实验3 进程运行轨迹的跟踪与统计
3.1 实验目的
- 掌握Linux下的多进程编程技术;
- 通过对进程运行轨迹的跟踪来形象化进程的概念;
- 在进程运行轨迹跟踪的基础上进行相应的数据统计,从而能对进程调度算法进行实际的量化评价,更进一步加深对调度和调度算法的理解,获得能在实际操作系统上对调度算法进行实验数据对比的直接经验。
3.2 实验内容
进程从创建(Linux下调用fork())到结束的整个过程就是进程的生命期,进程在其生命期中的运行轨迹实际上就表现为进程状态的多次切换,如进程创建以后会成为就绪态;当该进程被调度以后会切换到运行态;在运行的过程中如果启动了一个文件读写操作,操作系统会将该进程切换到阻塞态(等待态)从而让出CPU;当文件读写完毕以后,操作系统会在将其切换成就绪态,等待进程调度算法来调度该进程执行……
本次实验包括如下内容:
- 基于模板
process.c编写多进程的样本程序,实现如下功能:- 所有子进程都并行运行,每个子进程的实际运行时间一般不超过 30 秒;
- 父进程向标准输出打印所有子进程的 id ,并在所有子进程都退出后才退出;
- 在Linux0.11上实现进程运行轨迹的跟踪。基本任务是在内核中维护一个日志文件
/var/process.log,把从操作系统启动到系统关机过程中所有进程的运行轨迹都记录在这一log文件中。 - 在修改过的0.11上运行样本程序,通过分析log文件,统计该程序建立的所有进程的等待时间、完成时间(周转时间)和运行时间,然后计算平均等待时间,平均完成时间和吞吐量。可以自己编写统计程序,也可以使用python脚本程序stat_log.py进行统计。
- 修改 0.11 进程调度的时间片,然后再运行同样的样本程序,统计同样的时间数据,和原有的情况对比,体会不同时间片带来的差异。
/var/process.log文件的格式必须为:
pid X time
其中:
pid是进程的ID;X可以是N,J,R,W和E中的任意一个,分别表示进程新建(N)、进入就绪态(J)、进入运行态(R)、进入阻塞态(W)和退出(E);time表示X发生的时间。这个时间不是物理时间,而是系统的滴答时间(tick);
三个字段之间用制表符分隔。例如:
12 N 1056
12 J 1057
4 W 1057
12 R 1057
13 N 1058
13 J 1059
14 N 1059
14 J 1060
15 N 1060
15 J 1061
12 W 1061
15 R 1061
15 J 1076
14 R 1076
14 E 1076
...
3.3 实验问题
3.3.1 结合自己的体会,谈谈从程序设计者的角度看,单进程编程和多进程编程最大的区别是什么?
- 执行方式:单进程是一个进程按设计好的流程从上到下顺序执行,程序设计者需要在该进程内合理安排执行顺序;而多进程是多个进程同时执行的,是并行的(实际上是高速切换着运行这多个进程),程序设计者除了考虑每个进程内的执行顺序,还要合理安排每个进程的流程。
- 数据同步:单进程的数据是同步的,在该进程中改变数据,影响是全局的;而多进程中,子进程数据是父进程数据在内存另一位置的拷贝,是相互独立的,互不影响对父进程数据的操作不会影响子进程数据,子进程同样。
- CPU利用率:单进程在等待io时,cpu是空闲的;因此,CPU利用率低;多进程在某一进程等待io时,通过各种复杂而灵活的调度算法,运行另一个进程,所以CPU利用率高。
- 用途:单进程的用途较为单一,而多进程的用途广泛。
3.3.2你是如何修改时间片的?仅针对样本程序建立的进程,在修改时间片前后,log文件的统计结果(不包括Graphic)都是什么样?结合你的修改分析一下为什么会这样变化,或者为什么没变化?
- 修改include/linux/sched.h/INIT_TASK中的priority就可以改变时间片大小。变化不大的原因是,子进程连续占用cpu的时间要比时间片大很多。
- 将时间设置在不同的量之后,通过使用程序对得到的log进行分析可以发现:
a. 在一定的范围内,平均等待时间,平均完成时间的变化随着时间片的增大而减小。这是因为在时间片小的情况下,cpu将时间耗费在调度切换上,所以平均等待时间增加。
b. 超过一定的范围之后,这些参数将不再有明显的变化,这是因为在这种情况下,RR轮转调度会变成FCFS先来先服务。随着时间片的修改,吞吐量始终没有明显的变化,这是因为在单位时间内,系统所能完成的进程数量是不会变的。
3.4 实验过程
3.4.1 process.c文件
这个文件按照老师在网站上所给出的提示,可以写成5种甚至更多的状态,在这里只需按照老师给出的几种状态调用就可以了,本实验的难点不在这个地方。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/times.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define HZ 100
void cpuio_bound(int last, int cpu_time, int io_time);
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
pid_t p1, p2, p3, p4, p5;
if((p1 = fork())==0 )
{
printf("child:[%d] parent:[%d]
",getpid(),getppid());cpuio_bound(10, 0, 1);
//以IO为主要任务,只要cpu_time = 0,io_time < 0
}
else if((p2 = fork())==0)
{
printf("child:[%d] parent:[%d]
",getpid(),getppid());cpuio_bound(10, 1, 0);
//占用10s的cpu时间只要cpu_time > 0,io_time = 0
}
else if((p3 = fork())==0)
{
printf("child:[%d] parent:[%d]
",getpid(),getppid());cpuio_bound(10, 1, 1);
//CPU和I/O各1s轮回
}
else if((p4 = fork())==0)
{
printf("child:[%d] parent:[%d]
",getpid(),getppid());cpuio_bound(10, 1, 9);
//较多的I/O,较少的CPU
}
else if((p5 = fork())==0)
{
printf("child:[%d] parent:[%d]
",getpid(),getppid());cpuio_bound(10, 9, 1);
//较少的I/O,较多的CPU
}
else
{
printf("Pid list :
");
printf("Parent is %d
",getpid());
printf("Child1 is %d
",p1);
printf("Child2 is %d
",p2);
printf("Child3 is %d
",p3);
printf("Child4 is %d
",p4);
printf("Child5 is %d
",p5);
}
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}
/*
* 此函数按照参数占用CPU和I/O时间
* last: 函数实际占用CPU和I/O的总时间,不含在就绪队列中的时间,>=0是必须的
* cpu_time: 一次连续占用CPU的时间,>=0是必须的
* io_time: 一次I/O消耗的时间,>=0是必须的
* 如果last > cpu_time + io_time,则往复多次占用CPU和I/O
* 所有时间的单位为秒
*/
void cpuio_bound(int last, int cpu_time, int io_time)
{
struct tms start_time, current_time;
clock_t utime, stime;
int sleep_time;
while (last > 0)
{
/* CPU Burst */
times(&start_time);
/* 其实只有t.tms_utime才是真正的CPU时间。但我们是在模拟一个
* 只在用户状态运行的CPU大户,就像“for(;;);”。所以把t.tms_stime
* 加上很合理。*/
do
{
times(¤t_time);
utime = current_time.tms_utime - start_time.tms_utime;
stime = current_time.tms_stime - start_time.tms_stime;
} while ( ( (utime + stime) / HZ ) < cpu_time );
last -= cpu_time;
if (last <= 0 )
break;
/* IO Burst */
/* 用sleep(1)模拟1秒钟的I/O操作 */
sleep_time=0;
while (sleep_time < io_time)
{
sleep(1);
sleep_time++;
}
last -= sleep_time;
}
}
3.4.2 fork.c
由于创建新的进程需要调用的函数是fork(),在文件kernel/system_call.s中,发现主要创建进程的函数就是copy_process(),因此需要对这个函数进行修改。根据《注释》的内容进行修改。
int copy_process(int nr,long ebp,long edi,long esi,long gs,long none,
long ebx,long ecx,long edx,
long fs,long es,long ds,
long eip,long cs,long eflags,long esp,long ss)
{
struct task_struct *p;
int i;
struct file *f;
p = (struct task_struct *) get_free_page();
if (!p)
return -EAGAIN;
task[nr] = p;
*p = *current; /* NOTE! this doesn't copy the supervisor stack */
//fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",last_pid,'N',jiffies);
...
