From WIKI:
Random sample consensus (RANSAC) is an iterative method to estimate parameters of a mathematical model from a set of observed data that contains outliers, when outliers are to be accorded no influence on the values of the estimates. Therefore, it also can be interpreted as an outlier detection method.[1] It is a non-deterministic algorithm in the sense that it produces a reasonable result only with a certain probability, with this probability increasing as more iterations are allowed. The algorithm was first published by Fischler and Bolles at SRI International in 1981. They used RANSAC to solve the Location Determination Problem (LDP), where the goal is to determine the points in the space that project onto an image into a set of landmarks with known locations.
A basic assumption is that the data consists of "inliers", i.e., data whose distribution can be explained by some set of model parameters, though may be subject to noise, and "outliers" which are data that do not fit the model. The outliers can come, for example, from extreme values of the noise or from erroneous measurements or incorrect hypotheses about the interpretation of data. RANSAC also assumes that, given a (usually small) set of inliers, there exists a procedure which can estimate the parameters of a model that optimally explains or fits this data.
伪代码:
1 Given: 2 data – a set of observations 3 model – a model to explain observed data points 4 n – minimum number of data points required to estimate model parameters 5 k – maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm 6 t – threshold value to determine data points that are fit well by model 7 d – number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data 8 9 Return: 10 bestFit – model parameters which best fit the data (or nul if no good model is found) 11 12 iterations = 0 13 bestFit = nul 14 bestErr = something really large 15 while iterations < k { 16 maybeInliers = n randomly selected values from data 17 maybeModel = model parameters fitted to maybeInliers 18 alsoInliers = empty set 19 for every point in data not in maybeInliers { 20 if point fits maybeModel with an error smaller than t 21 add point to alsoInliers 22 } 23 if the number of elements in alsoInliers is > d { 24 % this implies that we may have found a good model 25 % now test how good it is 26 betterModel = model parameters fitted to all points in maybeInliers and alsoInliers 27 thisErr = a measure of how well betterModel fits these points 28 if thisErr < bestErr { 29 bestFit = betterModel 30 bestErr = thisErr 31 } 32 } 33 increment iterations 34 } 35 return bestFit
图解:
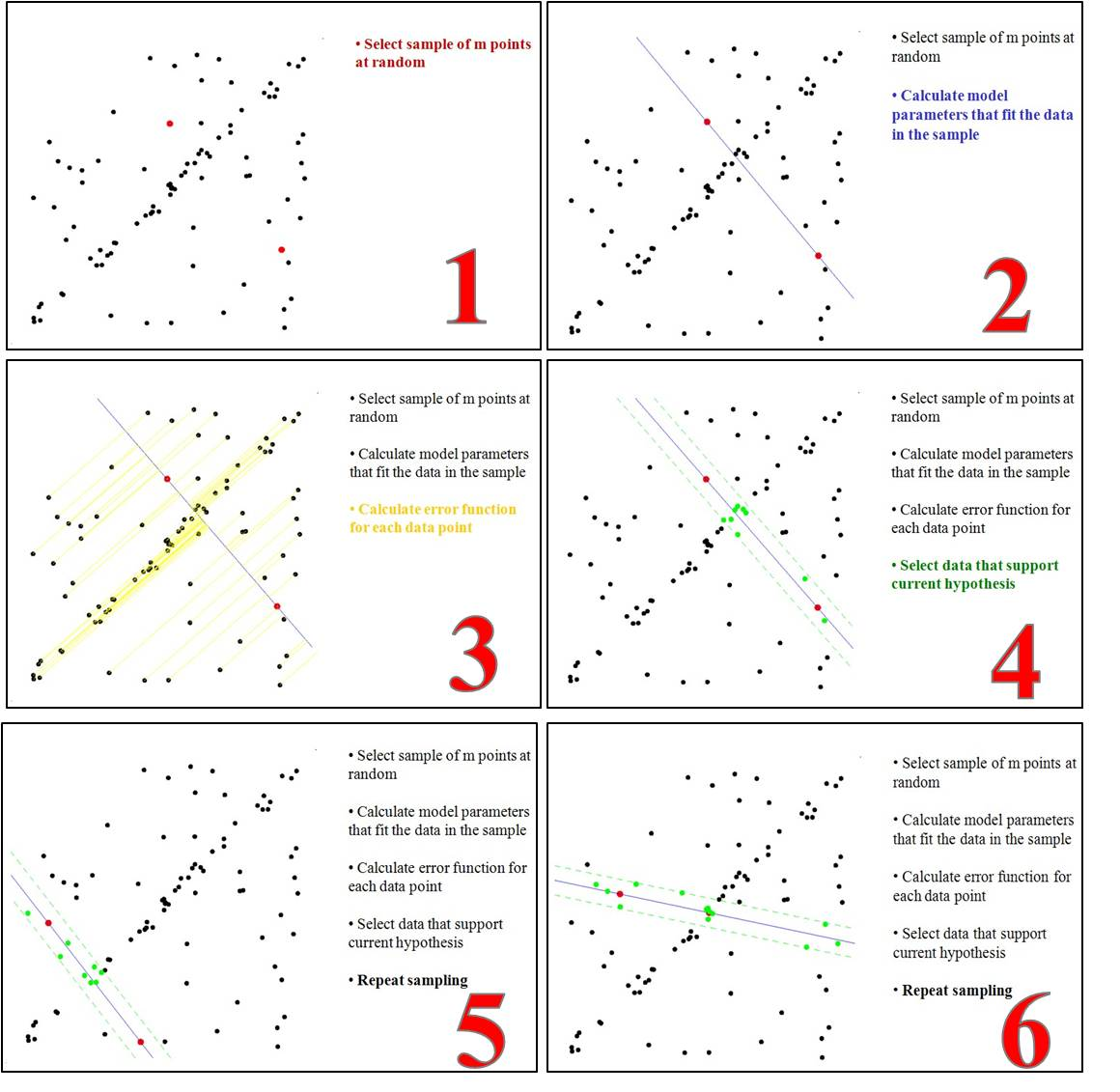
注意:一个完整的RANSAC算法,我们更愿意称作框架,你可以用在RANSAC框架下计算相机位姿变换、或者数据拟合等等。其中,最大迭代次数,这个不是固定的,他与当前迭代内点比例等等参数有关,请参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_sample_consensus 或者 https://www.cnblogs.com/cfantaisie/archive/2011/06/09/2076864.html
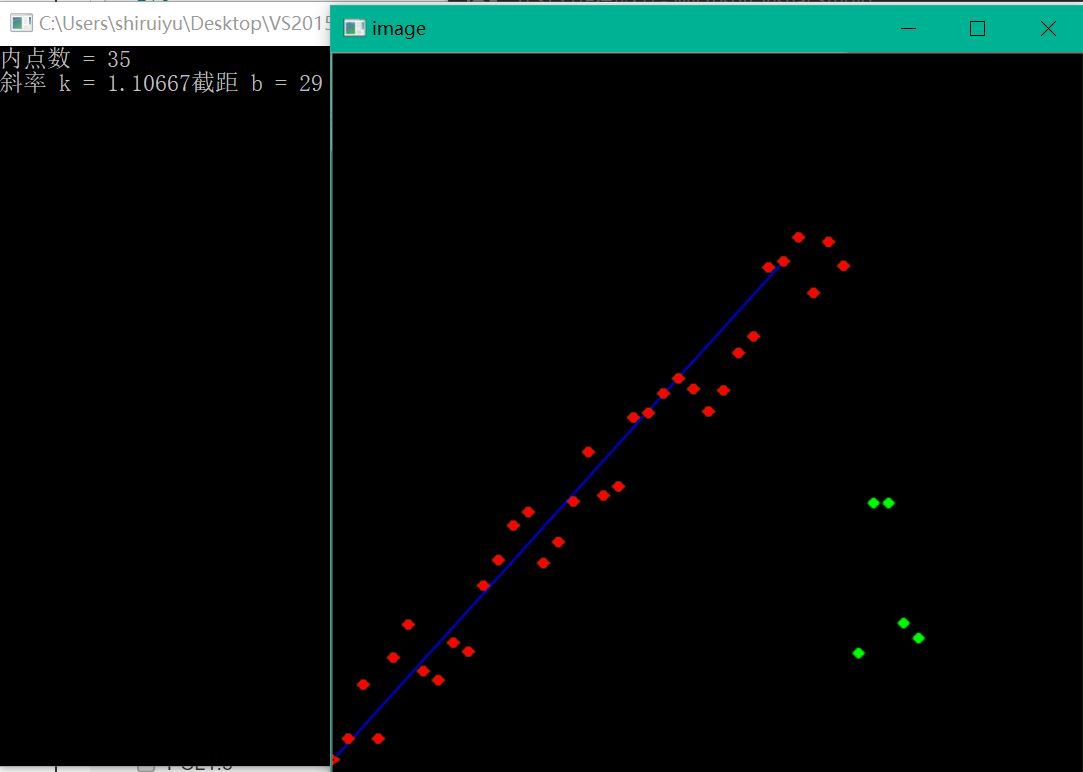
下面例子,我们在进行直线拟合,手动添加一些“较为夸张”的噪点,基于RANSAC框架,进行直线拟合,需要说明的是:循环迭代结束的时候,我们可以进一步采取最小二乘等手段进行曲线拟合,这样效果更好。同时,有关迭代次数问题,它涉及到程序的执行时效,所以,实际应用RANSAC框架来处理数据的时候,最大迭代次数,最好每次都更新。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<ctime> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #include<opencv2/opencv.hpp> 9 using namespace cv; 10 11 12 // 功能:画点 13 void drawPoints(vector<Point2d> points, Mat& image, bool is_green) 14 { 15 if (is_green) 16 { 17 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) 18 { 19 circle(image, Point2i(int(points[i].x), int(points[i].y)), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, CV_AA); 20 } 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) 25 { 26 circle(image, Point2i(int(points[i].x), int(points[i].y)), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, CV_AA); 27 } 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 // 功能:画线 33 void drawLine(Point2d begin, Point2d end, Mat& image) 34 { 35 line(image, Point2i(int(begin.x), int(begin.y)), 36 Point2i(int(end.x), int(end.y)), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, CV_AA); 37 } 38 39 // 功能:将一张图经行纵向镜像 40 void upDownMirror(Mat& image) 41 { 42 Mat image_cpy = image.clone(); 43 for (int j = 0; j < image.rows; j++) 44 { 45 for (int i = 0; i < image.cols; i++) 46 { 47 image.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(j)[i] = image_cpy.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(image.rows - 1 - j)[i]; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 // 功能:最简单的直线拟合 Ransac 框架 53 54 class Ransac 55 { 56 public: 57 Ransac(vector<double> x, vector<double> y); 58 ~Ransac(); 59 static int getRand(int min, int max);//[min, min + max - 1] 60 public: 61 vector<double> x_, y_; 62 }; 63 64 Ransac::Ransac(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) :x_(x), y_(y) 65 { 66 67 } 68 69 Ransac::~Ransac() 70 { 71 72 } 73 74 int Ransac::getRand(int min, int max)//[min, min + max - 1] 75 { 76 return rand() % max + min; 77 } 78 79 int main() 80 { 81 // time seed 82 srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr)); 83 84 // <1>产生随机数 85 vector<Point2d> points; 86 // 精确解 87 const int k = 1; 88 const int b = 10; 89 90 // x [0, 390]; y [10, 400] total_numbers = 40 91 for (int x = 0; x < 400; x += 10) 92 { 93 points.push_back(Point2d(x, k*x + b + Ransac::getRand(0, 60))); 94 } 95 //添加离群点 96 97 points[35].y = 100; 98 points[36].y = 200; 99 points[37].y = 200; 100 points[38].y = 120; 101 points[39].y = 110; 102 103 104 const int itr_nums = 300; 105 double k_estimate = 0; 106 double b_estimate = 0; 107 Point2d best_parameters; // [k, b] 108 109 // 统计纵向距离 y 110 int count = 0; // 内点计数器 111 int y_threshold = 50; // 判定内点的阈值 112 int total = 0; // 内点总数 113 114 //样本点 115 Point2d sample_first; 116 Point2d sample_second; 117 // 最佳样本点 118 Point2d best_sample_first; 119 Point2d best_sample_second; 120 121 for (int i = 0; i < itr_nums; i++) 122 { 123 // <1>、随机抽取两个样本 124 int index_first = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2); 125 int index_second = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2); 126 sample_first = points[index_first]; 127 sample_second = points[index_second]; 128 129 if (sample_first == sample_second) 130 { 131 continue; 132 } 133 // 计算斜率 k = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1) 134 k_estimate = (sample_second.y - sample_first.y) / (sample_second.x - sample_first.x); 135 // 计算截距 b = y1 - k * x1 136 b_estimate = sample_first.y - k_estimate * sample_first.x; 137 // <2>、根据距离,来找出所有样本点中的内点,并统计数量 138 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) 139 { 140 // delta = k * x + b - y 141 double y_error = abs(k_estimate * points[i].x + b_estimate - points[i].y) / sqrt((pow(k_estimate, 2) + 1)); 142 //cout << "y_error = " << y_error << endl; 143 if (y_error < y_threshold) 144 { 145 count++; 146 } 147 } 148 // <3>、找出内点数量最多的那一组 149 if (count > total) 150 { 151 total = count; 152 153 best_sample_first = sample_first; 154 best_sample_second = sample_second; 155 156 best_parameters.x = k_estimate; 157 best_parameters.y = b_estimate; 158 } 159 count = 0; 160 } 161 cout << "内点数 = " << total << endl; 162 cout << "斜率 k = " << best_parameters.x << "截距 b = " << best_parameters.y << endl; 163 164 // 统计内点 165 vector<Point2d> inliners_points; 166 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) 167 { 168 // delta = k * x + b - y 169 double y_error = abs(best_parameters.x * points[i].x + best_parameters.y - points[i].y) / sqrt((pow(k_estimate, 2) + 1)); 170 //cout << "y_error = " << y_error << endl; 171 if (y_error < y_threshold) 172 { 173 inliners_points.push_back(points[i]); 174 } 175 } 176 177 Mat image = Mat::zeros(500, 500, CV_8UC3); 178 179 drawLine(best_sample_first, best_sample_second, image); 180 drawPoints(points, image, true); 181 drawPoints(inliners_points, image, false); //画内点 182 upDownMirror(image); 183 imshow("image", image); 184 waitKey(0); 185 return 1; 186 }
总的样本数是40,内点数35,比例已经算很高了。绿色是外点,红色是内点。当然迭代次数越多,得到的解越精确。