IO流的基本概念
- 在java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以流的形式(stream)方式进行;
- j2SDK提供了各种各样的流的类,用以获取不同种类的数据,程序中通过标准输入或输出数据。
- java的流类型一般位于Java.io包中。
流的概念
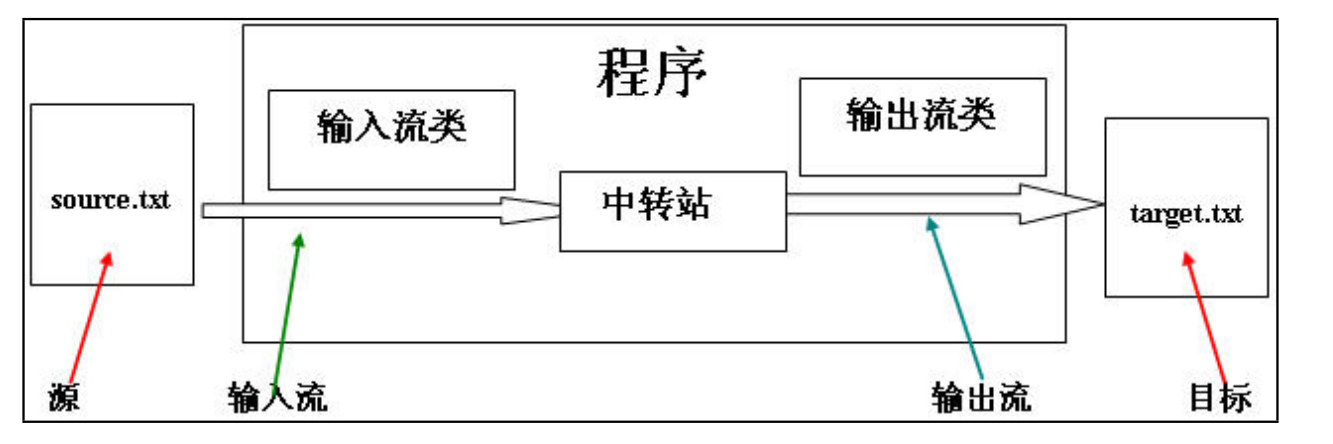
- 数据源(data source) 提供原始数据的原始媒介。常见的:数据库、文件、其他程序、网络连接、IO设备。
- 数据源就像水箱,流就像水管中的水流,程序就是我们最终的用户。流是一个抽象的、动态的概念,是一连串连续动态的集合。
流的细分和体系_四大抽象类
流的分类
流的方向:
- (1)输入流:数据源到程序(InputStream、Readr读进去)
- (2)输出流:程序到目的地(OutPutStream、Writer写进去)
处理数据单元
- (1)字节流:按照字节读取数据(InputStream、OutputStream)
- (2)字符流:按照字符读取数据(Reader、Writer)
注意:输入输出是相对于程序而言,而不是相对于源和目标而言。往程序里面来,叫做入。从程序里往外走,叫做出。
功能不同:
- (1)节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
- (2)包装类(包装流):不直接连接到数据源或者目的地,是其他流进行封装。目的主要是简化操作和提高性能。
节点流和处理流的关系:
- (1)节点流处于io操作的第一线,所有操作必须通过他们进行;
- (2)处理流可以对其他流进行处理(提高效率或操作灵活性)。
IO流的体系
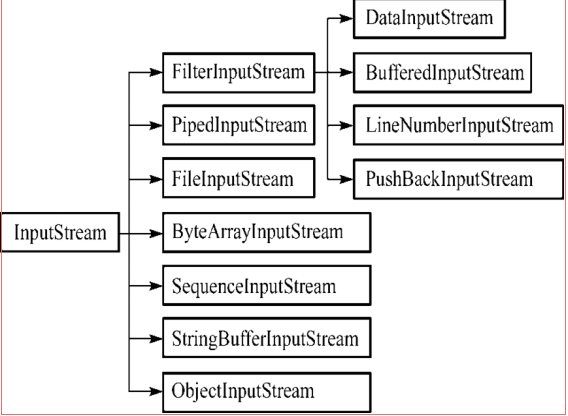