p->leader = 0; /* process leadership doesn't inherit */
p->utime = p->stime = 0;
p->cutime = p->cstime = 0;
p->start_time = jiffies;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",last_pid,'N',jiffies);
...
p->state = TASK_RUNNING; /* do this last, just in case */
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",last_pid,'J',jiffies);
return last_pid;
}
个人认为新建一个任务可以认为是给新的任务分配内存就代表了任务已经被创建,因此第一个位置可以加入输出为N的日志,根据《注释》中的内容,第二个输出N的位置,是在完成对任务的进程结构重构结束后,正式代表任务已经被创建,后边的内容是修改TSS中的内容而不是对任务本身进行修改,因此在此处增加新建的日志也可以,这个位置可以有不同的想法。当对新任务创建过程结束以及在操作系统中完成了所有的调度操作后,任务进入了就绪态,因此在这个时候可以输出就绪的日志。
3.4.3 sched.c文件
根据不同的转换过程,修改sched.c的不同位置。
3.4.3.1 就绪与运行-schedule()函数
schedule()是执行调度算法的函数,在这个函数中针对任务数组的每个任务检查alarm值,如果alarm时间过期,则在这个任务的信号位图中设置为SGIALRM。如果任务数组中没有任务,则运行进程0,进程0是唯一一个不管是什么状态均可以运行的进程。因为系统中不可能会出现一个进程也没有的情况,否则系统无法运行。而进程0也不会退出。第一处日志需要修改的位置是在任务处于可中断睡眠状态下被修改为就绪状态的地方,此时增加一个就绪内容的日志。第二处及第三处日志修改在切换调度之前,在完成调度过程后,有一个任务要进入就绪状态,而另一个任务要进入运行状态。根据当前任务的状态,可以判断出当前进程是时间片到期还是主动让出CPU后进入就绪状态的。修改的内容如下:
void schedule(void)
{
int i,next,c;
struct task_struct ** p;
/* check alarm, wake up any interruptible tasks that have got a signal */
for(p = &LAST_TASK ; p > &FIRST_TASK ; --p)
if (*p) {
if ((*p)->alarm && (*p)->alarm < jiffies) {
(*p)->signal |= (1<<(SIGALRM-1));
(*p)->alarm = 0;
}
if (((*p)->signal & ~(_BLOCKABLE & (*p)->blocked)) &&
(*p)->state==TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE)
{
(*p)->state=TASK_RUNNING;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",(*p)->pid,'J',jiffies);
}
}
/* this is the scheduler proper: */
while (1) {
c = -1;
next = 0;
i = NR_TASKS;
p = &task[NR_TASKS];
while (--i) {
if (!*--p)
continue;
if ((*p)->state == TASK_RUNNING && (*p)->counter > c)
c = (*p)->counter, next = i;
}
if (c) break;
for(p = &LAST_TASK ; p > &FIRST_TASK ; --p)
if (*p)
(*p)->counter = ((*p)->counter >> 1) +
(*p)->priority;
}
if(current->pid != task[next] ->pid)
{
if(current->state == TASK_RUNNING)
fprintk(3,"%d J %d
",current->pid,jiffies);
fprintk(3,"%d R %d
",task[next]->pid,jiffies);
}
switch_to(next);
}
3.4.3.2 运行到睡眠-sleep_on()/interruptible_sleep_on()/sys_pause()函数
sleep_on()/interruptible_sleep_on(),这两个函数的作用是将暂时无法运行的进程切换到阻塞态,并将该进程的task_struct添加到等待队列中。其中sleep_on()函数只能通过wake_up()函数进行唤醒;而interruptible_sleep_on()可以通过信号、任务超时等手段唤醒。
因此只需在执行这两个函数的时候增加记录为睡眠的语句即可。
void sleep_on(struct task_struct **p)
{
struct task_struct *tmp;
if (!p)
return;
if (current == &(init_task.task))
panic("task[0] trying to sleep");
tmp = *p;
*p = current;
current->state = TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",current->pid,'W',jiffies);
schedule();
if (tmp)
{
tmp->state=0;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",tmp->pid,'J',jiffies);
}
}
void interruptible_sleep_on(struct task_struct **p)
{
struct task_struct *tmp;
if (!p)
return;
if (current == &(init_task.task))
panic("task[0] trying to sleep");
tmp=*p;
*p=current;
repeat: current->state = TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",current->pid,'W',jiffies);
schedule();
if (*p && *p != current) {
(**p).state=TASK_RUNNING;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",(**p).pid,'J',jiffies);
