hero.resumeState("战斗1后"); 123 cout<<"-----恢复战斗1结果-----"<<endl; 124 hero.showState(); 125 cout<<endl; 126 127 hero.resumeState("战斗前"); 128 cout<<"-----恢复战斗前-----"<<endl; 129 hero.showState(); 130 cout<<endl; 131 132 return; 133 }
结果:
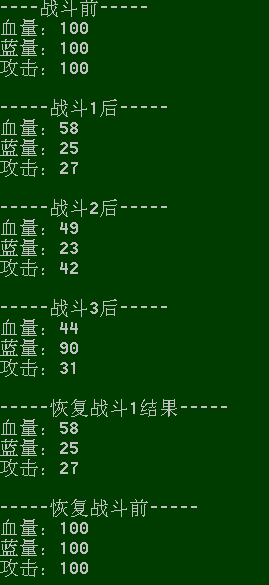
这样客户端实现了保存状态和恢复到对应状态,而内部处理过程却不知道。