Tensorflow2.0笔记
本博客为Tensorflow2.0学习笔记,感谢北京大学微电子学院曹建老师
7.常用Tensorflow API及代码实现
7.1学习率策略
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=False, name=None
)
功能:指数衰减学习率策略.
等价API:tf.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay
参数:
initial_learning_rate: 初始学习率
decay_steps: 衰减步数, staircase为True时有效.
decay_rate: 衰减率
staircase: Bool型变量.如果为True, 学习率呈现阶梯型下降趋势.
返回:tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(step)返回计算得到的学习率
链接:tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay
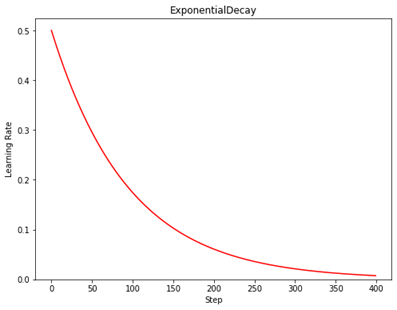
示例:
N = 400
lr_schedule =
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay( 0.5,
decay_steps=10,
decay_rate=0.9,
staircase=False)
y = []
for global_step in range(N):
lr = lr_schedule(global_step)
y.append(lr)
x = range(N)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.plot(x, y, 'r-')
plt.ylim([0,max(plt.ylim())])
plt.xlabel('Step')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.title('ExponentialDecay')
plt.show()
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries, values, name=None
)
功能:分段常数衰减学习率策略.
等价API:tf.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay
参数:
boundaries: [step_1, step_2, ..., step_n]定义了在第几步进行学习率衰减
values: [val_0, val_1, val_2, ..., val_n]定义了学习率的初始值和后续衰减时的具体取值
返回:tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(step)返回计算得到的学习率.
链接: tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay
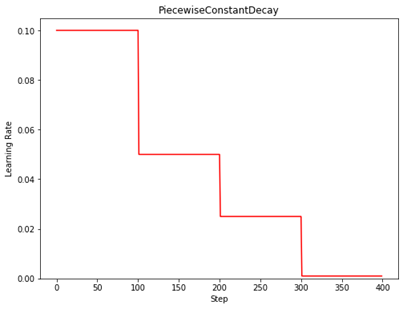
示例:
N = 400
lr_schedule =
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries=[100, 200, 300],
values=[0.1, 0.05, 0.025, 0.001])
y = []
for global_step in range(N):
lr = lr_schedule(global_step)
y.append(lr)
x = range(N)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.plot(x, y, 'r-')
plt.ylim([0,max(plt.ylim())])
plt.xlabel('Step')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.title('PiecewiseConstantDecay')
7.2激活函数
tf.math.sigmoid
tf.math.sigmoid(
x, name=None
)
功能:计算x每一个元素的sigmoid值.
等价API:tf.nn.sigmoid, tf.sigmoid
参数:
x是张量x
返回:
与x shape相同的张量
链接: tf.math.sigmoid
示例:
x = tf.constant([1., 2., 3.], )
print(tf.math.sigmoid(x))
>>> tf.Tensor([0.7310586 0.880797 0.95257413], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
# 等价实现
print(1/(1+tf.math.exp(-x)))
>>> tf.Tensor([0.7310586 0.880797 0.95257413], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
tf.math.tanh
tf.math.tanh(
x, name=None
)
功能:计算x每一个元素的双曲正切值.
等价API:tf.nn.tanh, tf.tanh
参数:
x是张量x
返回:
与x shape相同的张量
链接: tf.math.tanh
示例:
x = tf.constant([-float("inf"), -5, -0.5, 1, 1.2, 2, 3, float("inf")])
print(tf.math.tanh(x))
>>> tf.Tensor([-1. -0.99990916 -0.46211717 0.7615942 0.8336547 0.9640276
0.9950547 1.], shape=(8,), dtype=float32)
# 等价实现
print((tf.math.exp(x)-tf.math.exp(-x))/(tf.math.exp(x)+tf.math.exp(-x)))
>>> tf.Tensor([nan -0.9999091 -0.46211714 0.7615942 0.83365464 0.9640275
0.9950547 nan], shape=(8,), dtype=float32)
tf.nn.relu
tf.nn.relu(
features, name=None
)
功能:计算修正线性值(rectified linear):max(features, 0).
参数:
features:张量
链接: tf.nn.relu
例子:
print(tf.nn.relu([-2., 0., -0., 3.]))
>>> tf.Tensor([0. 0. -0. 3.], shape=(4,), dtype=float32)
tf.nn.softmax
tf.nn.softmax(
logits, axis=None, name=None
)
功能:计算softmax激活值.
等价API:tf.math.softmax
参数:
logits:张量
axis:计算softmax所在的维度. 默认为-1,即最后一个维度
返回:与logits shape相同的张量.
链接: tf.nn.softmax
logits = tf.constant([4., 5., 1.])
print(tf.nn.softmax(logits))
>>> tf.Tensor([0.26538792 0.7213992 0.01321289], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
# 等价实现
print(tf.exp(logits) / tf.reduce_sum(tf.exp(logits)))
>>> tf.Tensor([0.26538792 0.72139925 0.01321289], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)