一、RPC的定义
RPC:是Remote Procedure Call的缩写,中文名远程过程调用。RPC协议是一个计算机通信协议。该协议允许运行于一台计算机的程序调用另一个地址空间(通常为一个开发网络的一台计算机)的子程序,而程序员就像调用本地程序一样,无需额外地为这个交互作用编程。如果涉及的软件采用面向对象编程,那么远程过程调用亦可称为远程方法调用,例:Java RMI。
RPC有以下优势:
简单。RPC的语义十分清晰简单,便于建立分布式系统
高效。能高效的实现远程过程调用。
通用。RPC导出的服务可以供多个使用者用于不同的目的
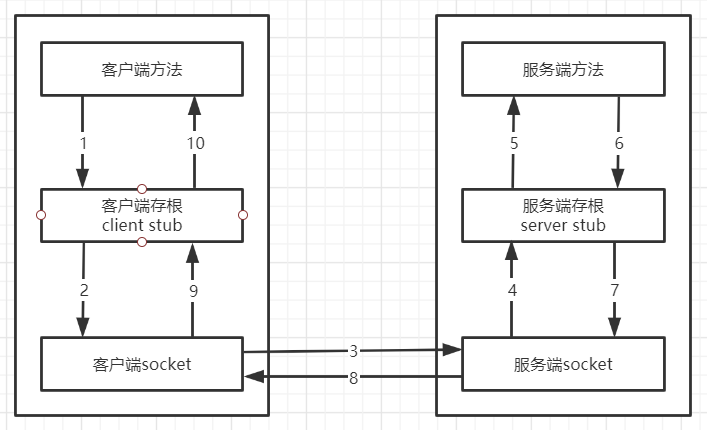
二、RPC调用过程
1 客户端调用客户端的stub(client stub)。这个调用是在本地,并将调用参数push到栈(stack)中。
2 客户端stub(client stub)将这些参数包装,并通过系统调用发送到服务器机器。打包的过程叫marshalling。(常见方式:XML、JSON、二进制编码)
3 客户端本地操作系统发送信息至服务器。(可通过自定义的TCP协议或HTTP协议传输)
4 服务器系统将信息传送至服务端stub(server stub)。
5 服务端stub(server stub)解析信息。这个过程叫unmarshalling。
6 服务端stub(server stub)调用程序,并把结果返回到服务端stub(server stub)中
7 服务器stub(server stub)将返回参数包装(marshalling),并通过系统调用发送到客户端机器。
8 客户端系统将返回信息传送到客户端stub(client stub)。
9 客户端存根从本地socket接口中读取结果信息。
10 客户端存根unmarshalling后,再将结果返回给客户端函数。
关于stub存根的个人理解:第一次见stub存根,不知道存根具体是什么,个人理解,存根就是一个抽象的概念。
只需要记住存根实现的功能:marshalling+unmarshalling、查找服务端提供服务地址、并调用操作系统的系统通用接口,控制socket传输数据。
那么在具体RPC协议的具体实现中,实现这一块逻辑的模块,我就认为是stub存根。
补充:
PRC协议在传输层与应用层之间。
IDL:interface definition language,接口定义语言。用来化解各个语言之间的特殊性。即RPC可跨语言调用
三、Java中实现RPC协议的框架
1、Java RMI
JavaRMI(Remote Method Invocation)是JDK提供的RPC协议实现,只支持Java语言,不能跨语言调用(没有使用IDL),因此简单、实用、效率高。
与上面RPC流程图不同是:Java RMI增加了一个命名服务(注册)。
命名服务的作用:把查找服务端服务地址的逻辑从本地存根stub中解耦出去,利用一个独立的注册空间实现。好处:
① 未提供服务早发现,例如:服务器奔溃
② 更利于分布式环境实现。网状结构(每台机器都需要管理服务地址,而且需要保证一致性)-->总线结构(由命名服务统一管理)
③ 统一的管理利于服务监控的实现。

RMI中分布式垃圾收集:
RMI创建了一个分布式环境,使客户端JVM上的进程可以访问服务端JVM进程中的对象。这意味着服务端JVM进程需要知道一个对象在什么时候不再被客户引用,并且可以被垃圾回收。
在使用RMI的JVM中,Java支持两种操作:标记脏数据和清理。当对象仍在使用时,客户端JVM会定期向服务端JVM发送一个标记脏数据的调用(类似于定期心跳检测)。当客户端JVM不再使用时,会发送一个清理的调用给服务端JVM,服务端JVM根据客户端发送信息,及本地对象使用情况,进行垃圾回收。RMI实现可分为三层:

简单代码实现:
public class Person implements Serializable { //必须支持序列化 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private int id; private String name; private int age; //省略getter/setter } public interface PersonService extends Remote { //接口必须实现Remote,方法必须throws RemoteException Person getPersonInfo(int n) throws RemoteException; } public class PersonServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements PersonService { //具体实现类,UnicastRemoteObject提供远程调用基础功能 protected PersonServiceImpl() throws RemoteException { } @Override public Person getPersonInfo(int id) throws RemoteException { System.out.println("get Person :" + id); Person person = new Person(); person.setId(id); return person; } } public class Server { //服务端启动 public static void main(String[] args) { try { PersonService personService = new PersonServiceImpl(); //提供服务的端口 LocateRegistry.createRegistry(5555); //注册接口命名 Context namingContext = new InitialContext(); namingContext.rebind("rmi://localhost:5555/PersonService", personService); //Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:6666/person-service",personService); System.out.println("Service started"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class Client { //客户端启动 public static void main(String[] args) { try { //远程对象调用的端口和注册类 PersonService personService = (PersonService) Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:5555/PersonService"); Person person = personService.getPersonInfo(5); System.out.println(person); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2、基于RPC协议的SOA框架
① SOA:
SOA:全称service-oriented architecture,面向服务的体系结构,它并不特指一种技术,而是一种分布式运算的软件设计方法。软件的部分组件(调用者),可以透过网络上的通用协议用另外一个应用软件组件运行、运作(与RPC契合)。让调用者获得服务。SOA将一项服务视为一个独立的功能单元,可以远程访问并独立运行与更新,例如在线查询信用卡账单。
企业系统的架构师认为SOA能够帮助业务迅速和高效地响应变化的市场条件。服务的导向架构在宏观(服务)上,而不是在微观上(对象),因此提高了重复使用性。
我简单理解就是面向服务编程。将服务视作一个对象。SOA使分布式系统设计更加清晰了,以服务为单位,将系统拆分。
②基于RPC协议的SOA框架——dubbo
基于PRC协议实现的SOA框架有很多,Facebook的Thrift、ZeroC的Ice、谷歌的gRPC、阿里巴巴的Dubbo。国内使用最多的是dubbo,所以接下来会慢慢研究下dubbo实现。
dubbo是阿里巴巴在2011年开源的分布式服务架构,是SOA服务化治理方案的核心框架。
dubbo简单代码使用:
API实现:
public interface GreetingService { String sayHi(String name); } public class GreetingServiceImpl implements GreetingService { @Override public String sayHi(String name) { return "hi, " + name; } } public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ServiceConfig<GreetingService> service = new ServiceConfig<>(); service.setApplication(new ApplicationConfig("first-dubbo-provider")); service.setRegistry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://mcip:2291?backup=mcip:2292,mcip:2293")); service.setInterface(GreetingService.class); service.setRef(new GreetingServiceImpl()); service.export(); System.out.println("dubbo service started"); new CountDownLatch(1).await(); } } public class ApplicationB { private static String zookeeperHost = System.getProperty("zookeeper.address","mcip"); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReferenceConfig<GreetingService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>(); reference.setApplication(new ApplicationConfig("first-dubbo-consumer")); reference.setRegistry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://mcip:2291?backup=mcip:2292,mcip:2293")); reference.setInterface(GreetingService.class); GreetingService service =reference.get(); System.out.println(service.sayHi("dubbo")); } }
基于springxml实现:
provider:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd"> <context:property-placeholder/> <!-- provider's application name, used for tracing dependency relationship --> <dubbo:application name="dubbo-demo"/> <!-- use multicast registry center to export service --> <dubbo:registry address="${dubbo.zk.address}"/> <!-- use dubbo protocol to export service on port 20880 --> <dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="${dubbo.port}" /> <!-- service implementation, as same as regular local bean --> <dubbo:service interface="org.study.service.UserService" ref="userService" protocol="dubbo"/> </beans>
consumer:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd"> <context:property-placeholder/> <!-- provider's application name, used for tracing dependency relationship --> <dubbo:application name="dubbo-demo1"/> <!-- use multicast registry center to export service --> <dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://mcip:2291?backup=mcip:2292,mcip:2293"/> <!-- use dubbo protocol to export service on port 20880 --> <dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20881" /> <!-- service implementation, as same as regular local bean --> <dubbo:reference interface="org.study.service.UserService" id="userService"/> </beans>
参考 维基百科、《可伸缩服务架构-框架与中间件》、dubbo官网