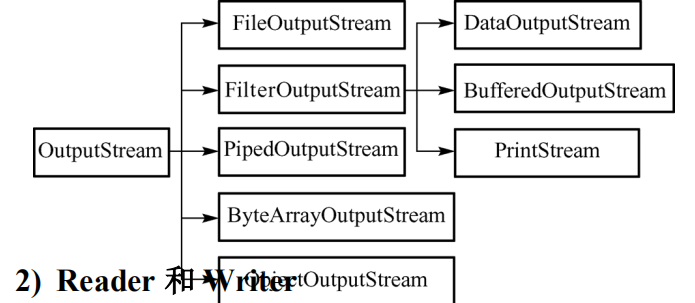
(1)InputStream 和OutputStream
- java语言中最基本的两个字节输入输出类。
- 其他所有字节输入输出流类都继承自这两个基类。
- 这两个类都是抽象类,不能创建他们的实例,只能使用他们的子类。
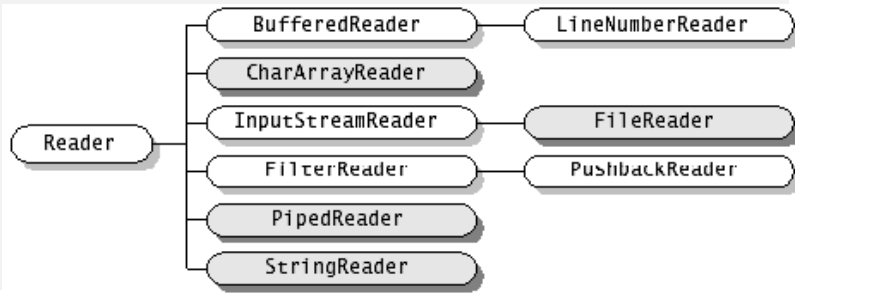
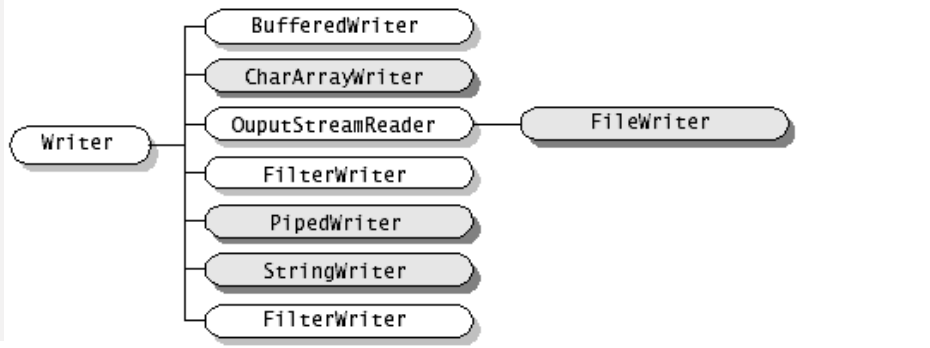
(2)Reader和Writer
- java语言中最基本的两个字符输入输出类。
- 其他所有字符输入输出流类都继承自这两个基类。
- 这两个类都是抽象类,不能直接创建他们的实例,只能使用他们的子类。
文件字节流
3.1FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
- 使用 FileInputStream 读取文件内容
1) abstract int read( );
2) int read( byte b[ ] );
3) int read( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
4) int available( ); 返回从此输入流中可以读取(或跳过)的剩余字节数的估计值,而不会被下一次调用此输入流的方法阻塞
5) close( );
- 使用 FileOutputStream 写内容到文件
1) abstract void write( int b );
2) void write( byte b[ ] );
3) void write( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
4) void flush( );
5) void close( );
相关代码如下:

import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class TestInputStream2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //搭桥 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\text.txt"); //(2)创建大一些的中转站 byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; int len=0;//用于存储每次读到的实际字节 while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){ //借助String类构造方法 System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len)); } //关闭 fis.close(); } }

import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class TestInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //(1)数据源与应用程序之间搭建管道 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\text.txt")); //(2)从数据源开始向程序中读数据 int count =fis.available(); System.out.println(count); //中转站比较小,一次读一个字节 //System.out.println(fis.read());//读取一个字节 int buf=0; int i=0; while((buf=fis.read())!=-1){ i++; System.out.print((char)buf);; } //关闭 fis.close(); System.out.println(i); } }

import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class TestFileOutStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //(1)搭桥 FileOutputStream fos=null; try { fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\text.txt",true);//true如果磁盘上有文件,而且文件中有内容,将在原来的内容的基础上进行追加。 //(2)写数据,一次写一个字节 //fos.write(97); //(2)一次写多个字节 byte [] buf="helloworld".getBytes(); fos.write(buf); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭 try { if(fos!=null){ fos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 7 public class TestFileCopy { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //数据源文件 10 FileInputStream fis=null; 11 //目的地 12 FileOutputStream fos=null; 13 try { 14 fis = new FileInputStream("D:\text.txt"); 15 fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\SS.txt"); 16 byte []buf=new byte[1024]; 17 int len=0; 18 while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){ 19 fos.write(buf,0,len); 20 } 21 /*int b=0;//用于存储读到的字节(中转站) 22 while((b=fis.read())!=-1){ 23 fos.write(b); 24 }*/ 25 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 }finally{ 32 //关闭 33 try {if(fos!=null){ 34 fos.close(); 35 } 36 } catch (IOException e) { 37 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 try {if(fis!=null){ 41 fis.close(); 42 } 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 }
文件字符流
相关代码如下:

1 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 2 import java.io.FileReader; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 6 public class TestFileReader { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 //(1)搭桥 9 FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\text.txt"); 10 //(2)读取 11 //int b=reader.read(); 12 //System.out.println((char)b); 13 /*int b=0;//用于存储每次读到的字符数据的整数值 14 while((b=reader.read())!=-1){ 15 System.out.print((char)b); 16 }*/ 17 char []cbuf=new char[1024]; 18 int len=0; 19 20 while((len=reader.read(cbuf))!=-1){ 21 System.out.println(new String(cbuf,0,len)); 22 } 23 //(3)关闭 24 reader.close(); 25 26 } 27 }

1 import java.io.FileWriter; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 5 public class TestWriter { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 //创建对象 10 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\a.txt"); 11 //写数据 12 try { 13 writer.write("你好吗");//写到了缓冲区中, 14 writer.flush();//如果没有写close就要加上这行 15 } catch (IOException e) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 }finally{ 19 if(writer!=null) 20 { 21 try { 22 writer.close(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 31 } 32 33 }
缓冲字节流_缓冲字符流
缓冲字节流
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
FieInputStream和FileOutputStream是节点流
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream是处理流(包装流)
- (1)读文件和写文件都使用了缓冲区,减少了读写次数,从而提高了效率。
- (2)当创建这两个缓冲流的对象时,会创建了内部缓冲数组,缺省使用32字节大小的缓冲区。
- (3)当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区。
- (4)当写入数据时,首先写入缓冲区,当缓冲区满时,其中的数据写入所连接的输出流。使用方法flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流。
- (5)关闭的顺序和打开流的顺序相反,只要关闭高层流即可,关闭高层流其实关闭的底层节点流。
- (6)Flush的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件。

1 package buffered; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 4 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 public class TestCopy { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ 12 //(1)数据源 13 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:\wps\jdk文档\jdk api 1.8.CHM"); 14 //(2)目的地 15 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\jdk api 1.8.CHM"); 16 /** 17 * 使用缓冲流 18 * */ 19 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 20 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 21 //(3)读数据和写数据 22 long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 byte []buf=new byte[1000]; 24 int len=0; 25 while((len=bis.read(buf))!=-1){ 26 bos.write(buf,0,len); 27 bos.flush(); 28 } 29 long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); 30 System.out.println("文件复制一共使用了:"+(end-start)+"毫秒"); 31 //(4)关闭 32 bos.close(); 33 bis.close(); 34 } 35 36 }
缓冲字符流
BufferedReader
readLine()读取一个文本行的数据。
BufferedWriter
newLine() 写入一个行分隔符。
使用缓冲字符流是复制文本文件常用的方式。

1 package buffered; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileReader; 7 import java.io.FileWriter; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 10 public class TestBuffered { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 //缓冲字符流 13 BufferedReader br=null; 14 BufferedWriter bw=null; 15 try { 16 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\a.txt")); 17 bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\copya.txt")); 18 String line=null; 19 while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ 20 bw.write(line); 21 bw.newLine(); 22 bw.flush(); 23 } 24 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 25 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 }finally{ 31 if(bw!=null){ 32 try { 33 bw.close(); 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 } 40 if(br!=null){ 41 try { 42 br.close(); 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 }
转换流
inputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
用于将字节流转换成字符流,字符流与字节流之间的桥梁InputStreamReader的作用是把InputStream转换成Reader。OutputStreamWriter的作用是把OutputStream转换成Writer存在将字节流转换成字符流,因为字符流操作文本更简单。不存在把字符流转换成字节流,因为没有必要。System.in代表标准输入,即键盘输入,是InputStream的实例。

1 package convert; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStream; 9 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 10 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 11 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 12 13 public class Test { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 //任务需求,从键盘获取数据,写入磁盘文件 18 19 20 BufferedReader br=null; 21 22 BufferedWriter bw=null; 23 try { 24 //(1)数据源是标准的输入设备,键盘System.in 25 InputStream is=System.in; 26 //(2)需要使用转换流,转换成字符流 27 InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(is,"gbk"); 28 //(3)提高读取效率 29 br = new BufferedReader(isr); 30 //(4)提高写入效率 31 bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\system.txt"),"gbk")); 32 //(5)写入磁盘文件 33 String line=null;//用于存储读到字符串 34 while(!"over".equals((line=br.readLine()))){ 35 bw.write(line); 36 bw.newLine(); 37 bw.flush(); 38 } 39 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 40 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 43 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } catch (IOException e) { 46 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 }finally{ 49 //(6)关闭 50 if(bw!=null){ 51 try { 52 bw.close(); 53 } catch (IOException e) { 54 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 } 57 } 58 if(br!=null){ 59 try { 60 br.close(); 61 } catch (IOException e) { 62 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 69 }
打印流
PrintStream
- (1)PrintStream提供了一系列的print()和println(),可以实现将基本数据类型格式化成字符串输出。对象类型将先调用toString(),然后输出该方法返回的字符串。
- (2)System.out就是PrintStream的一个实例,代表显示器
- (3)System.err也是PrintStream的一个实例,代表显示器
- (4)PrintStream的输出功能非常强大,通常需要输出文本内容,都可以将输出流包装成PrintStream后进行输出。
- (5)PrintStream的方法都不抛出IOException
PrintWriter
- (1)PrintStream的对应字符流,功能相同,方法对应。
- (2)PrintWriter的方法也不抛出IOException
- (3)复制文件时可以使用PrintWriter代替BufferedWriter完成,更简单

1 package print; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.PrintStream; 6 import java.io.PrintWriter; 7 import java.sql.Date; 8 /** 9 * 打印流虽然功能强大,但是打印到目的地后,会失去原来的类型,都成为字符型。比如19 会变成‘1’‘9’,需要转换 10 * @author Administrator 11 * 12 */ 13 public class Test { 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 15 //PrintStream ps=System.out;//显示器 16 //PrintStream ps=System.err; 17 //PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\print.txt")); 18 PrintWriter ps=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\print1.txt")); 19 ps.println("helloworld"); 20 ps.println(true); 21 ps.println(19); 22 ps.println(98.5); 23 ps.println(new Date(1000).toGMTString()); 24 ps.flush();//本来没有字符流,字符流是由字节流在缓存中形成的,而不会到目的地,需要刷新 25 ps.close(); 26 27 } 28 }
数据流
DataInputStream和DataOutputStream
- (1)提供了可以存取所有Java基础类型数据(如:int ,double等)和String的方法。
- (2)处理流,只针对字节流,二进制文件
- (3)输入流链和输出流链
- (4)注意:只要关闭上层流即可


