菜鸟学习并行编程,参考《C#并行编程高级教程.PDF》,如有错误,欢迎指正。
目录
TPL中引入了一个新命名空间System.Threading.Tasks,在该命名空间下Task是主类,表示一个类的异步的并发的操作,创建并行代码的时候不一定要直接使用Task类,在某些情况下可以直接使用Parallel静态类(System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel)下所提供的方法,而不用底层的Task实例。
Parallel.Invoke
试图将很多方法并行运行,如果传入的是4个方法,则至少需要4个逻辑内核才能足以让这4个方法并发运行,逻辑内核也称为硬件线程。
需要注意的是:1.即使拥有4个逻辑内核,也不一定能够保证所需要运行的4个方法能够同时启动运行,如果其中的一个内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行。
2.通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖与特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。
3.使用Parallel.Invoke方法一定要测量运行结果、实现加速比以及逻辑内核的使用率,这点很重要。
4.使用Parallel.Invoke,在运行并行方法前都会产生一些额外的开销,如分配硬件线程等。
好处:这是一种并行运行很多方法的简单方式,使用Parallel.Invoke,不需要考虑任务和线程的问题。
下面贴代码:

class Program { private static List<Product> ProductList = null; /* coder:释迦苦僧 * 没有特定的执行顺序 * 示例中 基于电脑配置 采用了4个方法的并行编程 * Parallel.Invoke 首先会尝试并行启动4个方法,充分利用一个或多个物理处理器所提供的多个逻辑内核 * 但是在实际的并行执行中,至少要有4个逻辑内核才能满足4个方法的并行运行 * 如果有个或者多个逻辑内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行 * 通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖与特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。 */ static void Main(string[] args) { ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); Stopwatch swTask = new Stopwatch(); swTask.Start(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(SetProcuct1_500, SetProcuct2_500, SetProcuct3_500, SetProcuct4_500); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000);/*防止并行操作 与 顺序操作冲突*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); SetProcuct1_500(); SetProcuct2_500(); SetProcuct3_500(); SetProcuct4_500(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); swTask.Restart(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(() => SetProcuct1_10000(), () => SetProcuct2_10000(), () => SetProcuct3_10000(), () => SetProcuct4_10000()); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); ProductList = new List<Product>(); Thread.Sleep(3000); sw.Restart(); SetProcuct1_10000(); SetProcuct2_10000(); SetProcuct3_10000(); SetProcuct4_10000(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void SetProcuct1_500() { for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_500() { for (int index = 500; index < 1000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_500() { for (int index = 1000; index < 2000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_500() { for (int index = 2000; index < 3000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct1_10000() { for (int index = 1; index < 20000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_10000() { for (int index = 20000; index < 40000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_10000() { for (int index = 40000; index < 60000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_10000() { for (int index = 60000; index < 80000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
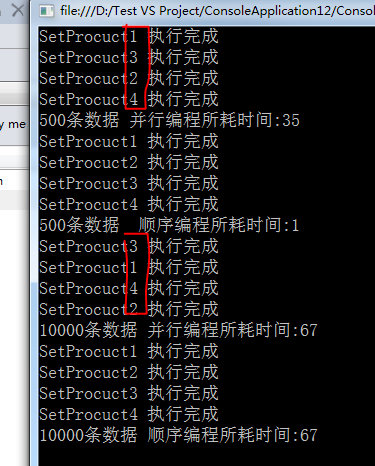
图中我们可以看出利用 Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代,它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。
但是所执行的时间上比不采用并行编程所耗的时间差不多。
这是因为我们在并行编程中操作了共享资源 ProductList ,如果我把代码做出以下修改,采用并行编程的好处就显现出来了。

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧 * 没有特定的执行顺序 * 示例中 基于电脑配置 采用了4个方法的并行编程 * Parallel.Invoke 首先会尝试并行启动4个方法,充分利用一个或多个物理处理器所提供的多个逻辑内核 * 但是在实际的并行执行中,至少要有4个逻辑内核才能满足4个方法的并行运行 * 如果有个或者多个逻辑内核处于繁忙状态,那么底层的调度逻辑可能会延迟某些方法的初始化执行 * 通过Parallel.Invoke编写的并发执行代码一定不能依赖与特定的执行顺序,因为它的并发执行顺序也是不定的。 */ static void Main(string[] args) { Thread.Sleep(3000); Stopwatch swTask = new Stopwatch(); swTask.Start(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(SetProcuct1_500, SetProcuct2_500, SetProcuct3_500, SetProcuct4_500); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000);/*防止并行操作 与 顺序操作冲突*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); SetProcuct1_500(); SetProcuct2_500(); SetProcuct3_500(); SetProcuct4_500(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("500条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000); swTask.Restart(); /*执行并行操作*/ Parallel.Invoke(() => SetProcuct1_10000(), () => SetProcuct2_10000(), () => SetProcuct3_10000(), () => SetProcuct4_10000()); swTask.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 并行编程所耗时间:" + swTask.ElapsedMilliseconds); Thread.Sleep(3000); sw.Restart(); SetProcuct1_10000(); SetProcuct2_10000(); SetProcuct3_10000(); SetProcuct4_10000(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("10000条数据 顺序编程所耗时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void SetProcuct1_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 500; index < 1000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1000; index < 2000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_500() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 2000; index < 3000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct1_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 20000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct1 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct2_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 20000; index < 40000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct2 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct3_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 40000; index < 60000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct3 执行完成"); } private static void SetProcuct4_10000() { List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 60000; index < 80000; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); } Console.WriteLine("SetProcuct4 执行完成"); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
我将每个方法中的资源隔离,性能显而易见。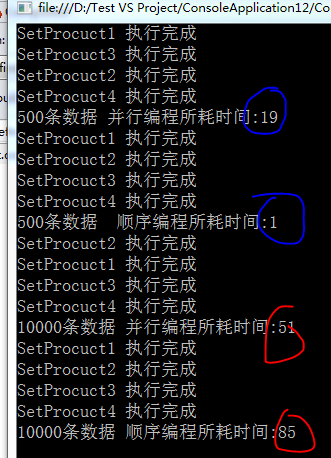
但是在操作500条数据时,显然采用并行操作并不明智,并行所带来的损耗比较大,在实际的开发中,还是要注意下是否有必要进行并行编程。
Parallel.For
将for循环替换成Parallel.For,并采用适合这个新方法的参数,就可以对这个已有的for循环进行重构,使其能够充分利用并行化优势。
需要注意的是:1.Parallel.For不支持浮点数的步进,使用的是Int32或Int64,每一次迭代的时候加1
2.由于循环体是并行运行,去迭代执行的顺序无法保证
下面贴代码

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { Thread.Sleep(3000); ForSetProcuct_100(); Thread.Sleep(3000); ParallelForSetProcuct_100(); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void ForSetProcuct_100() { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 100; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); Console.WriteLine("for SetProcuct index: {0}", index); } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("for SetProcuct 10 执行完成 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); } private static void ParallelForSetProcuct_100() { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); List<Product> ProductList = new List<Product>(); Parallel.For(1, 100, index => { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; ProductList.Add(model); Console.WriteLine("ForSetProcuct SetProcuct index: {0}", index); }); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ForSetProcuct SetProcuct 20000 执行完成 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
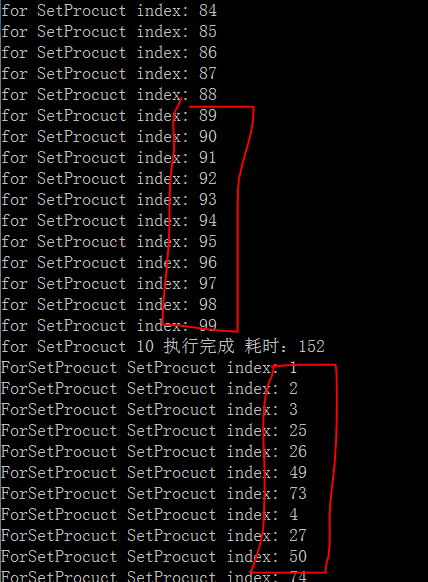
由图中我们可以看出,使用Parallel.For所迭代的顺序是无法保证的。
Parallel.ForEach
Parallel.ForEach提供一个并行处理一组数据的机制,可以利用一个范围的整数作为一组数据,然后通过一个自定义的分区器将这个范围转换为一组数据块,每一块数据都通过循环的方式进行处理,而这些循环式并行执行的。
下面贴代码:

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { List<Product> ProductList =GetProcuctList(); Parallel.ForEach(ProductList, (model) => { Console.WriteLine(model.Name); }); Console.ReadLine(); } private static List<Product> GetProcuctList() { List<Product> result = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 100; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; result.Add(model); } return result; } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }

ParallelLoopState
ParallelLoopState该实例提供了以下两个方法用于停止 Parallel.For,Parallel.ForEach
Break-这个方法告诉并行循环应该在执行了当前迭代后尽快地停止执行。吐过调用Break时正在处理迭代100,那么循环仍然会处理所有小于100的迭代。
Stop-这个方法告诉并行循环应该尽快停止执行,如果调用Stop时迭代100正在被处理,那么循环无法保证处理完所有小于100的迭代
下面贴代码

class Program { /* coder:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main(string[] args) { List<Product> productList = GetProcuctList_500(); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.For(0, productList.Count, (i, loopState) => { if (i < 100) { Console.WriteLine("采用Stop index:{0}", i); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,无法保证小于100的索引数据全部输出*/ loopState.Stop(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.For(0, productList.Count, (i, loopState) => { if (i < 100) { Console.WriteLine("采用Break index:{0}", i); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,保证小于100的索引数据全部输出*/ loopState.Break(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.ForEach(productList, (model, loopState) => { if (model.SellPrice < 10) { Console.WriteLine("采用Stop index:{0}", model.SellPrice); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,无法保证满足条件的数据全部输出*/ loopState.Stop(); return; } }); Thread.Sleep(3000); Parallel.ForEach(productList, (model, loopState) => { if (model.SellPrice < 10) { Console.WriteLine("采用Break index:{0}", model.SellPrice); } else { /* 满足条件后 尽快停止执行,保证满足条件的数据全部输出*/ loopState.Break(); return; } }); Console.ReadLine(); } private static List<Product> GetProcuctList_500() { List<Product> result = new List<Product>(); for (int index = 1; index < 500; index++) { Product model = new Product(); model.Category = "Category" + index; model.Name = "Name" + index; model.SellPrice = index; result.Add(model); } return result; } }
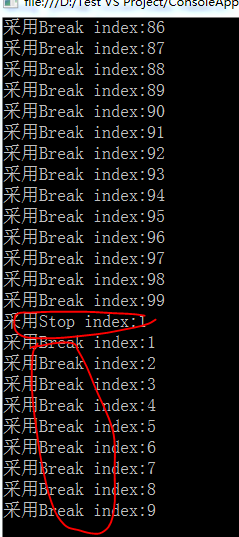
由图中可以看出Break可以保证输出满足所有条件的数据,而Stop则无法保证。
关于 Parallel 类提供的 Parallel.Invoke ,Parallel.For,Parallel.ForEach 的简介入门到这,如有错误欢迎指正
作者:释迦苦僧 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/woxpp/p/3925094.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。

