Beautiifulsoup
Beautiifulsoup:python语言写的
re:C语言写的
lxml:C语言写的
速度最快的是正则,其次是lxml,最后是Beautifulsoup
安装:
pip install Beautiifulsoup4
四大对象种类
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:
- Tag
- NavigableString
- BeautifulSoup
- Comment
(1)Tag
Tag 通俗点讲就是 HTML 中的一个个标签。
from bs4 import Beautiifulsoup html = """
print(soup.p) # <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> print(type(soup.p)) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
我们可以利用 soup 加标签名轻松地获取这些标签的内容,这些对象的类型是bs4.element.Tag。对于 Tag,它有两个重要的属性,是 name 和 attrs.
print(soup.name) # [document] soup 对象本身比较特殊,它的 name 即为 [document] print(soup.head.name) # head 对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称 print(soup.p.attrs) # {'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'} print(soup.p['class']) # 取出标签的属性 print(soup.p.get('class') # 取出标签的属性,找不到返回None # ['title'] print(soup.a.text) #等于print(soup.a.get_text()) 取出标签下的文本内容
NavigableString简单来讲就是一个可以遍历的字符串。
例如:
print(soup.p.string) # The Dormouse's story print(type(soup.p.string)) # <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>
(3)BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性来感受一下
print type(soup.name) #<type 'unicode'> print soup.name # [document] print soup.attrs #{} 空字典
(4)Comment
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其实输出的内容仍然不包括注释符号,但是如果不好好处理它,可能会对我们的文本处理造成意想不到的麻烦。
我们找一个带注释的标签
print soup.a print soup.a.string print type(soup.a.string)
运行结果如下
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a> Elsie <class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
a 标签里的内容实际上是注释,但是如果我们利用 .string 来输出它的内容,我们发现它已经把注释符号去掉了,所以这可能会给我们带来不必要的麻烦。
另外我们打印输出下它的类型,发现它是一个 Comment 类型,所以,我们在使用前最好做一下判断,判断代码如下
Beautiful Soup定义了很多搜索方法,这里着重介绍2个: find() 和 find_all() .其它方法的参数和用法类似。
使用find_all等类似的方法可以查找想要的文档内容。
在介绍find_all方法之前,先介绍一下过滤器的类型。
字符串
最简单的过滤器是字符串。在搜索方法中传入一个字符串参数,BeautifulSoup会查找与字符串完整匹配的内容。
例如:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = Beautiifulsoup(html,'lxml') soup.find_all('a') #匹配所有的a标签 soup.find_all('a',attrs={'class':'tittle'}) #匹配所有class为tittle的a标签 等于soup.find_all('a',class_='tittle')
find_all方法可以接受正则表示式作为参数,BeautifulSoup会通过match方法来匹配内容。
#匹配以b开头的标签 for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile('^b')): print(tag.name) # body b #匹配包含t的标签 for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile('t')): print(tag.name) # html title
find_all方法也能接受列表参数,BeautifulSoup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回。
#查找a标签和b标签 for tag in soup.find_all(['a','b']): print(tag.name) # b a a a
find_all方法也能接受列表参数,BeautifulSoup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回。
#匹配包含class属性,但是不包括id属性的标签。 def has_class_but_no_id(tag): return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id') print([tag.name for tag in soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)]) # ['p','p','p']
这就是另一种与 find_all 方法有异曲同工之妙的查找方法.