goto repeat;
}
*p=tmp;
if (tmp)
{
tmp->state=TASK_RUNNING;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",tmp->pid,'J',jiffies);
}
}
sys_pause()/sys_waitpid()这两个函数用于在不同情况下,让进程进入睡眠状态,因此需要在这两个函数中增加睡眠信息的日志。sys_waitpid()位于exit.c中。
int sys_pause(void)
{
current->state = TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
if (current->pid != 0)
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",current->pid,'W',jiffies);
schedule();
return 0;
}
3.4.3.3 睡眠与就绪-wake_up()函数
该函数用来唤醒等待的进程,主要是被sleep_on()函数导致睡眠的进程。
void wake_up(struct task_struct **p)
{
if (p && *p) {
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",(**p).pid,'J',jiffies);
(**p).state=0;
*p=NULL;
}
}
3.4.4 exit.c文件
该文件的主要目的是修改sys_waitpid()函数以及do_exit()函数,前一个函数与sys_pause()功能类似,而后一个函数用于退出进程,因此需要输出关于推出的日志信息。
修改内容如下所示:
int sys_waitpid(pid_t pid,unsigned long * stat_addr, int options)
{
int flag, code;
struct task_struct ** p;
verify_area(stat_addr,4);
repeat:
flag=0;
for(p = &LAST_TASK ; p > &FIRST_TASK ; --p) {
if (!*p || *p == current)
continue;
if ((*p)->father != current->pid)
continue;
if (pid>0) {
if ((*p)->pid != pid)
continue;
} else if (!pid) {
if ((*p)->pgrp != current->pgrp)
continue;
} else if (pid != -1) {
if ((*p)->pgrp != -pid)
continue;
}
switch ((*p)->state) {
case TASK_STOPPED:
if (!(options & WUNTRACED))
continue;
put_fs_long(0x7f,stat_addr);
return (*p)->pid;
case TASK_ZOMBIE:
current->cutime += (*p)->utime;
current->cstime += (*p)->stime;
flag = (*p)->pid;
code = (*p)->exit_code;
//fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",flag,'E',jiffies);
release(*p);
put_fs_long(code,stat_addr);
return flag;
default:
flag=1;
continue;
}
}
if (flag) {
if (options & WNOHANG)
return 0;
current->state=TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",current->pid,'W',jiffies);
schedule();
if (!(current->signal &= ~(1<<(SIGCHLD-1))))
goto repeat;
else
return -EINTR;
}
return -ECHILD;
}
int do_exit(long code)
{
int i;
free_page_tables(get_base(current->ldt[1]),get_limit(0x0f));
free_page_tables(get_base(current->ldt[2]),get_limit(0x17));
for (i=0 ; i<NR_TASKS ; i++)
if (task[i] && task[i]->father == current->pid) {
task[i]->father = 1;
if (task[i]->state == TASK_ZOMBIE)
/* assumption task[1] is always init */
(void) send_sig(SIGCHLD, task[1], 1);
}
for (i=0 ; i<NR_OPEN ; i++)
if (current->filp[i])
sys_close(i);
iput(current->pwd);
current->pwd=NULL;
iput(current->root);
current->root=NULL;
iput(current->executable);
current->executable=NULL;
if (current->leader && current->tty >= 0)
tty_table[current->tty].pgrp = 0;
if (last_task_used_math == current)
last_task_used_math = NULL;
if (current->leader)
kill_session();
current->state = TASK_ZOMBIE;
fprintk(3,"%ld %c %ld
",current->pid,'E',jiffies);
current->exit_code = code;
tell_father(current->father);
schedule();
return (-1); /* just to suppress warnings */
}
其中,退出日志个人认为可以有两个位置可以写。首先是在do_exit()中,就是上述代码中的位置,在设置为僵尸进程之后,进程就会被结束,此时说明确实是退出了进程。另一个位置是sys_waitpid()的位置,由于在这个函数中对于僵尸进程所在的内存进行了释放处理,因此在释放处理的位置也代表了进程结束的信息。因此个人认为这个位置有两种写法。
3.4.5 main.c文件
根据老师所给出的提示信息对main.c进行修改即可。
...
move_to_user_mode();
/***************添加开始***************/
setup((void *) &drive_info);
(void) open("/dev/tty0",O_RDWR,0); //建立文件描述符0和/dev/tty0的关联
(void) dup(0); //文件描述符1也和/dev/tty0关联
(void) dup(0); //文件描述符2也和/dev/tty0关联
(void) open("/var/process.log",O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY,0666);
/***************添加结束***************/
if (!fork()) { /* we count on this going ok */
init();
}
...
3.4.6 修改时间分片
修改位于/include/sched.h中的
#define HZ xxx
#define INIT_TASK
{ 0,15,15, //分别对应state;counter;和priority;
中的任何一个就可以达到修改时间分片的效果,这里使用的是修改priority。得到的三次结果如下。
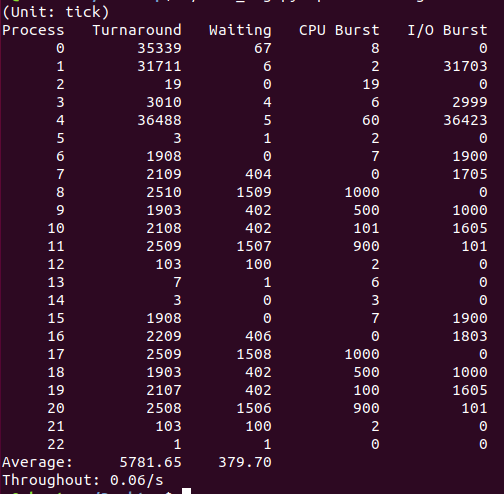
- 15:
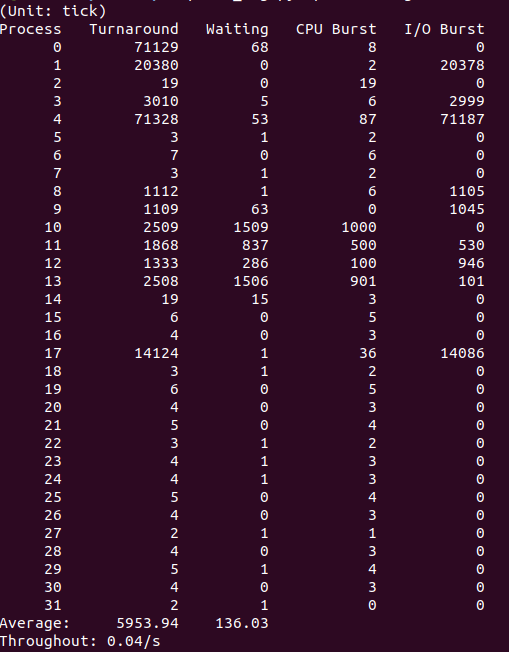
- 20:
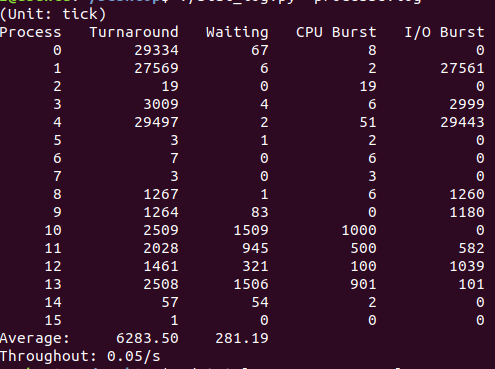
- 100: