一、简介
requests是使用Apache2 licensed 许可证的HTTP库。用python编写。比urllib2模块更简洁。
Request支持HTTP连接保持和连接池,支持使用cookie保持会话,支持文件上传,支持自动响应内容的编码,支持国际化的URL和POST数据自动编码。
在python内置模块的基础上进行了高度的封装,从而使得python进行网络请求时,变得人性化,使用Requests可以轻而易举的完成浏览器可有的任何操作。
Requests 完全满足今日 web 的需求。
- Keep-Alive & 连接池
- 国际化域名和 URL
- 带持久 Cookie 的会话
- 浏览器式的 SSL 认证
- 自动内容解码
- 基本/摘要式的身份认证
- 优雅的 key/value Cookie
- 自动解压
- Unicode 响应体
- HTTP(S) 代理支持
- 文件分块上传
- 流下载
- 连接超时
- 分块请求
- 支持
.netrc
requests主要收集了以下模块:
requests.Request
requests.Response
requests.Session 用于
requests.HTTPError 用于
requests主要包含了以下方法:
requests.request
requests.get
requests.post
requests.cookies
requests.sessions
requests.ssl
requests.head
requests.put
requests.delete
requests.options
requests.session
requests.pacth
二、requests模块定义了以下方法:
1、request

Help on function request in module requests.api: request(method, url, **kwargs) Constructs and sends a :class:`Request <Request>`. :param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object: ``GET``, ``OPTIONS``, ``HEAD``, ``POST``, ``PUT``, ``PATCH``, or ``DELETE``. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send in the query string for the :class:`Request`. :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the :class:`Request`. :param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the :class:`Request`. :param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (or ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload. ``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')`` or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers to add for the file. :param auth: (optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth. :param timeout: (optional) How many seconds to wait for the server to send data before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read timeout) <timeouts>` tuple. :type timeout: float or tuple :param allow_redirects: (optional) Boolean. Enable/disable GET/OPTIONS/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD redirection. Defaults to ``True``. :type allow_redirects: bool :param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy. :param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``. :param stream: (optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded. :param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response
简单代码如下:
>>> import requests >>> req = requests.request('GET', 'https://httpbin.org/get') >>> req <Response [200]>
2、get

Help on function get in module requests.api: get(url, params=None, **kwargs) Sends a GET request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send in the query string for the :class:`Request`. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response
简单代码如下:
import requests # requests.get = get(url, params=None, **kwargs) url = "http://www.bjgjwy.net/" user_agent = 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT)' response = requests.get(url) #response是<class 'requests.models.Response'> print(response.text) #response.text是str类型,response.content是bytes类型
3、post

Help on function post in module requests.api: post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs) Sends a POST request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response
简单代码如下:
#requests.post = post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs) >>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'} >>> r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data = payload) >>> print(r.text) { "args": {}, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "23", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.26.0", "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-6106c6ed-6b89c461168de0fc642b5bdd" }, "json": null, "origin": "183.8.9.128", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" }
4、总结
# HTTP请求类型 # get类型 r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json') # post类型 r = requests.post("http://m.ctrip.com/post") # put类型 r = requests.put("http://m.ctrip.com/put") # delete类型 r = requests.delete("http://m.ctrip.com/delete") # head类型 r = requests.head("http://m.ctrip.com/head") # options类型 r = requests.options("http://m.ctrip.com/get") # 获取响应内容 print(r.content) #以字节的方式去显示,中文显示为字符 print(r.text) #以文本的方式去显示 #URL传递参数 payload = {'keyword': '香港', 'salecityid': '2'} r = requests.get("http://m.ctrip.com/webapp/tourvisa/visa_list", params=payload) print(r.url) #示例为http://m.ctrip.com/webapp/tourvisa/visa_list?salecityid=2&keyword=香港 #获取/修改网页编码 r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json') print (r.encoding) #json处理 r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json') print(r.json()) # 需要先import json # 定制请求头 url = 'http://m.ctrip.com' headers = { 'User-Agent' : 'Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 4.2.1; en-us; Nexus 4 Build/JOP40D) AppleWebKit/535.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/18.0.1025.166 Mobile Safari/535.19' } r = requests.post(url, headers=headers) print (r.request.headers) #复杂post请求 url = 'http://m.ctrip.com' payload = {'some': 'data'} r = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload)) #如果传递的payload是string而不是dict,需要先调用dumps方法格式化一下 # post多部分编码文件 url = 'http://m.ctrip.com' files = {'file': open('report.xls', 'rb')} r = requests.post(url, files=files) # 响应状态码 r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com') print(r.status_code) # 响应头 r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com') print (r.headers) print (r.headers['Content-Type']) print (r.headers.get('content-type')) #访问响应头部分内容的两种方式 # Cookies url = 'http://example.com/some/cookie/setting/url' r = requests.get(url) r.cookies['example_cookie_name'] #读取cookies url = 'http://m.ctrip.com/cookies' cookies = dict(cookies_are='working') r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies) #发送cookies #Github 将所有的 HTTP 请求重定向到 HTTPS: >>> r = requests.get('http://github.com') >>> r.url 'https://github.com/' >>> r.status_code 200 >>> r.history [<Response [301]>] #如果你使用的是GET、OPTIONS、POST、PUT、PATCH 或者 DELETE,那么你可以通过 allow_redirects 参数禁用重定向处理: >>> r = requests.get('http://github.com', allow_redirects=False) >>> r.status_code 301 >>> r.history [] #设置超时时间 r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com', timeout=0.001) #设置访问代理 proxies = { "http": "http://10.10.1.10:3128", "https": "http://10.10.1.100:4444", } r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com', proxies=proxies) #如果代理需要用户名和密码,则需要这样: proxies = { "http": "http://user:pass@10.10.1.10:3128/", }
5、实战运用
(1)直接使用已知的cookie访问
特点:
简单,但需要先在浏览器登录
原理:
简单地说,cookie保存在发起请求的客户端中,服务器利用cookie来区分不同的客户端。因为http是一种无状态的连接,当服务器一下子收到好几个请求时,是无法判断出哪些请求是同一个客户端发起的。而“访问登录后才能看到的页面”这一行为,恰恰需要客户端向服务器证明:“我是刚才登录过的那个客户端”。于是就需要cookie来标识客户端的身份,以存储它的信息(如登录状态)。
当然,这也意味着,只要得到了别的客户端的cookie,我们就可以假冒成它来和服务器对话。这给我们的程序带来了可乘之机。
我们先用浏览器登录,然后使用开发者工具查看cookie。接着在程序中携带该cookie向网站发送请求,就能让你的程序假扮成刚才登录的那个浏览器,得到只有登录后才能看到的页面。
具体步骤:
1.用浏览器登录,获取浏览器里的cookie字符串
先使用浏览器登录。再打开开发者工具,转到network选项卡。在左边的Name一栏找到当前的网址,选择右边的Headers选项卡,查看Request Headers,这里包含了该网站颁发给浏览器的cookie。对,就是后面的字符串。把它复制下来,一会儿代码里要用到。
注意,最好是在运行你的程序前再登录。如果太早登录,或是把浏览器关了,很可能复制的那个cookie就过期无效了。
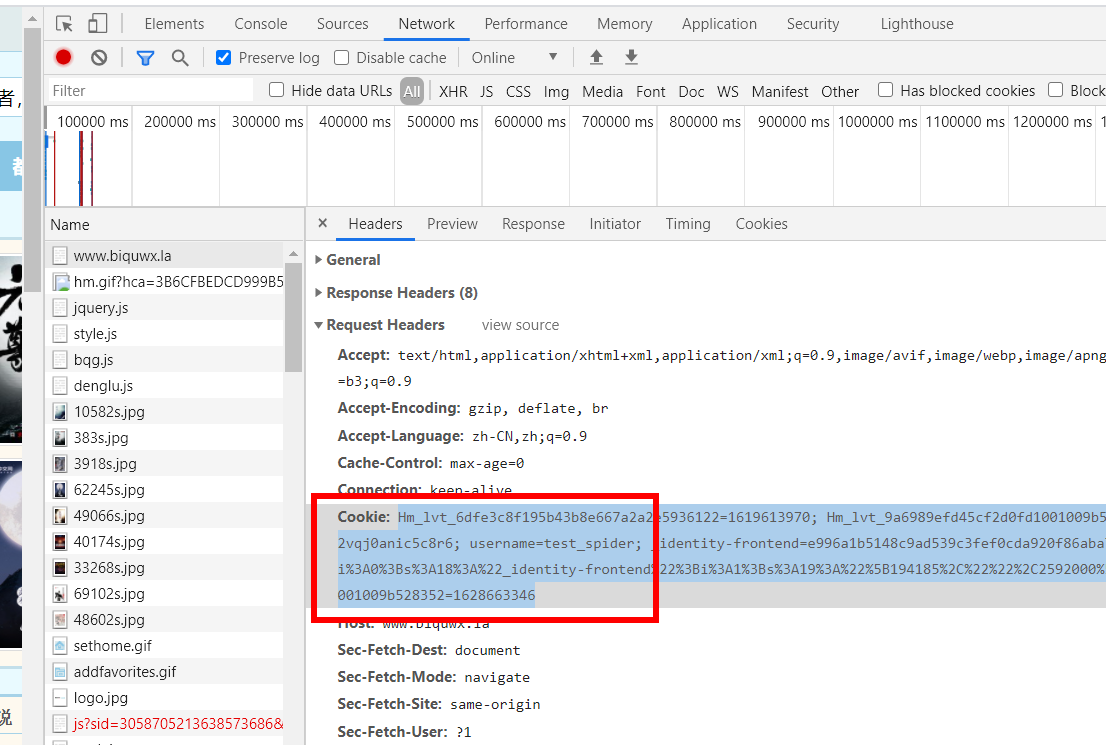
2.写代码
import requests headers = { 'Cookie': 'Hm_lvt_6dfe3c8f195b43b8e667a2a2e5936122=1619613970; Hm_lvt_9a6989efd45cf2d0fd1001009b528352=1628663333; PHPSESSID=v3j4e701lbbo2vqj0anic5c8r6; username=test_spider; _identity-frontend=e996a1b5148c9ad539c3fef0cda920f86aba775e47e22204b90777063e2b079aa:2:{i:0;s:18:"_identity-frontend";i:1;s:19:"[194185,"",2592000]";}; Hm_lpvt_9a6989efd45cf2d0fd1001009b528352=1628663346', 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.182 Safari/537.36' } url = 'https://www.biquwx.la/modules/article/bookcase.php' res = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers) print(res._content.decode("utf-8"))
(2)模拟登录后用session保持登录状态
原理:
我们先在程序中向网站发出登录请求,也就是提交包含登录信息的表单(用户名、密码等)。
session是会话的意思。和cookie的相似之处在于,它也可以让服务器“认得”客户端。简单理解就是,把每一个客户端和服务器的互动当作一个“会话”。既然在同一个“会话”里,服务器自然就能知道这个客户端是否登录过。
具体步骤:
1.找出表单提交到的页面
还是要利用浏览器的开发者工具。转到network选项卡,并勾选Preserve Log(重要!)。在浏览器里登录网站。然后在左边的Name一栏找到表单提交到的页面。怎么找呢?看看右侧,转到Headers选项卡。首先,在General那段,Request Method应当是POST。其次最下方应该要有一段叫做Form Data的,里面可以看到你刚才输入的用户名和密码等。也可以看看左边的Name,如果含有login这个词,有可能就是提交表单的页面(不一定!)。
这里要强调一点,“表单提交到的页面”通常并不是你填写用户名和密码的页面!所以要利用工具来找到它。
2.找出要提交的数据
虽然你在浏览器里登陆时只填了用户名和密码,但表单里包含的数据可不只这些。从Form Data里就可以看到需要提交的所有数据。

3.写代码
import requests #登录时需要POST的数据 data = { 'LoginForm[username]': 'test_spider', 'LoginForm[password]': 'test_spiders', 'action': 'login', 'submit': ' 登 录 ' } #设置请求头 headers = {'User-agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36'} #登录时表单提交到的地址(用开发者工具可以看到) login_url = 'https://www.biquwx.la/login.php' #构造Session session = requests.Session() #在session中发送登录请求,此后这个session里就存储了cookie #可以用print(session.cookies.get_dict())查看 resp = session.post(login_url, data) #登录后才能访问的网页 url = 'https://www.biquwx.la/modules/article/bookcase.php' #构造访问请求 resp = session.get(url) print(resp.content.decode('utf-8'))
(3)使用无头浏览器访问
特点:
功能强大,几乎可以对付任何网页,但会导致代码效率低
原理:
如果能在程序里调用一个浏览器来访问网站,那么像登录这样的操作就轻而易举了。在Python中可以使用Selenium库来调用浏览器,写在代码里的操作(打开网页、点击……)会变成浏览器忠实地执行。这个被控制的浏览器可以是Firefox,Chrome等,但最常用的还是PhantomJS这个无头(没有界面)浏览器。也就是说,只要把填写用户名密码、点击“登录”按钮、打开另一个网页等操作写到程序中,PhamtomJS就能确确实实地让你登录上去,并把响应返回给你。
具体步骤:
1.安装selenium库、PhantomJS浏览器
2.在源代码中找到登录时的输入文本框、按钮这些元素
因为要在无头浏览器中进行操作,所以就要先找到输入框,才能输入信息。找到登录按钮,才能点击它。
在浏览器中打开填写用户名密码的页面,将光标移动到输入用户名的文本框,右键,选择“审查元素”,就可以在右边的网页源代码中看到文本框是哪个元素。同理,可以在源代码中找到输入密码的文本框、登录按钮。

3.考虑如何在程序中找到上述元素
Selenium库提供了find_element(s)_by_xxx的方法来找到网页中的输入框、按钮等元素。其中xxx可以是id、name、tag_name(标签名)、class_name(class),也可以是xpath(xpath表达式)等等。当然还是要具体分析网页源代码。
webdriver.PhantomJS常用属性如下
['add_cookie', 'application_cache', 'back', 'close', 'create_web_element', 'current_url', 'current_window_handle', 'delete_all_cookies', 'delete_cookie', 'desired_capabilities', 'execute', 'execute_async_script', 'execute_script', 'file_detector', 'file_detector_context', 'find_element', 'find_element_by_class_name', 'find_element_by_css_selector', 'find_element_by_id', 'find_element_by_link_text', 'find_element_by_name', 'find_element_by_partial_link_text', 'find_element_by_tag_name', 'find_element_by_xpath', 'find_elements', 'find_elements_by_class_name', 'find_elements_by_css_selector', 'find_elements_by_id', 'find_elements_by_link_text', 'find_elements_by_name', 'find_elements_by_partial_link_text', 'find_elements_by_tag_name', 'find_elements_by_xpath', 'forward', 'fullscreen_window', 'get', 'get_cookie', 'get_cookies', 'get_log', 'get_screenshot_as_base64', 'get_screenshot_as_file', 'get_screenshot_as_png', 'get_window_position', 'get_window_rect', 'get_window_size', 'implicitly_wait', 'log_types', 'maximize_window', 'minimize_window', 'mobile', 'name', 'orientation', 'page_source', 'quit', 'refresh', 'save_screenshot', 'set_page_load_timeout', 'set_script_timeout', 'set_window_position', 'set_window_rect', 'set_window_size', 'start_client', 'start_session', 'stop_client', 'switch_to', 'switch_to_active_element', 'switch_to_alert', 'switch_to_default_content', 'switch_to_frame', 'switch_to_window', 'title', 'window_handles']
4.写代码
from selenium import webdriver from time import sleep # 创建一个浏览器对象,将驱动程序加载到浏览器中 pjs_obj = webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path='/root/python/requests/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin/phantomjs') # 浏览器对象执行get方法相当于手动打开对应的url网址 pjs_obj.get('https://www.biquwx.la/') sleep(2) # 使用开发者工具定位到要输入的文本框,拿到该标签的属性 username = pjs_obj.find_element_by_id('username') # 在文本框中录入关键字相当于手动输入账号 username.send_keys('test_spider') sleep(2) # 使用开发者工具定位到要输入的文本框,拿到该标签的属性 password = pjs_obj.find_element_by_id('password') # 在文本框中录入关键字相当于手动输入密码 password.send_keys('test_spiders') btn = pjs_obj.find_element_by_class_name('int') # 相当于手动点击按钮 btn.click() sleep(10) # 截图 pjs_obj.save_screenshot('1.png') # 这里可以进行别的代码,比如获取最终页面的源码数据 # 执行js代码(让滚动条向下偏移n个像素(作用:动态加载了更多的电影信息)) js = 'window.scrollTo(0,document.body.scrollHeight)' pjs_obj.execute_script(js) # 该函数可以执行一组字符串形式的js代码 sleep(2) pjs_obj.execute_script(js) # 该函数可以执行一组字符串形式的js代码 sleep(2) # 使用爬虫程序爬去当前url中的内容 html_source = pjs_obj.page_source # 该属性可以获取当前浏览器的当前页的源码(html) with open('./source.html', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fp: fp.write(html_source) pjs_obj.quit()
访问抽屉网站

#因为是模态浏览器对话框,所以先下载好浏览器驱动 from selenium import webdriver from time import sleep # 创建一个浏览器对象,将驱动程序加载到浏览器中 pjs_obj = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='D:\Ware\installwinsoft\chromedriver_win32\chromedriver.exe') pjs_obj.maximize_window() # 浏览器对象执行get方法相当于手动打开对应的url网址 pjs_obj.get('https://dig.chouti.com/') sleep(2) btn1 = pjs_obj.find_element_by_id('login_btn') # 相当于手动点击按钮 btn1.click() sleep(4) # 使用开发者工具定位到要输入的文本框,拿到该标签的属性 username = pjs_obj.find_element_by_name("phone") # 在文本框中录入关键字相当于手动输入账号 username.send_keys('1xxxxxxxxxx') sleep(2) # 使用开发者工具定位到要输入的文本框,拿到该标签的属性 password = pjs_obj.find_element_by_name("password") # 在文本框中录入关键字相当于手动输入密码 password.send_keys('spiders123456') sleep(2) #因为是模态对话框,所以用selenium是不能点击登录按钮的,需要执行js代码 btn = 'document.getElementsByClassName("btn-large")[0].click()' pjs_obj.execute_script(btn) sleep(10) pjs_obj.save_screenshot('1.png') 访问抽屉网站
6、验证码问题
(1)输入式验证码
这种验证码主要是通过用户输入图片中的字母、数字、汉字等进行验证。如下图:

解决思路:这种是最简单的一种,只要识别出里面的内容,然后填入到输入框中即可。这种识别技术叫OCR,这里我们推荐使用Python的第三方库,tesserocr。对于没有什么背影影响的验证码如图2,直接通过这个库来识别就可以。但是对于有嘈杂的背景的验证码这种,直接识别识别率会很低,遇到这种我们就得需要先处理一下图片,先对图片进行灰度化,然后再进行二值化,再去识别,这样识别率会大大提高。
(2)滑动式验证码
这种是将备选碎片直线滑动到正确的位置,如下图
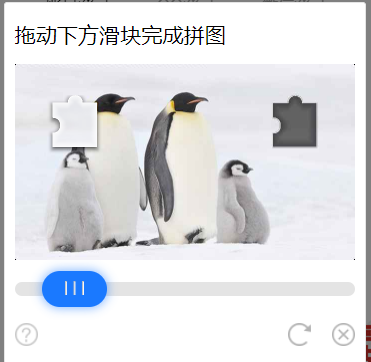
解决思路:对于这种验证码就比较复杂一点,但也是有相应的办法。我们直接想到的就是模拟人去拖动验证码的行为,点击按钮,然后看到了缺口 的位置,最后把拼图拖到缺口位置处完成验证。
第一步:点击按钮。然后我们发现,在你没有点击按钮的时候那个缺口和拼图是没有出现的,点击后才出现,这为我们找到缺口的位置提供了灵感。
第二步:拖到缺口位置。我们知道拼图应该拖到缺口处,但是这个距离如果用数值来表示?通过我们第一步观察到的现象,我们可以找到缺口的位置。这里我们可以比较两张图的像素,设置一个基准值,如果某个位置的差值超过了基准值,那我们就找到了这两张图片不一样的位置,当然我们是从那块拼图的右侧开始并且从左到右,找到第一个不一样的位置时就结束,这是的位置应该是缺口的left,所以我们使用selenium拖到这个位置即可。这里还有个疑问就是如何能自动的保存这两张图?这里我们可以先找到这个标签,然后获取它的location和size,然后 top,bottom,left,right = location['y'] ,location['y']+size['height']+ location['x'] + size['width'] ,然后截图,最后抠图填入这四个位置就行。具体的使用可以查看selenium文档,点击按钮前抠张图,点击后再抠张图。最后拖动的时候要需要模拟人的行为,先加速然后减速。因为这种验证码有行为特征检测,人是不可能做到一直匀速的,否则它就判定为是机器在拖动,这样就无法通过验证了。
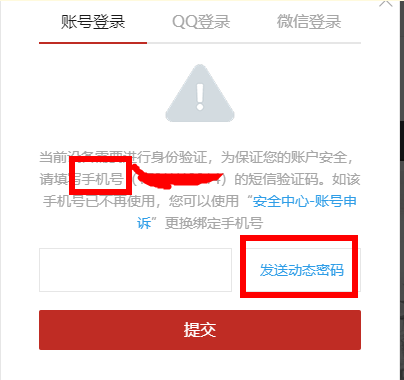
(3)手机验证码验证
(4)点击式的图文验证 和 图标选择
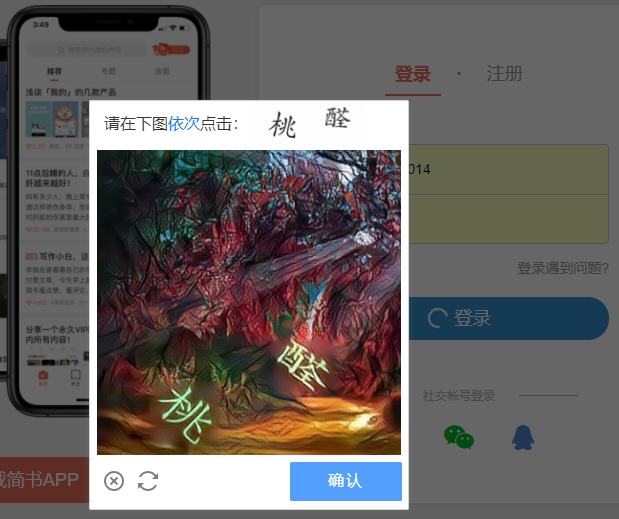
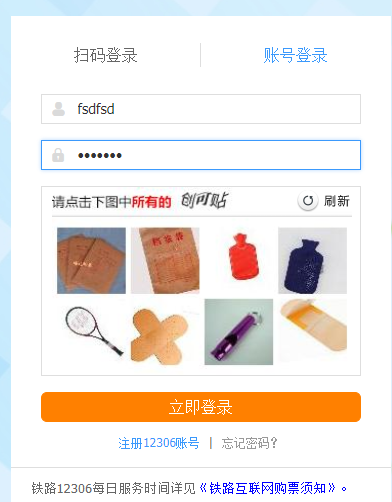
图文验证:通过文字提醒用户点击图中相同字的位置进行验证。
图标选择: 给出一组图片,按要求点击其中一张或者多张。借用万物识别的难度阻挡机器。
这两种原理相似,只不过是一个是给出文字,点击图片中的文字,一个是给出图片,点出内容相同的图片。
这两种没有特别好的方法,只能借助第三方识别接口来识别出相同的内容,推荐一个超级鹰,把验证码发过去,会返回相应的点击坐标。
然后再使用selenium模拟点击即可。具体怎么获取图片和上面方法一样。
三、requests.Request模块

Help on class Request in module requests.models: class Request(RequestHooksMixin) | Request(method=None, url=None, headers=None, files=None, data=None, params=None, auth=None, cookies=None, hooks=None, json=None) | | A user-created :class:`Request <Request>` object. | | Used to prepare a :class:`PreparedRequest <PreparedRequest>`, which is sent to the server. | | :param method: HTTP method to use. | :param url: URL to send. | :param headers: dictionary of headers to send. | :param files: dictionary of {filename: fileobject} files to multipart upload. | :param data: the body to attach to the request. If a dictionary or | list of tuples ``[(key, value)]`` is provided, form-encoding will | take place. | :param json: json for the body to attach to the request (if files or data is not specified). | :param params: URL parameters to append to the URL. If a dictionary or | list of tuples ``[(key, value)]`` is provided, form-encoding will | take place. | :param auth: Auth handler or (user, pass) tuple. | :param cookies: dictionary or CookieJar of cookies to attach to this request. | :param hooks: dictionary of callback hooks, for internal usage. | | Usage:: | | >>> import requests | >>> req = requests.Request('GET', 'https://httpbin.org/get') | >>> req.prepare() | <PreparedRequest [GET]> | | Method resolution order: | Request | RequestHooksMixin | builtins.object | | Methods defined here: | | __init__(self, method=None, url=None, headers=None, files=None, data=None, params=None, auth=None, cookies=None, hooks=None, json=None) | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature. | | __repr__(self) | Return repr(self). | | prepare(self) | Constructs a :class:`PreparedRequest <PreparedRequest>` for transmission and returns it. | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Methods inherited from RequestHooksMixin: | | deregister_hook(self, event, hook) | Deregister a previously registered hook. | Returns True if the hook existed, False if not. | | register_hook(self, event, hook) | Properly register a hook. | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data descriptors inherited from RequestHooksMixin: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined)
1、requests.Request 模块定义了以下方法:
四、requests.Response模块

Help on class Response in module requests.models: class Response(builtins.object) | The :class:`Response <Response>` object, which contains a | server's response to an HTTP request. | | Methods defined here: | | __bool__(self) | Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400. | | This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between | 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If | the status code, is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This | is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``. | | __enter__(self) | | __exit__(self, *args) | | __getstate__(self) | | __init__(self) | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature. | | __iter__(self) | Allows you to use a response as an iterator. | | __nonzero__(self) | Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400. | | This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between | 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If | the status code, is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This | is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``. | | __repr__(self) | Return repr(self). | | __setstate__(self, state) | | close(self) | Releases the connection back to the pool. Once this method has been | called the underlying ``raw`` object must not be accessed again. | | *Note: Should not normally need to be called explicitly.* | | iter_content(self, chunk_size=1, decode_unicode=False) | Iterates over the response data. When stream=True is set on the | request, this avoids reading the content at once into memory for | large responses. The chunk size is the number of bytes it should | read into memory. This is not necessarily the length of each item | returned as decoding can take place. | | chunk_size must be of type int or None. A value of None will | function differently depending on the value of `stream`. | stream=True will read data as it arrives in whatever size the | chunks are received. If stream=False, data is returned as | a single chunk. | | If decode_unicode is True, content will be decoded using the best | available encoding based on the response. | | iter_lines(self, chunk_size=512, decode_unicode=False, delimiter=None) | Iterates over the response data, one line at a time. When | stream=True is set on the request, this avoids reading the | content at once into memory for large responses. | | .. note:: This method is not reentrant safe. | | json(self, **kwargs) | Returns the json-encoded content of a response, if any. | | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``json.loads`` takes. | :raises ValueError: If the response body does not contain valid json. | | raise_for_status(self) | Raises :class:`HTTPError`, if one occurred. | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Readonly properties defined here: | | apparent_encoding | The apparent encoding, provided by the chardet library. | | content | Content of the response, in bytes. | | is_permanent_redirect | True if this Response one of the permanent versions of redirect. | | is_redirect | True if this Response is a well-formed HTTP redirect that could have | been processed automatically (by :meth:`Session.resolve_redirects`). | | links | Returns the parsed header links of the response, if any. | | next | Returns a PreparedRequest for the next request in a redirect chain, if there is one. | | ok | Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400, False if not. | | This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between | 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If | the status code is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This | is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``. | | text | Content of the response, in unicode. | | If Response.encoding is None, encoding will be guessed using | ``chardet``. | | The encoding of the response content is determined based solely on HTTP | headers, following RFC 2616 to the letter. If you can take advantage of | non-HTTP knowledge to make a better guess at the encoding, you should | set ``r.encoding`` appropriately before accessing this property. | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data descriptors defined here: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined) | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data and other attributes defined here: | | __attrs__ = ['_content', 'status_code', 'headers', 'url', 'history', '... jar = requests.cookies.RequestsCookie
1、requests.Response模块定义了以下方法:
五、requests.Session模块

Help on class Session in module requests.sessions: class Session(SessionRedirectMixin) | A Requests session. | | Provides cookie persistence, connection-pooling, and configuration. | | Basic Usage:: | | >>> import requests | >>> s = requests.Session() | >>> s.get('https://httpbin.org/get') | <Response [200]> | | Or as a context manager:: | | >>> with requests.Session() as s: | ... s.get('https://httpbin.org/get') | <Response [200]> | | Method resolution order: | Session | SessionRedirectMixin | builtins.object | | Methods defined here: | | __enter__(self) | | __exit__(self, *args) | | __getstate__(self) | | __init__(self) | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature. | | __setstate__(self, state) | | close(self) | Closes all adapters and as such the session | | delete(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a DELETE request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | get(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a GET request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | get_adapter(self, url) | Returns the appropriate connection adapter for the given URL. | | :rtype: requests.adapters.BaseAdapter | | head(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a HEAD request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | merge_environment_settings(self, url, proxies, stream, verify, cert) | Check the environment and merge it with some settings. | | :rtype: dict | | mount(self, prefix, adapter) | Registers a connection adapter to a prefix. | | Adapters are sorted in descending order by prefix length. | | options(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a OPTIONS request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | patch(self, url, data=None, **kwargs) | Sends a PATCH request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | post(self, url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs) | Sends a POST request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param json: (optional) json to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | prepare_request(self, request) | Constructs a :class:`PreparedRequest <PreparedRequest>` for | transmission and returns it. The :class:`PreparedRequest` has settings | merged from the :class:`Request <Request>` instance and those of the | :class:`Session`. | | :param request: :class:`Request` instance to prepare with this | session's settings. | :rtype: requests.PreparedRequest | | put(self, url, data=None, **kwargs) | Sends a PUT request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | request(self, method, url, params=None, data=None, headers=None, cookies=None, files=None, auth=None, timeout=None, allow_redirects=True, proxies=None, hooks=None, stream=None, verify=None, cert=None, json=None) | Constructs a :class:`Request <Request>`, prepares it and sends it. | Returns :class:`Response <Response>` object. | | :param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param params: (optional) Dictionary or bytes to be sent in the query | string for the :class:`Request`. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param json: (optional) json to send in the body of the | :class:`Request`. | :param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the | :class:`Request`. | :param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the | :class:`Request`. | :param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'filename': file-like-objects`` | for multipart encoding upload. | :param auth: (optional) Auth tuple or callable to enable | Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth. | :param timeout: (optional) How long to wait for the server to send | data before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, | read timeout) <timeouts>` tuple. | :type timeout: float or tuple | :param allow_redirects: (optional) Set to True by default. | :type allow_redirects: bool | :param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol or protocol and | hostname to the URL of the proxy. | :param stream: (optional) whether to immediately download the response | content. Defaults to ``False``. | :param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify | the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path | to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``. When set to | ``False``, requests will accept any TLS certificate presented by | the server, and will ignore hostname mismatches and/or expired | certificates, which will make your application vulnerable to | man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. Setting verify to ``False`` | may be useful during local development or testing. | :param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). | If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair. | :rtype: requests.Response | | send(self, request, **kwargs) | Send a given PreparedRequest. | | :rtype: requests.Response | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data and other attributes defined here: | | __attrs__ = ['headers', 'cookies', 'auth', 'proxies', 'hooks', 'params... | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Methods inherited from SessionRedirectMixin: | | get_redirect_target(self, resp) | Receives a Response. Returns a redirect URI or ``None`` | | rebuild_auth(self, prepared_request, response) | When being redirected we may want to strip authentication from the | request to avoid leaking credentials. This method intelligently removes | and reapplies authentication where possible to avoid credential loss. | | rebuild_method(self, prepared_request, response) | When being redirected we may want to change the method of the request | based on certain specs or browser behavior. | | rebuild_proxies(self, prepared_request, proxies) | This method re-evaluates the proxy configuration by considering the | environment variables. If we are redirected to a URL covered by | NO_PROXY, we strip the proxy configuration. Otherwise, we set missing | proxy keys for this URL (in case they were stripped by a previous | redirect). | | This method also replaces the Proxy-Authorization header where | necessary. | | :rtype: dict | | resolve_redirects(self, resp, req, stream=False, timeout=None, verify=True, cert=None, proxies=None, yield_requests=False, **adapter_kwargs) | Receives a Response. Returns a generator of Responses or Requests. | | should_strip_auth(self, old_url, new_url) | Decide whether Authorization header should be removed when redirecting | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data descriptors inherited from SessionRedirectMixin: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined)Help on class Session in module requests.sessions: class Session(SessionRedirectMixin) | A Requests session. | | Provides cookie persistence, connection-pooling, and configuration. | | Basic Usage:: | | >>> import requests | >>> s = requests.Session() | >>> s.get('https://httpbin.org/get') | <Response [200]> | | Or as a context manager:: | | >>> with requests.Session() as s: | ... s.get('https://httpbin.org/get') | <Response [200]> | | Method resolution order: | Session | SessionRedirectMixin | builtins.object | | Methods defined here: | | __enter__(self) | | __exit__(self, *args) | | __getstate__(self) | | __init__(self) | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature. | | __setstate__(self, state) | | close(self) | Closes all adapters and as such the session | | delete(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a DELETE request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | get(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a GET request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | get_adapter(self, url) | Returns the appropriate connection adapter for the given URL. | | :rtype: requests.adapters.BaseAdapter | | head(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a HEAD request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | merge_environment_settings(self, url, proxies, stream, verify, cert) | Check the environment and merge it with some settings. | | :rtype: dict | | mount(self, prefix, adapter) | Registers a connection adapter to a prefix. | | Adapters are sorted in descending order by prefix length. | | options(self, url, **kwargs) | Sends a OPTIONS request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | patch(self, url, data=None, **kwargs) | Sends a PATCH request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | post(self, url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs) | Sends a POST request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param json: (optional) json to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | prepare_request(self, request) | Constructs a :class:`PreparedRequest <PreparedRequest>` for | transmission and returns it. The :class:`PreparedRequest` has settings | merged from the :class:`Request <Request>` instance and those of the | :class:`Session`. | | :param request: :class:`Request` instance to prepare with this | session's settings. | :rtype: requests.PreparedRequest | | put(self, url, data=None, **kwargs) | Sends a PUT request. Returns :class:`Response` object. | | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. | :rtype: requests.Response | | request(self, method, url, params=None, data=None, headers=None, cookies=None, files=None, auth=None, timeout=None, allow_redirects=True, proxies=None, hooks=None, stream=None, verify=None, cert=None, json=None) | Constructs a :class:`Request <Request>`, prepares it and sends it. | Returns :class:`Response <Response>` object. | | :param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. | :param params: (optional) Dictionary or bytes to be sent in the query | string for the :class:`Request`. | :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like | object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. | :param json: (optional) json to send in the body of the | :class:`Request`. | :param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the | :class:`Request`. | :param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the | :class:`Request`. | :param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'filename': file-like-objects`` | for multipart encoding upload. | :param auth: (optional) Auth tuple or callable to enable | Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth. | :param timeout: (optional) How long to wait for the server to send | data before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, | read timeout) <timeouts>` tuple. | :type timeout: float or tuple | :param allow_redirects: (optional) Set to True by default. | :type allow_redirects: bool | :param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol or protocol and | hostname to the URL of the proxy. | :param stream: (optional) whether to immediately download the response | content. Defaults to ``False``. | :param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify | the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path | to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``. When set to | ``False``, requests will accept any TLS certificate presented by | the server, and will ignore hostname mismatches and/or expired | certificates, which will make your application vulnerable to | man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. Setting verify to ``False`` | may be useful during local development or testing. | :param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). | If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair. | :rtype: requests.Response | | send(self, request, **kwargs) | Send a given PreparedRequest. | | :rtype: requests.Response | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data and other attributes defined here: | | __attrs__ = ['headers', 'cookies', 'auth', 'proxies', 'hooks', 'params... | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Methods inherited from SessionRedirectMixin: | | get_redirect_target(self, resp) | Receives a Response. Returns a redirect URI or ``None`` | | rebuild_auth(self, prepared_request, response) | When being redirected we may want to strip authentication from the | request to avoid leaking credentials. This method intelligently removes | and reapplies authentication where possible to avoid credential loss. | | rebuild_method(self, prepared_request, response) | When being redirected we may want to change the method of the request | based on certain specs or browser behavior. | | rebuild_proxies(self, prepared_request, proxies) | This method re-evaluates the proxy configuration by considering the | environment variables. If we are redirected to a URL covered by | NO_PROXY, we strip the proxy configuration. Otherwise, we set missing | proxy keys for this URL (in case they were stripped by a previous | redirect). | | This method also replaces the Proxy-Authorization header where | necessary. | | :rtype: dict | | resolve_redirects(self, resp, req, stream=False, timeout=None, verify=True, cert=None, proxies=None, yield_requests=False, **adapter_kwargs) | Receives a Response. Returns a generator of Responses or Requests. | | should_strip_auth(self, old_url, new_url) | Decide whether Authorization header should be removed when redirecting | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data descriptors inherited from SessionRedirectMixin: | | __dict__ | dictionary for instance variables (if defined) | | __weakref__ | list of weak references to the object (if defined)