-
写 CSS 时,标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加.,id名前加#
-
在这里我们也可以利用类似的方法来筛选元素,用到的方法是 soup.select(),返回类型是 list
1.通过标签名查找
print(soup.select('title')) #[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>] print(soup.select('a')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] print(soup.select('b')) #[<b>The Dormouse's story</b>]
print(soup.select('.sister')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
print(soup.select('#link1')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>]
组合查找即和写 class 文件时,标签名与类名、id名进行的组合原理是一样的,例如查找 p 标签中,id 等于 link1的内容,二者需要用空格分开
print(soup.select('p #link1')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>] 直接子标签查找,则使用 > 分隔 print(soup.select("head > title")) #[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
查找时还可以加入属性元素,属性需要用中括号括起来,注意属性和标签属于同一节点,所以中间不能加空格,否则会无法匹配到。
print(soup.select('a[class="sister"]')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] print(soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>] 同样,属性仍然可以与上述查找方式组合,不在同一节点的空格隔开,同一节点的不加空格 print(soup.select('p a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>]
以上的 select 方法返回的结果都是列表形式,可以遍历形式输出,然后用 get_text() 方法来获取它的内容。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(type(soup.select('title'))) print(soup.select('title')[0].get_text()) for title in soup.select('title'): print(title.get_text())
总结:
通过tag标签逐层查找:
soup.select("body a")
找到某个tag标签下的直接子标签
soup.select("head > title")
通过CSS的类名查找:
soup.select(".sister")
通过tag的id查找:
soup.select("#link1")
通过是否存在某个属性来查找:
soup.select('a[href]')
通过属性的值来查找:
soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')
获取内容
soup.select(a #link1)[0].get_text()
XPATH
xpath也是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是如何解析和提取 HTML/XML 数据。并且在爬虫框架scrapy中应用广泛。
安装:
pip install lxml
xpath主要语法
选取节点
| / | 从根节点选取,假如路径起始于正斜杠( / ),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径! |
| // | 从匹配选择的当前节点选择文档中的节点,而不考虑它们的位置,若以//开头,表示在全局搜索 |
| . | 选取当前节点 |
| .. | 选取当前节点的父节点 |
| @ | 选取属性 |
| * | 匹配任何元素节点 |
例如:
| bookstore | 选取 bookstore 元素的所有子节点。 |
| /bookstore |
选取根元素 bookstore。 注释:假如路径起始于正斜杠( / ),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径! |
| bookstore/book | 选取属于 bookstore 的子元素的所有 book 元素。 |
| //book | 选取所有 book 子元素,而不管它们在文档中的位置。 |
| bookstore//book | 选择属于 bookstore 元素的后代的所有 book 元素,而不管它们位于 bookstore 之下的什么位置。 |
| //@lang | 选取名为 lang 的所有属性。 |
谓语(Predicates)
谓语用来查找某个特定的节点或者包含某个指定的值的节点。
谓语被嵌在方括号中。
在下面的表格中,我们列出了带有谓语的一些路径表达式,以及表达式的结果:
| /bookstore/book[1] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的第一个 book 元素。 |
| /bookstore/book[last()] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的最后一个 book 元素。 |
| /bookstore/book[last()-1] | 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的倒数第二个 book 元素。 |
| /bookstore/book[position()<3] | 选取最前面的两个属于 bookstore 元素的子元素的 book 元素。 |
| //title[@lang] | 选取所有拥有名为 lang 的属性的 title 元素。 |
| //title[@lang='eng'] | 选取所有 title 元素,且这些元素拥有值为 eng 的 lang 属性。 |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00] | 选取 bookstore 元素的所有 book 元素,且其中的 price 元素的值须大于 35.00。 |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title | 选取 bookstore 元素中的 book 元素的所有 title 元素,且其中的 price 元素的值须大于 35.00。 |
选取未知节点
XPath 通配符可用来选取未知的 元素。
| /bookstore/* | 选取 bookstore 元素的所有子元素。 |
| //* | 选取文档中的所有元素。 |
| //title[@*] | 选取所有带有属性的 title 元素。 |
选取若干路径
通过在路径表达式中使用"|"运算符,您可以选取若干个路径。
在下面的表格中,我们列出了一些路径表达式,以及这些表达式的结果:
| //book/title | //book/price | 选取 book 元素的所有 title 和 price 元素。 |
| //title | //price | 选取文档中的所有 title 和 price 元素。 |
| /bookstore/book/title | //price | 选取属于 bookstore 元素的 book 元素的所有 title 元素,以及文档中所有的 price 元素。 |
补充:div.xpath('string(.)') 选取div下面的所有文本
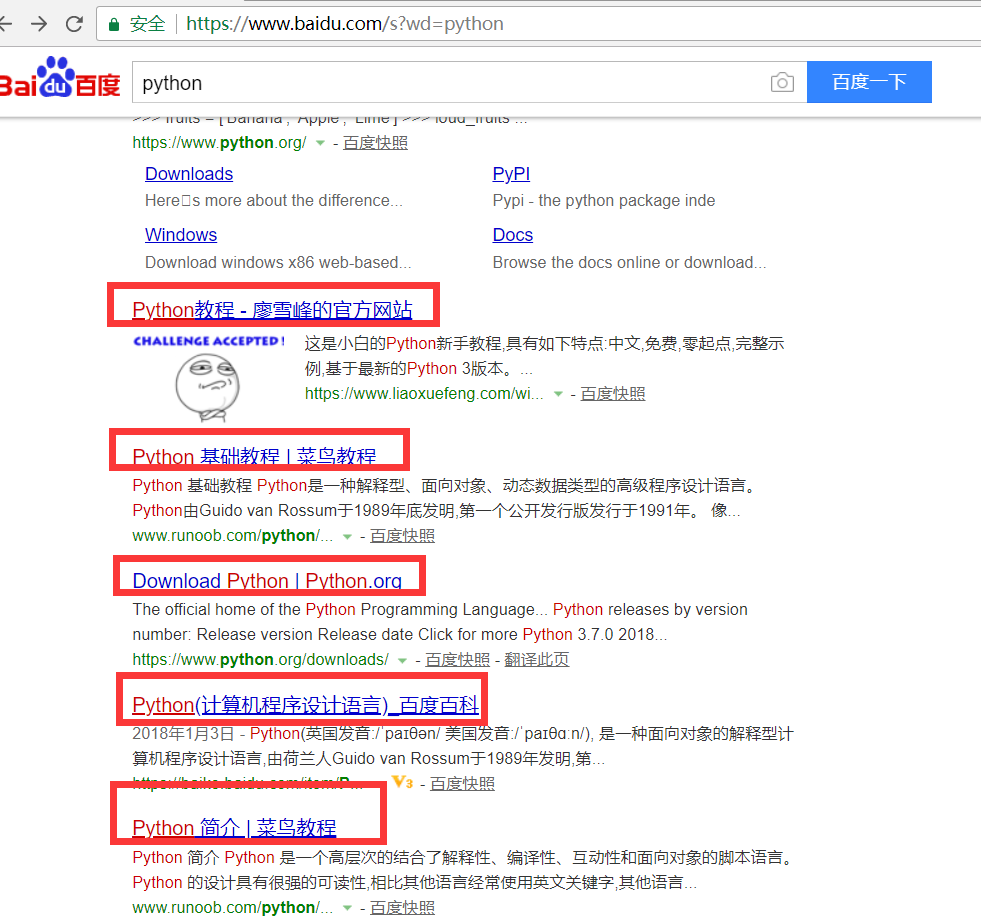
案例:在百度搜索python,提取出搜索结果中的网站的超链接和标题。如图,提取下面红框标记部分的链接和文本。
代码1:Beautifulsoup实现

import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup def get_response(): ''' :return:爬取需要的数据,在本例中就是百度搜索python结果的网页源代码 ''' url = 'http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=python' html = requests.get(url).text return html def parse(): info = {} soup = BeautifulSoup(get_response(),'lxml') nodelist = soup.find_all('div',class_='result c-container ') # 分析页面源码,所有的信息保存在类名为'result c-container '的div下面 for node in nodelist: href = node.select('h3 > a')[0].get('href') # 注意select得到的结果是个列表 title = node.select('h3 > a')[0].text # get_text() 和text 都会得到标签下所有的文本 info[title] = href return info if __name__ == '__main__': print(parse())
代码2:xpath实现

import requests from lxml import etree def get_response(): url = 'http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=python' html = requests.get(url).text return html def parse(): info = {} e = etree.HTML(get_response()) nodelist = e.xpath('//div[@class="result c-container "]') for node in nodelist: href = node.xpath('./h3/a/@href')[0] # title = ''.join(node.xpath('./h3/a/text()')) # 用/text()得到该标签下的文本,但是会按照标签隔开以列表形式保存,尝试用join拼接 # title = node.xpath('./h3/a')[0].text # 用text也只能得到该标签的文本,不包含子标签及子标签后面的文本,适用于精确定位 title = node.xpath('./h3/a')[0].xpath('string(.)') # 用xpath('string(.)')得到该标签下的所有文本 info[title] = href return info if __name__ == '__main__': print(parse())