1 package Data; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 4 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 5 import java.io.DataInputStream; 6 import java.io.DataOutputStream; 7 import java.io.FileInputStream; 8 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 11 public class Test { 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 13 //write(); 14 read(); 15 } 16 //读数据的方法 17 public static void read() throws IOException{ 18 //(1)数据源 19 /*FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\data.txt"); 20 //(2)提高读取效率 21 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); 22 //(3)处理java的基本数据类型和字符串 23 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(bis);*/ 24 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\data.txt"))); 25 //(4)读数据 --(读数据的顺序要与写数据的顺序完全一致) 26 System.out.println(dis.readInt()); 27 System.out.println(dis.readDouble()); 28 System.out.println(dis.readBoolean()); 29 System.out.println(dis.readChar()); 30 System.out.println(dis.readUTF()); 31 //关闭 32 dis.close(); 33 34 } 35 public static void write() throws IOException{ 36 //(1)目的地 37 /*FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\data.txt"); 38 //(2)缓冲流提高写入效率 39 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 40 //(3)数据流,增加对java基本数据类型和String的处理 41 DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(bos);*/ 42 DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\data.txt"))); 43 //(4)写入数据 44 dos.writeInt(98); 45 dos.writeDouble(98.5); 46 dos.writeBoolean(true); 47 dos.writeChar('a'); 48 dos.writeUTF("helloworld"); 49 //(5)关闭流 50 if(dos!=null){ 51 dos.close(); 52 } 53 } 54 }
对象流
对象序列化(Serialization)
- ObjectOutputStream->写对象->序列化,将对象以二进制/字节的形式写到文件
- ObjectInputStream->读对象->反序列化
- 将Java对象转换成字节序列(IO字节流)
对象反序列化(DeSerialization)
- 从字节序列化中恢复Java对象
为什么序列化
- 序列化以后的对象可以保存到磁盘上,也可以在网络上传输,使得不同的计算机可以共享对象。(序列化的字节序列是平台无关的)
对象序列化的条件
- 只有实现了Serializable接口的类的对象才可以被序列化。Serializable接口中没有任何的方法,实现该接口的类不需要实现额外的方法。
- 如果对象的属性是对象,属性对应类也必须实现Serializable接口。
如何实现序列化
- 创建ObjectOutputStream对象
- 调用writeObject()输出对象
1 OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/java6.txt")); 2 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); 3 oos.writeObject(stu); 4 oos.close();
如何实现反序列化
- 创建ObjectInputStream对象
- 调用readObject()读取对象
1 InputStream fis =new FileInputStream(new File("d:/java5.txt")); 2 3 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis); 4 5 Student stu=(Student) ois.readObject(); 6 7 System.out.println(stu.getAge()+" "+stu.getScore());

package com.bjsxt.object; import java.io.Serializable; public class Person implements Serializable {//具备一个能力,可序列化与反序列化的能力 private String name; private int age; public Person() { super(); } public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }

package com.bjsxt.object; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //write(); read(); } public static void read(){ //(1)创建对象流对象 ObjectInputStream ois=null; try { ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\object.txt")); //(2)读对象 System.out.println(ois.readInt()); System.out.println(ois.readUTF()); Person p=(Person) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(p); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //(3)关闭流 if(ois!=null){ try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //写对象的方法 public static void write(){ //(1)创建对象流对象 ObjectOutputStream oos=null; try { oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\object.txt")); //(2)写对象 oos.writeInt(98); oos.writeUTF("中国梦"); oos.writeObject(new Person("marry", 20)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //(3)关闭流 if(oos!=null){ try { oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
11.1 序列化与反序列化
1) 序列化能保存的元素
- a) 只能保存对象的非静态成员变量
- b) 不能保存任何成员方法和静态的成员变量
- c) 不保存 transient 成员变量
- d) 如果一个对象的成员变量是一个对象,这个对象的成员变量也会保存
- e) 串行化保存的只是变量的值,对于变量的任何修饰符, 都不能保存
2) 使用对象流把一个对象写到文件时不仅保证该对象是序列化的,而且该对象的成员对象也必须是可序列化的。
3) 如果一个可序列化的对象包含对某个不可序列化的对象的引用,那么整个序列化操作将会失败,并且会抛出一个NotSerializableException。我们可以将这个引用标记为transient,那么对象仍然可以序列化。
11.2 对象序列化注意事项
1) 同一个对象多次序列化的处理
- a) 所有保存到磁盘中的对象都有一个序列化编号
- b) 序列化一个对象中,首先检查该对象是否已经序列化过
- c) 如果没有,进行序列化
- d) 如果已经序列化,将不再重新序列化,而是输出编号即可
2) 如果不希望某些属性(敏感)序列化,或不希望出现递归序列
- a) 为属性添加 transient 关键字(完成排除在序列化之外)
- b) 自定义序列化(不仅可以决定哪些属性不参与序列化, 还可以定义属性具体如何序列化)
3) 序列化版本不兼容
- a) 修改了实例属性后,会影响版本号,从而导致反序列化不成功
- b) 解 决 方 案 : 为 Java 对 象 指 定 序 列 化 版 本 号serialVersionUID

package com.bjsxt.object; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Classes implements Serializable { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 8407410133605121812L; private String className;//班级名称 private ArrayList<Student> al; private String address; public Classes() { super(); } public Classes(String className, ArrayList<Student> al) { super(); this.className = className; this.al = al; } public String getClassName() { return className; } public void setClassName(String className) { this.className = className; } public ArrayList<Student> getAl() { return al; } public void setAl(ArrayList<Student> al) { this.al = al; } }

package com.bjsxt.object; import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -4502633718082654465L; private String name; private int age; public static String schoolName;//学校名称 private transient String pwd; //属性的值将不再被序列化 public Student() { super(); } public Student(String name, int age, String pwd) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.pwd = pwd; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + "]"+"schoolName="+schoolName; } }

1 package com.bjsxt.object; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 8 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 9 10 public class Test { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 //调用写对象的方法 13 //write(); 14 //调用读对象的方法 15 read(); 16 } 17 public static void write(){ 18 ObjectOutputStream oos=null; 19 try { 20 oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\student.txt")); 21 Student stu=new Student("marry", 20, "888888"); 22 Student.schoolName="JN校区"; 23 oos.writeObject(stu); 24 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 25 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 }finally{ 31 //关闭 32 if(oos!=null){ 33 try { 34 oos.close(); 35 } catch (IOException e) { 36 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 public static void read(){ 43 ObjectInputStream ois=null; 44 try { 45 ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\student.txt")); 46 Student stu=(Student) ois.readObject(); 47 System.out.println(stu); 48 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 49 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 52 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } catch (IOException e) { 55 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 }finally{ 58 //关闭流 59 if(ois!=null){ 60 try { 61 ois.close(); 62 } catch (IOException e) { 63 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 }

package com.bjsxt.object; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; public class TestClasses { public static void write(){ //创建班级对象 ArrayList<Student> al=new ArrayList<Student>(); al.add(new Student("marry",20,"888888")); al.add(new Student("lili",22,"123456")); al.add(new Student("jack",30,"654321")); Classes cl=new Classes("jn1001", al); //创建对象输出流 ObjectOutputStream oos=null; try { oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\classes.txt")); oos.writeObject(cl); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭流 if(oos!=null){ try { oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void read(){ ObjectInputStream ois=null; try { ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\classes.txt")); Classes cl=(Classes) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(cl.getClassName()+" "+cl.getAl()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭流 if(ois!=null){ try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { //write(); read(); } }
12.文件夹的复制
12.1 复制文件夹
字节流,字符流
- BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream
- FileInputStream,FileOutputStream
问题分解
(1) 复制一个文件
(2) 指定目录下的所有文件
(3) 指定目录下的所有文件及子目录下的所有文件

package com.bjsxt.copy; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class TestCopy { public static void main(String[] args) { /*File srcFile=new File("D:\180416\五一作业.docx"); File targetFile=new File("E:\五一作业.docx"); //调用复制文件的方法 copyFile(srcFile, targetFile);*/ File srcDir=new File("D:\180416"); File targetDir=new File("E:\180416"); //调用复制指定目录下所有文件的方法 copyDir(srcDir, targetDir); } public static void copyDir(File srcDir,File targetDir){ if(!targetDir.exists()){ targetDir.mkdir();//如果目的地的目录不存在,则需要使用File类的方法进行创建目录 } File []files=srcDir.listFiles(); //获取指定目录下的所有File对象 for (File file : files) { if (file.isFile()) { //复制 srcDir -->D:\180416 拼接 D:\180416\XXXX.doc文件 // targetDir-->E:\180416 拼接 E:\180416\XXXX.doc文件 copyFile(new File(srcDir+"\"+file.getName()), new File(targetDir+"\"+file.getName())); }else{ //继续调用该方法,使用递归实现 copyDir(new File(srcDir+"\"+file.getName()), new File(targetDir+"\"+file.getName())); } } } public static void copyFile(File srcFile,File targetFile){ //(1)提高读取效率,从数据源 BufferedInputStream bis=null; //(2)提高写入效率,写到目的地 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; try { bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(targetFile)); //(3)边读边写 byte [] buf=new byte[1024];//中转站 int len=0;//用于存储读到的字节的个数 while((len=bis.read(buf))!=-1){ bos.write(buf,0,len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //(4)关闭 if(bos!=null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis!=null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
13.字节数组流
13.1ByteArrayInutStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream
- 1) 数据源或目的地为:字节数组
- 2) 只有字节流,没有字符流
- 3) 节点流

package com.bjsxt.array; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.Date; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { byte [] buf=write();//调用写对象的方法 //调用读对象的方法 read(buf); } public static byte[] write(){ //创建字节数组流对象 ByteArrayOutputStream baos=null; ObjectOutputStream oos=null; try { baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();//创建字节数组流对象,目的地是字节数组,底层创建一个长度数为32的字节数组 oos=new ObjectOutputStream(baos); oos.writeInt(98); oos.writeDouble(98.5); oos.writeChar('a'); oos.writeBoolean(false); oos.writeObject(new Date(1000)); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭流 if (oos!=null) { try { oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } return baos.toByteArray(); } public static void read(byte [] buf){ ByteArrayInputStream bais=null; ObjectInputStream ois=null; //创建对象 try { bais=new ByteArrayInputStream(buf); //数据源是byte类型的数组 ois=new ObjectInputStream(bais); //读数据 System.out.println(ois.readInt()); System.out.println(ois.readDouble()); System.out.println(ois.readChar()); System.out.println(ois.readBoolean()); System.out.println(ois.readObject()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭流 if(ois!=null){ try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
14.设计模式_装饰器模式
14.1 装饰器模式 Decorator
职责:动态的为一个对象增加新的功能
- 装饰模式是一种用于代替继承的技术,无须通过继承增加子类就能扩展对象的新功能。使用对象的关联关系代替继承关系,更加灵活,同时避免类型体系的快速膨胀。
实现细节:
- (1) 抽象构件角色 ICar
- (2) 具体的构件角色 Car
- (3) 装饰器角色 SuperCar
- (4) 具体的装饰器角色 FlyCar、WaterCar、AICar
优点:
- 1) 扩展对象功能,比继承灵活,不会导致类个数急剧增加
- 2) 可以对一个对象进行多次装饰,创建出不同行为的组合,
- 3) 具体构建类和具体装饰类可以独立变化,用户可以根据需要自己增加新的具体构件子类和具体装饰子类
缺点
- 1) 产生很多小对象。大量小对象占据内存,一定程序上影响性能.
- 2) 装饰模式易于出错,调试排查比较麻烦
IO 流实现细节
- (1)抽象构件角色 InputStream,OutputStream,Reader,Writer
- (2)具体构件角色 FileInputStream,FileOutputStream
- (3)装饰器角色 FilterInputStream,FilterOutputStream持有一个抽象构件的引用
- (4)具体装饰角色 BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream 等

package com.bjsxt.pattern; public class AICar extends SuperCar{ public AICar(ICar car) { super(car); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public void move() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.move(); this.autoDrive(); } public void autoDrive(){ System.out.println("可以自动行驶"); } }

package com.bjsxt.pattern; public class Car implements ICar { public void move() { System.out.println("汽车可以在陆地上行驶"); } }

1 package com.bjsxt.pattern; 2 3 public class FlyCar extends SuperCar { 4 5 public FlyCar(ICar car) { 6 super(car); 7 8 } 9 //重写move()方法 10 @Override 11 public void move() { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 super.move(); //调用父类的行驶方法 14 15 //调用飞行的方法 16 this.fly(); 17 } 18 public void fly(){ 19 System.out.println("汽车可以飞行,因为有翅膀"); 20 } 21 }

package com.bjsxt.pattern; public interface ICar { void move();//行驶 }

package com.bjsxt.pattern; public class SuperCar implements ICar { private ICar car; public SuperCar(ICar car){ this.car=car; } @Override public void move() { car.move(); } }

package com.bjsxt.pattern; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ICar car=new Car(); car.move(); System.out.println(" 为汽车增加新的功能"); FlyCar fly=new FlyCar(car); fly.move(); System.out.println(" 再为汽车增加自动驾驶的功能"); AICar ai=new AICar(fly); ai.move(); System.out.println(" 以上代码可以简写为"); AICar ai2=new AICar(new FlyCar(new Car())); ai2.move(); System.out.println("各种组合"); WaterCar water=new WaterCar(new FlyCar(new AICar(new Car()))); water.move(); try { BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"))); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }

package com.bjsxt.pattern; public class WaterCar extends SuperCar { public WaterCar(ICar car) { super(car); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public void move() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.move(); this.water(); } public void water(){ System.out.println("汽车可以潜水"); } }
15.IO 流体系总结
15.1IO 流整体架构体系
- (1) 字节流 :InputStream,OutputStream
- (2) 字符流:Reader ,Writer
- (3) 数据流:DataInputStream,DataOutputStream
- (4) 对象流:ObjectInputStream,ObjectOutputStream
- (5) 缓冲流:BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
- (6) 转换流:InputStreamReader,OutputStreamWriter
- (7) 数组流: ByteArrayInputStream,ByteArrayOutputStream
- (8) 打印流:PrintStream,PrintWriter
