大家可以参考一下这个discusion:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 500) pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 500) import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport lightgbm as lgb from sklearn import preprocessing, metrics import gc import joblib import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
1. 加载数据
INPUT_DIR_PATH = '../input/m5-forecasting-accuracy/'
一个可以优化内存的方法:
def reduce_mem_usage(df, verbose=True): numerics = ['int16', 'int32', 'int64', 'float16', 'float32', 'float64'] start_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2 for col in df.columns: col_type = df[col].dtypes if col_type in numerics: c_min = df[col].min() c_max = df[col].max() if str(col_type)[:3] == 'int': if c_min > np.iinfo(np.int8).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int8).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int8) elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int16).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int16).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int16) elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int32).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int32).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int32) elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int64).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int64).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int64) else: if c_min > np.finfo(np.float16).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float16).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float16) elif c_min > np.finfo(np.float32).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float32).max: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float32) else: df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float64) end_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2 if verbose: print('Mem. usage decreased to {:5.2f} Mb ({:.1f}% reduction)'.format(end_mem, 100 * (start_mem - end_mem) / start_mem)) return df
加载数据
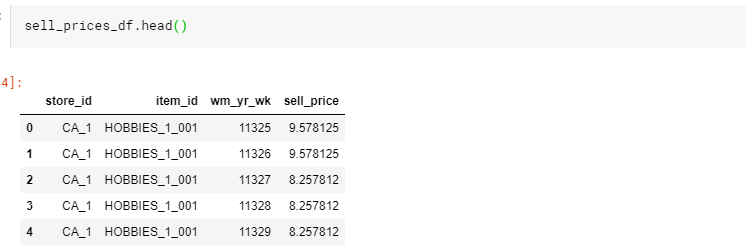
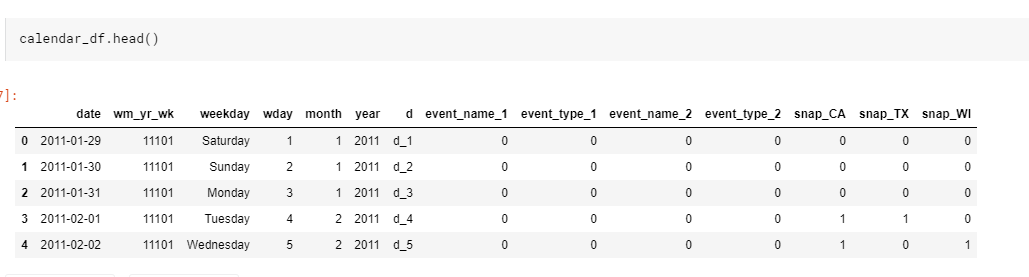
def read_data(): sell_prices_df = pd.read_csv(INPUT_DIR_PATH + 'sell_prices.csv') sell_prices_df = reduce_mem_usage(sell_prices_df) print('Sell prices has {} rows and {} columns'.format(sell_prices_df.shape[0], sell_prices_df.shape[1])) calendar_df = pd.read_csv(INPUT_DIR_PATH + 'calendar.csv') calendar_df = reduce_mem_usage(calendar_df) print('Calendar has {} rows and {} columns'.format(calendar_df.shape[0], calendar_df.shape[1])) sales_train_validation_df = pd.read_csv(INPUT_DIR_PATH + 'sales_train_validation.csv') print('Sales train validation has {} rows and {} columns'.format(sales_train_validation_df.shape[0], sales_train_validation_df.shape[1])) submission_df = pd.read_csv(INPUT_DIR_PATH + 'sample_submission.csv') return sell_prices_df, calendar_df, sales_train_validation_df, submission_df、
sell_prices_df, calendar_df, sales_train_validation_df, submission_df = read_data()
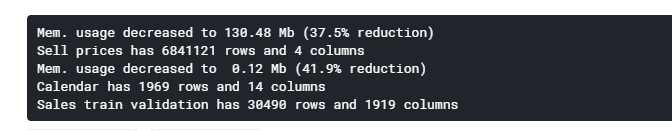
我们依旧再看一遍,各个数据:


2.catergory类型转换
def encode_categorical(df, cols,verbose=True): start_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2 for col in cols: # Leave NaN as it is. le = preprocessing.LabelEncoder() # not_null = df[col][df[col].notnull()] # df[col] = pd.Series(le.fit_transform(not_null), index=not_null.index) df[col]=df[col].astype('category').cat.codes df[col] -= df[col].min() end_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2 if verbose: print('encode_categorical make Mem. usage decreased to {:5.2f} Mb ({:.1f}% reduction)'.format(end_mem, 100 * (start_mem - end_mem) / start_mem)) return df
calendar_df = encode_categorical(calendar_df, ["event_name_1", "event_type_1", "event_name_2", "event_type_2"]).pipe(reduce_mem_usage) sales_train_validation_df = encode_categorical(sales_train_validation_df, ["item_id", "dept_id", "cat_id", "store_id", "state_id"]).pipe(reduce_mem_usage) sell_prices_df = encode_categorical(sell_prices_df, ["item_id", "store_id"]).pipe(reduce_mem_usage)
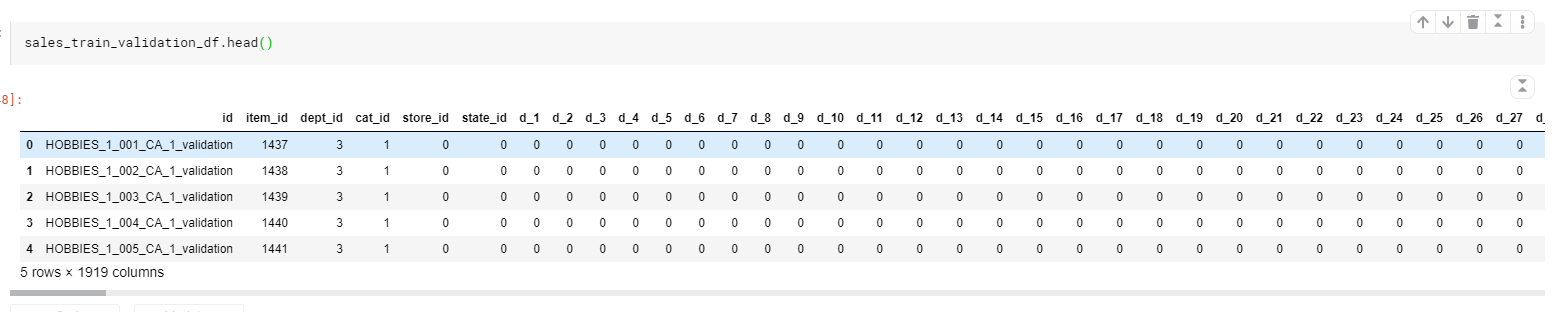

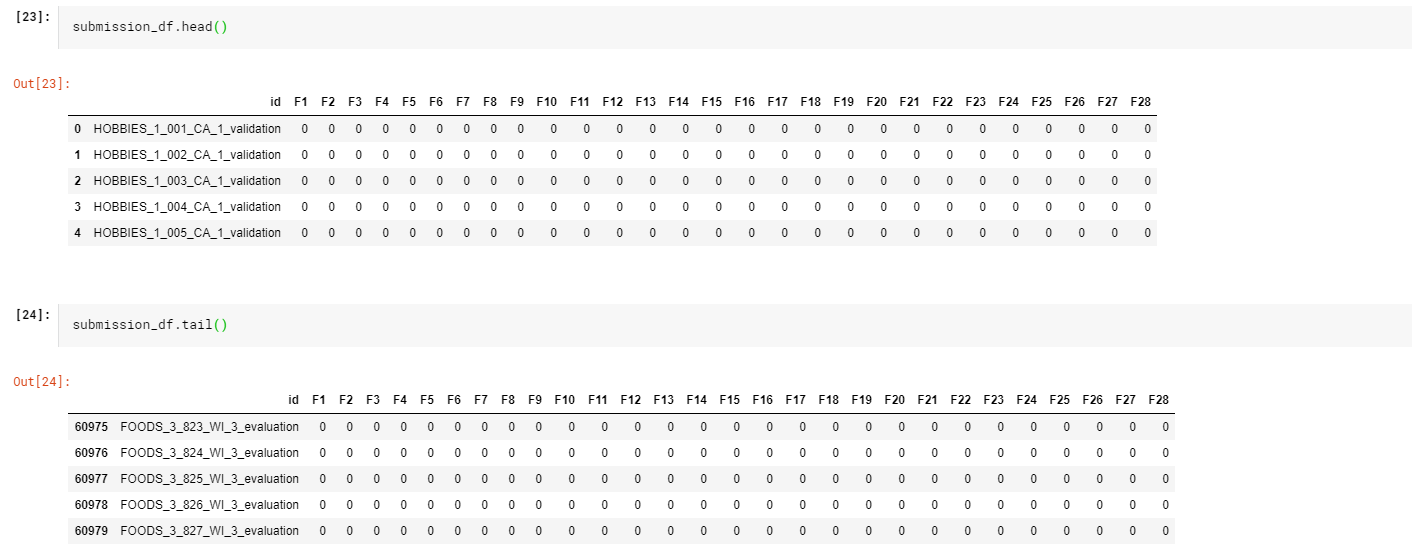
3.数据合并
设定变量
NUM_ITEMS = sales_train_validation_df.shape[0] # 30490 DAYS_PRED = 28 nrows = 365 * 2 * NUM_ITEMS nrows
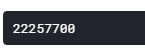
不知道为什么最后作者使用这个数值:
nrows = 27500000
合并数据
def melt_and_merge(calendar, sell_prices, sales_train_validation, submission, nrows = 55000000, merge = False): # melt sales data, get it ready for training sales_train_validation = pd.melt(sales_train_validation, id_vars = ['id', 'item_id', 'dept_id', 'cat_id', 'store_id', 'state_id'], var_name = 'day', value_name = 'demand') print('Melted sales train validation has {} rows and {} columns'.format(sales_train_validation.shape[0], sales_train_validation.shape[1])) #melt后 实际数据30490 * 1913=58327370 sales_train_validation = reduce_mem_usage(sales_train_validation) sales_train_validation = sales_train_validation.iloc[-nrows:,:] # seperate test dataframes test1_rows = [row for row in submission['id'] if 'validation' in row] test2_rows = [row for row in submission['id'] if 'evaluation' in row] test1 = submission[submission['id'].isin(test1_rows)] test2 = submission[submission['id'].isin(test2_rows)] # change column names test1.columns = ['id', 'd_1914', 'd_1915', 'd_1916', 'd_1917', 'd_1918', 'd_1919', 'd_1920', 'd_1921', 'd_1922', 'd_1923', 'd_1924', 'd_1925', 'd_1926', 'd_1927', 'd_1928', 'd_1929', 'd_1930', 'd_1931', 'd_1932', 'd_1933', 'd_1934', 'd_1935', 'd_1936', 'd_1937', 'd_1938', 'd_1939', 'd_1940', 'd_1941'] test2.columns = ['id', 'd_1942', 'd_1943', 'd_1944', 'd_1945', 'd_1946', 'd_1947', 'd_1948', 'd_1949', 'd_1950', 'd_1951', 'd_1952', 'd_1953', 'd_1954', 'd_1955', 'd_1956', 'd_1957', 'd_1958', 'd_1959', 'd_1960', 'd_1961', 'd_1962', 'd_1963', 'd_1964', 'd_1965', 'd_1966', 'd_1967', 'd_1968', 'd_1969'] # get product table product = sales_train_validation[['id', 'item_id', 'dept_id', 'cat_id', 'store_id', 'state_id']].drop_duplicates() # merge with product table #test1 test1 = test1.merge(product, how = 'left', on = 'id') #test2 test2['id'] = test2['id'].str.replace('_evaluation','_validation') test2 = test2.merge(product, how = 'left', on = 'id') test2['id'] = test2['id'].str.replace('_validation','_evaluation') # test1 = pd.melt(test1, id_vars = ['id', 'item_id', 'dept_id', 'cat_id', 'store_id', 'state_id'], var_name = 'day', value_name = 'demand') test2 = pd.melt(test2, id_vars = ['id', 'item_id', 'dept_id', 'cat_id', 'store_id', 'state_id'], var_name = 'day', value_name = 'demand') sales_train_validation['part'] = 'train' test1['part'] = 'test1' test2['part'] = 'test2' data = pd.concat([sales_train_validation, test1, test2], axis = 0) del sales_train_validation, test1, test2 print('pd.concat([sales_train_validation, test1, test2], axis = 0)=>data',data.shape) # get only a sample for fst training # data = data.loc[nrows:] # drop some calendar features calendar.drop(['weekday', 'wday', 'month', 'year'], inplace = True, axis = 1) # delete test2 for now data = data[data['part'] != 'test2'] if merge: # notebook crash with the entire dataset (maybee use tensorflow, dask, pyspark xD) data = pd.merge(data, calendar, how = 'left', left_on = ['day'], right_on = ['d']) data.drop(['d', 'day'], inplace = True, axis = 1) # get the sell price data (this feature should be very important) data = data.merge(sell_prices, on = ['store_id', 'item_id', 'wm_yr_wk'], how = 'left') print('Our final dataset to train has {} rows and {} columns'.format(data.shape[0], data.shape[1])) else: pass gc.collect() print('finish!') return data data = melt_and_merge(calendar_df, sell_prices_df, sales_train_validation_df, submission_df, nrows = nrows, merge = True)
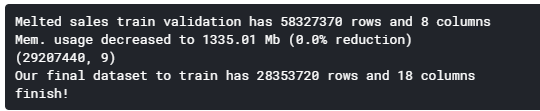
特征工程:
def simple_fe(data): # rolling demand features for val in [28, 29, 30]: data[f"shift_t{val}"] = data.groupby(["id"])["demand"].transform(lambda x: x.shift(val)) for val in [7, 30, 60, 90, 180]: data[f"rolling_std_t{val}"] = data.groupby(["id"])["demand"].transform(lambda x: x.shift(28).rolling(val).std()) data[f"rolling_mean_t{val}"] = data.groupby(["id"])["demand"].transform(lambda x: x.shift(28).rolling(val).mean()) data["rolling_skew_t30"] = data.groupby(["id"])["demand"].transform( lambda x: x.shift(28).rolling(30).skew()) data["rolling_kurt_t30"] = data.groupby(["id"])["demand"].transform(lambda x: x.shift(28).rolling(30).kurt()) # price features data['lag_price_t1'] = data.groupby(['id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x: x.shift(1)) data['price_change_t1'] = (data['lag_price_t1'] - data['sell_price']) / (data['lag_price_t1']) data['rolling_price_max_t365'] = data.groupby(['id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x: x.shift(1).rolling(365).max()) data['price_change_t365'] = (data['rolling_price_max_t365'] - data['sell_price']) / (data['rolling_price_max_t365']) data['rolling_price_std_t7'] = data.groupby(['id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x: x.rolling(7).std()) data['rolling_price_std_t30'] = data.groupby(['id'])['sell_price'].transform(lambda x: x.rolling(30).std()) data.drop(['rolling_price_max_t365', 'lag_price_t1'], inplace = True, axis = 1) # time features data['date'] = pd.to_datetime(data['date']) attrs = ["year", "quarter", "month", "week", "day", "dayofweek", "is_year_end", "is_year_start", "is_quarter_end", "is_quarter_start", "is_month_end","is_month_start", ] for attr in attrs: dtype = np.int16 if attr == "year" else np.int8 data[attr] = getattr(data['date'].dt, attr).astype(dtype) data["is_weekend"] = data["dayofweek"].isin([5, 6]).astype(np.int8) return data
需要的特征字段:
features = [ "item_id", "dept_id", "cat_id", "store_id", "state_id", "event_name_1", "event_type_1", "snap_CA", "snap_TX", "snap_WI", "sell_price", # demand features. "shift_t28", "rolling_std_t7", "rolling_std_t30", "rolling_std_t90", "rolling_std_t180", "rolling_mean_t7", "rolling_mean_t30", "rolling_mean_t60", # price features "price_change_t1", "price_change_t365", "rolling_price_std_t7", # time features. "year", "month", "dayofweek", ]
训练与预测:
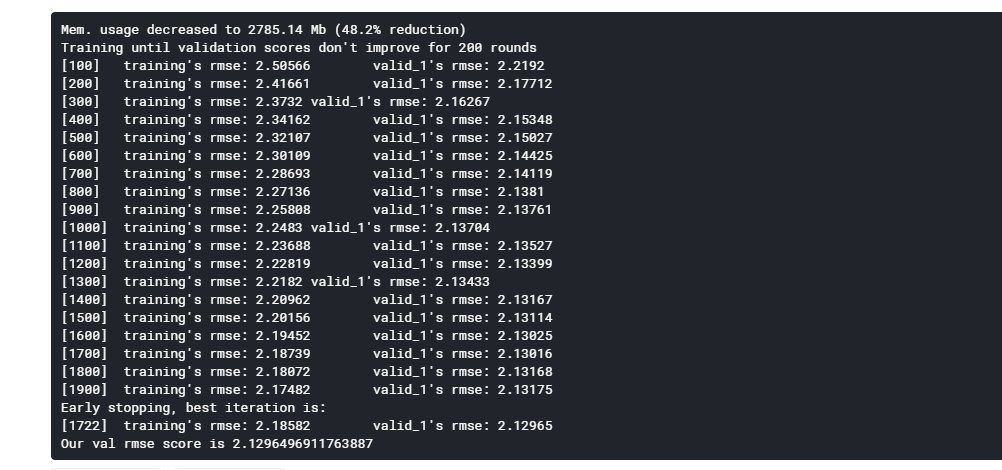
def run_lgb(data): # going to evaluate with the last 28 days x_train = data[data['date'] <= '2016-03-27'] y_train = x_train['demand'] x_val = data[(data['date'] > '2016-03-27') & (data['date'] <= '2016-04-24')] y_val = x_val['demand'] test = data[(data['date'] > '2016-04-24')] del data gc.collect() params = { # 'boosting_type': 'gbdt', 'metric': 'rmse', 'objective': 'poisson', 'n_jobs': -1, 'seed': 20, 'learning_rate': 0.1, 'alpha': 0.1, 'lambda': 0.1, 'bagging_fraction': 0.66, 'bagging_freq': 2, 'colsample_bytree': 0.77} train_set = lgb.Dataset(x_train[features], y_train) val_set = lgb.Dataset(x_val[features], y_val) del x_train, y_train model = lgb.train(params, train_set, num_boost_round = 2000, early_stopping_rounds = 200, valid_sets = [train_set, val_set], verbose_eval = 100) joblib.dump(model, 'lgbm_0.sav') val_pred = model.predict(x_val[features], num_iteration=model.best_iteration) val_score = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(val_pred, y_val)) print(f'Our val rmse score is {val_score}') y_pred = model.predict(test[features], num_iteration=model.best_iteration) test['demand'] = y_pred return test def predict(test, submission): predictions = test[['id', 'date', 'demand']] predictions = pd.pivot(predictions, index = 'id', columns = 'date', values = 'demand').reset_index() predictions.columns = ['id'] + ['F' + str(i + 1) for i in range(28)] evaluation_rows = [row for row in submission['id'] if 'evaluation' in row] evaluation = submission[submission['id'].isin(evaluation_rows)] validation = submission[['id']].merge(predictions, on = 'id') final = pd.concat([validation, evaluation]) final.to_csv('submission.csv', index = False) def transform_train_and_eval(data): # data = transform(data) data = simple_fe(data) # reduce memory for new features so we can train data = reduce_mem_usage(data) test = run_lgb(data) predict(test, submission_df)
结果:
transform_train_and_eval(data)