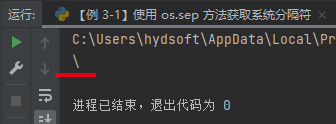
# 导入 os 库 import os # 获取本机操作系统的分隔符 print(os.sep)
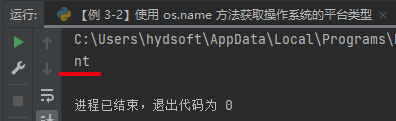
# 导入 os 库 import os # 获取本机操作系统的类型 print(os.name)
# 导入 os 库 import os # 获取当前的工作目录路径 print(os.getcwd())

# 导入 os库
import os
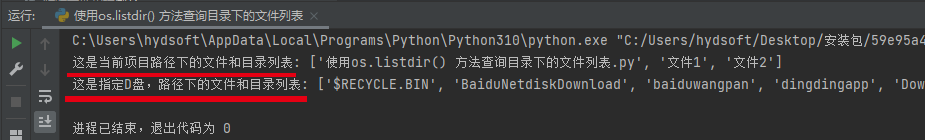
# 获取当前项目路径下的所有文件和目录列表,并以列表的形式展示
print("这是当前项目路径下的文件和目录列表:", os.listdir())
# 获取指定盘符的所有文件和目录列表,并以列表的形式展示
print("这是指定D盘,路径下的文件和目录列表:", os.listdir("D:\\"))
# 导入 os 库
import os
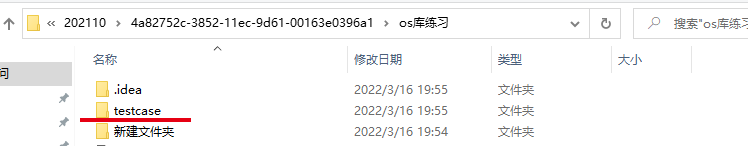
# 在当前项目路径下创建一个名为 testcase 的目录文件
os.mkdir("testcase")
# 在指定的盘符下建一个目录文件 testcase
os.mkdir("D:\\testcase")
# 导入 os 库
import os
# 在当前项目路径下删除空目录文件 testcase
os.rmdir("testcase")
# 去指定的盘符下删除空目录文件 testcase
os.rmdir("D:\\testcase")

# 导入 os 库
import os
# 删除当前项目路径下的 "123.txt 文件 "
os.remove("123.txt")
# 删除指定盘符下的文件
os.remove("D:\\data\\2.doc")
# 导入 os 库
import os
# 将项目路径下的工作簿名称 score.xlsx 修改成 score001.xlsx
print(os.rename("score.xlsx"," score001.xlsx"))
# __file__ 表示当前 Python 脚本文件的全路径 print(__file__)
os.getcwd()获取的是当前工作目录路径,但是不包含py.文件 比如: new/test/testcase
__file__ 获取的是包含当前py.文件在内的全路径 比如: new/test/testcase/case.py
# 导入 os 库 import os # os.path.dirname(__file__) 返回的是 Python 脚本文件所在的目录 path1 = os.path.dirname(__file__) print(path1)

# 导入 os 库 import os # os.path.abspath(__file__) 返回的是 Python 脚本文件的绝对路径(完整路径) path2 = os.path.abspath(__file__) print(path2)
# 导入 os 库 import os # 组合使用,返回的是 Python 脚本文件所在的目录 path3 = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) print(path3)
# 导入 os 库 import os # os.path.join() 拼接路径,输出 Test.py 文件的绝对路径 path1 = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__)) print(path1) path2 = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),'Test.py') print(path2) path3 = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) print(path3) # 加入 os.path.dirname() 和 os.path.abspath(),同样输出 Test.py文件的绝对路径 path4 = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'Test.py') print(path4) path5 = os.path.join(os.getcwd()) print(path5) # os.path.join() 拼接路径,输出 Test.py 文件的绝对路径 path6 = os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'Test.py') print(path6)

# 导入 os 库 import os # 返回的 .py 文件的绝对路径(完整路径) conf_file = os.path.abspath(__file__) # 返回 .py 文件所在的目录 conf_path = os.path.dirname(conf_file) # 通过 os.path.join() 方法来拼接 .py 文件的绝对路径(完整路径) conf_file1 = os.path.join(conf_path,"score001.xlsx") # 返回 .py 文件所在目录的上一级目录 conf_path1 = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(conf_path)) # 通过 os.sep 的方式来连接 .py 文件所在的绝对路径(完整路径) conf_file2 = conf_path1 + os.sep + " 接口自动化 " + os.sep + "score001.xlsx" # 通过 os.path.exists(conf_file) 判断文件是否存在 res_file = os.path.exists(conf_file) print(res_file) # 通过 os.path.exists(conf_path) 判断目录是否存在 res_dir = os.path.exists(conf_path) print(res_dir) # 通过 os.path.isfile(conf_file1) 判断是否为文件 is_file = os.path.isfile(conf_file1) print(is_file) # 通过 os.path.isdir(conf_path1) 判断是否为目录 is_dir = os.path.isdir(conf_path1) print(is_dir)
最后:多加练习!!!下班