spring源码分析
1、 spring源码中组件介绍:

2、spring启动工厂创建和实例化bean的流程:
下图是spring 容器的关系
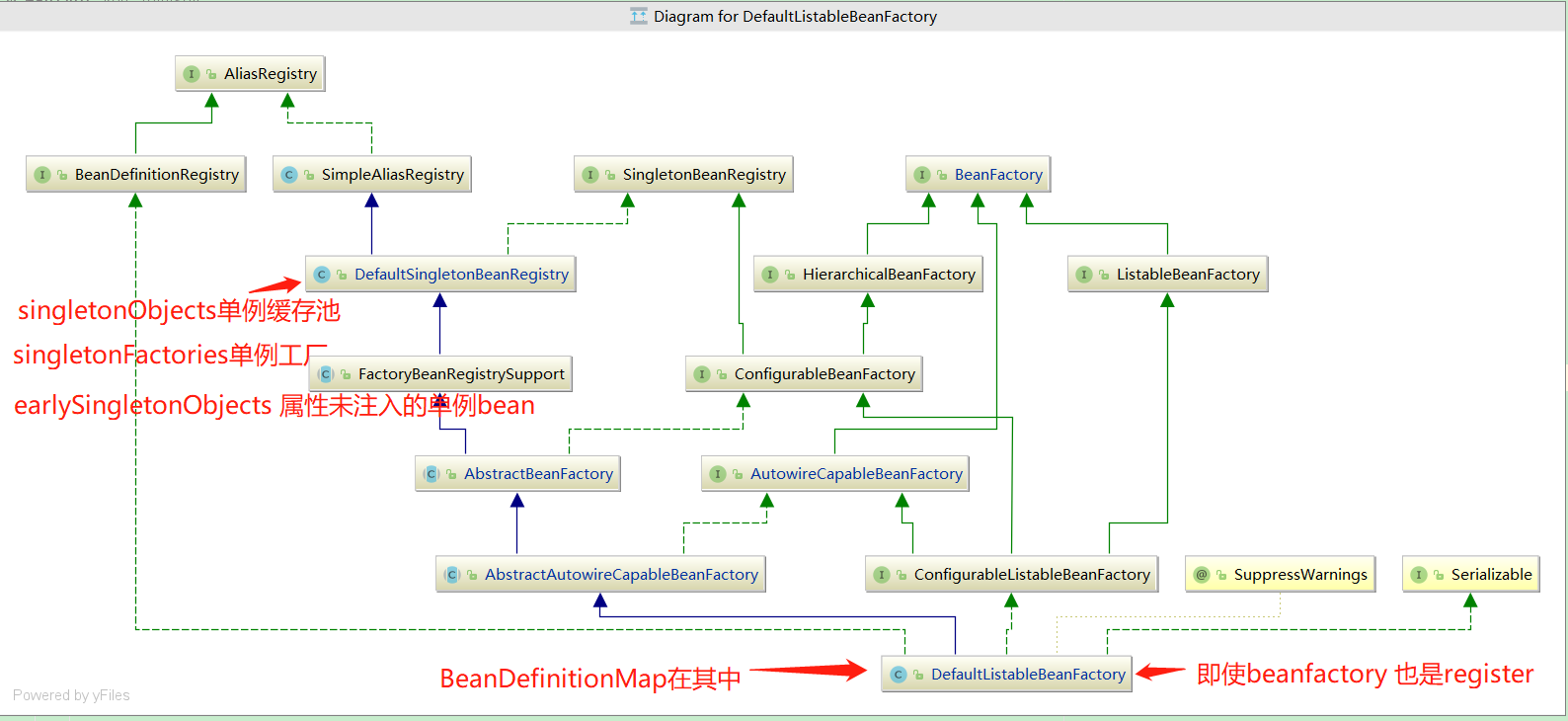
分析是基于注解的方式,非解析spring.xml的方式

说明:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 是ApplicationContext的子类;也是BeanDefinitionRegistry的实现类,即 即时spring的ioc容器,也是bd的注册器;
1、 创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ,参数 AppConfig,调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的构造方法,
说明:Appconfig是基于注解的方式配置bean,功能和spring.xm相同;需要 @ComponentScan和@Configuration一起使用;假如不使用@Configuration注解,会生成多例bean;使用该注解,当引用bean的时候会从spring的单例工厂取出bean。
2、 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses){} 构造方法,主要有一下处理逻辑:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) { //1. 初始化bean定义读取器和扫描器; // 2.调用父类GenericApplicationContext无参构造函数,初始化一个BeanFactory:DefaultListableBeanFactory // 3.注册Spring自带的bean,共5个 包括: ConfigurationClassPostProcessor // AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor // EventListenerMethodProcessor DefaultEventListenerFactory this(); // 注册AppConfig, ApplicationContext传入的配置类 //wl 此处只是注册了 @Configuration 注释的配置类, // wl register方法 作用是 将对应的Bean生成BeanDefinition,放到spring容器中;容器是一个 map,key是beanName(xml<Bean>标签里 id),value是BeanDefinition register(annotatedClasses); // wl 刷新容器,主要完成了 @Component 等相关注解注释的bean的初始化工作,将bean加载到 spring容器管理 refresh();// 启动容器 }
a、 this()方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { // 注册spring 自带的bean 5个 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); }
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);最终调用一下方法,注册spring 自带的5个后置处理器;
/** * Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry. * 注册所有的后置处理器 * @param registry the registry to operate on * @param source the configuration source element (already extracted) * that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}. * @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions * that have actually been registered by this call */ public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry); if (beanFactory != null) { if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) { //此处为一个比较器,应该是处理优先级的 beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); } if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) { beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver()); } } Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8); if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); // 注册 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); // 注册 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } // Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); // 注册 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } // Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(); try { def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader())); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex); } def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); // 注册 EventListenerMethodProcessor beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class); def.setSource(source); // 注册 DefaultEventListenerFactory beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)); } return beanDefs; }
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的无参构造方法,用来初始化定义读取器和扫描器
调用父类GenericApplicationContext无参构造函数,初始化一个BeanFactory:DefaultListableBeanFactory
这里的 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader注册了spring自带的5个bean,分别为:
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
EventListenerMethodProcessor
DefaultEventListenerFactory
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner :一个bean定义扫描器,它检测类路径上的bean候选对象;
b、 register(annotatedClasses)方法,方法参数可能为多个,
b.1 循环遍历,注册AppConfig, ApplicationContext传入的配置类
b.2 方法内部 主要调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils. registerBeanDefinition()方法,将配置类 转换为对应的 BeanDefination,注册到spring容器中
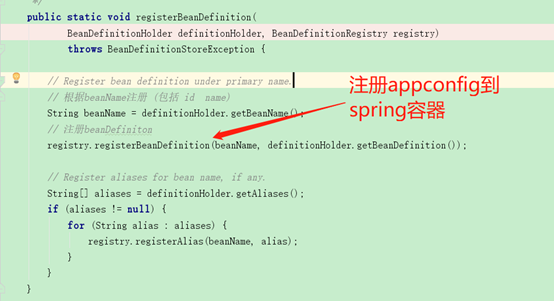
/** * Register one or more annotated classes to be processed. * <p>Calls to {@code register} are idempotent; adding the same * annotated class more than once has no additional effect. * @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes, * e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes */ public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) { for (Class<?> annotatedClass : annotatedClasses) { registerBean(annotatedClass); } } /** * Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from * class-declared annotations. * @param annotatedClass the class of the bean */ public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass) { doRegisterBean(annotatedClass, null, null, null); }
<T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name, @Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); // 注册bean AppConfig BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); /** * Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory. * @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases * @param registry the bean factory to register with * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed */ public static void registerBeanDefinition( BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name. // 根据beanName注册 (包括 id name) String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName(); // 注册beanDefiniton registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); // Register aliases for bean name, if any. String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases(); if (aliases != null) { for (String alias : aliases) { registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias); } } } }
c、 refresh() 属于 AbstractApplicationContext方法,spring启动时最终会调用该refresh()方法,
c.1 refresh()方法主要完成bean加载到spring容器的工作(非@Configuratiion bean修饰的配置bean)
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. // 获得刷新的beanFactory // 对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,作用: // 1.调用org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory, // 只是指定了SerializationId // 2.直接返回beanFactory(不用创建,容器中已存在) // 对于ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,作用: // 1.调用AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory // 2.如果存在beanFactory,先销毁单例bean,关闭beanFactory,再创建beanFactory // 3.注册传入的spring的xml配置文件中配置的bean,注册到beanFactory // 4.将beanFactory赋值给容器,返回beanFactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 准备bean工厂: 指定beanFactory的类加载器, 添加后置处理器,注册缺省环境bean等 // beanFactory添加了2个后置处理器 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor, ApplicationListenerDetector (new ) prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. // 空方法 // 允许在上下文的子类中对beanFactory进行后处理 // 比如 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext.postProcessBeanFactory postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. // 1.通过beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class) // 拿到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor // 2.通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,注册所有注解配置的bean // 注册的顺序: @ComponentScan>实现ImportSelector>方法bean>@ImportResource("spring.xml") // > 实现 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar (相对的顺序,都在同一个配置类上配置) // 3. 调用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory // 增强@Configuration修饰的配置类 AppConfig--->AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB // (可以处理内部方法bean之间的调用,防止多例) // 添加了后置处理器 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor (new) invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // 注册拦截bean创建的后置处理器: // 1.添加Spring自身的: BeanPostProcessorChecker (new) 以及注册了beanDefinition的两个 // CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor // 重新添加ApplicationListenerDetector(new ) ,删除旧的,移到处理器链末尾 // 2.用户自定义的后置处理器 // 注册了beanDefinition的会通过 beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class) 获取后置处理器 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. // 初始化事件多播器 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. // 空方法 onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. 注册监听器 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. // 实例化所有剩余的(非懒加载)单例,此处才是真正地将 singleton类型 bean初始化spring的 单例bean对象池 singleObjects中。。。。
//singleObjects 是一个map <beanName,singleBean>
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
//基于观察者模式,事件多播器将 publish 到 事件多波器的事件 通知到 对应的 listener
finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }