注:理解递归前,首先得有些jvm基础,了解下栈和栈帧。下面我便围绕栈来理解求二叉树深度的递归套娃。
b栈视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iJ411E7xW?p=95&spm_id_from=pageDriver(平时充电)
首先上代码:
二叉树定义:
package cn.itcast.algorithm.tree; import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.Queue; public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { //记录根结点 private Node root; //记录树中元素的个数 private int N; private class Node { //存储键 public Key key; //存储值 private Value value; //记录左子结点 public Node left; //记录右子结点 public Node right; public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } //获取树中元素的个数 public int size() { return N; } //向树中添加元素key-value public void put(Key key, Value value) { root = put(root, key, value); } //向指定的树x中添加key-value,并返回添加元素后新的树 private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) { //如果x子树为空, if (x==null){ N++; return new Node(key,value, null,null); } //如果x子树不为空 //比较x结点的键和key的大小: int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp>0){ //如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树 x.right = put(x.right,key,value); }else if(cmp<0){ //如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树 x.left = put(x.left,key,value); }else{ //如果key等于x结点的键,则替换x结点的值为value即可 x.value = value; } return x; } //查询树中指定key对应的value public Value get(Key key) { return get(root,key); } //从指定的树x中,查找key对应的值 public Value get(Node x, Key key) { //x树为null if (x==null){ return null; } //x树不为null //比较key和x结点的键的大小 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp>0){ //如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树 return get(x.right,key); }else if(cmp<0){ //如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树 return get(x.left,key); }else{ //如果key等于x结点的键,就找到了键为key的结点,只需要返回x结点的值即可 return x.value; } } //删除树中key对应的value public void delete(Key key) { delete(root, key); } //删除指定树x中的key对应的value,并返回删除后的新树 public Node delete(Node x, Key key) { //x树为null if (x==null){ return null; } //x树不为null int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp>0){ //如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树 x.right = delete(x.right,key); }else if(cmp<0){ //如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树 x.left = delete(x.left,key); }else{ //如果key等于x结点的键,完成真正的删除结点动作,要删除的结点就是x; //让元素个数-1 N--; //得找到右子树中最小的结点 if (x.right==null){ return x.left; } if (x.left==null){ return x.right; } Node minNode = x.right; while(minNode.left!=null){ minNode = minNode.left; } //删除右子树中最小的结点 Node n = x.right; while(n.left!=null){ if (n.left.left==null){ n.left=null; }else{ //变换n结点即可 n = n.left; } } //让x结点的左子树成为minNode的左子树 minNode.left = x.left; //让x结点的右子树成为minNode的右子树 minNode.right = x.right; //让x结点的父结点指向minNode x = minNode; } return x; } //查找整个树中最小的键 public Key min(){ return min(root).key; } //在指定树x中找出最小键所在的结点 private Node min(Node x){ //需要判断x还有没有左子结点,如果有,则继续向左找,如果没有,则x就是最小键所在的结点 if (x.left!=null){ return min(x.left); }else{ return x; } } //在整个树中找到最大的键 public Key max(){ return max(root).key; } //在指定的树x中,找到最大的键所在的结点 public Node max(Node x){ //判断x还有没有右子结点,如果有,则继续向右查找,如果没有,则x就是最大键所在的结点 if (x.right!=null){ return max(x.right); }else{ return x; } } //获取整个树中所有的键 public Queue<Key> preErgodic(){ Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>(); preErgodic(root, keys); return keys; } //获取指定树x的所有键,并放到keys队列中 private void preErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){ if (x==null){ return; } //把x结点的key放入到keys中 keys.enqueue(x.key); //递归遍历x结点的左子树 if (x.left!=null){ preErgodic(x.left,keys); } //递归遍历x结点的右子树 if (x.right!=null){ preErgodic(x.right,keys); } } //使用中序遍历获取树中所有的键 public Queue<Key> midErgodic(){ Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>(); midErgodic(root,keys); return keys; } //使用中序遍历,获取指定树x中所有的键,并存放到key中 private void midErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){ if (x==null){ return; } //先递归,把左子树中的键放到keys中 if (x.left!=null){ midErgodic(x.left,keys); } //把当前结点x的键放到keys中 keys.enqueue(x.key); //在递归,把右子树中的键放到keys中 if(x.right!=null){ midErgodic(x.right,keys); } } //使用后序遍历,把整个树中所有的键返回 public Queue<Key> afterErgodic(){ Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>(); afterErgodic(root,keys); return keys; } //使用后序遍历,把指定树x中所有的键放入到keys中 private void afterErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){ if (x==null){ return ; } //通过递归把左子树中所有的键放入到keys中 if (x.left!=null){ afterErgodic(x.left,keys); } //通过递归把右子树中所有的键放入到keys中 if (x.right!=null){ afterErgodic(x.right,keys); } //把x结点的键放入到keys中 keys.enqueue(x.key); } //使用层序遍历,获取整个树中所有的键 public Queue<Key> layerErgodic(){ //定义两个队列,分别存储树中的键和树中的结点 Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>(); Queue<Node> nodes = new Queue<>(); //默认,往队列中放入根结点 nodes.enqueue(root); while(!nodes.isEmpty()){ //从队列中弹出一个结点,把key放入到keys中 Node n = nodes.dequeue(); keys.enqueue(n.key); //判断当前结点还有没有左子结点,如果有,则放入到nodes中 if (n.left!=null){ nodes.enqueue(n.left); } //判断当前结点还有没有右子结点,如果有,则放入到nodes中 if (n.right!=null){ nodes.enqueue(n.right); } } return keys; } //获取整个树的最大深度 public int maxDepth(){ return maxDepth(root); } //获取指定树x的最大深度 private int maxDepth(Node x){ if (x==null){ return 0; } //x的最大深度 int max=0; //左子树的最大深度 int maxL=0; //右子树的最大深度 int maxR=0; //计算x结点左子树的最大深度 if (x.left!=null){ maxL = maxDepth(x.left); } //计算x结点右子树的最大深度 if (x.right!=null){ maxR = maxDepth(x.right); } //比较左子树最大深度和右子树最大深度,取较大值+1即可 max = maxL>maxR?maxL+1:maxR+1; return max; } }
test:
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test; import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.Queue; import cn.itcast.algorithm.tree.BinaryTree; public class BinaryTreeMaxDepthTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建树对象 BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>(); //往树中添加数据 tree.put("E", "5"); tree.put("B", "2"); tree.put("A", "1"); // tree.put("A", "1"); // tree.put("D", "4"); // tree.put("F", "6"); // tree.put("H", "8"); // tree.put("C", "3"); int maxDepth = tree.maxDepth(); System.out.println(maxDepth); } }
为了便于理解,我只插入了三个节点,而且还都是左子树:

打断点调试,一直递归到最后:
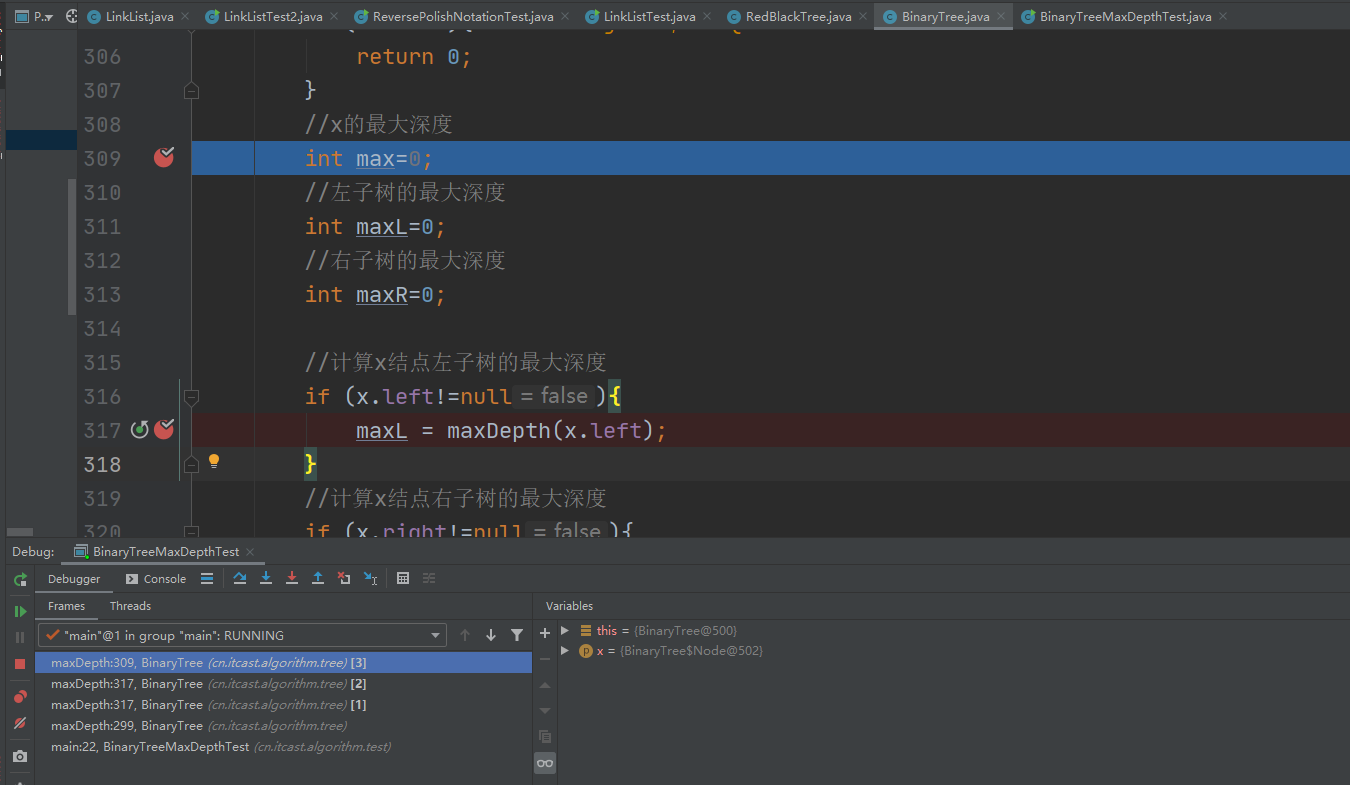
发现这个栈里面创建了五个栈帧,第一个栈帧是main函数,第二是 maxDepth()方法,第三、第四、第五个是递归调用 maxDepth(Node x)方法产生的栈帧。
首先我们来看下第三个栈帧里面创建的基本变量:

第四个栈帧里面创建的变量:
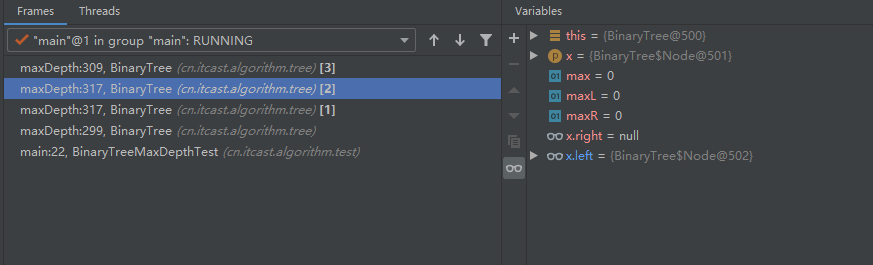
第五个栈帧中创建的变量:
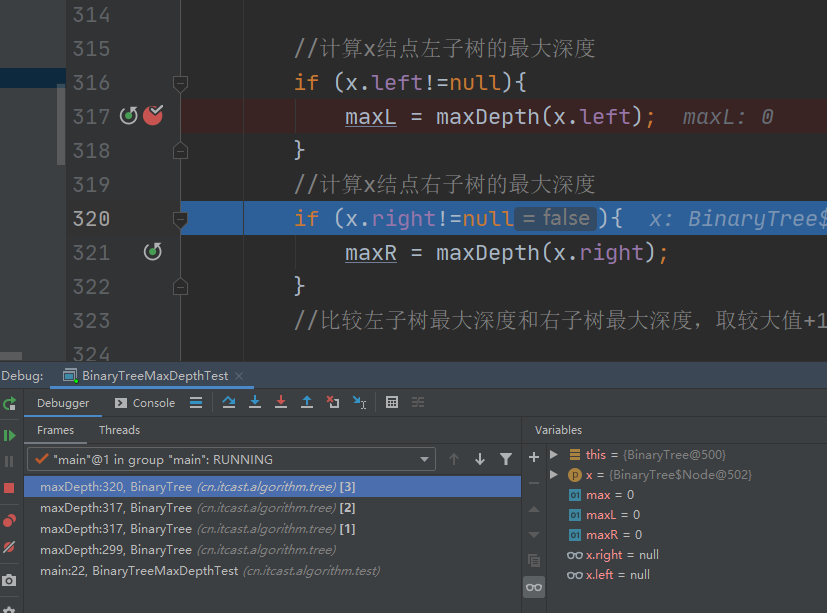
其实就是每次递归,都会产生栈帧,栈帧中创建方法中的变量。 结束最后一层递归,也就是第五次栈帧释放后。第四层栈帧中变量的值变化如下:
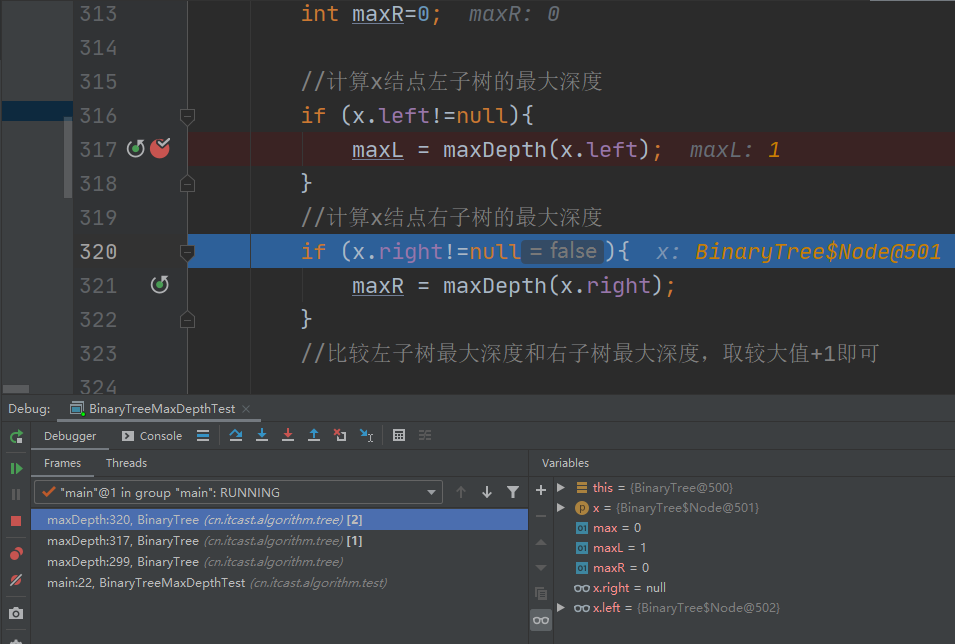
结束这层递归,也就是释放第四个栈帧,结果如下:
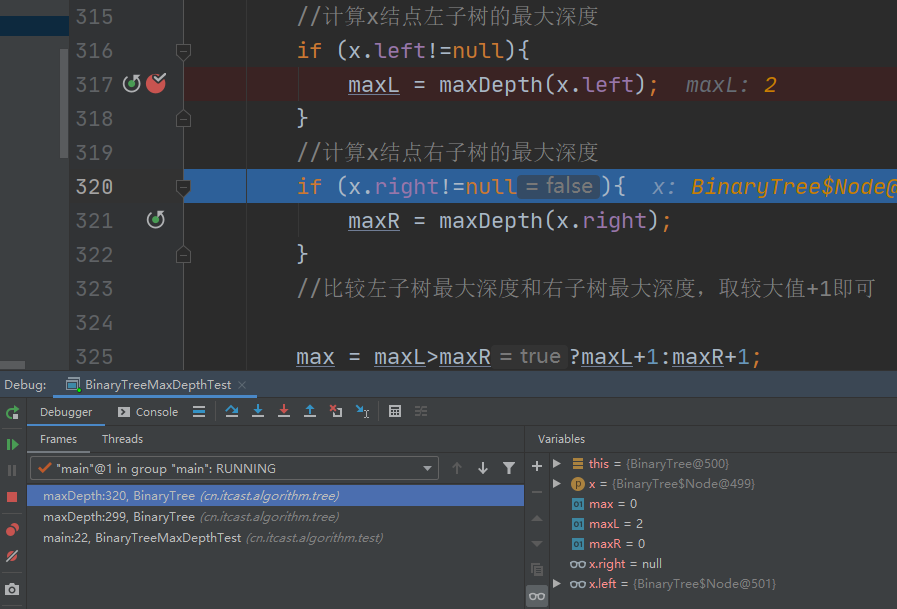
再结束最后一层递归,释放栈帧:(第二个栈帧只是方法的封装,无展示价值)
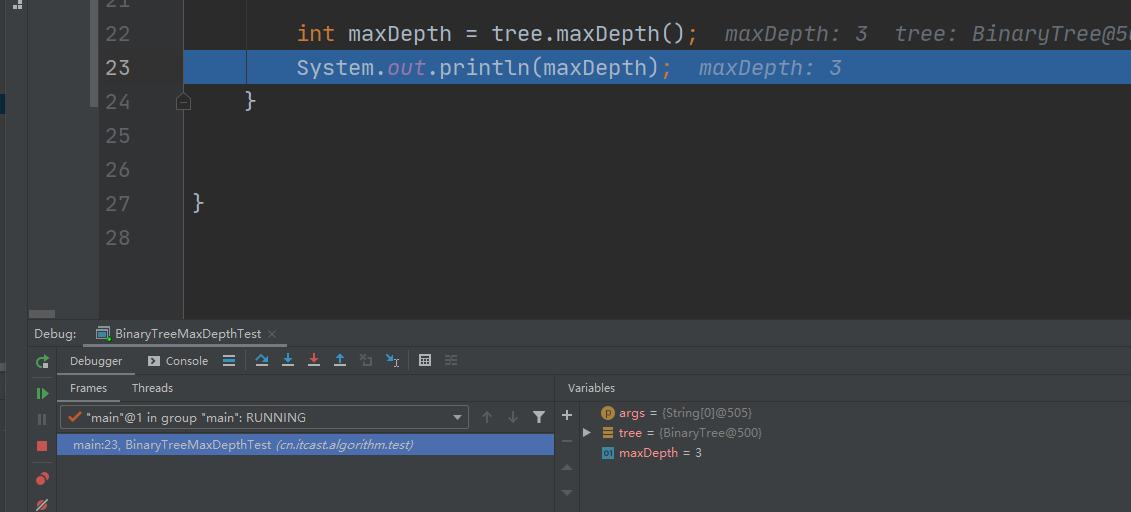
1111