
//【实现单例步骤】
// 1.构造函数私有化
// 2.增加静态的、私有的当前类的指针变量
// 3.提供一个静态的公有接口,可让用户获得单例对象
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class A 6 { 7 private: // 步骤1 8 A() {}; 9 public: 10 static A* getInstance() //步骤3 11 { 12 return a; 13 } 14 private: 15 static A* a; // 步骤2 16 }; 17 18 A* A::a = nullptr; 19 //【实现单例步骤】 20 // 1.构造函数私有化 21 // 2.增加静态的、私有的当前类的指针变量 22 // 3.提供一个静态的公有接口,可让用户获得单例对象 23 24 //单例:懒汉式 、恶汉式 25 // <1> 懒汉式 26 class Singleton_lazy 27 { 28 private: 29 Singleton_lazy() { cout << "创建 Singleton_lazy " << endl; }; 30 public: 31 static Singleton_lazy* getInstance() 32 { 33 if (pSingleton_lazy == nullptr) // 如果单例对象没被创建(如果创建了,那就跳过呗) 34 { 35 pSingleton_lazy = new Singleton_lazy; // 那就TM建一个 36 } 37 return pSingleton_lazy; 38 } 39 private: 40 static Singleton_lazy* pSingleton_lazy; 41 }; 42 Singleton_lazy* Singleton_lazy::pSingleton_lazy = nullptr; 43 44 // <2> 饿汉式 45 class Singleton_hungry 46 { 47 private: 48 Singleton_hungry() { cout << "创建 Singleton_hungry " << endl; }; 49 public: 50 static Singleton_hungry* getInstance() 51 { 52 return pSingleton_hungry; 53 } 54 private: 55 static Singleton_hungry* pSingleton_hungry; 56 }; 57 Singleton_hungry* Singleton_hungry::pSingleton_hungry = new Singleton_hungry;//直接在类外创建单例对象 58 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 //A::getInstance(); 63 cout << "main开始的地方" << endl; 64 Singleton_lazy::getInstance(); 65 Singleton_hungry::getInstance(); 66 }
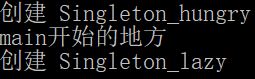
可以看到,恶汉模式在main执行之前已经初始化好了。
举例子:SLAM中我们需要在多个文件中读取参数文件,所以,这里必须把Config写成 Singleton。它只有一个全局对象,当我们设置参数文件时,创建该对象【整个程序之创建一个对象】并读取参数文件,随后可以在任意位置读取该文件中的参数值。
1 class Config 2 { 3 private: 4 // <1> 步骤1:构造函数私有化 5 Config(){}; 6 cv::FileStorage file_; 7 public: 8 ~Config(); 9 // <3> 步骤3:提供静态的、公有的接口;可让用户获取单例 10 static void setParameterFile(const std::string& filename); // 类似于 static void getInstance() 11 12 template<typename T> 13 static T get(const std::string& key) 14 { 15 return T(Config::config_->file_[key]); 16 } 17 18 private: 19 // <2> 步骤2:增加静态的、私有的当前类的指针 20 static std::shared_ptr<Config> config_; 21 }; 22 23 std::shared_ptr<Config> Config::config_ = nullptr; 24 25 void Config::setParameterFile(const std::string & filename) 26 { 27 if (config_ == nullptr) 28 { 29 config_ = std::shared_ptr<Config>(new Config); 30 } 31 config_->file_ = cv::FileStorage(filename.c_str(), cv::FileStorage::READ); 32 // 异常处理 33 if (config_->file_.isOpened() == false) 34 { 35 std::cerr << "parameter file " << filename << "do not exsit" << std::endl; 36 config_->file_.release(); 37 return; 38 } 39 } 40 41 Config::~Config() 42 { 43 if (file_.isOpened()) 44 { 45 file_.release(); 46 } 47 }
显然这里是懒汉模式,不过它新增了静态 模板类型的 get函数;
调用方式如下:
1 Config::setParameterFile("myparameter.yaml"); // 获取一个单例对象 2 double distance = Config::get<double>("distance");//通过静态成员函数获取参数,static能去掉?
不能去掉,原因:与普通的成员函数相比,静态成员函数由于不是与任何的对象相联系,因此它不具有this指针.从这个意义上来说,它无法访问属于类对象的非静态数据成员,也无法访问非静态成员函数,只能调用其他的静态成员函数.
//将上述两个模式中的指针改为 共享指针
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<memory> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Singleton_lazy 7 { 8 private: 9 Singleton_lazy() { cout << "Singleton_lazy" << endl; }; 10 public: 11 //static Singleton_lazy* GetInstance() 12 static shared_ptr<Singleton_lazy> GetInstance() 13 { 14 if (sp == nullptr) 15 { 16 //sp = new Singleton_lazy; 17 sp = shared_ptr<Singleton_lazy>(new Singleton_lazy); 18 } 19 return sp; 20 } 21 private: 22 //static Singleton_lazy* sp; 23 static shared_ptr<Singleton_lazy> sp; 24 }; 25 //Singleton_lazy* Singleton_lazy::sp = nullptr; 26 shared_ptr<Singleton_lazy> Singleton_lazy::sp = nullptr; 27 28 class Singleton_hungry 29 { 30 private: 31 Singleton_hungry() { cout << "Singleton_hungry" << endl; }; 32 public: 33 //static Singleton_hungry* GetInstance() 34 static void GetInstance() 35 { 36 //return sp; 37 return; 38 } 39 private: 40 //static Singleton_hungry* sp; 41 static shared_ptr<Singleton_hungry> sp; 42 }; 43 shared_ptr<Singleton_hungry> Singleton_hungry::sp = shared_ptr<Singleton_hungry>(new Singleton_hungry); 44 45 int main() 46 { 47 cout << "shiruiyu" << endl; 48 Singleton_lazy::GetInstance(); 49 Singleton_hungry::GetInstance(); 50 return 1; 51 }