C#的集合类命名空间介绍:
// 程序集 mscorlib.dll System.dll System.Core.dll // 命名空间 using System.Collections:集合的接口和类 using System.Collections.Generic:泛型集合的接口和类,强类型安全 using System.Collections.Specialized:专用的和强类型的集合 using System.Collections.Concurrent:线程安全的集合
集合基于ICollection接口、IList接口、IDictionary接口及其泛型接口版本、IEnumerable接口及其泛型版本,其中接口IList和IDictionary均从ICollection接口和IEnumerable接口派生,因此所有集合全部直接或间接基于ICollection接口和IEnumerable接口:
- 泛型IEnumerable接口继承IEnumerable接口,IEnumerable接口无父接口;
- 泛型ICollection接口继承泛型IEnumerable接口和IEnumerable接口,ICollection接口继承IEnumerable接口;
- 所有集合均实现IEnumerable接口,泛型集合均实现IEnumerable<T>接口;
- 所有集合(除StringDictionary、HashSet<T>)均实现ICollection接口,泛型集合(除Stack<T>、Queue<T>)均实现ICollection<T>接口;
注:集合是否实现ICollection接口及其泛型版本,注意两者的接口定义即可。
- IEnumerable - IEnumerable<T>:支持枚举器;
- IList、IList<T>:支持索引访问;
- IDictionary、IDictionary<T>:支持键值访问;
关于字典集的枚举访问
- 非泛型字典集类(除StringDictionary、NameValueCollection是普通的枚举器直接返回集合元素)枚举时返回DictionaryEntry对象:
foreach (DictionaryEntry de in myXxx) {
Console.WriteLine(de.Key, + ": " + de.Value);
}
- 泛型字典集类枚举时返回KeyValuePair对象:
foreach (KeyValuePair<TK, TV> kvp in myGenericXxxDic){
Console.WriteLine(kvp.Key + ": " + kvp.Value);
}
参考:
ICollection - ICollection<T>
ICollection:所有非泛型集合的大小、枚举器和同步方法
public interface ICollection : IEnumerable {
int Count { get; }
bool IsSynchronized { get; } // 对ICollection的访问是否是同步的(线程安全)
object SyncRoot { get; } // 获取可用于对ICollection同步访问的对象
void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
ICollection<T>:泛型集合的属性方法
public interface ICollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable {
int Count { get; }
bool IsReadOnly { get; }
void Add(T item);
bool Remove(T item);
void Clear();
bool Contains(T item);
void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex);
}

注:使用可变集合时,若不指定initCapacity,系统会使用默认的initCapacity。当元素个数超过initCapacity时,先在内部重新构建(二倍扩充)一个集合,再将原集合中的元素复制到新集合中。建议实例化可变集合时指定一个相对较大的initCapacity,避免在向可变集合中添加大量元素时因集合扩充容量带来的性能损失。
数组:Array - ArrayList - List<T>
本质是数组实现、支持索引访问。三个类都实现IList接口,List<T>泛型类还实现IList<T>泛型接口,List<T>是ArrayList对应的泛型版本实现。
参考:.net集合类的研究--Array, ArrayList, List<T>;
Array:抽象类,提供属性和方法操作(创建、搜索、排序)数组,用作所有数组的基类
数组是具有同一类型的多个对象的集合,所有数组均继承System.Array类。类型安全、非线程安全。
- 长度固定,不能伸缩,但数组可有多个维度;
- 可读可写,但不能声明只读数组;
- 支持下标索引访问,一次获取或设置一个元素的值;
- 数组必须声明元素的类型;
抽象类,不能使用构造函数创建数组,但是可以通过Array类的静态方法CreateInstance()创建数组:
// 创建索引从0开始、具有指定System.Type和长度的一维System.Array public static Array CreateInstance(Type elementType, int length);
C# - Array类代码
对于数据类型一致和容量固定的情况,首选数组、性能高,且数组存储数据对GC友好。
public abstract class Array : ICloneable, IList, ICollection, IEnumerable, IStructuralComparable, IStructuralEquatable {
public int Length { get; }
public long LongLength { get; } // 64位长度
public int Rank { get; } // 维数(秩)
public object SyncRoot { get; }
public bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public static Array CreateInstance(Type elementType, int len); // 创建Array实例
public void Initialize(); // 调用值类型的默认构造函数,初始化Array的元素
public object Clone(); // 浅表副本
public static ReadOnlyCollection<T> AsReadOnly<T>(T[] arr); // 返回指定数组的只读版本
public static void Clear(Array array, int index, int length);
public static void Resize<T>(ref T[] arr, int newSize); // 重置数组大小
// 指定维度的长度、下界、上界
public int GetLength(int dimension);
public int GetLower/UpperBound(int dimension);
public static int BinarySearch(XXX xxx);
public static int Sort(XXX xxx);
public static void Reverse(Array arr [, int idx, int len]);
public object Get/SetValue(int index);
public static int IndexOf(Array array, object value);
public static int LastIndexOf(Array array, object value);
public static void Copy(Array srcArr, Array destArr, int len);
public void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
// 函数式编程
public static void ForEach<T>(T[] array, Action<T> action); // 对指定数组的每个元素执行指定操作
public static bool Exists<T>(T[] array, Predicate<T> match);
public static T Find<T>(T[] array, Predicate<T> match);
public static T FindLast<T>(T[] array, Predicate<T> match);
public static T[] FindAll<T>(T[] array, Predicate<T> match);
public static int FindIndex<T>(T[] arr, [int startIdx, int cnt,] Predicate<T> match);
public static int FindLastIndex<T>(T[] arr, [int startIdx, int cnt,] Predicate<T> match);
}
ArrayList: 使用大小可按需动态增加的数组实现IList接口
动态数组,Array的复杂版本(ArrayList是对Array的封装,实际数据操作还是针对Array)、速度略慢,针对任意类型的元素(可为null)、任意长度,非类安全型、非线程安全。
原理实现
ArrayList内部维护一个数组,内置_items数组默认长度为4:
private object[] _items; private static readonly object[] emptyArray = new object[0]; // 用于初始化数组_items private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
初始化ArrayList:
ArrayList扩容:
使用示例
ArrayList myArrayList = new ArrayList(); Object obj = null; myArrayList.Add(obj); // 元素类型为Object,可为null myArrayList.Add(null); // 元素可为空null myArrayList.Add(null); // 空null可重复添加
线程安全性
内部类SyncArrayList是继承ArrayList类的私有类,通过lock同步构造lock(this._root)实现线程安全。
- SyncRoot属性
- Synchronized()方法
ArrayList mySyncArrayList = ArrayList.Synchronized(myArrayList);
C#-ArrayList类代码
public class ArrayList : IList, ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {
public virtual int Capacity { get; set; }
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public virtual object this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引访问器
public ArrayList();
public ArrayList(int capacity);
public ArrayList(ICollection c);
public virtual IEnumerator GetEnumerator([int idx, int cnt]); // 枚举器
public virtual object Clone(); // 创建ArrayList的浅表副本
public virtual ArrayList GetRange(int idx, int cnt); // 子集
public virtual void SetRange(int idx, ICollection c); // 设置ArrayList的值
public static ArrayList ReadOnly(ArrayList list); // 返回只读的ArrayList包装
public static IList ReadOnly(IList list); // 返回只读的IList包装
public static ArrayList Synchronized(ArrayList list); // 返回线程同步的ArrayList包装
public static IList Synchronized(IList list); // 返回线程同步的IList包装
public static ArrayList Adapter(IList list); // 返回IList的ArrayList包装
public virtual int Add(object val);
public virtual void AddRange(ICollection c);
public virtual void Insert(int idx, object val);
public virtual void InsertRange(int idx, ICollection c);
public virtual void Remove(object obj);
public virtual void RemoveAt(int idx);
public virtual void RemoveRange(int idx, int cnt);
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(object item);
public virtual int IndexOf(object val [, int startIdx, int cnt]);
public virtual int LastIndexOf(object val [, int startIdx, int cnt]);
public virtual void Reverse([int idx, int cnt]); // 反转
public virtual void Sort([IComparer cmp]); // 排序
public virtual int BinarySearch(object val [, IComparer cmp]); // 二分查找
public virtual object[] ToArray();
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array [, int arrayIdx]);
}
其中,接口IList表示对象的非泛型集合,可按照索引单独访问
public interface IList : ICollection, IEnumerable {
bool IsReadOnly { get; }
object this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引器:获取或设置指定索引处的元素
int Add(object value);
void Insert(int index, object value);
void Remove(object value);
void RemoveAt(int index);
void Clear();
bool Contains(object value);
int IndexOf(object value);
}
List<T>:对象的强类型列表,可通过索引访问的。提供搜索、排序和操作列表的方法
泛型,List<T>也是对Array的封装,实际数据操作还是针对Array,类型安全、非线程安全。
参考:.NET,你忘记了么?(三续)——重新理解List<T>; .net源码分析 – List<T>;
原理实现
List<T>内部维护一个数组,内置_items数组默认长度为4:
private object[] _items; private static readonly T[] _emptyArray = new T[0]; private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
初始化List<T>:
List<T>扩容:同ArrayList。
使用示例
List<string> myList = new List<string>(); string str = null; myList.Add(str); // 元素类型为string,可为null myList.Add(null); // 元素可为空null myList.Add(null); // 空null可重复添加
C#-List<T>类代码
public class List<T> : IList<T>, ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IList, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public int Capacity { get; set; }
public T this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引访问器
public List();
public List(int capacity);
public List(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Add(T item);
public void AddRange(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Insert(int index, T item);
public void InsertRange(int index, IEnumerable<T> collection);
public bool Remove(T item);
public void RemoveAt(int index);
public void RemoveRange(int index, int count);
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(T item);
public int IndexOf(T item [, int idx, int cnt]);
public int LastIndexOf(T item [, int idx, int cnt]);
public int BinarySearch(T item);
public int BinarySearch(T item, IComparer<T> comparer);
public void Sort();
public void Sort(Comparison<T> comparison);
public void Sort(IComparer<T> comparer);
public void Reverse();
public void Reverse(int index, int count);
public List<T> GetRange(int index, int count);
public T[] ToArray();
public void CopyTo(T[] array [, int arrayIndex]);
// 枚举器
public List<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator();
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator
// 支持函数式编程
public void ForEach(Action<T> action);
public bool Exists(Predicate<T> match);
public T Find(Predicate<T> match);
public T FindLast(Predicate<T> match);
public int FindIndex([int startIdx, int cnt, ] Predicate<T> match);
public int FindLastIndex([int startIdx, int cnt, ] Predicate<T> match);
public List<T> FindAll(Predicate<T> match);
public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match);
public bool TrueForAll(Predicate<T> match); // 每个元素是否与指定的谓词条件匹配
}
其中, public delegate bool Predicate<in T>(T obj); 表示定义一组条件并确定指定对象是否符合这些条件的方法。
其中,接口IList<T>表示可按照索引单独访问的一组对象的集合
public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable {
T this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引器:获取或设置指定索引处的元素
void Insert(int index, T item);
void RemoveAt(int index);
int IndexOf(T item);
}
参考:ArrayList 和 List 集合类型 - msdn;
哈希表:Hashtable - Dictionary<TKey, TValue>
本质是哈希表实现、支持键值访问。两个类都实现IDictionary接口,Dictionary<TK, TV>泛型类还实现IDictionary<TK, TV>泛型接口,Dictionary<TK, TV>是Hashtable对应的泛型版本实现。
参考:
Hashtable:根据键的哈希代码进行组织的键/值对集合
本质是哈希表实现(单一数组)、支持键值访问。每个元素都是一个存储在DictionaryEntry对象中的键值对。Hashtable对象由包含集合元素的存储桶组成,每一个存储桶与一个Hash代码关联,通过键检索值实质是检索键对应的Hash代码(调用GetHashCode()方法计算当前键的hash值)关联的存储桶。keyvalue键值对均为object类型,支持任何类型的keyvalue键值对,但键不可为null且键不允许重复,查找速度快接近O(1),但内存占用大、利用率低,空间换时间。非类安全型、线程安全。
哈希表内部实现存取的数组的长度总是一个素数,创建或者二倍扩充Hashtable时容量通常会偏大,而且加载因子(默认0.72f)的存在,Hashtable在未存满的情况下就要扩充。Hashtable内部维护一个bucket类型的数组变量,bucket是一个结构,用来保存Key,Value和哈希值
private struct bucket {
public object key;
public object val;
public int hash_coll;
}
其中,hash_coll的最高位表示当前位置是否发生冲突,“0”(正数)表示未发生冲突、“1”(负数)表示当前位置冲突,专门使用标志位标注是否发生冲突可以提高哈希表的运行效率。
原理实现
Hashtable内部维护一个数组,内置buckets数组的长度默认指定为3:
private Hashtable.bucket[] buckets; private const int InitialSize = 3; private float loadFactor;
初始化Hashtable:
其中,GetPrime()方法会在扩容时返回略大于原数组双倍大小的一个素数,作为新数组的大小:
其中,primes[]是.NET内部维护的一个素数数组,避免生成素数时的额外开销。
Hashtable扩容:
其中,rehash()方法的入参bool forceNewHashCode设置为false,表明扩容时不需要重新计算hashcode,但是取模运算和元素位置的重新分配是必须的:
使用示例:
Hashtable myHashtable = new Hashtable(20); Object key = null, val = null; myHashtable.Add(key,val); // error,键/值均为Object类型,但键不能为null myHashtable.Add(null,null); // error,键不能为null
遍历Hashtable元素
// 方法一
foreach (DictionaryEntry de in myHashtable) {
Console.WriteLine("Key: {0}, Value: {1}", de.Key, de.Value);
}
// 方法二
IDictionaryEnumerator iDe = myHashtable.GetEnumerator();
while (iDe.MoveNext()) {
Console.WriteLine("Key: {0}, Value: {1}", iDe.Key, iDe.Value);
}
排序Hashtable元素
ArrayList tmpKeysArrayList = new ArrayList(myHashtable.Keys);
tmpKeysArrayList.Sort();
foreach (var tmpKey in tmpKeysArrayList) {
Console.WriteLine("Key: {0}, Value: {1}", tmpKey, myHashtable[tmpKey]);
}
线程安全
内部类SyncHashtable是继承Hashtable类的私有类,通过lock同步构造lock(this._table.SyncRoot)实现线程安全,其中SyncRoot是Hashtable的公有属性。实现方法与ArrayList大同小异。多线程并发,同一时刻只能有一个线程写、其余阻塞,对读的线程不受影响。
- SyncRoot属性 同ArrayList。
- Synchronized()方法
// 方法一
Hashtable mySyncHashtable = Hashtable.Synchronized(myHashtable);
// 方法二
lock (myHashtable.SyncRoot) { try{...} catch(){...} }
// 方法三
Monitor.Enter(myHashtable.SyncRoot);
try{...} catch(){...}
Monitor.Exit(myHashtable.SyncRoot);
C#-Hashtable类代码
public class Hashtable : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback, ICloneable {
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public virtual ICollection Keys { get; }
public virtual ICollection Values { get; }
public virtual object this[object key] { get; set; } //键值访问器
protected IComparer comparer { get; set; } // 返回IComparer对象,用于比较
public Hashtable();
public Hashtable(int capacity);
public Hashtable(IDictionary d);
public virtual IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public virtual object Clone(); // 创建Hashtable的浅表副本
public static Hashtable Synchronized(Hashtable table); // 返回线程同步的Hashtable包装
public virtual void Add(object key, object value);
public virtual void Remove(object key);
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(object key);
public virtual bool ContainsKey(object key);
public virtual bool ContainsValue(object value);
protected virtual int GetHash(object key);
protected virtual bool KeyEquals(object item, object key); // 与键比较
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array, int arrayIndex);
}
其中,接口IDictionary表示键/值对的非泛型集合
public interface IDictionary : ICollection, IEnumerable {
bool IsReadOnly { get; }
Object this[Object key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
ICollection Keys { get; }
ICollection Values { get; }
void Add(object key, object value);
void Remove(object key);
void Clear();
bool Contains(object key);
IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
其中,IDictionaryEnumerator表示非泛型字典集的枚举器
public interface IDictionaryEnumerator : IEnumerator {
DictionaryEntry Entry { get; }
object Key { get; }
object Value { get; }
}
其中,DictionaryEntry表示字典集的元素(键/值对)
public struct DictionaryEntry {
public DictionaryEntry(object key, object value);
public object Key { get; set; }
public object Value { get; set; }
}
参考:
Dictionary<TKey, TValue>:键值对的泛型集合
本质是哈希表(数组+链表数组)、提供快速的基于键值的元素查找。Dictionary<[key], [value]>,键必须唯一且不能为空null,值若为引用类型则可为空,类型安全、非线程安全。
参考:.net源码分析 – Dictionary<TKey, TValue>;
原理实现
Dictionary<TK, TV>在内部维护两个数组:
private int[] buckets; private Dictionary<TKey, TValue>.Entry[] entries; // 链表数组
- 普通数组buckets:存放由多个同义词组成的静态单链表的头指针(单链表的第一个元素在entries数组中的索引号),当buckets[i]=-1(头指针=null)时表示此哈希地址目前不存在元素;
- 链表数组entries:存放哈希表中的实际数据,数据通过next指针构成多个单链表;
链表数组entries是一个Entry类型的数组变量,Entry是一个结构,用来保存Key、Value和哈希值:
private struct Entry {
public int hashCode;
public int next; // (链接法,指向下一个结点)
public TKey key;
public TValue value;
}
因为Dictionary<TK, TV>采用分离链接法存储元素,不受装填因子的限制(默认1.0f),链表数组entries也存在二次扩容的问题、但是扩容代价小于Hashtable。查找操作若需要遍历单链表会造成性能损耗、且链表对GC没有数组友好。
初始化Dictionary<TK, TV>:
插入操作:Dictionary<TK, TV>的Add()方法会调用内部的Insert()方法,具体:
Dictionary<TK, TV>扩容:通过Resize()方法实现,入参bool forceNewHashCode设置为false,表明不需要重新计算hashcode,但是取模运算和元素位置的重新分配是必须的。
其中,GetPrime()和ExpandPrime()方法同Hashtable。二次扩容不需要再次哈希。
使用示例
Dictionary<string, string> myDictionary = new Dictionary<string, string>();
myDictionary.Add("", null); // 正确,值为引用类型时,允许为空null
myDictionary.Add(null, null); // error,键不能为空null
遍历Dictionary<K,V>元素
// 方法一:By KeyValuePair
foreach (KeyValuePair<T1, T2> kvp in myDictionary) 或 foreach(var kvp in myDictionary)
// 方法二:By Key
Dictionary<T1, T2>.KeyCollection keyCollection = myDictionary.Keys;
foreach (T1 key in keyCollection) 或 foreach(T1 key in myDictionary.Keys)
// 方法三:By Value
Dictionary<T1, T2>.ValueCollection valueCollection = myDictionary.Values;
foreach (T2 val in valueCollection) 或 foreach(T2 val in myDictionary.Values)
// 方法四:By IEnumerator
Dictionary<TK, TV>.Enumerator myIE = myDictionary.GetEnumerator();
while (myIE.MoveNext()) {
Console.WriteLine(myIE.Current.Key + ": " + myIE.Current.Value);
}
TryGetValue()
获取与指定的键相关联的值,避免因获取不到相应的值发生异常。通过键取值,包括两个参数,一个是要查询的键,另一个是获取的值,注意值前面使用out关键字,否则编译失败。
public bool TryGetValue(TK key, out TV val);
注:“判断键存在”和“根据键取值”两步转化为一步,键的哈希值只计算一次,效率高,时间复杂度接近O(1)。
C#-Dictionary<TKey, TValue>类代码
public class Dictionary<TKey, TValue> : IDictionary<TKey, TValue>, ICollection<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback {
public int Count { get; }
public Dictionary<TKey, TValue>.KeyCollection Keys { get; }
public Dictionary<TKey, TValue>.ValueCollection Values { get; }
public TValue this[TKey key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public Dictionary();
public Dictionary(int capacity);
public Dictionary(IDictionary<TKey, TValue> dictionary);
public Dictionary<TKey, TValue>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public void Add(TKey key, TValue value);
public bool Remove(TKey key);
public void Clear();
public bool ContainsKey(TKey key);
public bool ContainsValue(TValue value);
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value);
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IDisposable, IDictionaryEnumerator, IEnumerator {}
public sealed class KeyCollection : ICollection<TKey>, IEnumerable<TKey>, ICollection, IEnumerable {}
public sealed class ValueCollection : ICollection<TValue>, IEnumerable<TValue>, ICollection, IEnumerable {}
}
其中,接口IDictionary<TKey, TValue>表示键/值对的泛型集合
public interface IDictionary<TKey, TValue> : ICollection<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IEnumerable {
TValue this[TKey key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
ICollection<TKey> Keys { get; }
ICollection<TValue> Values { get; }
void Add(TKey key, TValue value);
bool Remove(TKey key);
bool ContainsKey(TKey key);
bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value);
}
其中,KeyValuepair定义可设置或检索的键/值对:
public struct KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> {
public KeyValuePair(TKey key, TValue value);
public TKey Key { get; }
public TValue Value { get; }
public override string ToString();
}
参考:
下面部分是关于有序字典集及部分专用字典集:
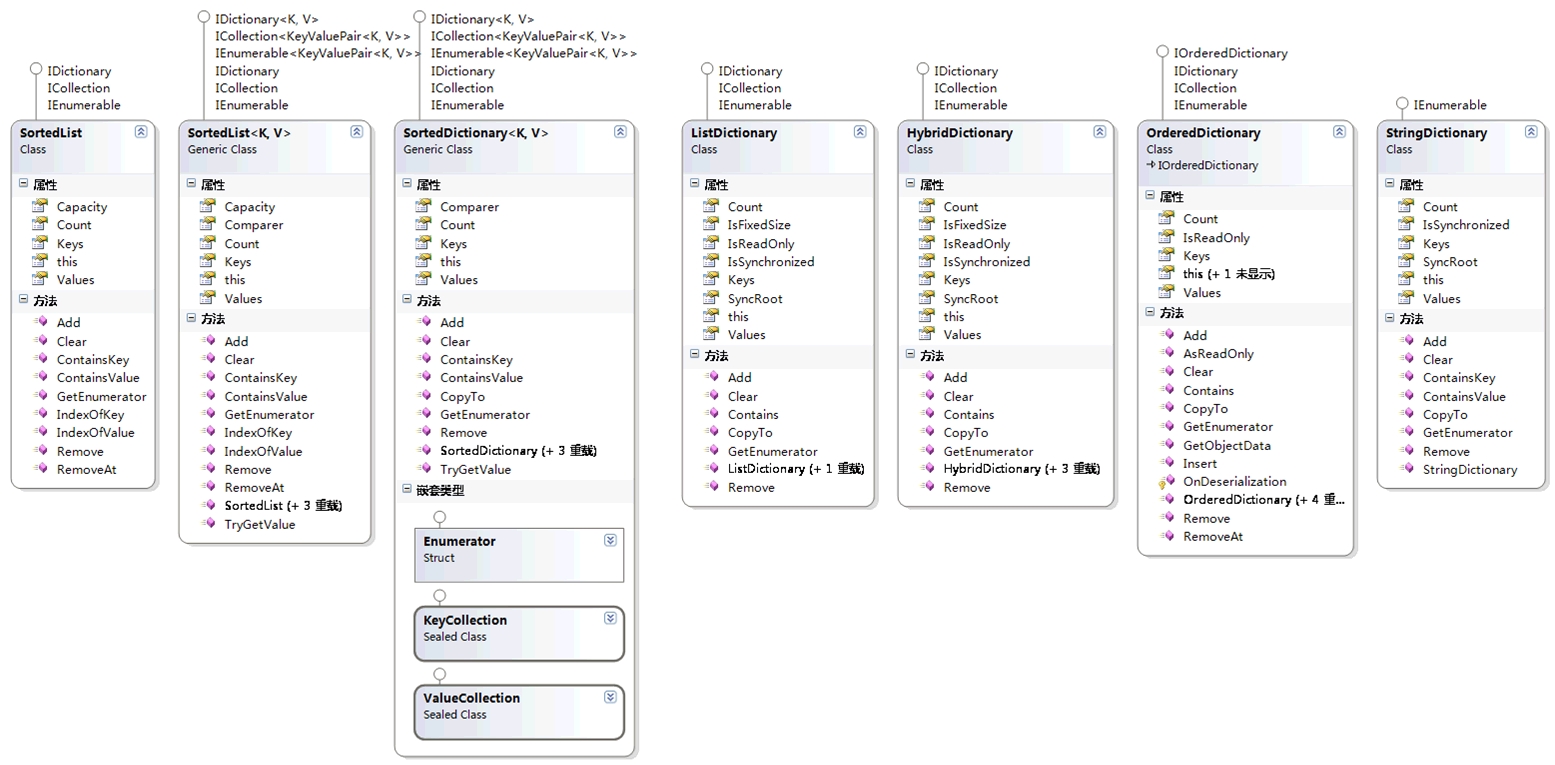
有序字典集:SortedList - SortedList<TK, TV> - SortedDictionary<TK, TV>
三个类都实现IDictionary接口,两个泛型类还实现IDictionary<TK, TV>泛型接口,SortedList<TK, TV>和SortedDictionary<TK, TV>是Dictionary<TK, TV>的排序版本实现,SortedDictionary<K, V>提供比Dictionary<K, V>更快的查找速度。非泛型SortedList类枚举时返回DictionaryEntry对象,两个泛型类枚举时返回KeyValuePair对象。
SortedList、SortedList<T>双数组实现(本质还是数组)、支持索引访问和键值访问,SortedDictionary红黑树实现(二叉平衡树)、支持键值访问。
参考:
SortedList:按键排序的键/值对集合,可按键和索引访问
双数组实现、支持索引,在内部维护两个数组用于存储列表中的元素:一个数组用于键,一个数组用于相关联的值。键不能为空null、值可以为null。由于排序,SortedList性能略差于Hashtable。非类型安全、非线程安全。
原理实现
SortedList内部维护两个数组:一个键数组和一个值数组。SortedList集合的核心:二分查找法的运用。
private object[] keys; private object[] values; private static object[] emptyArray = new object[0]; // 用于初始化数组keys和values private const int _defaultCapacity = 16;
初始化SortedList:
SortedList扩容:同样存在二次扩容问题,代码同ArrayList/List<T>,默认_defaultCapacity = 16。
C#-SortedList类代码
public class SortedList : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {
public virtual int Capacity { get; set; }
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public virtual ICollection Keys { get; }
public virtual ICollection Values { get; }
public virtual object this[object key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
// 未指定IComparer比较器的SortedList,根据键实现的System.IComparable接口排序
public SortedList();
public SortedList(int initCapacity);
public SortedList(IDictionary d);
public SortedList(IComparer comparer);
public virtual object Clone(); // 创建SortedList对象的浅表副本
public virtual IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public static SortedList Synchronized(SortedList list);
public virtual void Add(object key, object value);
public virtual void Remove(object key);
public virtual void RemoveAt(int index);
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(object key);
public virtual bool ContainsKey(object key);
public virtual bool ContainsValue(object value);
public virtual object GetByIndex(int index);
public virtual void SetByIndex(int index, object value);
public virtual object GetKey(int index);
public virtual IList GetKeyList();
public virtual IList GetValueList();
public virtual int IndexOfKey(object key);
public virtual int IndexOfValue(object value);
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array, int arrayIndex);
}
SortedList<TK, TV>:基于关联的System.Collections.Generic.IComparer<T>实现的按键排序的键/值对集合
具有O(logN)检索的二进制搜索树,双数组实现、支持索引。类型安全、非线程安全。
原理实现
SortedList<TK, TV>内部维护两个数组:一个键数组和一个值数组,与SortedList大同小异。
private TKey[] keys; private TValue[] values; private static TKey[] emptyKeys = new TKey[0]; private static TValue[] emptyValues = new TValue[0]; private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
初始化SortedList<TK, TV>:
SortedList扩容:同样存在二次扩容问题,代码同ArrayList/List<T>,默认_defaultCapacity = 4。
C#-SortedList<TK, TV>类代码
public class SortedList<TK, TV> : IDictionary<TK, TV>, ICollection<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>>, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>>, IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public int Capacity { get; set; }
public IList<TK> Keys { get; }
public IList<TV> Values { get; }
public TV this[TK key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public IComparer<TK> Comparer { get; } // 比较器
public SortedList();
public SortedList(int capacity);
public SortedList(IDictionary<TK, TV> dictionary);
public SortedList(IComparer<TK> comparer);
public IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>> GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public void Add(TK key, TV val);
public bool Remove(TK key);
public void RemoveAt(int index);
public void Clear();
public bool ContainsKey(TK key);
public bool ContainsValue(TV val);
public int IndexOfKey(TK key);
public int IndexOfValue(TV value);
public bool TryGetValue(TK key, out TV value);
}
SortedDictionary<TKey, TValue>:按键排序的键/值对集合
SortedDictionary<TK, TV>通过TreeSet<T>实现,TreeSet<T>继承SortedSet<T>,SortedSet<T>是红黑树实现,不支持索引、具有O(logN)检索的二进制搜索树。类型安全、非线程安全。
原理实现
SortedDictionary<TK, TV>内部维护一个TreeSet<T>变量(结点类型是KeyValuePair<TK, TV>):
private TreeSet<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> _set;
C#-SortedDictionary<TK, TV>类代码
public class SortedDictionary<TK, TV> : IDictionary<TK, TV>, ICollection<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>>, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>>, IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public SortedDictionary<TK, TV>.KeyCollection Keys { get; }
public SortedDictionary<TK, TV>.ValueCollection Values { get; }
public TValue this[TKey key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public IComparer<TK> Comparer { get; } // 比较器
public SortedDictionary();
public SortedDictionary(IDictionary<TK, TV> dictionary);
public SortedDictionary(IComparer<TK> comparer);
public void Add(TK key, TV value);
public bool Remove(TK key);
public void Clear();
public bool ContainsKey(TK key);
public bool ContainsValue(TV value);
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value);
public void CopyTo(KeyValuePair<TK, TV>[] array, int index);
public SortedDictionary<TK, TV>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>>, IDisposable, IDictionaryEnumerator, IEnumerator {}
public sealed class KeyCollection : ICollection<TK>, IEnumerable<TK>, ICollection, IEnumerable {}
public sealed class ValueCollection : ICollection<TV>, IEnumerable<TV>, ICollection, IEnumerable {}
}
参考:SortedList 和 SortedDictionary 集合类型 - msdn;
字典集其他部分:System.Collections.Specialized
ListDictionary、HybridDictionary、OrderedDictionary三个类均实现了IDictionary接口、支持键值访问,StringDictionary仅实现了IEnumerable接口、但是支持键值访问。
ListDictionary:使用单链接列表实现IDictionary,适于小集合(<10)
本质是链表实现、支持键值访问。链表插入/删除方便,节省内存空间、不存在空间浪费的问题,但是Add()方法需要遍历链表、效率低。对于小集合,ListDictionary比Hashtable快。
原理实现
ListDictionary内部维护一个单链表:
private ListDictionary.DictionaryNode head; // 单链表头指针
ListDictionary不存在二次扩容的问题,但是ListDictionary在添加新数据时,Add()方法要遍历链表(找到尾结点):
C# - ListDictionary类代码
public class ListDictionary : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public object SyncRoot { get; }
public ICollection Keys { get; }
public ICollection Values { get; }
public object this[object key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public ListDictionary();
public ListDictionary(IComparer comparer);
public void Add(object key, object value);
public void Remove(object key);
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(object key);
public void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
其中,单链表结点DictionaryNode
private class DictionaryNode{
public object key;
public object value;
public ListDictionary.DictionaryNode next;
}
HybridDictionary:集合较小时,使用ListDictionary实现IDictionary,集合变大时,切换到Hashtable
支持键值访问。结合了ListDictionary(占用内存空间少)和Hashtable(查询效率高)的优点。
原理实现
HybridDictionary在内部维护一个ListDictionary链表和一个Hashtable变量:
private ListDictionary list;
private ListDictionary List {
get {
if (this.list == null)
this.list = new ListDictionary(this.caseInsensitive ? StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase : null);
return this.list;
}
}
private Hashtable hashtable;
private const int FixedSizeCutoverPoint = 6; // 初始化判定
private const int CutoverPoint = 9; // 运行时判定(ListDictionary -> Hashtable)
private const int InitialHashtableSize = 13;
初始化HybridDictionary:(如果初始initialSize >= 6,直接初始化Hashtable)

HybridDictionary运行中,ListDictionary到Hashtable的转变:
HybridDictionary扩容:内置Hashtable变量,必然存在二次扩容问题,具体见Hashtable。
C# - HybridDictionary类代码
public class HybridDictionary : IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public object SyncRoot { get; }
public ICollection Keys { get; }
public ICollection Values { get; }
public object this[object key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public HybridDictionary([int initSize, bool caseInsensitive]);
public void Add(object key, object value);
public void Remove(object key);
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(object key);
public void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
OrderedDictionary:表示支持键或索引访问的键/值对的集合
本质是哈希表 + 数组实现,支持键值访问和索引访问。
原理实现
OrderedDictionary内部维护一个ArrayList和一个Hashtable,增删改查均保持ArrayList和Hashtable的同步
private ArrayList _objectsArray;
private ArrayList objectsArray {
get {
if (this._objectsArray == null)
this._objectsArray = new ArrayList(this._initialCapacity);
return this._objectsArray;
}
}
private Hashtable _objectsTable;
private Hashtable objectsTable {
get {
if (this._objectsTable == null)
this._objectsTable = new Hashtable(this._initialCapacity, this._comparer);
return this._objectsTable;
}
}
private int _initialCapacity;
初始化OrderedDictionary:
OrderedDictionary扩容:参见ArrayList和Hashtable。
C# - OrderedDictionary类代码
public class OrderedDictionary : IOrderedDictionary, IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public ICollection Keys { get; }
public ICollection Values { get; }
public object this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引访问器
public object this[object key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public virtual IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public OrderedDictionary([int capacity, IEqualityComparer cmp]);
public OrderedDictionary AsReadOnly();
public void Add(object key, object value);
public void Insert(int index, object key, object value);
public void Remove(object key);
public void RemoveAt(int index);
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(object key);
public void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
StringDictionary:将键和值强类型化为字符串而不是对象来实现哈希表
本质是哈希表实现、支持键值访问。
原理实现
StringDictionary内部维护一个Hashtable,支持Hashtable的默认初始化:
internal Hashtable contents = new Hashtable();
初始化StringDictionary和StringDictionary扩容:参见Hashtable。
C# - StringDictionary类代码
public class StringDictionary : IEnumerable {
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public virtual ICollection Keys { get; }
public virtual ICollection Values { get; }
public virtual string this[string key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public virtual IEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public StringDictionary();
public virtual void Add(string key, string value);
public virtual void Remove(string key);
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool ContainsKey(string key);
public virtual bool ContainsValue(string value);
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
字典集小结:

从时间复杂度看,查找耗时:
- Hashtable、Dictionary<T, V>、OrderedDictionary:O(1)
- SortList、SortList<T, V>、SortedDictionary<T, V>:O(logN)
- ListDictinary:O(N)
参考:C#集合--Dictionary;
System.Collections.Specialized其他部分
StringCollection:表示字符串的强类型化集合
本质是ArrayList、支持索引访问。
原理实现
StringCollection内部维护一个ArrayList:
private ArrayList data = new ArrayList();
初始化StringCollection和StringCollection扩容:参见ArrayList。
C# - StringCollection类代码
public class StringCollection : IList, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsReadOnly { get; }
public bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public object SyncRoot { get; }
public string this[int index] { get; set; } // 索引访问器
public StringEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public StringCollection();
public int Add(string value);
public void AddRange(string[] value);
public void Insert(int index, string value);
public void Remove(string value);
public void RemoveAt(int index);
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(string value);
public int IndexOf(string value);
public void CopyTo(string[] array, int index);
}
其中,StringEnumerator支持在StringCollection上进行简单迭代
public class StringEnumerator {
public string Current { get; }
public bool MoveNext();
public void Reset();
}
NameValueCollection:表示可通过键或索引访问的键(String)和值(String)的集合
本质是哈希表,一个键、多个值,支持索引访问和键值访问。
原理实现
NameValueCollection通过父类NameObjectCollectionBase内部维护的一个ArrayList和一个Hashtable实现字典集功能:
// System.Collections.Specialized.NameObjectCollectionBase private ArrayList _entriesArray; // 保存所有的键值对(NameObjectEntry类型) private volatile Hashtable _entriesTable; // Hashtable的常规运用
其中,NameObjectEntry定义结点:
internal class NameObjectEntry{
internal string Key;
internal object Value;
internal NameObjectEntry(string name, object value){
this.Key = name; this.Value = value;
}
}
NameValueCollection扩容:参见ArrayList和Hashtable。
C# - NameValueCollection类代码
public class NameValueCollection : NameObjectCollectionBase {
public virtual string[] AllKeys { get; }
public string this[int index] { get; } // 索引访问器
public string this[string name] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public void Add(NameValueCollection c);
public virtual void Add(string name, string value);
public virtual void Remove(string name);
public virtual void Clear();
public bool HasKeys();
public virtual string Get(int index);
public virtual string Get(string name);
public virtual void Set(string name, string value);
public virtual string GetKey(int index);
public virtual string[] GetValues(int index);
public virtual string[] GetValues(string name);
public void CopyTo(Array dest, int index);
}
KeyedCollection<TKey, TItem>:提供集合的键嵌入在值中的集合的抽象基类
支持键值(项)访问。内部维护一个Dictionary<TK, TI>字典集:
private Dictionary<TKey, TItem> dict;
下面部分是集合类的其余部分:

链表:LinkedList
LinkedList:表示双向链表
本质是链表实现、支持键值访问。插入非常灵活:四种位置,两种模式,支持“从前往后”和“从后往前”双向查找。
原理实现
LinkedList内部维护一个双向链表:
internal LinkedListNode<T> head; // 双向链表头结点
链表实现,不存在二次扩容的问题。
C# - LinkedList类代码
public class LinkedList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback {
public int Count { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> First/Last { get; } // 首尾结点
public LinkedList<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public LinkedList();
public LinkedList(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void AddAfter/Before(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode);
public LinkedListNode<T> AddAfter/Before(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value);
public void AddFirst/Last(LinkedListNode<T> node);
public LinkedListNode<T> AddFirst/Last(T value);
public void Remove(LinkedListNode<T> node);
public bool Remove(T value);
public void RemoveFirst/Last();
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(T value);
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
public LinkedListNode<T> Find(T value);
public LinkedListNode<T> FindLast(T value);
}
其中,LinkedListNode表示结点:
public sealed class LinkedListNode<T> {
public LinkedListNode(T value);
public LinkedListNode<T> Next { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Previous { get; }
public T Value { get; set; } // 结点包含的值
public LinkedList<T> List { get; } // 结点所属的链表
}
参考:.net集合类的研究--链表—ListDictionary,LinkedList<T>;
栈:Stack - Stack<T>
Stack:对象的后进先出(LIFO)非泛型集合
原理实现
Stack内部维护一个数组:
private object[] _array; private const int _defaultCapacity = 10;
初始化Stack:
Stack扩容:存在二倍扩容问题。
C# - Stack类代码
public class Stack : ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public Stack();
public Stack(int initCapacity);
public Stack(ICollection col);
public virtual object Clone(); // 浅表副本
public static Stack Synchronized(Stack stack);
public virtual IEnumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public virtual object Peek();
public virtual void Push(object obj);
public virtual object Pop();
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(object obj);
public virtual object[] ToArray();
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
}
Stack<T>:大小可变的后进先出 (LIFO) 泛型集合,存储同一类型的任意实例
原理实现
Stack<T>内部维护一个数组:
private T[] _array; private static T[] _emptyArray = new T[0]; private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
初始化Stack<T>:

Stack<T>扩容(入栈):

C# - Stack<T>类代码
public class Stack<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public Stack();
public Stack(int capacity);
public Stack(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public T Peek();
public void Push(T item);
public T Pop();
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(T item);
public T[] ToArray();
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex);
public Stack<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator {}
}
队列:Queue - Queue<T>
Queue:对象的先进先出(FIFO)非泛型集合
原理实现
Queue内部维护一个数组:
private object[] _array;
private int _growFactor; // 增长因子
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4;
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32;
public Queue() : this(32, 2f) {}
初始化Queue:
Queue扩容:存在二倍扩容问题。
C# - Queue类代码
public class Queue : ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable {
public virtual int Count { get; }
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
public Queue();
public Queue(int capacity);
public Queue(ICollection col);
public virtual object Clone();
public static Queue Synchronized(Queue queue);
public virtual IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
public virtual object Peek();
public virtual void Enqueue(object obj);
public virtual object Dequeue();
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(object obj);
public virtual void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
public virtual object[] ToArray();
}
Queue<T>:对象的先进先出(FIFO)泛型集合
原理实现
Queue<T>内部维护一个数组:
private T[] _array; private const int _GrowFactor = 200; private const int _MinimumGrow = 4; private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32; // 未用到 private static T[] _emptyArray = new T[0]; // 用于初始化数组 private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4;
初始化Queue<T>:

Queue<T>扩容(入队):
C# - Queue类代码
public class Queue<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public Queue();
public Queue(int capacity);
public Queue(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public T Peek();
public void Enqueue(T item);
public T Dequeue();
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(T item);
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex);
public T[] ToArray();
public Queue<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator {}
}
Set集合:HashSet<T> - SortedSet<T>
ISet<T>:提供用于集合的抽象化的基接口
public interface ISet<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable {
bool Add(T item);
bool Overlaps(IEnumerable<T> other); // 重叠(是否有交集)
bool SetEquals(IEnumerable<T> other); // 相等
// 修改当前集合
void UnionWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // 并集
void IntersectWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // 交集
void ExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // 差集
void SymmetricExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // 并集 - 交集
}
HashSet<T>和SortedSet<T>均实现ISet<T>接口,用于唯一项、不允许重复元素(若添加重复元素,Add()方法返回false,而Hashtable/Dictionary<TK,TV>会直接抛出异常),支持交集、并集、差集等运算,但Set集合不支持键值访问、也不支持索引访问。
HashSet<T>:表示值的集合
本质是哈希表,但不支持键值访问、也不支持索引访问。
参考:.net集合类的研究--哈希表(二)--HashSet<T>;
.NET 3.5 新增,“哈希集合”,与Dictionary<TK,TV>采用相同的存储方式和哈希冲突算法,查找速度快O(1)。
原理实现
HashSet<T>内部维护两个数组:一个常规数组m_buckets和一个Slot类型的数组变量,Slot是一个结构,用来保存Value、哈希值和指针:
private int[] m_buckets; private HashSet<T>.Slot[] m_slots;
其中,Slot结构类型定义
internal struct Slot{
internal int hashCode;
internal T value;
internal int next;
}
初始化HashSet<T>:
HashSet<T>扩容:具体问题参见Dictionary<TK, TV>。
C# - HashSet<T>类代码
public class HashSet<T> : ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback, ISet<T>, ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public IEqualityComparer<T> Comparer { get; } // 相等比较器
// 未指定相等比较器IEqualityComparer<T>的HashSet<T>,使用集合类型默认的相等比较器
public HashSet();
public HashSet(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public HashSet(IEqualityComparer<T> comparer);
public bool Add(T item);
public bool Remove(T item);
public int RemoveWhere(Predicate<T> match); // 支持函数式编程,Lambda表达式
public void Clear();
public bool Contains(T item);
public void CopyTo(T[] array [, int arrayIdx, int cnt]);
public bool Overlaps(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool SetEquals(IEnumerable<T> other);
public void IntersectWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public void UnionWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public void ExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public HashSet<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator {}
}
SortedSet<T>:表示值的有序集合
本质是红黑树实现,不支持键值访问、也不支持索引访问。
.NET 4.0 新增,有序的Set集合。
原理实现
SortedSet<T>内部维护一棵红黑树:
private SortedSet<T>.Node root;
其中,红黑树结点定义
internal class Node{
public bool IsRed;
public T Item;
public SortedSet<T>.Node Left;
public SortedSet<T>.Node Right;
public Node(T item){
this.Item = item; this.IsRed = true;
}
public Node(T item, bool isRed){
this.Item = item; this.IsRed = isRed;
}
}
C# - SortSet<T>类代码
public class SortedSet<T> : ISet<T>, ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback {
public int Count { get; }
public T Max { get; }
public T Min { get; }
public IComparer<T> Comparer { get; } // 比较器
public SortedSet();
public SortedSet(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public SortedSet(IComparer<T> comparer);
public bool Add(T item);
public bool Remove(T item);
public int RemoveWhere(Predicate<T> match); // 函数式编程
public virtual void Clear();
public virtual bool Contains(T item);
public void CopyTo(T[] array [, int idx, int cnt]);
public bool Overlaps(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool SetEquals(IEnumerable<T> other);
public virtual void IntersectWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public void UnionWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public void ExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other);
public virtual SortedSet<T> GetViewBetween(T lowerValue, T upperValue); // 子集合的视图
public IEnumerable<T> Reverse(); // 返回一个逆序访问SortedSet<T>的枚举器
public SortedSet<T>.Enumerator GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback {}
}
线程安全集合:ConcurrentXxx
.NET-4.0之前,线程安全性通过Synchronized()方法实现,对每个添加或移除操作锁定整个集合,导致每个尝试访问集合的线程必须一直等待,直到轮到它来获取锁,无法伸缩、性能低。
.NET-4.0提供新的线程安全和扩展的并发集合,能解决潜在的死锁问题和竞争条件问题,使集合尽可能减少需要使用锁的次数、优化为最佳性能,避免产生不必要的同步开销。命名空间System.Collections.Concurrent包含多个线程安全、可伸缩的集合类,5种新的集合类型专用于为多线程安全高效地添加和移除操作提供支持,其中,ConcurrentStack<T>和ConcurrentQueue<T>是完全无锁的,通过System.Threading.Interlocked操作实现线程安全性。
- Allows for multiple readers in a lock, and then once a writer grabs the lock it blocks all further readers until the writer is done.

参考
- 线程安全集合 - msdn;
- C#/.NET Little Wonders: The ConcurrentStack and ConcurrentQueue;
- C#/.NET Little Wonders: The ConcurrentDictionary;
- C#/.NET Little Wonders: ConcurrentBag and BlockingCollection;
IProducerConsumerCollection<T>:定义供制造者/消费者用来操作线程安全的集合的方法
实现该接口可以实现具有"生产者-消费者"行为的类。
public interface IProducerConsumerCollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
T[] ToArray();
bool TryAdd(T item);
bool TryTake(out T item);
}
ConcurrentStack<T>:线程安全的后进先出 (LIFO) 集合
本质是单链表实现。

原理实现
ConcurrentStack<T>内部维护一个单链表:
private volatile ConcurrentStack<T>.Node m_head; private const int BACKOFF_MAX_YIELDS = 8;
其中结点定义:
private class Node {
internal readonly T m_value;
internal ConcurrentStack<T>.Node m_next;
internal Node(T value) {
this.m_value = value; this.m_next = null;
}
}
Count 与 IsEmpty

C# - ConcurrentStack<T>类代码
public class ConcurrentStack<T> : IProducerConsumerCollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsEmpty { get; }
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public ConcurrentStack();
public ConcurrentStack(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Push(T item);
public void PushRange(T[] items [, int startIdx, int cnt]);
public bool TryPeek(out T result);
public bool TryPop(out T result);
public int TryPopRange(T[] items [, int startIdx, int cnt]);
public void Clear();
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
public T[] ToArray();
}
参考:.Net中的并行编程-2.ConcurrentStack的实现与分析;
ConcurrentQueue<T>:线程安全的先进先出 (FIFO) 集合
本质是数组+链表。

原理实现
ConcurrentQueue<T>采用分段存储的方法,内存分配以段(Segment)为单位,一个段内部含有一个默认长度为32的数组和指向下一个段的指针,内部结构示意图:

ConcurrentQueue<T>内部维护一个Head和Tail指针分别指向起始段和结束段,操作ConcurrentQueue实质是对Segment(数据段)的操作:
private volatile ConcurrentQueue<T>.Segment m_head; // 起始段 private volatile ConcurrentQueue<T>.Segment m_tail; // 结束段 private const int SEGMENT_SIZE = 32; // 段大小
其中,数据段Segment定义:
private class Segment {
internal volatile T[] m_array; // 存储实际数据
internal volatile VolatileBool[] m_state; // 指示该位置是否可用
private volatile ConcurrentQueue<T>.Segment m_next; // 段指针
internal readonly long m_index; //当前段在(数据段)链表中的位置
private volatile int m_low; // m_array的头指针
private volatile int m_high; // m_array的尾指针
private volatile ConcurrentQueue<T> m_source; // 数据段链表(整个队列)
internal Segment(long index, ConcurrentQueue<T> source){
this.m_array = new T[32];
this.m_state = new VolatileBool[32];
this.m_high = -1;
this.m_index = index;
this.m_source = source;
}
}

1 internal ConcurrentQueue.Segment Next{ 2 get{ return this.m_next; } 3 } 4 internal bool IsEmpty{ 5 get{ return this.Low > this.High; } 6 } 7 internal int Low{ 8 get{ return Math.Min(this.m_low, 32); } 9 } 10 internal int High{ 11 get{ return Math.Min(this.m_high, 31); } 12 } 13 14 internal void UnsafeAdd(T value){ 15 this.m_high++; 16 this.m_array[this.m_high] = value; 17 this.m_state[this.m_high].m_value = true; 18 } 19 20 internal ConcurrentQueue.Segment UnsafeGrow(){ 21 ConcurrentQueue.Segment segment = new ConcurrentQueue.Segment(this.m_index + 1L, this.m_source); 22 this.m_next = segment; 23 return segment; 24 } 25 internal void Grow(){ 26 ConcurrentQueue.Segment next = new ConcurrentQueue.Segment(this.m_index + 1L, this.m_source); 27 this.m_next = next; 28 this.m_source.m_tail = this.m_next; 29 } 30 internal bool TryAppend(T value){ 31 if (this.m_high >= 31){ 32 return false; 33 } 34 int num = 32; 35 try{ 36 } 37 finally{ 38 num = Interlocked.Increment(ref this.m_high); 39 if (num <= 31){ 40 this.m_array[num] = value; 41 this.m_state[num].m_value = true; 42 } 43 if (num == 31){ 44 this.Grow(); 45 } 46 } 47 return num <= 31; 48 } 49 internal bool TryRemove(out T result){ 50 SpinWait spinWait = default(SpinWait); 51 int i = this.Low; 52 int high = this.High; 53 while (i <= high) 54 { 55 if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref this.m_low, i + 1, i) == i){ 56 SpinWait spinWait2 = default(SpinWait); 57 while (!this.m_state[i].m_value){ 58 spinWait2.SpinOnce(); 59 } 60 result = this.m_array[i]; 61 if (this.m_source.m_numSnapshotTakers <= 0){ 62 this.m_array[i] = default(T); 63 } 64 if (i + 1 >= 32){ 65 spinWait2 = default(SpinWait); 66 while (this.m_next == null){ 67 spinWait2.SpinOnce(); 68 } 69 this.m_source.m_head = this.m_next; 70 } 71 return true; 72 } 73 spinWait.SpinOnce(); 74 i = this.Low; 75 high = this.High; 76 } 77 result = default(T); 78 return false; 79 } 80 internal bool TryPeek(out T result){ 81 result = default(T); 82 int low = this.Low; 83 if (low > this.High){ 84 return false; 85 } 86 SpinWait spinWait = default(SpinWait); 87 while (!this.m_state[low].m_value){ 88 spinWait.SpinOnce(); 89 } 90 result = this.m_array[low]; 91 return true; 92 } 93 internal void AddToList(List list, int start, int end) 94 for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) 95 { 96 SpinWait spinWait = default(SpinWait); 97 while (!this.m_state[i].m_value){ 98 spinWait.SpinOnce(); 99 } 100 list.Add(this.m_array[i]); 101 } 102 } 103 104 ConcurrentQueue<T>.Segment
初始化ConcurrentQueue<T>:

Count 与 IsEmpty
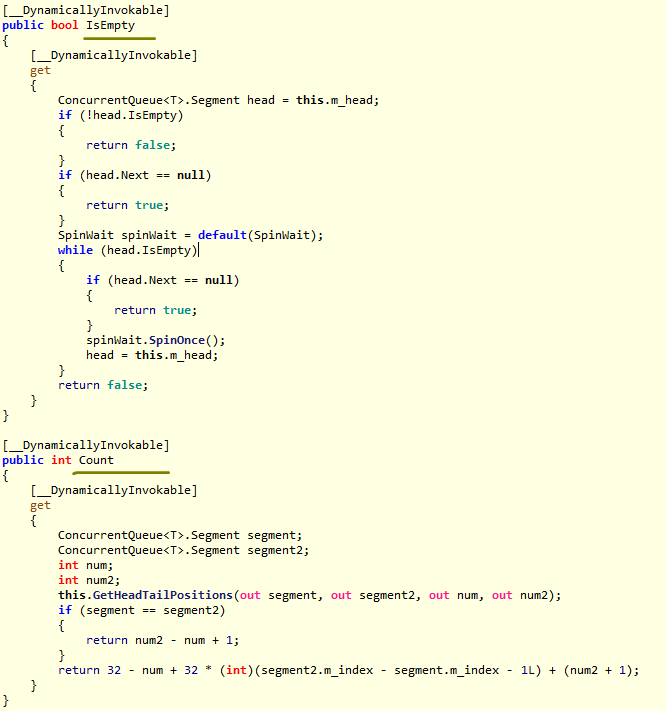
C# - ConcurrentQueue<T>类代码
public class ConcurrentQueue<T> : IProducerConsumerCollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsEmpty { get; }
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public ConcurrentQueue();
public ConcurrentQueue(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Enqueue(T item);
public bool TryDequeue(out T result);
public bool TryPeek(out T result);
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
public T[] ToArray();
}
参考:.Net中的并行编程-3.ConcurrentQueue实现与分析;
ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>:允许多个线程同时访问的线程安全的键值对集合
本质是哈希表(数组+链表)、支持键值访问。

原理实现
ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>的内部类Tables维护一个数组变量m_buckets存储实际数据(内部存储结构类似邻接表):
private volatile ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Tables m_tables;
private const int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 31;
private const int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_MULTIPLIER = 4;
private class Tables{
internal readonly ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>.Node[] m_buckets;
internal readonly object[] m_locks;
internal volatile int[] m_countPerLock;
internal readonly IEqualityComparer<TK> m_comparer; // 比较器
internal Tables(ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>.Node[] buckets, object[] locks, int[] countPerLock, IEqualityComparer<TK> comparer){
this.m_buckets = buckets;
this.m_locks = locks;
this.m_countPerLock = countPerLock;
this.m_comparer = comparer;
}
}
其中,字典集元素Node定义:
private class Node {
internal TKey m_key;
internal TValue m_value;
internal volatile ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node m_next;
internal int m_hashcode;
internal Node(TKey key, TValue value, int hashcode, ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node next){
this.m_key = key;
this.m_value = value;
this.m_next = next;
this.m_hashcode = hashcode;
}
}
初始化ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>:
![]()
插入操作:ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>的TryAdd()方法会调用TryAddInternal()方法添加元素,具体:
其中,num是元素在桶内的位置(GetBucketAndLockNo()方法的bucketNo参数),node是某个链表的尾结点:
ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>扩容:通过GrowTable()方法实现,类似Dictionary<TK, TV>,但是并没有明确重新计算hashcode。
遍历字典集
GetEnumerator() or iterate using a foreach会导致数据脏读(Dirty Read),推荐遍历方法:
foreach ( var item in myConcurrentDic.ToArray() ){
Console.WriteLine(item.Key + ": " + item.Value);
}
C# - ConcurrentDictionary<TK, TV>类代码
public class ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue> : IDictionary<TKey, TValue>, ICollection<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>, IDictionary, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsEmpty { get; }
public ICollection<TK> Keys { get; }
public ICollection<TV> Values { get; }
public TValue this[TKey key] { get; set; } // 键值访问器
public IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>> GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public ConcurrentDictionary();
public ConcurrentDictionary(IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TK, TV>> collection, IEqualityComparer<TK> cmp);
public ConcurrentDictionary(int concurrencyLevel, int capacity); // 并发级别(估计的线程数量)
public bool TryAdd(TKey key, TValue value);
public bool TryRemove(TKey key, out TValue value);
public void Clear();
public bool ContainsKey(TKey key);
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value);
public KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>[] ToArray();
public bool TryUpdate(TKey key, TValue newValue, TValue comparisonValue);
public TValue GetOrAdd(TKey key, TValue value);
public TValue GetOrAdd(TKey key, Func<TKey, TValue> valueFactory);
public TValue AddOrUpdate(TK key, TV addValue, Func<TK, TV, TV> updateValueFactory);
public TValue AddOrUpdate(TK key, Func<TK, TV> addValueFactory, Func<TK, TV, TV> updateValueFactory);
}
参考:.net源码分析 - ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>;
ConcurrentBag<T>:对象的线程安全的无序集合
本质是双向链表。

元素可重复的无序集合,允许为空null:This makes the bag handy for those cases when all you care about is that the data be consumed eventually, without regard for order of consumption or even fairness.
- 在纯生产者-消费者中,ConcurrentBag<T>执行速度可能会比其他并发集合类型的执行速度慢得多;
- 在混合生产者-消费者中,无论是少量工作负荷还是大量工作负荷情况下,ConcurrentBag<T>执行速度会比任何其他并发集合类型更快、可伸缩性更好;
![]()
- Take advantage of the new ThreadLocal<T> type, so that each thread using the bag has a list local to just that thread.
- The work-stealing synchronization would outweigh the thread-local optimization for a thread taking its own items.
原理实现
ConcurrentBag<T>的内部类ThreadLocalList定义一个双向链表(每一个双向链表对应归属一个线程):
internal class ThreadLocalList {
internal Thread m_ownerThread; //当前链表所属的线程
internal volatile ConcurrentBag<T>.Node m_head; // 表头
private volatile ConcurrentBag<T>.Node m_tail; // 表尾
private int m_count; // 当前链表元素数
internal volatile int m_currentOp; // 当前链表在链表池中的位置
internal volatile ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList m_nextList; // 指向下一个链表
internal int m_stealCount;
internal bool m_lockTaken;
}
ConcurrentBag<T>内部维护一个双向链表池:
private ThreadLocal<ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList> m_locals; private volatile ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList m_headList; // 首链表 private volatile ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList m_tailList; // 尾链表
其中,链表节点Node定义:
internal class Node{
public readonly T m_value;
public ConcurrentBag<T>.Node m_next;
public ConcurrentBag<T>.Node m_prev;
public Node(T value){
this.m_value = value;
}
}
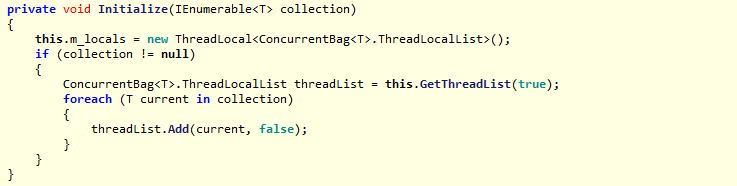
构造函数会调用Initialize()方法初始化ConcurrentBag<T>:
C# - ConcurrentBag<T>类代码
public class ConcurrentBag<T> : IProducerConsumerCollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable {
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsEmpty { get; }
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator(); // 枚举器
public ConcurrentBag();
public ConcurrentBag(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Add(T item);
public bool TryPeek(out T result);
public bool TryTake(out T result);
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
public T[] ToArray();
}
参考:.NET 4.0 and System.Collections.Concurrent.ConcurrentBag;
BlockingCollection<T>:为实现了IProducerConsumerCollection<T>接口的线程安全集合提供阻止和限制功能
对IProducerConsumerCollection<T>接口的实现,适合构建实现基于"生产者-消费者"的应用程序,相当于将一个非阻塞集合转变成一个阻塞集合,与经典的阻塞队列数据结构类似,适用于多个任务对集合添加、删除数据。
![]()
其他:
- 支持可选的最大容量,封装实现IProducerConsumerCollection<T>接口的任何集合类型;
- 在集合为空或已满时发生阻塞的插入和移除操作;
- 计时阻塞操作:不会发生阻塞或只在指定的时间段内发生阻塞的“尝试”插入和移除操作;
- 支持foreach的两类枚举:[1]. 只读枚举(静态,a snapshot of the Collection at the time of the call);[2]. 在枚举项时将项移除的枚举(动态,等待-执行-等待-执行 ...);
注:默认集合类型ConcurrentQueue<T>,Because it is fairly light and maximizes fairness by ordering items so that they are consumed in the same order they are produced.
在需要限制和阻塞语义时,BlockingCollection<T>执行速度可能会比任何自定义实现的执行速度都快。

原理实现
- 添加:多个线程或任务可同时向集合中添加Add项,若集合达到上限容量,则生成线程阻塞、直到集合中的某个项被移除(if a producer creates an item, but there is no space to store it, it must wait until an item is consumed);
- 移除:多个消费者可同时移除Take项,若集合变为空,则消费线程发生阻塞、直到生产者添加某个项(if a consumer goes to consume an item and none exists, it must wait until an item is produced);
方法CompleteAdding()和属性IsCompleted
当使用CompleteAdding()方法后且集合内没有元素时,属性IsCompleted此时会为True,(在生产者-消费者问题中)可用于判断当前集合内的所有元素是否都被处理完。

C# - BlockingCollection<T>类代码
public class BlockingCollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable, IDisposable {
public int BoundedCapacity { get; } // 默认值int.MaxValue
public int Count { get; }
public bool IsAddingCompleted { get; } // 集合是否已被标记为已完成添加
public bool IsCompleted { get; } // 集合是否已被标记为已完成添加并且集合当前为空
// 枚举器:从集合中返回并移除某一项
public IEnumerable<T> GetConsumingEnumerable([CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
// 构造函数(+4 重载)
// collection:用作基础数据存储区的集合,boundedCapacity:上限容量
public BlockingCollection([IProducerConsumerCollection<T> collection, int boundedCapacity]);
public void Add(T item [, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public T Take([CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public bool TryAdd(T item [, int millisecondsTimeout, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public bool TryTake(out T item [, int millisecondsTimeout, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public static int AddToAny(BlockingCollection<T>[] collections, T item [, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public static int TakeFromAny(BlockingCollection<T>[] collections, out T item [, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public static int TryAddToAny(BlockingCollection<T>[] collections, T item [, int millisecondsTimeout, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public static int TryTakeFromAny(BlockingCollection<T>[] collections, out T item [, int millisecondsTimeout, CancellationToken cancellationToken]);
public void CompleteAdding(); // 将BlockingCollection<T>实例标记为不再接受任何添加
public void Dispose(); // 释放BlockingCollection<T>实例占用的资源
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing);
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index);
public T[] ToArray();
}
其中,CancellationToken表示传播有关应取消操作的通知
public struct CancellationToken {
public bool CanBeCanceled { get; } // 标记是否能处于已取消状态
public bool IsCancellationRequested { get; } // 是否已请求取消此标记
public static CancellationToken None { get; } // 返回空CancellationToken值
public WaitHandle WaitHandle { get; } // 获取在取消标记时处于有信号状态的System.Threading.WaitHandle
public CancellationToken(bool canceled);
}
参考:
下面部分是几个易混淆知识点总结:
关于数组
- Array:数组基类,针对任意类型(可以初始化为任意类型、但初始化后类型固定)、固定长度
- []:常规数组,针对特定类型、固定长度
- ArrayList:动态数组,针对任意类型、任意长度
- List<T>:泛型线性表,针对特定类型、任意长度
List<T> 与 Dictionary<K, V>
- List<T>内存中连续存储、遍历效率高,Dictionary<K, V>/HashTable由均Hash算法产生内存地址、遍历效率低、且存储空间耗费代价大;
- List<T>查找元素通过Exists()方法循环查找、效率低,Dictionary<K, V>通过Hash查找、效率高;
参考:Dictionary<T1,T2>和List<T>效率问题;
Dictionary<K, V> 与 Hashtable
- Dictionary<K, V>类型约束新加元素,HashTable可添加任意类型的元素;
- Dictionary<K,V>无须装箱、拆箱操作,HashTable添加时装箱、读取时拆箱(耗时);
- Dictionary<K,V>根据插入顺序来遍历、注重顺序性,HashTable遍历顺序与插入顺序不一致;
- 单线程程序中推荐使用Dictionary<K,V>(泛型优势、类型安全,读取速度快,空间利用充分,但非线程安全、需人为lock锁定、效率低),多线程程序中推荐使用Hashtable(允许单线程写入、多线程读取,Synchronized()方法可获得完全线程安全的类型);
- 从数据结构角度,两者均需要对键值进行散列操作,区别是处理哈希冲突碰撞的方法:Dictionary<K,V>采用链接法(Chaining),Hashtable采用开放寻址法(Open Addressing);
- Hashtable扩容非常耗时,空间占用大、利用率偏低、受填充因子影响大,扩容时所有的数据需要重新进行散列计算,Dictionary<K,V>虽然也有扩容问题、但不需要重新散列;
参考:关于Hashtable与Dictionary性能讨论; 闲话Hashtable与Dictionary之哈希寻址方法;
SortedList/SortedList<K, V> 与 SortedDictionary<K, V>
- 前者通过2个数组实现(检索O(logN)、插入删除O(N)),后者通过红黑树实现(检索插入删除O(logN))、占用存储空间大;
- 前者支持索引、快速检索性能好,后者不支持索引;
- 前者是有序线性表,后者是平衡二叉树;
HashSet<T> 与 SortedSet<T>
- HashSet<T>是无序不重复的Hash集合,SortedSet<T>是有序不重复的Set集合(自动排序);
- HashSet<T>基于哈希的查询、Contains执行非常快速、O(1)增删改查,SortedSet<T>是O(log(N))的增删改查;
集合选择问题分析
参考:



























