- 1、链表基本概念以及注意事项
- a、构造函数与析构函数
- b、插入
- c、重载运算符[]
- 2、打印链表
- 3、删除链表节点
- 4、链表中倒数第k个节点
- 5、反转链表
- 6、合并两个排序的链表
- 7、两个链表当中的第一个公共节点
【查看之前笔记】
在编写函数之前,请务必注意以下三点:
i、输入的指针、各类容器可能是空的
ii、输入的容器可能只有一个元素
iii、输入的容器可能有多个元素,这个是最常见的情况。
【做完下面代码后,请你再按照上面三条,将异常情况加上!!!】

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<set> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Node 6 { 7 public: 8 int data_;//数据阈 9 Node* next_;//指针阈 10 public: 11 Node():data_(-1), next_(nullptr) {} 12 }; 13 14 class List 15 { 16 public: 17 List() 18 { 19 this->head_ = new Node();// 不分配空间,下面赋值是不合理的! 20 //this->head_->data_ = 0;//多余? 21 this->head_->next_ = nullptr; 22 this->size_ = 0; 23 }; 24 void insert(int pos, int value); 25 void remove(int pos); 26 int get_reverse_element(int reverse_pos);//链表中倒数第k个节点 27 void reverse(); 28 29 int operator[](int i); 30 void print(); 31 ~List(); 32 33 34 public: 35 Node* head_; 36 int size_;//维护一个size 37 }; 38 //在第pos个元素前一个位置插入(创建、找到位置、入链表) 39 void List::insert(int pos, int value) 40 { 41 if (pos < 0 || pos > size_) 42 return; 43 44 //创建新的节点接受数据 45 Node* newnode = new Node(); 46 newnode->data_ = value; 47 //cout << "newnode->data_ = " << *newnode->data_ << endl; 48 newnode->next_ = nullptr; 49 50 //利用辅助指针找到pos前一个节点 51 // 其实这里不断next,无非就是希望p_curr = nullptr 52 // 然后56行 让newnode->next_ = nullptr(这个nullptr是从head_->next 传过来的);也就是尾部插入嘛 53 // 而循环链表 同理 让newnode->next_ = &(head_)(这个 &(head_) 是从head_->next 传过来的); 54 Node* p_curr = head_; 55 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) //这个for循环本质上是head_->next_->next_...... 56 { 57 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 58 } 59 //现在p_curr就是pos前一个节点的指针阈 60 //新节点入链表 61 newnode->next_ = p_curr->next_;//右边 62 p_curr->next_ = newnode;//左边 63 size_++; 64 } 65 66 void List::remove(int pos) 67 { 68 if (pos < 0 || pos > size_) 69 { 70 return; 71 } 72 Node* p_curr = head_; 73 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)// 3 74 { 75 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 76 } 77 p_curr->next_ = p_curr->next_->next_; 78 size_--; 79 } 80 81 //链表中倒数第k个节点 82 int List::get_reverse_element(int reverse_pos) 83 { 84 int pos = size_ - reverse_pos; 85 Node* p_curr = head_; 86 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) 87 { 88 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 89 } 90 return p_curr->data_; 91 } 92 93 //反转链表 94 void List::reverse() 95 { 96 // head -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> nullptr 97 //nullptr <- 1 <- 2 <- 3 <- 4 98 99 Node* p_curr = head_->next_; 100 Node* p_prev = nullptr; 101 while (p_curr != nullptr) 102 { 103 Node* p_next = p_curr->next_; 104 if (p_next == nullptr) 105 if(p_curr->next_ == nullptr) 106 { 107 head_->next_ = p_curr; 108 } 109 p_curr->next_ = p_prev; 110 p_prev = p_curr; 111 p_curr = p_next; 112 } 113 } 114 115 int List::operator[](int i) 116 { 117 Node* p_curr = head_; 118 int count = 0; 119 while (count <= i) 120 { 121 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 122 count++; 123 } 124 return p_curr->data_; 125 } 126 void List::print() 127 { 128 if (size_ == 0) 129 { 130 cout << "size = 0" << endl; 131 return; 132 } 133 //遍历 134 Node* p_curr = head_->next_;//【注意这里next】 135 while (p_curr != nullptr) 136 { 137 cout << p_curr->data_ << " "; 138 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 139 } 140 cout << endl; 141 } 142 List::~List() 143 { 144 while (size_ != 0) 145 { 146 Node* p_curr = head_; 147 for (int i = 0; i < (size_ - 1); i++)// 012345 i < 5 148 { 149 p_curr = p_curr->next_;//for循环执行完,p_curr指向4 150 } 151 delete p_curr->next_;//删除最后一个元素 152 p_curr->next_ = nullptr;//末尾元素 空指针 153 size_--; 154 print(); 155 } 156 delete head_; //【这个容易忘记!】 157 cout << "delete!" << endl; 158 } 159 160 //合并两个排序链表 161 void mergeLists(List& list3, List& list4, List& list34) 162 { 163 Node* p_curr3 = list3.head_->next_; 164 Node* p_curr4 = list4.head_->next_; 165 Node* p_curr34 = list34.head_->next_; 166 int location = 0; 167 while ((p_curr3 != nullptr) || (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 168 { 169 if ((p_curr3 != nullptr) && (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 170 { 171 if (p_curr3->data_ < p_curr4->data_) 172 { 173 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 174 location++; 175 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 176 location++; 177 } 178 else 179 { 180 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 181 location++; 182 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 183 location++; 184 } 185 p_curr3 = p_curr3->next_; 186 p_curr4 = p_curr4->next_; 187 } 188 else if ((p_curr3 != nullptr) && (p_curr4 == nullptr)) 189 { 190 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 191 location++; 192 p_curr3 = p_curr3->next_; 193 } 194 else if ((p_curr3 == nullptr) && (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 195 { 196 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 197 location++; 198 p_curr4 = p_curr4->next_; 199 } 200 } 201 } 202 203 204 int main() 205 { 206 List list1; 207 //插入 208 for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) 209 { 210 list1.insert(i, i); 211 } 212 213 //删除 214 list1.remove(10); 215 list1.remove(5); 216 //打印 217 list1.print(); 218 list1.reverse(); 219 list1.print(); 220 //访问倒数元素 221 for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) 222 { 223 cout << "倒数第" << i << "个元素是:" << list1.get_reverse_element(i) << endl; 224 } 225 list1.insert(2, 9999); 226 //重载符[] 227 for (int i = list1.size_ - 1; i >= 0; i--) 228 { 229 cout << list1[i] << " "; 230 } 231 cout << endl; 232 List list2; 233 list2.insert(0, 10); 234 list2.insert(1, 20); 235 list2.insert(2, 30); 236 list2.print(); 237 int size2 = list2.size_; 238 239 //合并两个排序链表 240 List list3, list4; 241 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 242 { 243 list3.insert(i, 2 * i); 244 list4.insert(i, 2 * i + 1); 245 } 246 list4.insert(5, 12); 247 list4.insert(6, 21); 248 list3.print(); 249 list4.print(); 250 251 List list34; 252 mergeLists(list3, list4, list34); 253 list34.print(); 254 255 256 return 1; 257 }
a、构造函数与析构函数
节点 ,初始化数据一定要做。
1 class Node 2 { 3 public: 4 int data_;//数据阈 5 Node* next_;//指针阈 6 public: 7 Node():data_(-1), next_(nullptr) 8 {} 9 };
构造函数
1 List() 2 { 3 this->head_ = new Node();// 分配空间 4 this->size_ = 0; 5 };
整个链表,实现任何功能,我们都要维护一个头节点和size_
析构函数
1 List::~List() 2 { 3 while (size_ != 0) 4 { 5 Node* p_curr = head_; 6 for (int i = 0; i < (size_ - 1); i++)// 012345 i < 5 7 { 8 p_curr = p_curr->next_;//for循环执行完,p_curr指向4 9 } 10 delete p_curr->next_;//删除最后一个元素 11 p_curr->next_ = nullptr;//末尾元素 空指针 12 size_--; 13 print(); 14 } 15 delete head_; // 16 cout << "delete!" << endl; 17 }
在保证不断链的前提下;释放整个链表,似乎只能从后面开始delete。循环当中,每次遍历到 待删除节点前一个p_curr, 然后delete p_curr->next_
b、插入
1 //在第pos个元素前一个位置插入(创建、找到位置、入链表) 2 void List::insert(int pos, int value) 3 { 4 if (pos < 0 || pos > size_) 5 return; 6 7 //创建新的节点接受数据 8 Node* newnode = new Node(); 9 newnode->data_ = value; 10 11 Node* p_curr = head_; 12 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) 13 { 14 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 15 } 16 17 //新节点入链表 18 newnode->next_ = p_curr->next_; 19 p_curr->next_ = newnode; 20 size_++; 21 }
18行、19行代码很好诠释了插入过程;其中18行代码:将当前节点的指针域指向 对象的地址 赋给 newnode->next_;保证了新数据与链表中后面连接;
19行代码:当前节点指针域指向 新的节点
例如: 1 2 3 4 5 要在 4 和 5 之间插入 一个 666
步骤如下:
遍历至节点4; 1 2 3 4 5
将666 指向5:; 1 2 3 4 666 5
再将 4 指向 666; 1 2 3 4 666 5
c、重载运算符
1 int List::operator[](int i) 2 { 3 Node* p_curr = head_; 4 int count = 0; 5 while (count <= i) 6 { 7 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 8 count++; 9 } 10 return p_curr->data_; 11 }
在做上面几道题之前,我们先给出一个基本链表。
总代码,顺便解释构造函数、析构函数为什么这样写
2、打印链表
1 void List::print() 2 { 3 if (size_ == 0) 4 { 5 cout << "size = 0" << endl; 6 return; 7 } 8 //遍历 9 Node* p_curr = head_->next_;//【注意这里next】 10 while (p_curr != nullptr) 11 { 12 cout << p_curr->data_ << " "; 13 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 }
3、删除链表节点
1 //功能:删除索引位置为pos的节点 2 void List::remove(int pos) 3 { 4 if (pos < 0 || pos > size_) 5 { 6 return; 7 } 8 Node* p_curr = head_; 9 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)// 3 10 { 11 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 12 } 13 p_curr->next_ = p_curr->next_->next_; 14 size_--; 15 }
思想就是找到要删除的Node的前一个节点,让前一个节点的指针指向Node的下一个节点就行了。
例如:pos = 3的时候,for循环执行完毕,p_curr表示索引值为2的节点地址,接着我们让p_curr->next 指向 下一个节点的下一个节点。
4、链表中倒数第k个节点
1 //链表中倒数第k个节点 2 int List::get_reverse_element(int reverse_pos) 3 { 4 int pos = size_ - reverse_pos; 5 Node* p_curr = head_; 6 for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) 7 { 8 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 9 } 10 return p_curr->data_; 11 }
你可以去看看剑指offer上的做法,我这里类List维护了一个size_,所以比较简单。
5、反转链表
修改前:
1 //反转链表 2 void List::reverse() 3 { 4 // head -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> nullptr 5 //nullptr <- 1 <- 2 <- 3 <- 4 6 7 Node* p_curr = head_; 8 Node* p_prev = nullptr; 9 while (p_curr != nullptr) 10 { 11 Node* p_next = p_curr->next_; 12 if (p_next == nullptr) 13 { 14 head_ = p_curr; 15 } 16 p_curr->next_ = p_prev; 17 p_prev = p_curr; 18 p_curr = p_next; 19 } 20 }

可以看到,有一个元素错位了。由于第7行 p_curr一开始 = 头节点指针,执行到第16行的时候,可以看到头节点的下一个节点是nullptr,但是头节点本身 data_ = -1; 当循环执行到if语句的时候,你又把第一个节点直接赋值给头节点,那么头节点的data_ = 15;这个在类List的print()中是不会打印出来的。
第7、14行做了如下修改:
1 //反转链表 2 void List::reverse() 3 { 4 // head -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> nullptr 5 //nullptr <- 1 <- 2 <- 3 <- 4 6 7 Node* p_curr = head_->next_; 8 Node* p_prev = nullptr; 9 while (p_curr != nullptr) 10 { 11 Node* p_next = p_curr->next_; 12 if (p_next == nullptr) 13 { 14 head_->next_ = p_curr; 15 } 16 p_curr->next_ = p_prev; 17 p_prev = p_curr; 18 p_curr = p_next; 19 } 20 }

思考:
当初写出来的链表应当是这样的:
1 //反转链表 2 void List::reverse() 3 { 4 // head -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> nullptr 5 //nullptr <- 1 <- 2 <- 3 <- 4 6 7 Node* p_curr = head_->next_; 8 Node* p_prev = nullptr; 9 while (p_curr != nullptr) 10 { 11 //Node* p_next = p_curr->next_; 12 //if (p_next == nullptr) 13 if(p_curr->next_ == nullptr) 14 { 15 head_->next_ = p_curr; 16 } 17 p_curr->next_ = p_prev; 18 p_prev = p_curr; 19 //p_curr = p_next; 20 p_curr = p_curr->next_; 21 } 22 }
输出结果:
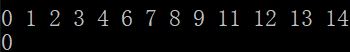
首先,必须知道算法第17行是核心!
这里显然断链了。17行 p_curr->next_ 的赋值导致20行(为了遍历原链表)赋值错误。原本,在17行,我们的目的是:将next_指向前一个节点,以达到倒序的目的。所以在执行17行之前,我们必须想办法缓存地址值:p_curr->next_,也就是11行,缓存之后用于19行刷新p_curr。18行的刷新很好理解。
6、合并两个排序链表
1 //合并两个排序链表 2 void mergeLists(List& list3, List& list4, List& list34) 3 { 4 Node* p_curr3 = list3.head_->next_; 5 Node* p_curr4 = list4.head_->next_; 6 Node* p_curr34 = list34.head_->next_; 7 int location = 0; 8 while ((p_curr3 != nullptr) || (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 9 { 10 if ((p_curr3 != nullptr) && (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 11 { 12 if (p_curr3->data_ < p_curr4->data_) 13 { 14 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 15 location++; 16 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 17 location++; 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 22 location++; 23 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 24 location++; 25 } 26 p_curr3 = p_curr3->next_; 27 p_curr4 = p_curr4->next_; 28 } 29 else if ((p_curr3 != nullptr) && (p_curr4 == nullptr)) 30 { 31 list34.insert(location, p_curr3->data_); 32 location++; 33 p_curr3 = p_curr3->next_; 34 } 35 else if ((p_curr3 == nullptr) && (p_curr4 != nullptr)) 36 { 37 list34.insert(location, p_curr4->data_); 38 location++; 39 p_curr4 = p_curr4->next_; 40 } 41 } 42 }
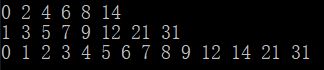
例如现在有两个升序序列:
A:0 2 4 6 8 14
B:1 3 5 7 9 12 21 31
要将他们变成一个生序序列;
思路:假设现在两个序列元素个数相等;我们将 0 1对比将得到 0 1, 再将1和2 3 对比 得到 0 1 2 3;再将3和4 5 对比;依次类推,(对应第10行代码)
现在考虑 A序列长度 > B序列长度;对应第29行代码; A序列长度 < B序列长度;对应第35行代码
1 //合并两个排序链表 2 List list3,list4; 3 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 4 { 5 list3.insert(i, 2*i); 6 list4.insert(i, 2 * i + 1); 7 } 8 list3.insert(5, 14); 9 list4.insert(5, 12); 10 list4.insert(6, 21); 11 list4.insert(7, 31); 12 list3.print(); 13 list4.print(); 14 15 List list34; 16 mergeLists(list3, list4, list34); 17 list34.print();
测试用例: